Gujarat Board GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 10 Marketing Management Important Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 10 Marketing Management
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What does the marketing process tries to balance?
Answer:
The needs of the consumers and the products.
![]()
Question 2.
Give a general definition of marketing.
Answer:
“Marketing is a total system of business activities which are designed to plan a product, to determine its price and to distribute goods which can satisfy wants of the consumers and reach the target as well as objectives of organizations.”
Question 3.
State Kotler’s definition of marketing.
Answer:
“Marketing is a social process, in which private groups based on their requirement, produce valuable products and independently exchange goods and services.”
Question 4.
State few methods/sources of data collection for marketing research.
Answer:
Methods to collect information include preparing questioñnaire and getting it filled from people, observation, obtaining sales data from POS, etc.
Question 5.
What is collection of products?
Answer:
In many cases products are manufactured at different places and they need to be collected centrally. This is known as collection of products.
Question 6.
What is standardization?
Answer:
Standardization refers to making a product lot of specific and nearly same colour, feel, size, quantity, etc.
Question 7.
What is gradation? Give one example.
Answer:
Gradation refers to grading the product on the basis of its quality and other characteristics. For example, fruits are graded as first quality fruit, second quality and so on.
Question 8.
State two advantages of gradation.
Answer:
(a) By grading the product, the producer can create a unique identity for his products,
(b) The producer can charge differently for graded product such as separate price of grade A product and grade B product. This way he can earn more.
Question 9.
Which agencies grade Indian products?
Answer:
In India, AGMARK grades agricultural products whereas Bureau of Indian Standard (BIS) grades industrial products.
Question 10.
State two advantages of labeling.
Answer:
(a) A label differentiates the product of one producer from that of other competitors,
(b) Labels help to prevent cheating of consumers through fake products.
Question 11.
Which details are put on a label?
Answer:
Details such as weight, size, price, date of manufacturing, ingredients, expiry date, etc. of the product.
Question 12.
Why the price determination is to be done before packaging?
Answer:
Because it is mandatory to print the price of the product on the pack.
Question 13.
Mention two benefits of packing.
Answer:
(a) Proper packing prevents the goods from getting damaged and makes them easier to transport
(b) Packing helps to preserve product quality and its features.
Question 14.
Why goods are insured?
Answer:
Insurance protects the goods while storing and transporting. Insurance covers a variety of risks such as theft, fire, decoit, loss due to riots, sinking of product in water, etc.
Question 15.
Name some types of insurance taken , for goods.
Answer:
Fire insurance, property insurance, insurance against accident, marine insurance, riot insurance, etc.
Question 16.
Define selling.
Answer:
The process in which the product is handed over to the consumer in exchange of money is called selling.
![]()
Question 17.
State the scope of selling.
Answer:
The scope of selling is limited to the transfer of ownership of products from the seller to the consumer
Question 18.
What is the difference in the objective of marketing research and selling?
Answer:
The objective of marketing is to earn profit through customer satisfaction where as that of selling is to earn profit by selling products.
Question 19.
Which parties are involved in marketing?
Answer:
Suppliers of product, middlemen involved in sale distribution, consumers, etc.
Question 20.
What requires more capital marketing or selling or both equally?
Answer:
Marketing
Question 21.
Define production concept.
Answer:
Consumers will favour products that are available and highly affordable.
Question 22.
What is preferred in production concept?
Answer:
Under this concept, not quality but ‘availability of product’ and ‘low price’ are given preference.
Question 23.
On what principle does the product concept work?
Answer:
Consumers will favour products that offer the most in quality, performance and innovative features.
Question 24.
What is selling concept?
Answer:
The selling concept holds the idea that “consumers will not buy enough of the firm’s products unless it undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort”
Question 25.
Give an idea about the marketing concept.
Answer:
Marketing concept believes in the philosophy that “Consumer is the king of the market.” “The aim of this concept is to provide effective and efficient product as compared to competitors.”
Question 26.
Why ethically social concept is higher than the marketing concept?
Answer:
Marketing concept gives priority only to the preferences of the consumers and ignores loss that might occur to the society. Social concepts says that the marketing management should be such that the society or the environment is least affected. Hence,…………..
![]()
Question 27.
Give an example of social concept that can be used in marketing.
Answer:
The initiative of a company of giving paper bags to customers in place of plastic bag.
Question 28.
What is fat tax?
Answer:
A tax proposed on foods or drinks judged to be unhealthy and whose consumption is believed to be linked to rising obesity levels is called fat tax.
Question 29.
Define marketing mix.
Answer:
The set of marketing tools that the firm uses to attain its marketing objectives is ..
Question 30.
What do you mean by 4Ps?
Answer:
- Under marketing mix, the firm has to take several marketing decisions that fall under four categories namely,
- Product
- Price
- Place and
- Promotion.
- Together these four constituents of the marketing mix are also known as 4Ps.
Question 31.
Define product.
Answer:
A product can be a tangible good or intangible service that fulfills the need or want of consumers.
Question 32.
What does the concept product says under marketing mix?
Answer:
This concept says that the producer needs to have a clear cut and exact idea about his product and what makes it unique before he can successfully market it.
Question 33.
What does price means with respect to a product?
Answer:
Price refers to the value paid by the consumer for the physical, economic, social and psychological satisfaction received from the product.
Question 34.
What does the place component of the promotion mix refer to?
Answer:
Place or placement refers to the decision as to where to place the product so that the product can be accessed by potential buyers.
Question 35.
What is the main function of promotion?
Answer:
To provide information regarding new product to the existing and the potential consumers, attract them and create demand for the product.
Question 36.
Define branding.
Answer:
When the product of one producer is to be easily identified from that of products of other producers and no one else can copy it by using name, logo, number, design on the label, etc. it is known as branding.
Question 37.
What is trademark?
Answer:
When the producer gets the brand name and logo registered with government so that no other company can copy it or use it than such a legal certification is called trademark.
Question 38.
State two factors affecting price determination.
Answer:
(a) Production cost and
(b) Demand for the product
![]()
Question 39.
Enlist few factors that affect demand of the product.
Answer:
Taste and preference of the consumer, number of consumers, purchasing power of consumer, number of competitors in the market, price of competitor’s product, etc.
Question 40.
How does government intervene in case of monopolistic products?
Answer:
The government imposes several control on such products in order to protect the interest of consumers.
Question 41.
When do producers keep very low price?
Answer:
When they want to attract maximum consumers and hence create a dominant market position.
Question 42.
Define zero-level distribution system.
Answer:
The selling strategy in which the producer himself supplies product to the buyer without any mediator is called zero-level distribution system. The producer sells the products directly from his factory or his own shop or show-room.
Question 43.
State the limitations of zero-level distribution system.
Answer:
(a) The producer cannot reach a large mass of consumer,
(b) This method is possible only for limited products such as bakery, sweet shop, furniture manufacturer, etc.
Question 44.
What is indirect selling?
Answer:
When the producer sells his products by distributing it to one or more mediators the sale pattern is called indirect selling or sale by mediator.
Question 45.
What is single level distribution system?
Answer:
The distribution system where there is only mediator between the producer and consumer is called single level distribution system.
Question 46.
What is double level distribution system?
Answer:
The distribution system where there are two level mediators between the producer and the retailer, the first one is wholesalerand second, the retailer is called double level distribution system.
![]()
Question 47.
State the chain of distribution and selling in double level distribution system.
Answer:
In this system, the wholesaler buys the products from the producer in large quantities and sells it to various retailers in small quantities who in turn sell to the consumers.
Question 48.
