Gujarat Board GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 4 Organizing Important Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 4 Organizing
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which function of management decides the goal of the organization?
Answer:
Planning
Question 2.
Which function of management is the body of the organization?
Answer:
Organizing
![]()
Question 3.
Define organizing according to Louie Allen.
Answer:
Organizing is the process of identifying and classifying the work to be performed, defining and delegating responsibility and authority, and establishing relationships for the purpose of enabling people to work most effectively together in accomplishing objectives.
Question 4.
List down any four characteristics of organizing.
Answer:
- Goal oriented activity,
- Planning based,
- Delegation of authority,
- Importance to human element,
- Flexibility,
- Establishment of inter relationships,
- Monitoring and control,
- Group activities, and
- Controlled administrative structure.
Question 5.
Why is organizing known as a goal oriented activity?
Answer:
Because it acts as a linear structure that co-ordinates goals of business, departmental goals and goals of employees.
Question 6.
Which management function precedes “organizing?
Answer:
Planning
Question 7.
In which management function does delegation of authority and responsibility take place?
Answer:
Organizing
Question 8.
When are changes required in the organizing function?
Answer:
Changes are required when there are changes or variations in the business environment, technological advancement or new discoveries.
Question 9.
Why is monitoring and controlling required in organizing?
Answer:
To see whether the employee is performing his task as per the powers and responsibilities assigned to him or not.
Question 10.
Who said, “The lack of proper formation of organization cannot sustain for longtime. Hence, the unit is slowly destroyed”.
Answer:
Peter F. Drucker
Question 11.
State the steps of process of organizing.
Answer:
- Clarification of objectives,
- List of functions,
- Departmentalization of function,
- To determine departmental position and abilities,
- Delegation of power and responsibilities,
- Establishment of inter relationship, and
- Prepare organizational chart.
![]()
Question 12.
What special care has to be taken while preparing list of functions in business unit?
Answer:
The special care to be taken while preparing list of work is that not a single task should be left out or gets repeated.
Question 13.
What is done in an organization, to have a proper idea of each one’s position?
Answer:
An organizational chart is prepared.
Question 14.
Write down the different types of organizational structures.
Answer:
- Linear organization,
- Functional organization,
- Formal organization,
- Informal structure organization,
- Matrix structure Organization.
Question 15.
Which type of organization structure is used in army?
Answer:
Linear organization
Question 16.
What is linear organization?
Answer:
Linear organization is that organization structure where there is centralization of power at the top level. The distribution of power and responsibilities is done in straight line from top to bottom.
Question 17.
How is the division done in linear organization?
Answer:
On the basis of departments
Question 18.
Who has the greatest power in linear organization?
Answer:
Board of Directors
Question 19.
What is the role of General Manager in departmental organization?
Answer:
The role of the General Manager is that of an administrative head in departmental organization. General Manager’s work is to ensure that the lower employees follow the task and decisions taken by the Board of Directors.
Question 20.
In which types of business units is linear organization most favourable?
Answer:
Linear organization is most favourable in small size companies where the work area is limited, and the problems of control and discipline are also limited.
Question 21.
Give one limitation of linear organization
Answer:
Linear organization gives more importance to department than work which is its biggest limitation.
Question 22.
What is functional organization?
Answer:
Functional organization is an organi¬zational structure where the structure is built on the basis of distribution of work.
Question 23.
Who has the supreme power in functional organization?
Answer:
Chief Executive Officer.
![]()
Question 24.
In which type of organization is functional organization more favourable?
Answer:
In organizational units where more variety is seen in work.
Question 25.
Define formal organization.
Answer:
To achieve the predefined goals, the formal structure of relationship among persons and work is establishes which is known as formal organization.
Question 26.
List down the characteristics of formal organization.
Answer:
- Formal organization,
- Lacking flexibility,
- Delegation of power from upper to lower level,
- Large size,
- Particular relations, and
- Communication.
Question 27.
Why does formal organization lack flexibility?
Answer:
Formal organization lacks flexibility because fixed places are assigned to employees who are non-changeable or non-alterable.
Question 28.
List down the characteristics of informal organization.
Answer:
- Informal structure,
- Based on human relations,
- Ever-changing,
- Universal,
- Informal communication,
- Small size,
- Lack of control, and
- Complements formal structure]
Question 29.
How does inter-relationship develop informally in the organization?
Answer:
Informal inter-relationships develop naturally when the employees work together for a common defined goal.
Question 30.
Which is the fast form of communication in the organization?
Answer:
Informal communication
Question 31.
In which type of organization structure, control cannot be maintained?
Answer:
In informal organization
Question 32.
