Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 6 Physical and Chemical Changes
Gujarat Board Class 7 Science Physical and Chemical Changes Textbook Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
Classify the changes involved in the following processes as physical or chemical changes:
(a) Photosynthesis
(b) Dissolving sugar in water
(c) Burning of coal
(d) Melting of wax
(e) Beating aluminium to make aluminium foil
(f) Digestion of food
Answer:
(a) Chemical change
(b) Physical change
(c) Chemical change
(d) Physical change
(e) Physical change
(f) Chemical change
Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true or false. In case a statement is false, write the corrected statement in your notebook.
(a) Cutting a log of wood into pieces is a chemical change. (True/False)
Answer:
(a) False
Correct statement: Cutting a log of wood into pieces is an irreversible physical change.
(b) Formation of manure from leaves is a physical change. (True/False)
Answer:
False
Correct statement: Formation of manure from leaves is a chemical change.
![]()
(c) Iron pipes coated with zinc do not get rusted easily. (True/False)
Answer:
True
(d) Iron and rust are the same substances. (True/ False)
Answer:
False
Correct statement: Iron and rust are two different chemical substances.
(e) Condensation of steam is not a chemical change. (True/False)
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks in the following statements:
(a) When carbon dioxide is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of _______.
(b) The chemical name of baking soda is _______
(c) Two methods by which rusting of iron can be prevented are _______ and _______.
(d) Changes in which only _______ properties of a substance change are called physical changes.
(e) Changes in which new substances are formed are called _______ changes.
Answer:
(a) calcium carbonate
(b) sodium hydrogen carbonate
(c) painting or greasing, galvanisation
(d) physical
(e) chemical
Question 4.
When baking soda is mixed with lemon juice, bubbles are formed with the evolution of a gas. What type of change is it? Explain.
Answer:
The reaction between baking soda and lemon juice can be given as below:

It is a chemical change.
Question 5.
When a candle bums, both physical and chemical changes take place. Identify these changes. Give another example of a familiar process in which both the chemical and physical changes take place.
Answer:
When a candle bums, both physical and chemical changes occur:
- Physical change: melting of wax, vapourisation of melted wax.
- Chemical change: Burning of vapours of wax to give carbon dioxide, heat and light.
LPG is another example in which physical change occurs when LPG comes out of cylinder and is converted from liquid to gaseous state and a chemical change occurs when gas bums in air.
![]()
Question 6.
How would you show that setting of curd is a chemical change?
Answer:
We can say that setting of curd is a chemical change because we can not get the original substance, i.e., milk back and a new substance is formed with different taste, smell and other chemical properties.
Question 7.
Explain why burning of wood and cutting it into small pieces are considered as two different types of changes.
Answer:
Burning of wood is a chemical change because in burning new substances are formed as
Wood + Oxygen → Charcoal + Carbon dioxide + Heat + Light
But cutting it into small pieces is physical change because no new substance is formed. We can only reduce the size of wood.
Question 8.
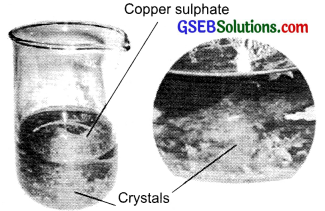
Describe how crystals of copper sulphate are prepared.
Answer:
Take a cup full of water in a beaker and add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid. Heat the water. When it starts boiling, add copper sulphate powder slowly. Continue to add copper sulphate powder till no more powder can be dissolved. During this process continuously stir the solution. Filter the solution. Leave it for cooling.
Look it after some time, you can see the crystals of copper sulphate add copper sulphate powder till no more powder can be dissolved. During this process continuously stir the solution. Filter the solution. Leave it for cooling. Look it after some time, you can see the crystals of copper sulphate Copper sulphate
Question 9.
Explain how painting of an iron gate prevents it from rusting?
Answer:
It is known that for rusting the presence of oxygen and moisture is essential. Painting prevents the iron gate from coming in contact with oxygen and moisture.
Question 10.
Explain why rusting of iron objects is faster in coastal areas than in deserts.
Answer:
As content of moisture in the air in coastal areas is higher than in the air in deserts. So, the process of rusting is faster in coastal areas.
![]()
Question 11.
The gas we use in the kitchen is called liquified petroleum gas (LPG). In the cylinder it exists as a liquid. When it comes out from the cylinder it becomes a gas (Change-A) then it burns (Change-B). The following statements pertain to these changes. Choose the correct one.
(i) Process-A is a chemical change.
(ii) Process-B is a chemical change.
(iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes.
(iv) None of these processes is a chemical change.
Answer:
(ii) Process-B is a chemical change.
Question 12.
Anaerobic bacteria digest animal waste and produce biogas (Change-A). The biogas is then burnt as fuel (Change-B). The following statements pertain to these changes. Choose the correct one.
(i) Process-A is a chemical change.
(ii) Process-B is a chemical change.
(iii) Both processes A and B are chemical changes.
(iv) None of these processes is a chemical change.
Answer:
(iii) Both processes A and B are chemical change.
Extended Learning – Activities And Projects
Question 1.
Describe two changes that are harmful. Explain why you consider them harmful. How can you prevent them?
Answer:
Harmful changes:
- Rusting of iron
- Decaying of fruits.
Rusting of iron is harmful in the sense that it destroys iron articles slowly. As iron is used in making bridges, ships, cars, etc., it may cause huge monetary loss. Similarly decaying of fruits causes health hazards.
Prevention: Rusting can be prevented by oiling, polishing and painting. Fruits can be preserved by keeping them at low temperature and by using some specific preservatives.
![]()
Question 2.
Take three glass bottles with wide mouths. Label them A, B and C. Fill about half of bottle A with ordinary tap water. Fill bottle B with water which has been boiled for several minutes, to the same level as in A. In bottle C, take the same boiled water and of the same amount as in other bottles. In each bottle put a few similar iron nails so that they are completely under water. Add a teaspoonful of cooking oil to the water in bottle C so that it forms a film on its surface. Put the bottles away for a few days. Take out nails from each bottle and observe them. Explain your observations.
Answer:
In test tube A which contains ordinary water rusting takes place because in it iron nail is in direct contact of air and water. The nail in test tube B becomes dull while no rusting takes place in test tube C because it does not come in the contact of air but only water is there. By the above observations we conclude that both air and water are essential for rusting.
Question 3.
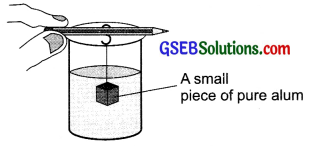
Prepare crystals of alum.
Answer:
Preparation of crystals of alum: Place a beaker half filled with water on a stand and heat it till it starts boiling. Mix some impure alum powder in boiled water. Continue the mixing of powder till the alum powder stops dissolving. Filter the hot solution into another beaker. Hang a small crystal of pure alum in this solution to obtain a big crystal. Allow the solution to cool slowly for 24 hours. We see a large crystal of alum is formed around the small crystal. The crystals can be removed by filtration.
Question 4.
Collect information about the types of fuels used for cooking in your area. Discuss with your teachers/parents/ others which fuels are less polluting and why.
Answer:
The following types of fuels are used in our area:
- Solid fuels: Coal, dung cake, wood etc.
- Liquid fuel: Kerosene oil.
- Gaseous fuel: LPG.
We observe that the solid fuels produce more smoke and unburnt particles. So they are more polluting fuels. Liquid fuels are less polluting fuels. Gaseous fuels are clean fuels and do not produce any pollution.