This GSEB Class 12 Commerce Accounts Notes Part 2 Chapter 2 Accounting for Debentures covers all the important topics and concepts as mentioned in the chapter.
Accounting for Debentures Class 12 GSEB Notes
Generally, the company satisfies the long term financial needs by issuing share capital. Sometime company needs financial requirement for development, expansion, modernisation or any other reasons. For this company obtained long term loans from financial institution or from bank. Most of the time company on the basis of implied authority to obtained borrowed money, issued securities to public and obtained fund for long from purpose. Against the money so borrowed or investment, the company issue a document or certificate acknowledging its debt to the investor. Such a certificate is known as debenture. It is issued under the common seal of the company. Company has to pay interest at a specified rate and on specific time and also repays the money borrowed against a debenture at a future date as per the terms of issue of debentures. In this chapter we will study about types and redemption method of debentures and its accounting effects.
Debenture:
Debenture is a document showing debt and accepting debts of company which is released with the company common seal. In which the detail are shown just like name of debentureholder number of debentures, amount of debenture, No. of debentures, rate of interest and shows when the debenture money will be paid at a future date.
Methods for Issue of Debentures:
There are three methods to issue the debenture:
(a) Issued at Face Value (at par)
(b) Issued at Premium
(c) Issued at Discount Accounting Effects for issue of Debentures: The accounting effects done in books of the company about the debentures being issued are as under:
When the full amount of the debentures is called up at a time:
(a) Issue of Debentures at Par:
| Bank A/c Dr To …………. % debenture application and allotment A/c [Being application money fully received on debentrues at ₹ …….per debentures] |
||||
| …. % debenture application and Allotment A/c Dr. To …………. % debenture A/c [Being application money transfer to debenture account] |
(b) Issue of Debentures at Permium:
| (i) Bank A/c Dr. To Debenture application and allotment A/c [Being ₹ …….. for per debenture application money fully received ₹……… while issued by premium.] |
…………… | …………. | |
| (ii)………% debenture application and allotment A/c Dr. To ….. % debenture A/c To Securities premium reserve A/c [Being application money transfer to debenture account and premium account] |
……… | …………… |
![]()
(c) Issue of Debentures at Discount:
| Bank A/c Dr. To Debenture application and allotment A/c [Being application A/c money fully received by debentures at ₹ ……. per debenture] |
………… | ……….. | |
| Debenture application and allotment A/c Dr. Discount on debenture A/c Dr. To ………. % debenture A/c [Being the application amount of debenture is credited to application and allotment A/c and amount of discount on debenture are debited to discount A/c and credited to debenture A/c) |
……….
………. |
………
…….. |
When the amount of debentures is called up in installments:
| On receipt of application money- | Bank A/c Dr. To debenture application A/c [Being application money received) |
| On transfer of application money to debenture account it means allotment of debentures | …. % debenture application A/c Dr. To …. % debenture A/c (Allotted debentures x Called up amount per debenture) To Bank A/c (Rejected debenture application x Called up amount per debenture) To …. % debenture allotment A/c [Being application amount of debenture on total allotted debenture transferred to debenture A/c. Money returned to applicants on rejected application and excess application money transferred to allotment account) |
| When allotment money due | …. % debenture allotment A/c Dr. To….. % debenture A/c (Being allotment money due) Called up amount = Allotted debenture × Called up amount per debenture at the time of allotment. |
| On receipt of allotment money | Bank A/c Dr. To …. % debenture allotment A/c (Being allotment money received) Received amount = Total amount called at the time of allotment of debenture – Pre received amount at the time of application of debenture for allotment. |
| When amount due on call | …. % debenture call A/c Dr. To …. % debenture A/c (Being respective call amount due on debentures) Called up amount = Allotted debentures × Called up amount per debenture |
| On receipt of call money | Bank A/c Dr. To….. % debenture call A/c (Being money received on calls on debenture) Received amount = Called up amount on calls – Not received amount of calls from debenture holders. |
Issue of Debentures for Consideration Other than Cash:
Like shares, debentures are also sometimes issued for consideration other than cash. For example, the issue of debentures to vendor against the purchase of assets like land-building, plant and machinery etc. Similarly issue of debentures to vendor’s againt purchase consideration at the time of purchase of business. Debenture can be issued to vendors at par, at a premium or at a discount.