Why the burden and risk of sale is less in double level distribution system?
Answer:
In this distribution channel, the burden and risk of sales reduces for the producers because the wholesaler purchases the product in large quantities.
Question 49.
Define three-level distribution system
Answer:
The distribution system that consists of three mediators between the producer and the consumer namely, agent, wholesaler and retailer is known as three level distribution system.
Question 50.
What is an advertisement?
Answer:
An advertisement is a paid form of non-personal information of goods and services in which advertiser’s identity is easily traced.
Question 51.
State the advantage of personal selling over advertisement.
Answer:
Personal selling not only creates awareness about the product but also creates a preference for the product and faith in the seller and the company. As a result, chances of sale increases.
Question 52.
State few techniques of sales promotion.
Answer:
Offering discounts, sale, gifts, coupons, etc.
Question 53.
Which are few methods of publicity?
Answer:
Addressing public or giving a presentation or an interview in newspaper or on radio or on T.V channel, giving donation, getting the office or showroom inaugurated by a film star or a cricketer, to attract people, etc.
Question 54.
State two roles that an advertisement play.
Answer:
(a) It creates demand and
(b) Enables large scale production
Question 55.
How does advertisement lead to large scale production?
Answer:
Advertisement can be targeted to a very large number of consumers at one go. This increases the demand many-folds. To fulfill this demand the company needs to undergo large scale production.
Question 56.
State two advantages of large scale production.
Answer:
(a) Reduces production cost and
(b) Increases profitability.
Question 57.
How can you say that advertisement gives rise to employment?
Answer:
Due to advertisement, demand for a product or service increases. This leads to rise in employment in several sectors such as production, logistics, service and repair, etc.
Question 58.
State two disadvantages of advertisement.
Answer:
(a) In most cases, advertisements are exaggerated which leads to cheating with the consumer,
(b) Many times advertisements that are irritating and obscene are shown.
Question 59.
Define sale as a means of sales promotion.
Answer:
When the product is genuinely offered at lower price than its actual price for a limited period of time, it is known as sale.
Question 60.
What is discount?
Answer:
When actual price charged for a product is less than its original price it is known as discount.
![]()
Question 61.
What is an advertisement coupon?
Answer:
A coupon printed in newspaper or circulated through pamphlet or some other modes where in the consumer is given discount on producing the coupons to the seller is called an advertisement coupon.
Question 62.
What are the chief objectives of giving advertisement coupons?
Answer:
(a) To check how well is the sale response by offering such coupons,
(b) To provide discount to the one who produces the coupons to the seller.
Question 63.
What is a gift with respect to sales promotion?
Answer:
A small gift given along with the main product so as to promote the main product is called a gift. For example, giving 1 soap free on purchasing 3 soap bars.
Question 64.
What is lucky draw?
Answer:
In this technique the customer is given a coupon as a code and on a particular day results are declared. The person whose coupon number gets selected in the lucky draw gets a gift.
Question 65.
What is interest-free loan? When is it generally given?
Answer:
Interest-free loan is a loan where in the consumer who buys a product on loan does not need to pay interest. It is given generally to buy home appliances like AC, refrigerator, 2-wheelers, etc.
Question 66.
State two roles of publicity in promotion mix.
Answer:
(a) The company need not pay anything for publicity of its product and hence it is the cheapest promotion tool,
(b) Publicity creates awareness among potential customers about the product or the company. This way it directly boosts the selling efforts of sellers and distributors.
Question 67.
What do you mean by public relations?
Answer:
Public relations is a group of activities designed or presented in such a way that it creates and maintains effective impression of the company on different parties involved with the product or service of the company.
Question 68.
State two activities included in the public relations.
Answer:
(a) For giving news in the newspaper about the company,
(b) Publishing the speech of director of the company
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
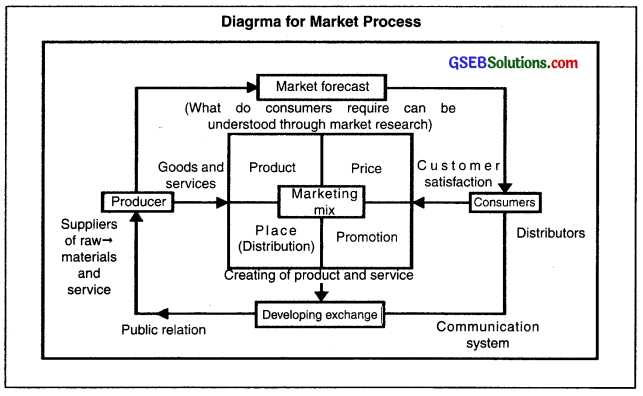
What is marketing? Give a brief idea about marketing process.
Answer:
- According to the American Marketing Association, ‘Marketing is a business activity, in which products or services are diverted from the producer to the consumer.’
- The firms produce goods and services keeping in mind future needs of the consumers.
- The marketing process tries to balance the needs of the consumers and the products.
- The type of product to be produced is decided on the basis of preference of consumers whereas the price is decided according to the purchasing power of the consumers.
- Finally, at the end of marketing process, exchange is developed between two parties i.e. buyers and sellers. This exchange enables the producers to fulfill their business objectives and buyers satisfy their needs.
Question 2.
State various definitions of marketing and explain marketing process with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Definitions of marketing:
- According to The American Marketing Association: “Marketing is a business activity in which products or services are diverted from the producer to the consumer.”
- According to Kapoor and Lacobucci: “Marketing is a mutual exchange between consumers and firms.”
- “Marketing is a total system of business activities which are designed to plan a product, to determine its price and to distribute goods which can satisfy wants of the consumers and reach the target as well as objectives of organizations.”
- According to Prof. Philip Kotler: “Marketing is a social process, in which private groups based on their requirement, produce valuable products and independently exchange goods and services.”
![]()
Question 3.
State the various functions of marketing process.
Answer:
- Market Research
- Collection of products
- Transformation of raw materials into consumable products
- Standardization and gradation of product
- Labeling of product
- Price determination
- Packing of product
- Storage of products
- Transportation facilities
- Insurance of the products
- Financial arrangement
- Advertisement
- Arrangement of sales and distribution
- Selling
- After sales services
Question 4.
For big companies, marketing research is pre-requisite to a product launch. Explain.
Answer:
- Big companies engage in large scale production, employee large number of people and invest heavily in their products and services. They even have a separate marketing department that takes care of marketing activities round the year.
- As per the practice, marketing research is the first and foremost work in marketing.
- Marketing research provides detailed information about scope of market, taste and preference of consumers, readiness to pay a certain price, consumer satisfaction, etc.
- A large company undergoes large scale production and has to bear high risk of success of the product or service. As a result, when the company wishes to produce some product it becomes necessary to gather knowledge regarding what a consumer wants in the product. Whether the consumer is ready to accept such a product and if yes then at what price.
Question 5.
Marketing research is a cyclic activity. Explain.
Answer:
- It is said that marketing research is the first step towards marketing.
- When a producer launches a new product he wishes to gain insight about the preference of consumer about the product and so he engages in marketing research.
- Marketing research provides detailed information about scope of market, taste and preference of consumers, readiness to pay a certain price, etc.
- On the basis of the information, the producer moves ahead with production.
- The process of marketing research does not end here. Once the product is launched, it is also necessary to understand consumer satisfaction with the product and the changes he expects. This again calls for the need of research and fresh inputs from the market.
- Moreover, when competitor launches their products, marketing research again becomes helpful to compare the product already existing in the market with the new product being launched.
- If the product fails, the research is again conducted to know the reason for failures, make changes in the product and give it a fresh start.