In which type of organization structure are benefits of project management obtained?
Answer:
Matrix organization
Question 33.
What is centralization?
Answer:
The concentration of control of an activity or organization under a single authority is called centralization.
Question 34.
What is decentralization of authority?
Answer:
The delegation of power from upper to lower level in orderly manner is known as decentralization of power.
![]()
Question 35.
What are the two main aspects of decentralization?
Answer:
Authority and responsibility
Question 36.
Define decentralization according to Henry Fayol.
Answer:
To assign powers to the superiors, to enable distribution of work, and to include in decision making process is called decentralization.
Question 37.
What limitations are generally seen in centralization of authority?
Answer:
- Hierarchy,
- Non-scientifically taken decisions,
- Non-cooperation,
- Lack of specialization, and more work load, etc.
Question 38.
List down the importance of decentralization.
Answer:
- Quick decisions,
- Less work load on top level,
- Increased motivation,
- Increase in management abilities,
- Effective control and
- Harmony is created.
Question 39.
‘Future managers emerge with decentralization’, explain.
Answer:
In decentralization, middle and lower level employees take decision as per powers and independence given to them, hence they become efficient leaders and develop skills of future managers. Hence, …
Question 40.
What are the limitations of decentralization?
Answer:
Decentralization is not possible in small size companies were business secrets are to be maintained with great vigilance. Also, if coordination is not maintained properly in business unit, decentralization fails.
Question 41.
List down the importance of delegation of authority.
Answer:
- Work efficient management,
- Development of employees,
- Motivation,
- Benefit of specialization,
- Co-ordination and
- Scope for expansion.
Question 42.
List down the elements of delegation of authority given by Louis Allen
Answer:
- Entrustment of responsibility,
- Conferment of authority and
- Creation of accountability.]
Question 43.
Give an example of accountability.
Answer:
In a business unit, the accounts officer can give work of writing accounts to his accountant but when the accounts are written, it is the account officer who has to check the accuracy of the work done and not the accountant.]
![]()
Question 44.
What is the flow of accountability in the organization?
Answer:
Accountability flows from lower level management to upper level management in the organization
Question 45.
Given an example of delegation of authority in a business unit.
Answer:
General Manager of the business unit gives power to marketing manager to incur necessary expenditure in their work area, appointment of employees, to take disciplinary actions against the employees, etc.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the various definition of organizing.
Answer:
Various definitions:
- The structure formed in order to enable delegation of authority and responsibility towards the people actively engaged for common goal is known as organizing.
- As per Chester I. Bernard, “The activity conducted by the co-operation of two or more people and their co-ordination is called organizing.”
- As Per Louie Allen, “Organizing is the process of identifying and classifying the work to be performed, defining and delegating responsibility and authority, and establishing relationships for the purpose of enabling people to work most effectively together in accomplishing objectives.”
Question 2.
What is organizing? Explain briefly.
Answer:
- The structure formed in order to enable delegation of authority and responsibility towards the people actively engaged for common goal is known as organizing. Organizing is also called arrangement.
- For smooth and effective administration and management there should be proper organization in the unit.
- Most of problems of management arise due to ineffective organization in the management.
- Proper organizing can enable the unit to achieve its goals that too in desired time. It also enables optimum use of resources, time, energy and money.
Question 3.
State the characteristics of organizing.
Answer:
The characteristics of organizing are:
- Goal oriented activity
- Planning based
- Delegation of authority and responsibilities
- Gives importance to human element
Question 4.
Why is it important to follow proper steps of organizing?
Answer:
Forming an organizing is a scientific process.
- According to Peter F. Drucker, “The lack of proper formation of organization cannot sustain for longtime. Hence, the unit slowly gets destroyed.”
- Organizing gives a proper direction and flow to the business unit.
- Goals, roles, responsibilities and authorities are clearly understood by all the . employees if organizing is done properly.
- It is therefore necessary to see that organizing done by following proper steps and that the functional relations are established in proper manner.
Question 5.
What is departmentalization?
Answer:
- In a business unit, after preparing the list of functions, the works that are similar in nature are classified and similar functions are placed together. Then the division of work is done accordingly. This is called departmentalization.
- For example, work related to purchase is put under purchase department, work related to sales is put under sales department, work related to finance is put under accounts department and Sb on.
Question 6.
State the various types of structures that an organization can have.
Answer:
Mainly the organization can have any of the following structures:
- Linear Organization
- Functional Organization
- Formal Organization
- Informal Organization
- Matrix Organization
- By looking at the structure of the organization one can know the type of organization.
- What structures will the business follow depends on the nature, size and responsibilities of business unit and its classification.