Following entries will be passed:
1. At the time of purchase of any business:
| (i) Sundry assets A/c Dr. (Business assets taken over) To Sundry liabilities A/c (Business liabilities taken over) To Vendor’s A/c (Purchase consideration) (Being business assets and liabilities taken over on Purchase of business) |
…………….. | …………………. | |
| (ii) Vendor’s A/c Dr. To Debentures’ A/c (Being issue of debentures by the company for purchase consideration.) |
…………….. | …………….. |
2. When any assets is purchased:
| On purchase of assets, Asset A/c Dr. To Vendor’s A/c (Being purchase of asset) |
…………….. | …………….. | |
| Vendor’s A/c Dr. To Debentures A/c (Being issue of debentures to vendor for asset) |
…………….. | …………….. |
![]()
Accounting Effects at the time of Issue of Redeemable Debentures:
Debentures are issued at par, at a premium or at a discount, but when debentures are to be redeemed to the debentureholders then it is redeemed at par or at a premium only. Debentures can not be redeemed at a discount.
|
Situation (Condition) |
Entry at the time of Issue | Entry at the time of Redemption |
Entry at the time of Debentureholders are paid |
| When debentures are issued at par and redeemable at par | (i) Bank A/c Dr. To Debenture application and allotment A/c (ii) Debenture Application and allotment A/c Dr. To Debenture A/c |
Debenture A/c Dr. To Debenture holders A/c |
Debenture holders A/c Dr. To Bank A/c |
| When debentures are issued at permium and redeemable at par | (i) Bank A/c Dr. To Debenture application and allotment A/c (ii) Debenture application and allotment A/c Dr. To Debenture A/c To Security premium reserve A/c |
Debenture A/c Dr. To Debenture holders A/c |
Debenture holders A/c Dr. To Bank A/c |
| When debentures are issued at discount and redeemable at par | (i) Bank A/c Dr. To Debenture application and allotment A/c (ii) Debenture application allotment A/c Dr. Discount on debenture A/c Dr. To Debenture A/c |
Debenture A/c Dr. To Debenture holders A/c |
Debentureholders A/c Dr. To Bank A/c |
| When debentures are issued at par and redeemable at a premium | (i) Bank A/c Dr. To ….% Debenture application and allotment A/c |
….% Debenture A/c Dr. Premium on redemption of debenture A/c Dr. To Debentre holders A/c |
Debentureholders A/c Dr. To Bank A/c |
| (ii) Debenture application and allotment A/c Dr. Loss on issues of debenture A/c Dr.To Debenture A/c To Premium on redemption of debenture A/c |
|||
| When debentures are issued at a premium and redeemable at a premium | (i) Bank A/c Dr. To Debentures’ application and allotment A/c (ii) Debenture application and allotment A/c Dr. Loss on issue of debenture A/c Dr. To Debenture A/c To Securities Premium reserve A/c To Premium on redemption of debenture A/c |
….% Debenture A/c Dr. Premium on redemption of debentures A/c Dr. To Debenture holders A/c |
Debenture holders A/c Dr. To Bank A/c |
| When debentures are issued at discount and are redeemable at a premium | (i) Bank A/c Dr. To Debenture application and allotment A/c (ii) Debenture application and allotment A/c Dr. Discount on debentures A/c Dr. Loss on issue of debenture A/ c Dr. To Debentures A/c To Premium on redemption of debenture A/c |
….%Debenture A/c Dr. Premium on redemption of debenture A/c Dr. To debenture holders A/c |
Debenture holders A/c Dr. To Bank A/c |
Provisions for the Redemption of Debentures:
Amount required for the redemption of debentures may be managed by a company from the following sources:
(i) Redemption of debentures from the fresh issue of shares and debentures.
(ii) Redemption of debentures out of capital.
(iii) Redemption of debentures out of profit.