- Thus, we can say that the marketing research is a cyclic activity.
Question 6.
How is standardization and gradation beneficial for the farmer?
Answer:
- By standardization, the farmer sorts his produce according to a specific and nearly same colour, feel, size, quantity, etc.
- Through gradation the farmer grades his produce on the basis of its quality and other characteristics. For example, fruits are graded as first quality fruit, second quality and so on.
- By grading the products into various categories, the farmer can fix different prifces for various grades and earn accordingly.
- Similarly standardizing helps him to assure his seller that the product belongs to a specific standard and hence he can charge high and earn more.
- Thus, standardization and gradation increases faith and loyalty of consumers towards the products. This increases the sale.
Question 7.
What are the advantages of packaging?
Answer:
Packing the product:
- Packing can be considered as the garment for the product.
- Packing does two tasks, providing protection to the product as well as attracting consumers. Depending on the type of product, the producer also prints details regarding the use of the product on the product.
- A variety of materials such as paper, plastic jars, tinned boxes, glass jar, etc. are used to pack different products.
Advantages of packaging:
- Proper packing prevents the goods from getting damaged and makes them easier to transport.
- Packing helps to preserve product quality and its features.
- Consumers easily come to know the price of the product from the packing itself (For example: We can easily make out that a wafer or kurkure pack is worth Rs. 10 without looking at the price.).
Question 8.
State the duties of a marketing manager.
Answer:
Financial arrangement:
- Each and every activity of marketing requires money or say working capital.
- To satisfy these requirements well planned financial management is required.
- The financial manager decides how much finance to raise and allocate to the various activities.
- For certain seasonal product, advertisements are required in particular season only and so financial arrangement can be done well in advance.
Marketing manager’s main duties under marketing process includes:
- Avail finance at the right time
- Organize advertisement campaigns
- Set-up distribution channels
- Branding the product in the market
- Conducting market research, etc.
![]()
Question 9.
Although the latent objective of marketing is to sell, a marketing person is not called a sates person. Explain.
Answer:
- All the activities in the business at the end are done to generate, maintain or increase sale.
- Marketing activities understand the requirement of consumer, develop new products, determining price and provide after sale service. These activities play a vital role in sale of the product.
- On the other hand, selling is purely focused on to sell the product and earn the profit. Hence, in spite the latent objective of marketing is to sell, a marketing person is not called a sales person.
Question 10.
Explain in short the ideologies (concepts/views) of marketing management.
Answer:
Business firms keep in mind various philosophies or concepts and develop marketing programmes for marketing. There are five main concepts that are kept in mind while working on the marketing.
They are:
Ideologies of marketing management:
1. Production concept:
- The idea of production concept is “Consumers will favour products that are available and highly affordable”. This concept is one of the oldest marketing management concept which guide the sellers.
- Under this concept, not quality but ‘availability of product’ and ‘low price’are given preference.
- According to this concept, the producer does not believe in giving any extra facility or feature in the product. The objective is to simply sell a basic product at a reasonable or say cheap price.
2. Product concept:
- The product concept works under the principle that the consumers will favour products that offer the most in quality, performance and innovative features.
- Under this concept, marketing strategies are focused on making continuous product improvements.
- Products falling in this category are relatively costly.
3. Selling concept:
- The selling concept holds the idea that “consumers will not buy enough of the firm’s products unless it undertakes a large-scale selling and promotion effort”. Hence, the company believes it should undertake aggressive production and selling steps.
- Here aggressive efforts are made to create demand for products being produced and sell rather than understand the demand and produce accordingly. The complete emphasis is not given on the need of consumer but to sell what the company is producing.
4. Marketing concept:
This is the most modern and widely used concept. It can be called as user-based concept.
- The company undertakes production by taking up research on preferences, habits, desires, etc. of the consumers.
- This concept believes in the philosophy that “Consumer is the king of the market.”
- “The aim of this concept is to provide effective and efficient product as compared to competitors.”
5. Social concept:
- This concept is also known as ‘societal oriented concept’.
- Marketing concept gives priority only to the preferences of the consumers and ignores loss that might occur to the society.
- It is quite possible that by giving too much focus on the preference of the consumer, the society or the nation suffers. This might also lead to wastage of resources.
- On the contrary, the social concept says that marketing management should be done in such a way that consumers’ wants get fulfilled and at the same time environment or society gets least affected.
- A fine example of this concept is banning the plastic bags which degrade the environment just to provide the convenience to consumers.
Question 11.
Write a short note on production concept.
Answer:
Production concept:
- The idea of production concept is “Consumers will favour products that are available and highly affordable”. This concept is one of the oldest marketing management concept which guide the sellers.
- Thus, the production concept emphasizes on product availability and price. It also says that a consumer prefers cheap product.
- Under this concept, not quality but ‘availability of product’ and ‘low price’are given preference.
- According to this concept, the producer does not believe in giving any extra facility or feature in the product. The objective is to simply sell a basic product at a reasonable or say cheap price. This concept can be widely seen in underdeveloped countries.
Question 12.
Write a short note on product concept.
Answer:
Product concept:
- The product concept works under the principle that the consumers will favour ‘ products that offer the most in quality, performance and innovative features.
- Under this concept, marketing strategies are focused on making continuous product improvements.
- Companies following this concept keep on improving the product quality continuously and work day and night on research and development of the product.
- Products falling in this category are relatively costly.
Question 13.
Write a note on marketing concept.
Answer:
Marketing concept:
- This is the most modern and widely used concept. It can be called as user-based concept.
- The company undertakes production by taking up research on preferences, habits, desires, etc. of the consumers.
- All marketing policies are formulated by keeping consumers at the center.
- This concept believes in the philosophy that “Consumer is the king of the market.”
- “The aim of this concept is to provide effective and efficient product as compared to competitors.”
- Company focuses on delighting and satisfying the consumers.
- This concept benefits number of firms, consumers and society. India also highly adopts this concept for its success.
Question 14.
Explain social concept giving examples.
Answer:
Social concept:
- Social concept is also known as ‘societal oriented concept’.
- Although marketing concept is good, it has been criticized too. The criticism is that the marketing concept gives priority only to the preferences of the consumers and ignores loss that might occur to the society.
- It is quite possible that by giving too much focus on the preference of the consumer, the society or the nation suffers. This might also lead to wastage of resources.
- On the contrary, the social concept says that marketing management should be done in such a way that consumers’ wants get fulfilled and at the same time environment or society gets least affected.
- A fine example of this concept is banning the plastic bags which degrade the environment at the cost of the convenience of consumers.
- Similarly, regulations are made so that air pollution can be reduced by controlling industrial emissions.
- The trend of ready-to-eat food is rising. But, at the same time it should be taken care that the food does not contain harmful preservatives or do not pass through harmful processes to compromise the nutritional value and purity.
- Similarly, to control the consumption of junk food, some states have imposed ‘fat tax’ on food rich in fats and carbohydrates.
- Certain laws have been passed to control air and noise pollution so as to prevent damage the surroundings.
Question 15.
Explain briefly the 4Ps.
Answer:
Marketing mix consists of four main components known as the 4Ps. These 4Ps are
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion.
1. Product:
- The first of the 4Ps is the product.
- A product can be a tangible good or intangible service that fulfills the need or want of consumers.
- Product is considered as the base of marketing process.
- This concept says that the producer needs to have a clear cut idea about his product and what makes it unique before he can successfully market it.
- Decisions that a producer needs to take under the product component include features of the product, packaging, branding, labeling, after sales service, complaint redressal, etc.