![]()
Question 7.
Give an introduction of linear organization along with the help of a diagram.
Answer:
Linear organization:
- Linear organization is the most simple and ancient type of organization.
- This format of organization is used in Army since a very long time and so it is also known as Army organization.
- In linear organization, the top level holds the maximum power. In other words, the power is centralized at the top level.
- The distribution of power and responsibilities is done in straight line from top level to bottom level.
- Since, the distribution of power is in a straight line from top to bottom level, it is called linear organization.
- Each employee is answerable to his or her superior authority.
- Owing to the structure of linear organization, higher degree of power is at the top level whereas there is minimal power at the lower level.
- Linear organization is more favourable if the organization is of small size, the work area is limited and the problems of control and discipline are also limited.
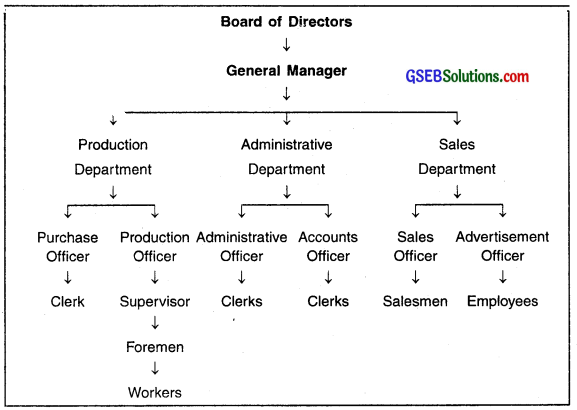
Linear Organization
Formation of linear organization:
- In a linear organization, the greatest power is with the Board of Directors.
- They take policy based decisions for the organization.
- The Board of Directors empowers the General Manager.
- The General Manager is the main Administrative Head. It is his work to ensure that the lower employees follow the task and decisions taken by the Board of Directors. ‘
- Below the General Manager are various departments such as production department, administrative department and sales department.
- For each department, there is a department head. The department head is responsible for the work going on his entire department.
- Under each department head there are several officers. For example, there will be purchase officer and production officer in the production department. Similarly there will be administrative officer and accounts officer in the administrative department, etc.
- Under such officers, supervisors, foreman and clerks, etc. work. Finally, the workers work under the foreman.
Question 8.
Linear organization is also known as departmental (divisional) organization.
Answer:
- In a linear organization, the entire business unit is classified into different departments.
- Then a department head is appointed for each section or area. This departmental head is answerable to the superior head of his area.
- The area head or say departmental head holds the supreme power for his department.
- In this type of organization, division is hot done according to the work but according to departments.
- Hence linear organization is also known as departmental (divisional) organization.
Question 9.
Explain the limitation of linear organization structure.
Answer:
- Linear organization flows from top to bottom with top having unlimited powers and bottom level, minimal.
- Linear organization gives more importance to department than work. This is the greatest limitation of linear organization structure.
- Linear organization does not have scope for specialized work because the stress is more on departments and less on functions.
- The administrators and officers in one unit have to perform many several types of tasks. Naturally, all of them are not experts in all the types of works.
Question 10.
Linear organization is the most commonly found organizational structure. Explain.
Answer:
- Linear organization is the most simple and ancient type of organization.
- Linear organization is more favourable if the organization is of small size, the work area is limited and the problems of control and discipline are also limited.
- In such types of organization there is a unity of command which follows from top to bottom.
- These characteristics are quite suitable even for organizations which are pretty small size. As a result, linear organization is most commonly found organizational structure.
Question 11.
What is a functional organization? Explain briefly. Why did the need arise to set-up functional organization structure?
Answer:
Functional (Work-based) Organization
- Linear organization gives more importance to department than work. This is the greatest limitation of this kind of structure.
- Keeping this limitation in mind, the ‘work based’ or say ‘function based’ organization came into existence.
- An organization with a functional structure is divided based on functional areas, such as IT, finance, or marketing.
- In this structure, the experts with specialized knowledge are given special responsibilities for areas of their expertise. This type of structure is called ‘ functional organization. For example, Human Resource Manager will look after the recruitment, transfer, promotions, etc.
- Thus, in functional organization, the distribution of work is not done according to the departmental but according to the nature of work.
Question 12.
Explain the formation of functional organization.
Answer:
Formation of functional organization:
The core of functional organization lies in giving special importance to work distribution on the basis of specialization.
- Specialized experts are appointed for each kind of work. These experts do not serve only as advisors but they are also administrative heads of their work areas. They are fully responsible for the task assigned to them. For example, the purchase officer is fully responsible for all type of purchase related work.