Methods of Redemption of Debentures:
The methods of redemption of debentures and their accounting entries are as under:
1. Lump-sum Payment at the end of final period:
|
Transaction |
Entry |
| 1. At the beginning of financial year (up to 30th April): On making investment at 15% of face value of debentures to be redeemed. | Debenture redemption investment A/c Dr. To Bank A/c |
| 2. At the time of Redemption : (i) When debentures are to be sold (ii) On transfer of profit from surplus in statement of profit and loss at the rate of of the face value of debenture issued |
Bank A/c Dr. To debenture redemption inbvestment A/c Surplus in statement of profit and loss A/c Dr. To Debenture redemption reserve A/c |
| 3. On redemption of debentures : | (i) Debenture A/c Dr. To Debentures A/c (ii) Debentureholders A/c Dr. To Bank A/c |
| 4. When all the debentures are redeemed : | Debenture redemption reserve A/c Dr. To General reserve A/c |
![]()
Note:
- If the payment of redemption of debenture is to be done from capital then, an amount transferred from surplus in statement of profit and loss to debenture redemption reserve account is 25% of total face or nominal value of redemption of debentures
- If the payment of redemption of debentures is to be done from profit then an amount transferred from surplus in statement of profit and loss to debenture redemption reserve A/c is 100% of total face or nominal value of redemption of debentures
- If there is no clarification in example then calculate with assumption that company has paid amount out of capital.
2. Redemption of Debentures in installments by Drawing of Lots:
According to this method, the debentures are redeemed by the company in annual installments. The serial number of debentures which should be redeemed each year are selected by lottery. This procedure is known as “Drawings by Lots”.
3. Redemption of debentures by the purchase of own debentures in the Open Market:
According to the Companies Act, if authorised by company’s articles of association, a company can purchase the own debentures in the open market. After purchasing the debentures from the open market, the company may use either of the following two options:
(i) Company may immediately cancel the debentures purchased after passing the resolution by board of directors: In this situation, the following entries will be passed in the books of company:
[A] When debentures are purchased at less price as compare to face value of the debentures:
| Own debenture A/cDr. To Bank A/c (Being……. debentures purchased in the open market at ₹…….. per debenture) |
…………….. | …………….. | |
| Debenture A/c Dr. To Own debentures A/c To Profit on redemption of debentures A/c (Being cancellation of own purchased debentures) |
…………….. |
…………….. …………….. |
|
| Profit on redemption of debentures A/c To capital reserve A/c (Being capital profit arised on redemption of debenture is transferred to capital reserve A/c) Dr. |
…………….. | …………….. |
[B] When debentures are purchased at more price as compared to face value of the debentures:
| Own debentures A/c Dr. To Bank A/c (Being purchased …… debentures from the market at……. ₹ per debenture) |
…………….. | …………….. | |
| Debenture A/c Dr. Loss on redemption of debenture A/c Dr. To Own debentures A/c (Being cancellation of own purchased debentures) |
……………..
…………….. |
…………….. |
|
| Capital profit (if any) A/c Dr. Or statement of P & L A/c Dr. To Loss on redemption of debenture A/c (Being capital loss on redemption of debenture is written off from capital profit/profit-loss statement) |
…………….. …………….. |
…………….. |
(ii) When the company purchases own debentures in the open market and these debentures are kept as investment: In this situation following journal entry is made:
[A] Company purchases own debentures and kept as investment:
| Investment in own debentures A/c Dr. To Bank A/c (Being …….. debentures at …………. purchased from market to do investment) |
…………….. | . ……………. |
|
| Investment in the own debentures will be shown as non-current assets assets side in the balance sheet. on the | |||
![]()
[B] Investment in own debentures used for debentures cancellation:
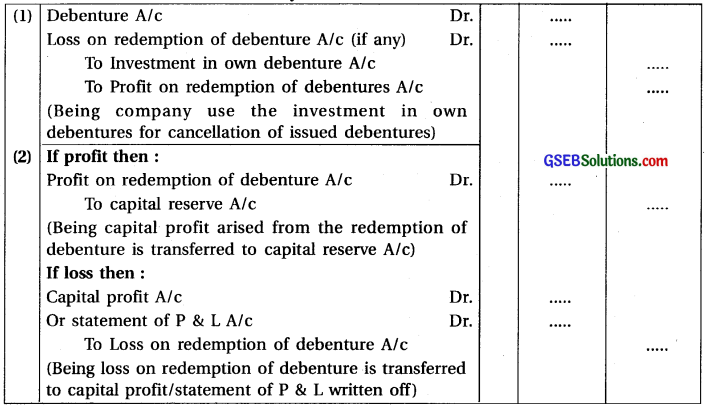
[C] When investment in own debenturs may be sold by company in open market:
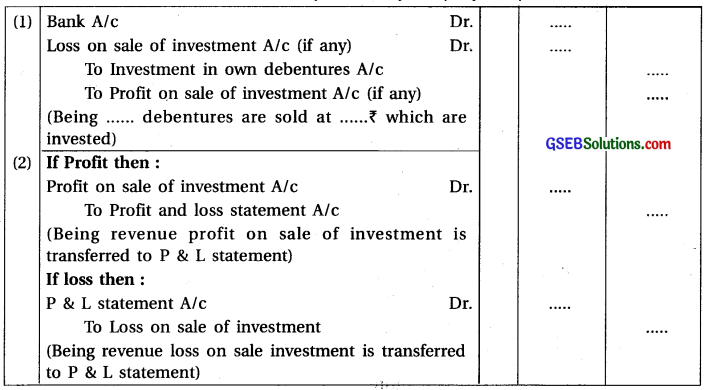
Note: When investment is done in the own debentures by the company itself and these debentures may be sold by the company in the open market then profit or loss realised from it is treated as revenue profit or revenue loss which is transferred to statement of profit and loss.