2. Price:
- Once, the producer gets a concrete knowledge about his product, he can move towards the second ‘P’ i.e. Price.
- Price refers to the value paid by the consumer for the physical, economic, social and psychological satisfaction received from the product. Price is the economic value of a product, which is generally depicted in the form of money.
- Price determination of a product is most important for any business unit. Price is extremely important for both, the buyers and sellers.
- Demand for a product is inversely related to the price of that product. This means that when price of the product rises, demand falls and when price falls the demand rises.
- Determining the price will impact income, profit, demand and also marketing strategy.
- Thus, every firm has to set its price in such a manner that the product becomes successful.
3. Place (Placement/Distribution):
- Place or placement refers to the decision as to where to place the product so that the product can be accessed by potential buyers.
- A firm can identify the place of putting the product by thoroughly understanding the target market and then setting up the distribution network. (Note: For example, it will be wrong placement decision to set-up a fine dine premium restaurant in a low income group area.)
- Thus, distribution refers to an arrangement of making the final product available at a place where it is required, whenever it is required and in whatever quantity it is required.
- Distribution decision plays a very important role when the expected consumer group is large and is spread in heterogeneous geographical areas.
- The producer does not come into direct contact with the consumer but has a link through various middlemen. The middlemen may include super stockist, wholesaler, retailer, etc. As a result, the distribution system is designed on the basis of type of product, number of consumers, geographical area, etc.
- At the same time, the firm also sees that the product reaches the consumer in the proper packing and at least handling and distribution cost.
4. Promotion:
- Promotion is an important part of marketing mix.
- An important function of promotion is to provide information regarding new product to the existing and the potential consumers.
- In this process, the producer attempts to convert existing customers as well as potential customers to purchase the products.
- Thus, promotion aims at creating awareness, attracting customers, increasing demand and motivating people to purchase.
![]()
Question 16.
Write a detailed note on branding.
Answer:
Branding:
Definition:
When the product of one producer is to be easily identified from that of products of other producers and no one else can copy it by using its name, logo, number, design on the label, etc. it is known as branding.

Meaning:
- Branding is necessary in order to distinguish own product from the products of competitors. To achieve this, the producer tries to develop a specific name, logo, design or number for the product through which consumers can easily identify the product. (Note: For example, sports accessory company Nike has a unique logo similar to a tick mark. Consumers can identify a Nike product just by looking at its logo even if Nike is not written.)
- At times, the producer also gets the brand name and logo registered with government so that no other company can use it. This prevents duplicating. Such a legal certification is called trademark.
- A brand provides identity to the product. The producer while deciding the name of the product keeps in mind various things about the product such as its features, utility, part of owner’s name etc.
- The product name should convey a particular meaning and should be easy to remember. Often the philosophy of the organization is kept in mind while deciding the name or a symbol.
Features of branding:
- Branding makes people trust the consistent quality that they expect from the said brand.
- Specific colours are used while labeling and creating designs for a brand. Also, specific pattern or designs are used to symbolize the brand.
- The finalized logo is printed on the packing of the product and many a times at the product itself.
- Brand of a firm shows the features, advantages, uses, personality and culture of the product.
- Symbol creates a unique identity.
- Symbol is a verbal and visual identity.
- Product with a symbol can be sold in the market at a high price.
- It is easy to sell a product carrying a famous symbol. In fact, the sale is higher for a product carrying a famous symbol. (Note: For example, ADIDAS shoe company has a logo consisting three stripes. This logo is famous itself to give the product a high value in consumer’s mind.)

Question 17.
State the features of branding.
Answer:
Features of branding:
- Branding makes people trust the consistent quality that they expect from the said brand.
- Specific colours are used while labeling and creating designs for a brand. Also, specific pattern or designs are used to symbolize the brand.
- The finalized logo is printed on the packing of the product and many a times at the product itself.
- Brand of a firm shows the features, advantages, uses, personality and culture of the product.
- Symbol creates a unique identity.
- Symbol is a verbal and visual identity.
- Product with a symbol can be sold in the market at a high price.
- It is easy to sell a product carrying a famous symbol. In fact, the sale is higher for a product carrying a famous symbol. (Note: For example, ADIDAS shoe company has a logo consisting three stripes. This logo is famous itself to give the product a high value in consumer’s mind.)

Question 18.
Explain labeling and the functions it performs in product positioning.
Answer:
Labeling:
- A product label is a description about the product to make consumer aware about the product he wish to purchase.
- Generally, a label is printed on paper or plastic material and put up on the primary packing of the product.
- Generally, the label provides all information in detail about the product. Details such as weight, size, price, date of manufacturing, ingredients, expiry date, etc. of the product are shown on the label.
- At times, the label also contains the procedure to use the product, its applications, etc. Quite often it also provides directions for opening the packing.
- The label also contains contact details of the company and for complaint and suggestion.
Functions:
- Label helps in identifying the product.
- It gives complete information about the quality and type of the product.
- All information regarding product is provided to the consumer.
- Direction of use of product is given to the consumer.
- It creates attraction for the product which helps in advertisement and personal service.
- It complies with the legal requirement of product packing and providing all the ‘ necessary information to the consumer.
Question 19.
State the functions of labeling.
Answer:
Functions:
- Label helps in identifying the product.
- It gives complete information about the quality and type of the product.
- All information regarding product is provided to the consumer.
- Direction of use of product is given to the consumer.
- It creates attraction for the product which helps in advertisement and personal service.
- It complies with the legal requirement of product packing and providing all the ‘ necessary information to the consumer.
Question 20.
Write a brief note on packaging of product as a marketing function.
Answer:
Packaging:
- Packaging does two important functions, first protecting the product and second making it attractive so that consumers can be attracted.
- Various materials are used in packaging. The materials include plastic bags, cloth bags, cardboard box, plastic barrels, wooden boxes, etc.
Advantages of packaging:
- Provides protection to the product
- Helps in advertising and attracting consumers
- Success of many products lies in their packing
- It helps in easy transportation
- Product can better be used when it is packed
![]()
Question 21.
What are the advantages of packaging?
Answer:
Advantages of packaging:
- Provides protection to the product
- Helps in advertising and attracting consumers
- Success of many products lies in their packing
- It helps in easy transportation
- Product can better be used when it is packed
Question 22.
Write a detailed note on price as a component of marketing mix.
Answer:
- Price is the second P of marketing mix.
- Price refers to the value paid by the consumer for the physical, economic, social and psychological satisfaction received from the product. Price is the economic value of a product, which is generally depicted in the form of money.
- Price determination of a product is most important for any business unit. Price is extremely important for both, the buyers and sellers.
- Demand for a product is inversely related to the price of that product. This means that when price of the product rises, demand falls and when price falls the demand rises.
- Determining the price will impact income, profit, demand and also marketing strategy.
- Thus, every firm hast to set its price in such a manner that the product becomes successful.
Factors affecting pricing:
There are several factors that affect price determination. These are discussed below:
1. Production cost:
- Cost of producing a good that the producer has to bear is the most important of all aspects for determining the price.
- Production cost includes cost borne to procure raw material, labour, production and processing costs, administrative cost, sales and distribution expenses, etc.
- Over and above these costs, if the product is newly launched then there are also several other expenses incurred for promoting the product and putting up in the market. These costs also affect the price and can be considered indirect production cost.
- It is quite obvious that price of a product can never be lower than its production cost.
2. Demand for the product:
- Demand for the product and its price are directly related.
- Factors that affect demand include taste and preference of the consumer, number of consumers, purchasing power of consumer, number of competitors in the market, price of competitor’s product, etc.