- The Chief Executive Officer is at the top and holds the supreme powers of the functional organization.
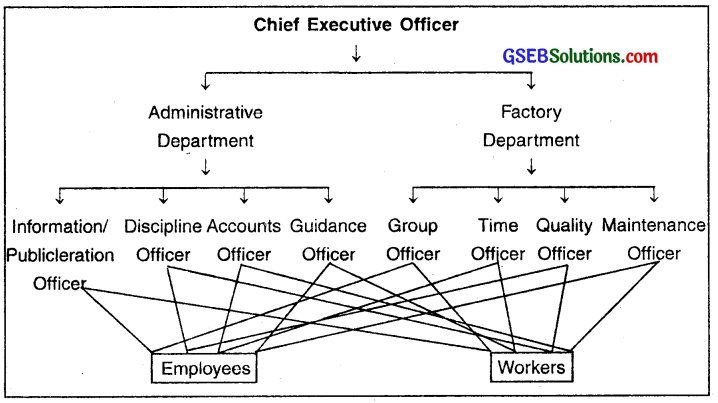
Functional Organization
- As demonstrated in the chart, the unit can be divided into two (or more) parts. Each unit has its assigned list of activities and works.
- The units then assign the tasks and works to different officers. For example, the factory unit (or department) will assign the work to Quality Control Officer, ‘ Chief Maintenance Engineer and so on.
- Each officer then gives orders to the employees under him to perform the task.
- In functional organization, not a single work remains unassigned and at the same time not a single work is assigned twice.
- This structure is more favourable for units where there are a variety of works to be done. For example, IT Industry, Telecom industry, etc.
Question 13.
Differentiate between linear and functional organization.
Answer:
| Basis of comparison | Linear organization | Functional organization |
| 1. Formation | It consists of several departments | It is based on specific functions of the organization |
| 2. Authority | The authority flows from top level to lower level | Authority is given as per the functions taken care of |
| 3. .Specialized knowledge | Benefit of specialized knowledge is not available | Benefit of specialized knowledge and skills is available |
| 4. Co ordination | Co ordination among various division is required | Here, co ordination among various functions is required |
| 5. Discipline | Discipline is properly followed | It is difficult to follow proper discipline |
| 6. Suited for | Any type of organization | More favourable for units where there are a variety of works to be done |
Question 14.
What is a formal organization?
Answer:
Formal organization:
- In order to achieve the predefined goals, the formal structure of relationship established among persons and work is called formal organization.
- Linear organization and functional organization are types of formal organization.
- In formal organization, necessary powers are given to enable the person to perform certain kind of responsibilities.
- The organization also clarifies matters related to delegation of authority among superior officers.
![]()
Question 15.
State the characteristics of formal organization.
Answer:
Characteristics of formal organization:
- Formal structure: The administrators form the formal structure very cautiously to achieve the desired goals.
- Lacking flexibility: In this kind of structure, the position assigned to the employees generally cannot be changed or altered. So, this structure is not flexible.
- Delegation of power from upper to lower level: The delegation of power is done by superior officer and it flows from upper level to lower level.
- Large size: Formal organization structure is a large size structure.
- Particular relations: Since the formal organization is formed with proper method, the relations among the employees are particularly formed.
- Communication: Communication is done only through a formal method. There is no scope for informal communication.
Question 16.
What is an informal organization? How is it formed?
Answer:
Informal organization:
- In the formal organizational structure, individuals are assigned various job positions. While working at those job positions, the individuals interact with each other and develop some social and friendly groups in the organization.
- This network of social and friendly groups forms another structure in the organization which is called informal organizational structure.
- The informal organizational structure gets created automatically and the main purpose of such structure is getting psychological satisfaction.
- The existence of informal structure depends upon the formal structure because people working at different job positions interact with each other to form informal structure. So, if there is no formal structure, there will be no job position and there will be no informal structure.
- Informal organization can be considered as a shadow of forma! structure of Organization. It can also be considered a subordinate structure to formal organization.
- The members while doing the formal work also interact at social level, bring ‘ their own values and assumptions during work discussion. The members of informal organization develop friendship, alliances, trusted sources of information and share preferences on how work should be done.
- One of the best examples of informal organization is the several group of friends formed within class 12. Although, school follows some specific structure of organization but groups of friends are informal organizations within this structure.
Question 17.
Informal organization is now acceptable and has become widespread. Explain.
Answer:
- In the formal organizational structure individuals are assigned various job positions. While working at those job positions, the individuals interact with each other and develop some social and friendly groups in the organization. This network of social and friendly groups forms another structure in the organization which is called informal organizational structure.
- The members while doing the formal work also interact at social level, bring their own values and assumptions during work discussion.
