Gujarat Board GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 6 Directing Important Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 6 Directing
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the definition of direction as given by Koontz and O’Donnell.
Answer:
Direction is the executive function of guiding and observing subordinates.
![]()
Question 2.
State two characteristics of directing.
Answer:
- Goal oriented activity and
- Function at every level of management.
Question 3.
Why direction is called goal oriented activity?
Answer:
The purpose of directing or say direction is to guide and motivate the employees to achieve business goals. Thus
Question 4.
Till when does the direction continue in an organization?
Answer:
As long as the organization exists.
Question 5.
Why it is said that direction has a wider scope?
Answer:
Directing is not merely guiding and advising to the employees but also making them understand the business decisions and encourage them to work for their implementation. Hence,…
Question 6.
What is the flow of direction?
Answer:
Top level to bottom level
Question 7.
How can you say that direction motivates employees?
Answer:
Proper direction helps to remove work related confusions and problems, re-work and repetition of same work. This motivates them for doing the work.
Question 8.
How does direction helps in control?
Answer:
Direction reduces the chances of work related mistakes and errors. This makes taking work from the employees easier. As a result the work remains controlled.
Question 9.
How does direction increases/enthusiasm?
Answer:
Direction brings changes in the attitude of employees towards the work. Their interest and enthusiasm in work increases. This …
Question 10.
State the elements of motivation.
Answer:
Supervision, motivation, leadership and communication.
Question 11.
What is supervision?
Answer:
Supervision means to supervise the function or work done by employees.
Question 12.
Give the definition of supervision as given by R.C. Davis.
Answer:
Supervision is the function of assuring that the work is being done in accordance with the plan and instructions.
Question 13.
State two functions of supervisor.
Answer:
- To plan the functions and to remove the hurdles, and
- To provide necessary guidance and direction to complete the work on time.
Question 14.
Define motivation.
Answer:
The process of stimulating people to perform action and to make it possible to have maximum work satisfaction is called motivation.
Question 15.
State the definition of motivation as given by Jucious,
Answer:
Motivation is the act of stimulating someone or oneself to get the desired course of action.
Question 16.
State the definition of motivation as given by Morgan.
Answer:
Motivation is that state of mind that leads workers towards objectives.
Question 17.
How does motivation increase efficiency of employees?
Answer:
Motivated workers are encouraged to produce more. Motivation boosts their morale. Their productivity and efficiency also increase.
![]()
Question 18.
How does motivation reduce labour turnover rate?
Answer:
Motivation gives internal satisfaction to the employees and inspires them. This keeps them motivated to stay in the organization and remain loyal to the company. This …
Question 19.
How does motivation change the attitude of employees?
Answer:
Workers often face several problems. When these problems are heard and solved, they experience a feeling of respect for staffing as well as organization, i.e. their attitude becomes positive.
Question 20.
State human needs as given by Maslow.
Answer:
- Physiological or primary needs,
- Safety needs
- Social needs
- Esteem and status needs and
- Self-esteem and self-actualization needs.
Question 21.
What is included in safety needs?
Answer:
Safety needs include physical safety, job safety, safety against risk, regularity, of wages, etc.
Question 22.
What des social need include?
Answer:
Social needs include feeling of getting love and respect from the family members, friends and relatives as well as by his colleagues at work place and by others in society.
Question 23.
What is incentive?
Answer:
In the terminology of commerce, the inspiration that the business units give their workers to maintain their work aptitude, continuously increase efficiency, maintain high quality standards, etc. is called incentives.
Question 24.
State two financial incentives.
Answer:
Share in profit and Commission.
Question 25.
State two non-financial needs.
Answer:
Security of employment and welfare activities and amenities.
Question 26.
What are financial incentives?
Answer:
Monetary benefit offered to employees to encourage behavior or actions is called financial incentive.
Question 27.
What is co-partnership?
Answer:
When employees or workers are taken as partners in ownership, management and distribution of pro’it, it is known as co- partners
Question 28.
What is promotion?
Answer:
The process of placing the staff in a higher and beneficial position is known as promotion.
Question 29.
What are non-financial incentives?
Answer:
Incentives not based on money are called non-monetary or non-financial incentives.