- The producer may charge a high price if the demand is high, but if the demand is low, the price has to be kept low and competitive.
- In case if the product of competitor is in high demand or if there are more competitors in the market, the producer launching new product might have to lower its price.
- When the market is less competitive, the producer can keep a higher price and earn higher profit.
3. Competition in the market:
- The extent of competition directly affects the price of the product.
- Producers keeps competitive price when the number of competitors are more and competition is high.
- During competition, the prices are also fixed with objectives such as beating the competitor’s price, or making their entry or survival difficult in the market
or even with an objective to force them to withdraw their product and quit the market. - Contrary to this, a product having a very high brand reputation can be sold at higher price than the competitors’ product (Note: For example, iPhone).
4. Governmental and legal controls:
- Producers of monopolistic products (especially, of daily use) usually charge high price. So, the government imposes control on such business units in order to protect the interest of consumers.
- Prices of products like petrol keep on fluctuating quite frequently. Hence, the government puts a number of legal controls on such products. These factors have to be taken into consideration while determining product price.
- Government also imposes certain regulatory control on products which are essential for life such as lifesaving drugs, petrol, diesel, paper for daily newspaper, etc. So, the producers of these products have to consider these factors too while determining prices.
5. Price determination on the basis of objectives:
Over and above the factors discussed above, there are some other objectives too which the producer might consider while determining the price.
Some of them are:
(A) Maximum profit:
Under this objective, the producer determines the price of the product with an aim of earning maximum profit. He does so either because there is no competition in the market or he has spent heavily in the research and development of the product.
(B) To acquire dominant position in the market:
In most cases the producers keep a very low price of his product so that they can attract maximum customers and dominate the market.
(C) To sustain competition:
When competitors are more and when competition is high, the business firms tend to fix prices lower than or at par with competitors.
6. Economic condition:
- Economic condition of the market plays an important role in determining the price of the product.
- If the economic condition of the country is good, price can be fixed at a higher level and if there is a recession, product price is reduced.
7. Buying behaviour:
- Consumer behavior plays an important role in determining price.
- Behaviour of consumers towards a product is affected by factors such as consumer’s habits, social and cultural structure, individual preference, his financial condition, etc.
- Due to these factors, the attitude towards the product may change and it may not get desired or expected response from the consumers. Hence, it is quite important to consider these factors too before determining the price.
Question 23.
Demand for the product and its price are directly related. Explain.
Answer:
Demand for the product:
- Demand for the product and its price are directly related.
- Factors that affect demand include taste and preference of the consumer, number of consumers, purchasing power of consumer, number of competitors in the market, price of competitor’s product, etc.
- The producer may charge a high price if the demand is high, but if the demand is low, the price has to be kept low and competitive.
- In case if the product of competitor is in high demand or if there are more competitors in the market, the producer launching new product might have to lower its price.
- When the market is less competitive, the producer can keep a higher price and earn higher profit.
Question 24.
Explain – Price determination on the basis of objectives.
Answer:
Price determination on the basis of objectives:
Over and above the factors discussed above, there are some other objectives too which the producer might consider while determining the price.
Some of them are:
(A) Maximum profit:
Under this objective, the producer determines the price of the product with an aim of earning maximum profit. He does so either because there is no competition in the market or he has spent heavily in the research and development of the product.
(B) To acquire dominant position in the market:
In most cases the producers keep a very low price of his product so that they can attract maximum customers and dominate the market.
(C) To sustain competition:
When competitors are more and when competition is high, the business firms tend to fix prices lower than or at par with competitors.
![]()
Question 25.
Behaviour of consumer can lead to the failure of a product. Explain.
Answer:
Buying behaviour:
- Consumer behavior plays an important role in determining price.
- Behaviour of consumers towards a product is affected by factors such as consumer’s habits, social and cultural structure, individual preference, his financial condition, etc.
- Due to these factors, the attitude towards the product may change and it may not get desired or expected response from the consumers. Hence, it is quite important to consider these factors too before determining the price.
Question 26.
What kind of regulations does the government put on producers?
Answer:
- The government imposes control on prices of monopolistic goods in order to protect the interest of consumers.
- Prices of products like petrol keep on fluctuating quite frequently. Hence, the government puts a number of legal controls on such products.
- Government also imposes certain regulatory control on products which are essential for life such as lifesaving drugs, petrol, diesel, paper for daily newspaper, etc.
Question 27.
Which is the most important aspect for determining the price of the product?
Answer:
Also, state the costs incurred under this aspect.
- Cost of producing a good that the producer has to bear is the most important of all aspects for determining the price.
- Production cost includes cost borne to procure raw material, labour, production and processing costs, administrative cost, sales and distribution expenses, etc.
- Over and above these costs, if the product is newly launched then there are also several other expenses incurred for promoting the product and putting up in the market. These costs also affect the price and can be considered indirect production cost.
Question 28.
Explain place or distribution as the pillar of marketing mix.
Answer:
Place (Placement/Distribution):
- Place or placement refers to the decision as to where to place the product so that the product can be accessed by potential buyers.
- A firm can identify the place of putting the product by thoroughly understanding the target market and then setting up the distribution network. (Note: For example, it will be wrong placement decision to set-up a fine dine premium restaurant in a low income group area.)
- Thus, distribution refers to an arrangement of making the final product available at a place where it is required, whenever it is required and in whatever quantity it is required.
- Distribution decision plays a very important role when the expected consumer group is large and is spread in heterogeneous geographical areas.
- The producer does not come into direct contact with the consumer but has a link through various middlemen. The middlemen may include super stockist, wholesaler, retailer, etc. As a result, the distribution system is designed on the basis of type of product, number of consumers, geographical area, etc.
- At the same time, the firm also sees that the product reaches the consumer in the proper packing and at least handling and distribution cost.
Question 29.
Which channels of distribution are adopted by the producers? Explain in detail.
Answer:
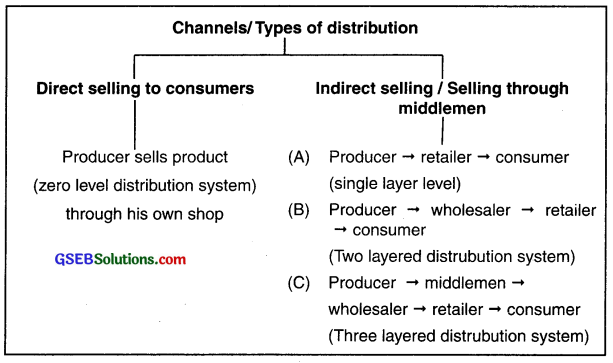
The channels of distribution can be understood with the following diagram:
1. Direct sales (Zero level distribution):
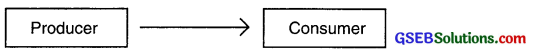
- In this type of selling strategy, the producer himself supplies proctuct to the buyer.
- The producer sells the products directly from his factory or his own shop or show-room.
- This method of distribution is the shortest and easiest method of distribution.
- Apart from this method, he may also adopt selling through post, door-to-door selling by salesman, sales through on – line shopping, etc.
- In this type of distribution system there are no layers/levels. Hence this system is known as zero level distribution system.
Limitations:
- The producer cannot reach a large mass of consumer.
- This method is possible only for limited products such as bakery, sweet shop, furniture manufacturer, etc.
2. Indirect sale: (Sale by mediator):
- When the producer sells his products by distributing it to one or more mediators the sale pattern is called indirect selling or sale by mediator.