- The members of informal organization develop friendship, alliances, trusted sources of information and share preferences on how work should be done.
- This makes achieving the goals easily and in a harmonious manner.
- Owing to several benefits the organization gets, it accepts informal organization.
Question 18.
Differentiate between format and informal organization.
Answer:
| Basis of comparison | Formal organization | Informal organization |
| 1. Formation | Formed systematically with proper guidelines | Formed informally by members while working in the organization and interacting with each other |
| 2. Objective | To fulfill business goals | To satisfy social and psychological needs |
| 3. What is it? | A systematic organization | A group of like minded people |
| 4. Size | Members of the entire organization | Small sized on the basis of like mindedness of employees |
| 5. Nature | Stable. Continues for a long time | Unstable and keeps on changing |
| 6. Control mechanism | Controlled through rules and regulations of the organization | Controlled through values and beliefs of the associated people |
| 7. Focus on | Work performance | |
| 8. Authority | Members follow the authority as decided by the hierarchy of the organization | Inter personal relationships All members have equal authority |
Question 19.
What is a matrix organization?
Answer:
Matrix Organization:
- The organizational structure in which people with similar skills are pooled for work assignments, resulting in more than one manager is called a matrix organization.
- Matrix organization is a combination of work based (functional organization) and project based organization.
- Matrix management is the practice of managing individuals with more than one reporting line i.e. in a matrix organization structure.
- For example, all engineers may be in one engineering department and report to an engineering manager (i.e. part of functional organization structure), but these same engineers may be assigned to different projects and report to a different engineering manager or a project manager while working on that project. Therefore, each engineer may have to work under several managers at same point of time.
Question 20.
Discuss the design (or formation) of matrix organization.
Answer:
Design of matrix organization:
- In matrix organization we find the combination of work based and project based organization.
In this type of organization, several project managers are appointed for various projects and each project manager is given different type of work responsibilities. - The responsibility of the project manager is to successfully complete the project assigned to him that too on time.
- For each project, a pooj of employees is made from different areas of the company. Each of these employees holds some specific skill which is needed by the project.
Example:
- An IT company has a typical functional organization structure. So, it has various departments such as Research Department, Programming Department, Marketing, Accounts, etc.
- The company takes various projects from its clients. Let us say a project from Vodafone, Torrent Power, etc.
- For Vodafone project, the company may form a team of a computer expert,
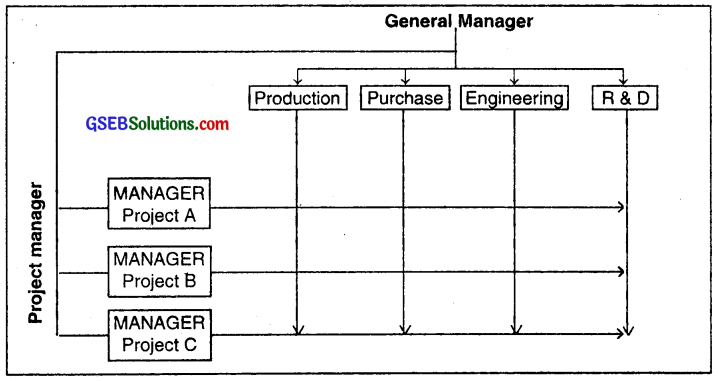
Matrix Organization
research expert, production engineer, technical expert and an accounts expert for executing the project. All these experts already work in specific departments of the company and report to their own bosses. But, under the Vodafone project they will also report to their new temporary manager who is handling the Vodafone Project.
The authority of the functional managers goes downwards (vertical) whereas that of project managers goes sideways i.e. horizontal and so the structure of the organization takes a matrix design.
Once when the work is done, they are sent to their respective work areas / to which they belonged.
Question 21.
Matrix organization is multi-faced. Explain.
Answer:
- Matrix organization is a modern form of organization, which has two different types of structures.
One is the functional structure which forms the part of decision making. The second is the technical problems solution based structure which is called project structure. The combination of both these structures results in matrix organization. - Moreover, in matrix organization, the organization gets the benefits of specialized work as well as that of project management.
- Hence, matrix organization is multi-faced structure.
Question 22.
State the limitations of matrix organization.
Answer:
Matrix structure can result in internal complexity. Some employees may become confused as to who is their direct supervisor. For example, an employee may receive different directions concerning the same thing from supervisors in different departments.
- Miscommunication and ineffective managing can result in employee dissatisfaction and low morale.
- Prolonged issues may cause the organization to experience high employee turnover.
- Matrix organizational structure is expensive to maintain.