Conversion of debenture into shares:
At the time of issuing debentures as per the terms of the issue of debentures, a company can issue its equity or perference shares in lieu of debentures to the debentureholders. When debentures are converted into shares the following journal entries are passed.
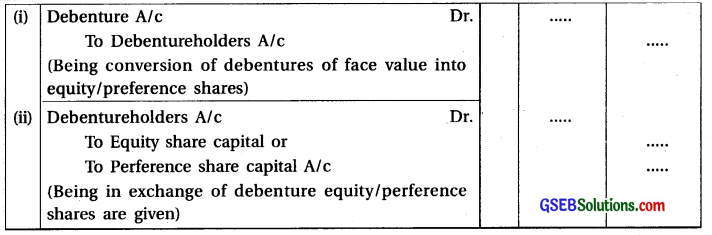
Accounting entries at the time of transaction of debentures:
1. If company gets less application than issued debenture then keeping number of application received into account, do all the necessary accounting entries.
2. If there is more application received than the debenture issued of the company then the additional money will be return to the debenture applicants.
Regarding this, debited Debenture application A/c and credited Bank A/c.
Then after do all the entries keeping allotment of the debenture into account.
3. In case of getting amount in advance from the debentureholders on allotment or calls of debentures:
- Regarding advanced received amount on allotment, credited to Debenture Allotment A/c and advance received amount on calls then credited to Calls in advance A/c
- When amount of call on debenture is actual received then it is debited to Bank A/c and Calls in advance A/c and credited Debenture calls A/c.
4. If any debenture holder is not paid the amount of allotment of debenture or calls on debenture in time then in such circumtances.
- Amount not received from debentureholders will be transferred to Calls-in-arrears A/c and credited to Debenture allotment A/c or Debenture calls A/c.
- If such amount is received from debentureholders in future then that amount is debited to Bank A/c and credited to Calls-in-arrears A/c.
5. Debentures are company’s debt so that if any debentureholder does not pay amount of installment then debenture can not be forfeited.
6. When the full amount of debenture is called up at the time of application, then debited to Bank A/c and credited to Debenture application and allotment A/c.
7. If debenture issued at premium then that amount of premium is transferred to “Security Premium Reserve A/c”. It is capital profit.
8. If company issued debenture at discount then this discount amount is debited to Debenture discount A/c. Debenture discount or amount of loss at the time of issuing debenture-is capital loss. Generally this amount is written off against Security premium Reserve A/C dr Profit and loss statement.
9. When a company purchase any business and issue more debenture to vendor’s against purchase consideration then the difference amount is transferred to Goodwill A/c and if paid less amount then that difference amount is transferred to Capital Reserve A/c.
In short, Goodwill = Purchase consideration of business – Net assets
Capital Reserve = Net Assets – Purchase consideration
10. When debentures are redeemed at premium then that premium amount is debited to Loss on issue of debenture A/c and credited to Debenture redemption premium A/c. Debenture redemption premium is a debt of company:
11. As per the rule 18(7)(c) of the Companies rule 2014, company required to deposit or invest, a sum which shall not be less then 15% of the total face value of the debentures to be redeemed at the end of the year i.e. during the ending on 31st March, on or before 30th April, i.e. beginning of the year.