- The biggest advantage of this method is that the producer can reach a large consumer base. This method is quite often used for the products that are cheap and used by consumer on daily basis for example, cooking gas cylinder distribution system.
Types of indirect sales:
(A) Single level distribution:

- In this distribution system there is only mediator between the producer and consumer. This mediator is called retailer. The retailer purchases the product directly from the producer and distributes it to consumer. There can be a number of retailers for the product.
- Generally, this distribution system is adopted for specialized products.
(B) Double level distribution system:
![]()
- In this distribution system there are two level mediators between the producer and the retailer. The first one is wholesaler and second, the retailer.
- The wholesaler buys the products from the producer in large quantities and sells it to various retailers in small quantities who in turn sell to the consumers. There can be more than one wholesaler.
- In this distribution channel, the burden and risk of sales reduces for the producers because the wholesaler purchases the product in large quantities. It then becomes his duty to sell and supply to the retailers whatever the quantity.
- After purchasing the products, the wholesaler stores the products in their ware houses. This saves warehousing costs for the producer.
- Sometimes the producer frames the retailing network for each wholesaler so that the products can reach to the final consumer easily and without disputes between the wholesalers.
- Daily use products like soap, toothpaste, battery, and shaving cream, etc. can be easily distributed under this distribution system.
(C) Three-level distribution system:
![]()
- The distribution system that consists of three mediators between the producer and the consumer namely, agent, wholesaler and retailer is known as three level distribution system.
- In this system of distribution, the products first reach the agents or middlemen from producer. The agents supply the product to various wholesalers, wholesalers to retailers and retailers finally to consumers.
- The producers are in direct contact only with agents or middlemen.
- Since the producer deals with only agents, monetary transactions and other dealings become quite hassle-free for the producers.
- This method is useful either when the production is limited or when the product is accepted to everyone.
Question 30.
Write a short note on zero level distribution.
Answer:
Zero level distribution:

- In this type of selling strategy, the producer himself supplies proctuct to the buyer.
- The producer sells the products directly from his factory or his own shop or show-room.
- This method of distribution is the shortest and easiest method of distribution.
- Apart from this method, he may also adopt selling through post, door-to-door selling by salesman, sales through on – line shopping, etc.
- In this type of distribution system there are no layers/levels. Hence this system is known as zero level distribution system.
Limitations:
- The producer cannot reach a large mass of consumer.
- This method is possible only for limited products such as bakery, sweet shop, furniture manufacturer, etc.
![]()
Question 31.
What is indirect selling? State its types and define each of them.
Answer:
When the producer sells his products by distributing it to one or more mediators the sale pattern is called indirect selling or sale by mediator.
Types of indirect sales:
(A) Single level distribution:
In this distribution system there is only mediator between the producer and consumer. This mediator is called retailer. He purchases the product directly from the producer and distributes it to consumer. There can be a number of retailers for the product.
(B) Double level distribution system:
- In this distribution system there are two level mediators between the producer and the retailer. The first one is wholesaler and second, the retailer.
- The wholesaler buys the products from the producer in large quantities and sells it to various retailers in small quantities who in turn sell to the consumers. There can be more than one wholesaler.
(C) Three level distribution system:
- The distribution system that consists of three mediators between the producer and the consumer namely, agent, wholesaler and retailer is known as three level distribution system.
- In this system of distribution, the products first reach the agents or middlemen from producer. The agents supply the product to various wholesalers, wholesalers to retailers and retailers finally to consumers.
Question 32.
Simpler the distribution channel, cheaper the product. Explain.
Answer:
- There are several channels of distribution ranging from zero level distribution to three level distribution.
- Simplest of all is the zero level channel whereas the three level is the most complex one.
- In zero level distribution the producer sells his product directly to the customers. There are no mediators, agents, wholesalers or retailers involved. Naturally, the producer does not need to bear all the costs and commissions involved in maintaining these mediators. So, the producer can sell his product keeping minimum cost and sell it in the market.
- Hence, it is said, simpler the distribution channel, cheaper the product.
Question 33.
What is promotion and promotion mix? What are the components of promotion mix? Explain briefly.
Answer:
Promotion:
- Promotion is an important part of marketing mix.
- An important function of promotion is to provide information regarding new product to the existing and the potential consumers.
- In this process, the producer attempts to convert existing customers as well as potential customers to purchase the products.
- Thus, promotion aims at creating awareness, attracting customers, increasing demand and motivating people to purchase.
Components of promotion (or promotion mix):
- Promotion mix is a group of tools to create awareness about the product and services among consumers so that they can be attracted and motivated to purchase.
- The four main components or tools are:
- Advertisement,
- Personal selling,
- Sales promotion and
- Publicity.
- Business firms use these tools in different extents to lure the consumers.
- Which component to use in which manner and quantity is determined after considering factors such as attitude of consumer for purchase of product, nature of product, price of product, etc.
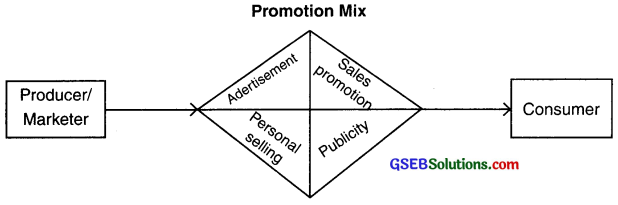
1. Advertisement:
- An advertisement is a paid form of non-personal information of goods and services in which advertiser’s identity is easily traced.
- Producers use different medium of advertisement to promote their product and service in the market.
- Advertisement is considered as the most important, famous and acceptable tool of promotion.
- The advertisement works as boon for products which are low in demand.
- Advertising can be done through TV, radio, mobile phones, dailies, magazines, internet, etc.
2. Personal selling:
- Although advertisement conveys the information of the product of a business unit to the consumer but still sometimes, it may not generate desired sales. Under such situations, the marketing manager takes help of the next component of promotion mix known as personal selling.
- In personal selling, the seller (or sales man/sales executive/sales manager) directs and explains about the product to the prospective consumer.
- Personal selling helps the seller to develop a rapport with the potential consumer. At the same time, the consumer develops a faith in the seller.
- The seller helps the consumer to clear his doubts regarding the product and assure him to extend his support in case of any problem with the product in the future.
- A big advantage of personal selling is that it not only creates awareness about the product but also creates a preference for the product. Moreover, it tries to develop faith of customer in the seller and the company. As a result, chances of sales increase.
3. Sales promotion:
- The process of persuading a potential customer to buy the product is called sales promotion.
- According to Kotler, “Sales promotions are short-term incentives that encourage the customer to buy the product or service.”
- Sales promotion has quick effects on customers.
- Sales promotion is an important component of promotion mix which when applied with advertisement and personal selling, increases the chances of sale quite drastically.
- Advertisement and personal selling mainly give information about the product while sales promotion gives prompt reason to buy the product.
- A variety of techniques are used for promoting the sale. Some of them are offering discounts, sale, gifts, coupons, etc.
- Sales promotion quickly attracts the customers and results into sales.
4. Publicity:
- Any form of non-personal presentation of goods, services or ideas done through public media which is free of charge is known as publicity. The business firm does not need to pay any charge for this form of publicity. Sometimes it is also considered as a part of public relations.
- Publicity is done by addressing public or giving a presentation or an interview in newspaper or on radio or on T.V channel, giving donation, getting the office or showroom inaugurated by a film star or a cricketer, to attract people, etc.
Question 34.
Advertisements have the power to lead to large scale production. Explain.
Answer:
Benefit of large scale production:
- Advertisement can be targeted to a very large number of consumers at one go. This increases the demand many-folds.