- A company’s overhead cost typically increases because of the need for double management.
Question 23.
Define centralization and decentralization of power.
Answer:
Centralization:
The concentration of control of an activity or organization under a single authority is called centralization.
Decentralization:
The delegation of power from upper to lower level in orderly manner is known as decentralization of power.
Question 24.
Define and explain the concept of decentralization.
Answer:
Decentralization:
The delegation of power from upper to lower level in orderly manner is known as decentralization of power.
- According to Henri Fayol, “To assign powers to the superiors, to enable distribution of work, and to include in decision making process is called decentralization.”
- Whether to opt for centralization or decentralization largely depends of the size of the unit and the approach of the administrators.
- Small sized organization can have centralized powers but generally large sized organizations should have decentralized form of management for successful organizing.
- Under decentralization not all but some major powers such as executive powers are given by the upper level administrators to the lower level.
Question 25.
What is the limitation of decentralization?
Answer:
- Decentralization cannot be adopted in very small units, especially because the business secrets cannot be maintained.
- Sometimes when common policies are not implemented or if co-ordination is not maintained properly, decentralization becomes unsuccessful.
Question 26.
State the difference between centralization and decentralization.
Answer:
| Basis for comparison | Centralization | Decentralization |
| 1. Meaning | The concentration of control of an activity or organization under a single authority is called centralization. | The delegation of power from upper to lower level in orderly manner is known as decentralization of power. |
| 2. Workload at top level | Increases | Decreases |
| 3. Communication flow | Vertical | Open and free |
| 4. Decision making | Decision making is slow | Decision making is comparatively faster |
| 5. Advantage | Centralization results in proper coordination and leadership | Decentralization leads to sharing of burden and responsibility |
| 6. Power of decision making | Lies with the top management | Multiple persons have the power of decision making |
| 7. Best suited for | Small sized organization | Large sized organization |
![]()
Question 27.
What is delegation of authority? Explain.
Answer:
- In business terminology, ‘power’ refers to giving orders and also to see to it that the orders are followed.
- When the size of the organization becomes large, the upper level administrators assign some work to their subordinates.
- These subordinates have to see that the orders are followed properly. For this the subordinates are given some powers.
- This vesting of powers is called delegation of power.
- Thus, the system of giving power to the other person for doing a particular task is called delegation of power.
- According to Louis Allen, “Delegation of authority means assignment of responsibility and power to the subordinates by creating accountability for effective performance.” He also says that “Delegation of power is such kind of process in which the administrator gives a part of the powers to his helpers along with duties, and the helpers, with the help of others, for the purpose of work performance, accepts such powers consciously.”
- It should be noted that although the subordinates are given powers and they are responsible to get the work done but the final completion of the work and its responsibility rests with the upper level administrator only and he cannot free himself from that.
- Delegation of authority can be for various purposes. For example, Marketing Managers are given power to incur necessary expenditure in their work area, the appointment of employees, to take disciplinary actions against the employees, etc.
Question 28.
Define delegation of authority and state one example.
Answer:
- The system of giving power to the other person for doing a particular task is called delegation of power.
- For example, marketing managers are given power to incur necessary expenditure in their work area, appointment of employees, take disciplinary actions against the employees, etc.
Question 29.
State the definition and views of Louis Allen on delegation of authority.
Answer:
- According to Louis Allen, “Delegation of authority means assignment of responsibility and power to the subordinates by creating accountability for effective performance.”
- He also says that “Delegation of power is such kind of process in which the administrator gives a part of the powers to his helpers along with duties, and the helpers, with the help of others, for the purpose of work performance, accepts such powers consciously.”
Question 30.
Write a short note on creation of accountability.
Answer:
- During delegation of work, the person who has been delegated the power and work is accountable for this work to the higher authorities.
- He needs to provide proper explanation and follow reporting process to the top level management. This is known as accountability.
- The delegated person may be having the powers to get the work done by / others but finally the responsibility of getting the work done rests with the upper level administrators only.
- Hence the middle level authority holders i.e. the ones who are delegated the power should take care to ensure that the work is properly done by the lower level staff.
- The middle level authority holder cannot free himself from his responsibility of getting work done. Note that this accountability flows from lower level to upper level i.e. the lower level is accountable to the middle level and middle to upper level.
- This accountability cannot be passed on. For example, the Accounts Officer may give the work of writing accounts to his accountant but when the accounts are written, it is the Accounts Officer who has to check the accuracy of the work done and not the Accountant.
Question 31.
Power is the key to administration, but delegation of power is the key to organization. OR Delegation is the base for the success of an organization. Explain.
Answer:
- In business terminology, ‘power’ refers to giving orders and also to see to it that the orders are followed.