12. According to section 71(4) of the Companies Act, 2013 and as per the guideline of SEBI, it is necessary to create debenture redemption reserve account equivalent to fixed % of the total face value of issued debentures before redemption commence.
- When debentures are redeemable at the end of the financial year then, at the end of the year amount transferred to Debenture Redemption Reserve A/c from surplus in Statement of profit and loss of the respective year.
- If payment of redemption of debentures is to be done from capital then, an amount transferred from surplus in Statement of profit and loss to Debenture Redemption Reserve A/c is 25% and if it is to be done from profit then, an amount transferred from surplus in Statement of profit and loss to Debenture Redemption Reserve A/c is 100% of total face value or nominal value of redemption of debentures.
- When debentures are redeemable during any time in between the financial year then required amount is to be transferred from surplus in Statement of profit and loss of the previous year to Debenture Redemption Reserve A/c. The amount to be transferred to Debenture Redemption Reserve A/c.
- If there is no clarification regarding required amount of redemption of debentures which is out of capital or out of profit then, calculate with the assumption that company has paid out of capital.
13. Profit on redemption of debentures is capital profit which is transferred to capital reserve account and when investment in own debentures may be sold by company in open market then profit realised from it is treaded as revenue profit and transferred to Statement of profit and loss.
14. When debentures are converted into shares by the company then shares may be issued to debentureholders at par or at premium. These shares may not be issued at discount, otherwise it violates the provisions of Companies Act.
15. Company can redeem the debenture in different considerations:
- By Cash
- By Giving new equity share or preference share
- By Giving new debentures.
![]()
To Be Keep in Mind:
1. Debenture is a document that confirms the debt of the company and its acknowledgment of the debt.
2. It is necessary or compulsory to pay the interest of debenture in time while company hasn’t any profit.
3. There is no right of debentureholder to take part in management of company or voting for directorship of company. They are the creditors of company.
4. At the time of company’s dissolution debentuerholders get first chance to take their money back.
5. When debentures are issued for a fixed term, the money borrowed against such debentures is repaid at the end of a fixed term in accordance with the agreed terms.
6. As per Companies Act, 2013 no company is allowed to issue debentures having a maturity date of more than 10 years from the date of issue. However a company engaged in infrastructure projects can be issue debenture for more than 10 years but not exceeding 30 years.
7. Debentures which are listed in share market only those are sold or purchased in stock exchanges.
8. Debentures can not be forfeited even if the amount of installment are remaing because debentures are the debt of company.
9. Debentures can be issued at face or nominal value or at premium or at discount.
10. As per Companies Act 2013, minimum subscription should be 90% of the issued amount.
11. Bearer debentures are like currency notes and can be transferred by mere delivery.
12. In the balance sheet of compnay:
- Debenture: It is shown on Equity and Liability side under the heading of Non-current liabilities and under the sub head of ‘Long term borrowings.’
- Securities Premium Reserve: It is shown on Equity and Liability side under the heading of ‘Shareholder Fund’ and under sub heading of ‘Reserve and Surplus’.
- Debenture Discount: It is shown on Assets side under the heading of ‘Non-current Assets’ and under the sub heading of ‘Other Non-current Assets’.
- Unpaid interest on Debenture: It is shown on Equity and Liability side, under the heading of ‘Current Liabilities’ and under the sub heading of ‘Other current Liabilities’.
- Loss on issue of Debentures: It is shown on Assets side under the heading of Non-Current Assets and under the sub heading of ‘Other Non-current Assets’.
- Debenture Redemption Premium: It is shown on Equity and Liability side under the heading of ‘Non-current Liability’ and under the sub heading of ‘Other long-term liabilities.’
- Debenture Redemption Premium: It is shown on Equity Liability side under the heading of ‘Shareholders fund’ and under the sub heading of ‘Reserve and Surplus.’
13. As per section 17(4) with rule 18(7) of Companies Act 2013, a banking company is not required to create Debenture Redemption Reserve.
14. It is compulsory to open a demat account for dematerialisation of debenture between company and debentureholders. Purchase and sell of debenture is noted in that account.