- In order to meet the huge demand, the company has to undergo large-scale production. Large scale production reduces production cost and increases profitability.
- As a result, the company earns more return as compared to the advertisement cost.
![]()
Question 35.
Advertisement leads to product awareness. Explain.
Answer:
Product awareness:
- Advertisement helps in providing information about the product to the consumer. The information can be utility of the product, features, how to use the product, etc.
- When a product has more than one usage then through advertisement such information is passed on to the potential consumers.
- Producer also creates a trust in consumer’s mind regarding the quality of the product.
- By sharing the trust and satisfaction of current consumers, new consumers can be convinced to purchase the product.
- Thus, there are several ways in which advertisement creates awareness about the product.
Question 36.
What are the objections against advertisement?
Answer:
Objections against advertisement:
- Promotion and advertisement are two sides of the same coin, but there are many evils of advertisement.
Advertisements attract consumer and lure them to buy products. Many times, the consumer does not think whether the product is useful for him or not and . still buys it. Unnecessary expenditure is a social evil. - The rich can buy more products than the poor. Higher expenses by the upper class creates inferiority complex for the poor.
- Advertisement is an expensive activity. Often the business units spend huge amount on advertisement. Naturally, the advertisement costs are added up in the product. This makes the product costlier and the consumer has to bear higher price.
- Many times, advertisers portray a fine image of one product and show the other product as inferior. This misleads consumers.
- Through attractive and misleading advertisement it is possible to sell goods of sub-standard quality to the consumer.
- Many times advertisements that are irritating and obscene are shown.
- Very often consumers get information regarding bidi, cigarettes, liquor, chewing tobacco, etc. which results in harmful effects in the long run due to addiction.
- Companies which produce almost identical products, heavily advertise their products. This forces other competitors to advertise as well.
- In most cases, advertisements are exaggerated which leads to cheating with the consumer.
Question 37.
What is personal selling? Explain.
Answer:
Personal selling:
- Although advertisement conveys the information of the product of a business unit to the consumer but still sometimes, it may not generate desired sales. Under such situations, the marketing manager takes help of the next component of promotion mix known as personal selling.
- In personal selling, the seller (or sales man/sales executive/sales manager) directs and explains about the product to the prospective consumer.
- Personal selling helps the seller to develop a rapport with the potential consumer. At the same time, the consumer develops a faith in the seller.
- The seller helps the consumer to clear his doubts regarding the product and assure him to extend his support in case of any problem with the product in the future.
- A big advantage of personal selling is that it not only creates awareness about the product but also creates a preference for the product. Moreover, it tries to develop faith of customer in the seller and the company. As a result, chances of sales increase.
Question 38.
Who is a salesman according to Kotler?
Answer:
According to Prof. Philip Kotler, “Salesman is that person who represents the business unit to the consumer and his job is to highlight the nature of the product, demonstrate the product, and explain its usefulness to the consumer and clear doubts. Through personal selling the business unit creates a definite type of relationship with the consumer.”
Question 39.
Explain: Sales promotion.
Answer:
Sales promotion:
- The process of persuading a potential customer to buy the product is called sales promotion.
- According to Kotler, “Sales promotions are short-term incentives that encourage the customer to buy the product or service.”
- Sales promotion has quick effects on customers.
- Sales promotion is an important component of promotion mix which when applied with advertisement and personal selling, increases the chances of sale quite drastically.
- Advertisement and personal selling mainly give information about the product while sales promotion gives prompt reason to buy the product.
- A variety of techniques are used for promoting the sale. Some of them are offering discounts, sale, gifts, coupons, etc.
- Sales promotion quickly attracts the customers and results into sales.
Question 40.
What do you mean by public relations? Which activities are included in public relations?
Answer:
- Public relations is a group of activities designed or presented in such a way that it creates and maintains effective impression of the company on different parties involved with the product or service of the company.
- In other words, a company makes use of public relations for maintaining its prestige.
Public relations include the following activities:
- Giving news in the newspaper about the company
- Publishing the speech of director of the company
- Planning activities like seminar, workshops, competitions or sports activities
- Circulating newsletter of company among share-holders, clients, etc.
- Informing society about public welfare activities organized by the company
- Planning social or cultural programmes
![]()
Question 41.
Discuss the functions of public relation.
Answer:
Functions of public relation:
1. Maintaining good relations with audio-visual media is very important for creating good image of the company. Good relations with these channels can help the company to communicate well with society about the product of the company or company itself.
2. When the company develops a new product and introduces it in the market as a part of customer awareness programme, information about the product can be given officially.
3. Matters such as company’s news, achievements of employees, company’s achievements and awards or prizes won by the company can be published with the help of company’s news bulletin or a magazine. These steps can help to create good image of the company.
4. Parties involved with the company can come to know about company’s future policies by listening to the speech and interview of company’s directors on different media.
5. By organizing social activities and cultural programmes, society can be informed about company’s social responsibility. This helps to create good impression of the company.
6. Activities of public interest such as maintenance of garden, repairs of roads, health check-up, tree plantation, etc. can help to solve the problems in the society and in creating social image of the company.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
“Marketing is a mutual exchange between consumers and firms.” Who gave this definition?
(A) Kapoor and Lacobucci
(B) Philip Kotler
(C) American Marketing Association
(D) Gary Hamel
Answer:
(A) Kapoor and Lacobucci
Question 2.
A company decides its marketing policy on the basis of
(A) Product
(B) Customer
(C) Producer’s research and preference
(D) Sales
Answer:
(B) Customer
Question 3.
Which of the following does not fall under marketing process?
(A) Collection of products
(B) Storage of products
(C) After sales services
(D) None of these
Answer:
(D) None of these
Question 4.
What is marketing manager not directly involved in?
(A) Availing finance
(B) Selling
(C) Branding
(D) Setting-up distribution channel
Answer:
(B) Selling
![]()
Question 5.
Which is the oldest marketing concept?
(A) Product concept
(B) Production concept
(C) Selling concept
(D) Marketing concept
Answer:
(B) Production concept
Question 6.
Which is the most widely accepted marketing concept?
(A) Product concept
(B) Selling concept
(C) Marketing concept
(D) Production concept
Answer:
(C) Marketing concept
Question 7.
What is the other name of social concept?
(A) Societal oriented concept
(B) Sociology concept
(C) Social based concept
(D) Society oriented concept
Answer:
(A) Societal oriented concept
Question 8.
Decisions related to are not a part of marketing mix.
(A) Price
(B) Product
(C) Place
(D) Performance
Answer:
(D) Performance
Question 9.
Which of the following is not a decision to be taken under product component of marketing mix?
(A) Features
(B) Campaigning
(C) Labeling
(D) After sales
Answer:
(B) Campaigning
Question 10.
Demand for a product is related to the price of that product.
(A) Directly
(B) Inversely
(C) Compoundly
(D) Partially
Answer:
(B) Inversely
![]()
Question 11.
A producer can determine his price keeping maximum profit when
(A) There is no competition in the market
(B) He has spent heavily in the research and development of the product
(C) He aims to earn maximum return
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Question 12.
There are majorly ______ types of channels of distribution.
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 5
(D) Several
Answer:
(B) 2
Question 13.
Direct selling to consumers is also called
(A) Single layer distribution system
(B) Two layer distribution system
(C) Zero layer distribution system
(D) Three layer distribution system
Answer:
(C) Zero layer distribution system
Question 14.
How many types of indirect selling are there?
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 5
(D) Many
Answer:
(B) 3
Question 15.