- Person having power has right to make decisions and execute tasks. This leads to smooth functioning of management and administration.
- However, when the size of the organization becomes large, it becomes difficult .for the upper level administrators to conduct all work on their own and execute all their powers on own. Hence, they assign some work to their assistants.
- By delegating power to the lower level, the upper level administrators get free from such works that can be performed by junior level staff. This helps the upper level people to focus upon their core tasks i.e. policy making.
- This increases efficiency of the management and organizing.
Question 32.
A task may be delegated but not the accountability. Explain.
Answer:
- During delegation of work, the person who has been delegated the power and work is accountable for this work to the higher authorities.
- He needs to provide proper explanation and follow reporting process to the top level management.
- The delegated person may be having the powers to get the work done by others but finally the responsibility of getting the work done rests with the upper level administrators only.
- This means if the delegated work is not done as planned, the person who has delegated cannot put the blame on the shoulder of the person to whom the work was delegated. Hence, a task may be delegated but not the accountability.
![]()
Question 33.
Differentiate between delegation and decentralization.
Answer:
| Basis for comparison | Delegation | Decentralization |
| 1. Meaning | Delegation means handing over an authority from one person of high level to the person of low level. | The delegation of power from upper to lower level in orderly manner is known as decentralization of power. |
| 2. What it is? | Technique of management | Philosophy of management |
| 3. Accountability | Superiors are accountable for the acts done by subordinates. | Department heads are accountable for the acts of the concerned department. |
| 4. Requirement | Delegation of authority is very important and necessary for all the organizations. | Decentralization is optional. It depends on the management whether it wants to go for decentralization or not. |
| 5. Liberty of work | Subordinates do not have full liberty. | A substantial amount of freedom is there. |
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which management function sets the goal for organizing in a business unit?
(A) Planning
(B) Controlling
(C) Directing
(D) Staffing
Answer:
(A) Planning
Question 2.
What is the formal administrative structure that is formed to enable effective implementation of planning known as?
(A) Directing
(B) Organizing
(C) Decentralization
(D) Controlling
Answer:
(B) Organizing
Question 3.
Which of the following does not lead to success and goal achievement of business unit?
(A) Distribution of authority and responsibility
(B) Proper division of work
(C) Delegation of authority
(D) Delegation of accountability
Answer:
(D) Delegation of accountability
Question 4.
What is organizing for the business?
(A) Brain
(B) Soul
(C) Blood
(D) Body
Answer:
(D) Body
Question 5.
Who said, The activity conducted by the co-operation of two or more people and their co-ordination is called organizing.’?
(A) Chester I. Bernerd
(B) Louie Allen
(C) Henry Fayol
(D) Henry Gantt
Answer:
(A) Chester I. Bernerd
Question 6.
Which structure does organizing function follow to co-ordinate with the goals of business, departmental goals and goals of employees?
(A) Matrix structure
(B) Informal structure
(C) Linear structure
(D) Any of these
Answer:
(C) Linear structure
Question 7.
_________ is the structure to establish relationship of authority and responsibility among the people.
(A) Matrix
(B) Staffing
(C) Organizing
(D) Linear
Answer:
(C) Organizing
Question 8.
What is the main objective of monitoring and control in an organization?
(A) To see whether employees are performing their tasks based on powers and responsibilities assigned
(B) To check whether the employees are not taking undue advantage of the facilities provided to them
(C) To keep a watch on the establishment of inter-relations between employees
(D) To see enough importance is given to the human element in the organization
Answer:
(A) To see whether employees are performing their tasks based on powers and responsibilities assigned
Question 9.
Who said, ‘The lack of proper formation of organization cannot sustain for long time. Hence, the unit is slowly destroyed.’?
(A) Louie Allen
(B) Chester I. Bernerd
(C) Peter F. Drucker
(D) Henry Fayol
Answer:
(C) Peter F. Drucker
Question 10.
What is the first step of process of organizing?
(A) Clarification of objectives
(B) List of functions
(C) Determining departmental position and abilities
(D) Delegation of power and responsibilities
Answer:
(A) Clarification of objectives
Question 11.
In which of the following steps of organizing process, division of work is done?
(A) Clarification of objectives
(B) Listing of functions
(C) Departmentalization of functions
(D) Delegation of authority and responsibility
Answer:
(C) Departmentalization of functions
![]()
Question 12.
‘Packing task’ is a part of which department in the organization?
(A) Purchase department
(B) Sales department
(C) Marketing department
(D) HR department
Answer:
(B) Sales department
Question 13.
What has to be done once the work is departmentalized properly?