Question 30.
What is job security?
Answer:
Job security means an assurance to the employee that he will remain in job if he keeps on performing as per set standards.
Question 31.
What is leadership?
Answer:
The quality that influences people to make efforts willingly for achieving goals is called leadership.
Question 32.
State the definition of leadership as given by Dr. George R. Terry.
Answer:
Leadership is the quality of influencing others to work willingly for the realization of specified goals.
Question 33.
State two characteristics of leadership.
Answer:
- Existence of followers and
- Creates formal and effective relationship.
Question 34.
State important qualities of a good leader.
Answer:
A leader should have good health and intellect and psychological qualities.
Question 35.
What is communication?
Answer:
Communication is the process of exchange of words, letters, instructions and opinions.
![]()
Question 36.
Define communication in the words of New Mann and Summer.
Answer:
Communication is an exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions by two or more persons.
Question 37.
State four characteristics of communication.
Answer:
- Goal oriented process,
- Two-way process,
- Continuous process and
- Many types and methods.
Question 38.
What does oral communication consists of?
Answer:
Conversation, discussion, lectures, etc.
Question 39.
What does written communication consists of?
Answer:
Communication through newspaper, magazines, pamphlets, e-mail, etc.
Question 40.
What does visual communication consists of?
Answer:
Communication through maps, pictures, figures, graphs, etc.
Question 41.
What silent communication consists of?
Answer:
Gestures such as nodding, raising eye brows, moving head in affirmation, etc.
Question 42.
What is formal communication?
Answer:
Any communication that depends on the structure of an organization and its rules and regulations and is implemented for the accomplishment of business objective is called formal communication.
Question 43.
What is informal communication?
Answer:
Communication which depends on human relations and friendship among employees of an organization is known as informal communication.
Question 44.
State two characteristics of formal communication.
Answer:
- Its main objective is control and co-ordination and
- Formal communication is generally in written form.
Question 45.
State two characteristics of informal communication.
Answer:
- It depends on the human relations and
- Control or order is not required in informal communication.
Question 46.
What do you mean by barriers of communication?
Answer:
The factors of human limitations such as affection, mistakes, estimations, misunderstanding, distrust, fear, etc. that affect communication are called barriers of communication.
Question 47.
State few barriers of communication.
Answer:
Lack of planning, Faulty translation, Unclear messages and unclear assumptions, etc.
Question 48.
State two steps to overcome barriers of communication.
Answer:
- Communication system should be arranged as per organizational structure and it should not obstruct the information, and
- Information given by sender should be precise so that the receiver can understand properly.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is directing?
Answer:
- In layman language, direction means to guide the workers, make them aware of the work, supervise them and to maintain their enthusiasm for the work.
- According to Koontz and O’Donnell, “Direction is the executive function of guiding and observing subordinates.”
- Thus, direction or directing is that function of management which gives orders and supervises the subordinates for the accomplishment of pre-determined objectives.
![]()
Question 2.
State the characteristics of directing.
Answer:
- Goal oriented activity
- Function at every level of management
- Continuous process
- Observation of functions
- Wider scope
- Communication
- Motivation
- Flow of direction
- Managerial function
Question 3.
State the elements of directing and define them.
Answer:
The function of directing has four elements. They are:

- Supervision: Supervision means to supervise the function or work done by employees.
- Motivation: ‘Motivation means the process of stimulating people to perform action and to make it possible to have maximum work satisfaction.’
- Leadership: The art and skill of creating the desire in others, for achieving objectives is called leadership.
- Communication: Communication is the process of exchange of words, letters, instructions and opinions.
Question 4.
State the various definitions of motivation.
Answer:
- The process of stimulating people to perform action and to make it possible to have maximum work satisfaction is called motivation.
- As per Jucious, “Motivation is the act of stimulating someone or oneself to get the desired course of action.”
- As per Morgan, “Motivation is that state of mind that leads workers towards objectives.”
Question 5.
Who was Maslow? Which important contribution he made in the field of motivation?
Answer:
- Abraham Maslow was a human psychologist.
- He presented hierarchy of needs in his article ‘Principle of Human Motivation’ in 1943.