Which of the following is not a tool of promotion mix?
(A) Personal selling
(B) Advertisement
(C) Sales promotion
(D) None of these
Answer:
(D) None of these
Question 16.
______ is considered as the most important, famous and acceptable tool of promotion.
(A) Advertisement
(B) Personal selling
(C) Sales promotion
(D) Publicity
Answer:
(A) Advertisement
Question 17.
If advertisement is done at level, it will prove more fruitful.
(A) National
(B) State
(C) Local
(D) Depends on the advertisement
Answer:
(C) Local
Question 18.
If advertisement fails, is the second best option.
(A) Sales promotion
(B) Publicity
(C) Personal selling
(D) Online selling
Answer:
(C) Personal selling
Question 19.
The process of persuading a potential customer to buy the product is called
(A) Sales promotion
(B) Personal selling
(C) Publicity
(D) Emotional selling
Answer:
(A) Sales promotion
Question 20.
______ lies at the heart of marketing.
(A) Sales
(B) Product
(C) Market
(D) Sales promotion
Answer:
(B) Product
Question 21.
Which of the following modes of promotion mix is free?
(A) Sales promotion
(B) Personal selling
(C) Publicity
(D) All of these
Answer:
(C) Publicity
![]()
Question 22.
Which of the following is not a very desirable characteristic of a good salesman?
(A) Salesman should be good in communication, intelligent and efficient.
(B) Salesman should be very well educated.
(C) Salesman should be smart, interactive and physically fit.
(D) Salesman should be honest
Answer:
(B) Salesman should be very well educated.
Question 23.
Discount is mostly offered for products that are
(A) Obsolete
(B) Soon going to be out of fashion/technology, etc.
(C) Slightly defective
(D) Costly
Answer:
(C) Slightly defective
Question 24.
Packaging is also referred as
(A) Garments
(B) Cover
(C) Decoration
(D) All of these
Answer:
(A) Garments
Question 25.
______enables immediate sales.
(A) Personal selling
(B) Advertisement
(C) Sales promotion
(D) Publicity
Answer:
(C) Sales promotion
Question 26.
Production concept of marketing is mainly observed in countries.
(A) Backward countries
(B) Underdeveloped countries
(C) Developed countries
(D) Developing countries
Answer:
(B) Underdeveloped countries
Question 27.
The main objective of adopting public relation is
(A) To increase sales
(B) To listen to customer complaints
(C) To develop personal rapport
(D) To maintain prestige of the company and the product
Answer:
(D) To maintain prestige of the company and the product
Marketing Management – GSEB Std 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Notes
Marketing process:
Marketing process is a business activity in which products or services are diverted from the producer to the consumer.
Functions of marketing process:
- Marketing research
- Collection of goods
- Transformation of raw material into consumable goods
- Standardization and gradation
- Labeling distribution
- Pricing
- Packing
- Storage of goods
- Transportation
- Insurance
- Financial arrangement
- Advertisment
- Arrangement of sales and
- Sales
- Aftersales service
Difference between selling and marketing:
- Meaning
- Scope
- Objectives
- Parties
- Beginning and end
- Capital requirements
- Direction of efforts
![]()
Concepts of marketing management:
Different concepts to understand and implement the marketing management.
- Production Concept: It focuses on offering the product to consumer at the lowest cost.
- Product Concept: Producing better quality product and selling it at a high price, assuming that customer is quality conscious.
- Selling Concept: It focuses on an aggressive selling and promotion technique to increase stock turnover rate.
- Marketing Concept: The customer is at the centre and product is made from the view point of customer satisfaction.
- Social Marketing Concept: This concept talks about social responsibility over and above marketing. It says that the social interest should be protected when marketing is done. This means maintaining a balance between the satisfaction of customer and the interest of the society.
Marketing mix:
- The set of marketing tools that the firm uses to attain its marketing objectives is called marketing mix.
- There are four components of marketing management. They are Product, Price, Place and Promotion.
They are also known as 4 Ps.
(A) Product:
- A product can be a tangible good or intangible service that fulfills the need or want of consumers. Product is considered as the base of marketing process.
- Branding: Branding means any type of sign, symbol or design which is intended to differentiate the product from competitor’s product.
Characteristics of brand:
- Quality
- Use of colours in symbols
- Sign/symbol on packing
- Name of brand emphasizing the basic features or benefits or usages of the product
- Identification of the product
- Sale on high price
- Easy for the salesman
Labeling:
A product label is a description about the product to make consumer aware about the product he wish to purchase. It consists of displaying information such as product size or weight, price, date of manufacturing, ingredients, expiry date, method to use the product, etc.
Functions:
- Easy identification of the product
- Sufficient information about type and quality of the product
- Information about product
- Method of usage
- Create attractiveness
- Satisfy legal and ethical needs.
Packaging:
Covering a product to protect it is known as packaging.
(B) Price:
Value paid by a customer for a product or service for his physical, economical, , social or psychological satisfaction.
Factors affecting price:
- Cost of product
- Demand of product
- Competition in the market
- Government and legal restrictions
(C) Distribution:
It refers to an arrangement of making the final product available at place where it is required, when it is required and in whatever quantity it is required.
Types of distribution:
- Direct sales
- Sales through middlemen
1. Direct Sales or selling directly to the customer: The manufacturer or seller directly sells to the customers. It is also known as zero-level distribution channel.
2. Indirect sales/Sale through middlemen: Sale done using one or more levels of mediators is called indirect selling. There are three such channels. They are
(A) One Level: Only one mediator between a buyer and a seller.
(B) Two Level: Two mediators between a buyer and a seller.
(C) Three Level: Three mediators between a buyer and a seller.
Promotion:
It is an important marketing mix that creates attraction toward the product among the customers and converts potential customers into actual customers. In promotion advertisement, sales promotion, publicity and personal selling are included.
Advertisement:
Producers use different mediums to advertise goods or services. The advertisements are released in newspaper, T.V., radio, etc.
Functions of advertisement:
- Creates demand
- Advantages of large scale production
- Information about product
- Helps in job creation
- Raises living standard
- Maintains sales
Objections against advertisements:
- Leads to unnecessary purchasing which is a social evil
- Gives inferiority complex to poor.
- Expensive activity
- Misleads consumers by showing products of competitors as inferior
- At times sell inferior quality product
- Unimpressive presentation/obscenity irritates consumer
- Information regarding unwanted/harmful goods are displayed
- Forces to advertise others
- Exaggeration
![]()
Personal selling:
The activity of presenting the product before the potential customers, solving their doubts and converting them into actual buyers by a salesmen is called personal selling.
Characteristics of a good salesman:
- Smart, efficient, interactive, physically fit
- Efficient in communication
- Style of presentation of new product
- Technical information
- Honesty
- Politeness
- Enthusiasm
Sales promotion:
Short-term benefits offered to the customers that motivate the customer to buy the product is called sales promotion.
Sales promotion techniques:
- Sale
- Discount
- Advertisement coupon
- Gift
- Additional gifts
- Lucky draw
- Interest-free loan
- Distribution of samples
- Organizing competitions.
Publicity:
Impersonal communication about the product of the company with help of mass media without paying any charges for it.
Role:
- Most reliable
- Free of cost
- Includes public relations
- Effective use of mass media
- Helps the salesman and the middlemen.
Public relations:
Maintaining good relationship with all the parties involved with the company and creating a good image of the company among them.
Role:
- Good relationships with newspaper editors
- Information about new products
- Achievements of the company and its employees
- Director’s speech
- Organizing social and cultural programmes
- Public interest activities