(A) Goals have to be clearly defined
(B) Powers and responsibilities have to be delegated to all the heads
(C) The task to determine departmental positions and abilities
(D) Organizational chart has to be prepared
Answer:
(C) The task to determine departmental positions and abilities
Question 14.
Out of the following organizational structures which one is the most simple and ancient type?
(A) Functional structure
(B) Linear structure
(C) Matrix structure
(D) Formal structure
Answer:
(B) Linear structure
Question 15.
In linear structure, less power is in whose hands?
(A) Top level management
(B) Middle level management
(C) Bottom level management
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(C) Bottom level management
Question 16.
The linear organization is also known as
(A) Functional organization
(B) Informal organization
(C) Simple organization
(D) Departmental organization
Answer:
(D) Departmental organization
Question 17.
Which types of decisions are taken by board of directors in linear organization?
(A) Routine decisions
(B) Departmental decisions
(C) One time decisions
(D) Policy based decisions
Answer:
(D) Policy based decisions
Question 18.
What is the main limitation of linear organization?
(A) More importance to departments than work
(B) No involvement of experts
(C) Multiple heads giving multiple work
(D) Over-burden of work
Answer:
(A) More importance to departments than work
Question 19.
Who has the supreme power in functional organization?
(A) Board of Directors
(B) General Manager
(C) Chief Executive Officer
(D) Project Manager
Answer:
(C) Chief Executive Officer
Question 20.
Which of the following is a type of formal organization?
(A) Linear organization
(B) Functional organization
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Matrix structure
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
Question 21.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of formal organization?
(A) Lacking flexibility
(B) Large size
(C) Communication
(D) Based on human relations
Answer:
(D) Based on human relations
![]()
Question 22.
Which of the following organization is formed based on internal relations on its own?
(A) Formal structure
(B) Informal structure
(C) Matrix structure
(D) Functional structure
Answer:
(B) Informal structure
Question 23.
Which of the following is a characteristic of informal organization?
(A) Universal
(B) Particular relations
(C) Formal communication
(D) Large size
Answer:
(A) Universal
Question 24.
What is the relation of informal organization with formal organization?
(A) Informal organization contradicts formal organization
(B) Informal organization complements formal organization
(C) Depends on the type of organization
(D) Depends on the main head of the organization
Answer:
(B) Informal organization complements formal organization
Question 25.
Which of the following is the modem type of organization?
(A) Matrix organization
(B) Linear organization
(C) Functional organization
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(A) Matrix organization
Question 26.
What is the other name of matrix structure?
(A) Project structure
(B) Departmental structure
(C) Formal structure
(D) Army structure
Answer:
(A) Project structure
Question 27.
Who decides whether to have a centralized or decentralized power in the organization?
(A) Owner
(B) Administrators
(C) Subordinates
(D) Shareholders
Answer:
(B) Administrators
Question 28.
Who said, To assign powers to the superiors, enable distribution of work, and to include in decision making process is called decentralization.
(A) Henry Gantt
(B) Peter F. Drucker
(C) Henri Fayol
(D) Louis Allen
Answer:
(C) Henri Fayol
Question 29.
Which of the following cannot be seen in centralization of power in an organization?
(A) Non-scientifically taken decisions
(B) Lack of specialization
(C) Non-cooperation
(D) Less work load on top level management
Answer:
(D) Less work load on top level management
Question 30.
According to, delegation of authority is such kind of process in which the administrator gives a part of the powers to his helpers along with duties, and the helpers with the help of others for the purpose of work performance, accepts such powers consciously.’
(A) Louis Allen
(B) Henri Fayol
(C) Peter F. Drucker
(D) Fredrick Taylor
Answer:
(A) Louis Allen
Question 31.
Which of the following is not a result of delegation of authority?
(A) Work efficient management
(B) Development of employees
(C) Co-ordination
(D) More work load
Answer:
(D) More work load
Question 32.
Which structure does the elements of delegation of authority form?
(A) Linear structure
(B) Table structure
(C) Tripod structure
(D) Circular structure
Answer:
(C) Tripod structure
Question 33.
What is the duty assigned by the top level officer to the subordinates for a particular work?
(A) Authority
(B) Responsibility
(C) Accountability
(D) None of these
Answer:
(B) Responsibility
Question 34.
When power is given to an authorized person, what functions does the authorized person have?
(A) Power to give decisions
(B) Power to give orders
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Power to expand business in other countries
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
![]()
Question 35.
Delegated authority holder has to provide proper explanation and follow reporting process to the top level management is known as
(A) Accountability
(B) Responsibility
(C) Centralization
(D) Authority
Answer:
(A) Accountability