- He stated five important needs of man and arranged them as per their priority in a man’s life.
- The five needs in ascending order are:
- (1) Physiological or primary needs,
- (2) Safety needs,
- (3) Social needs,
- (4) Esteem and status needs and
- (5) Self-esteem and self-actualization needs.
- The first three needs are of lower order. The last two needs are of higher order.
- As per Maslow, man’s needs vary from person to person. These needs are decided on the basis of their mental status. He is motivated, if these needs are satisfied.
Question 6.
What are non-financial incentives? Explain.
Answer:
Non-financial incentives:
Incentives not based on money are called non-monetary or non-financial incentives.
Types of non-financial incentives:
1. Security of employment:
- Over and above employment, security of employment is also equally important.
- Job security means an assurance to the employee that he will remain in job if he keeps on performing as per set standards.
- Lack of job security makes one stressed whereas assurance oi job security inspires to work with enthusiasm. This increases the productivity and production.
2. Appreciation of work and reward:
- When employees over-exceed production targets within the given time, that too economically and efficiently, they are honoured publicly i.e. before other staff.
- Such appreciation and reward system motivates the employees. This also motivates other employees to work hard and earn such awards.
3. Assigning of responsibility:
- To encourage the employees, officers assign special responsibility of giving training and direction to subordinates or others.
- When such responsibilities are assigned, the person who shoulders such responsibility feels confident and proud for his knowledge and achievement. This motivates him and he further motivates his juniors.
4. Advisor:
- When a worker has been working efficiently for quite a long time in the organization his rich experience and knowledge becomes invaluable.
- The organization seeks his advice in policy formulation as well as other strategic decision.
The worker feels encouraged, confident and proud that he is an important part of the company.
5. Welfare activities and amenities:
- Organizations undertake various welfare activities and provide various amenities to employees. Medical services, canteen facility, library, leave- with-pay, sports, entertainment activities, training facility and many more such welfare facilities are given to employees.
- These inspire the employees and they work with enthusiasm and higher efficiency.
6. Other incentives:
Housing facility, life insurance, free education to children, books, transportation facility to pick up and drop from residence to place of work, etc. are several other incentives that the organization may provide to keep the employees motivated.
![]()
Question 7.
What is leadership? Why is it needed in industries?
Answer:
- The quality that influences people to make efforts willingly f6r achieving goals is called leadership.
- Leadership is the art and skill of creating the desire in others, for achieving objectives.
- According to Dr. George R. Terry, “Leadership is the quality of influencing others to work willingly for the realization of specified goals.”
- A leader is an influential person of the group who without any pressure provides guidance and inspiration and thus gets the expected work willingly done.
Need of leadership in industries:
- Several people work in industrial units. Even after paying wages and incentives and motivating them, the desired results may not be obtained if they are not led well. A good leader can lead the unit and extract work smoothly.
- Leadership is a process of encouraging in a mutual way.
- It is a base for efficient organization.
- Leader with his attitude and behaviour channelizes the efforts of the group members in a proper direction. He provides guidance to achieve decided targets, motivates to achieve objectives, inspiration, faith, etc. Thus, leadership is a source of motivation for others.
Question 8.
Discuss the characteristics of leadership.
Answer:
Characteristics of leadership:
1. Existence of followers:
A leader always provides leadership to followers. Therefore, existence of followers is must for implementation of leadership.
2. Continuous process:
As long as business unit exists, leader has to provide leadership to his subordinates. Thus, leadership is a continuous process.
3. Acceptance of leadership:
The subordinates must accept the leader for the existence of leadership. Leader directs subordinates and they follow him.
4. Creates formal and effective relationship:
Formally, leader is the head of specific groups. But informally the leader can influence the person coming into his contact and can stimulate him for achieving objectives.
5. Ideal personality:
- Leader must be an ideal person.
- Leader influences his subordinates by his behaviour and nature. He possesses leadership qualities whereas some qualities he cultivates. Such a skillful person can only be a leader.
6. Motivation:
Leadership includes motivation of employees. So, the leader first motivates employees to get the expected result.
7. Harmony of interest:
- Leadership brings harmony of interest among leader and his subordinates.
- Leadership becomes inefficient and useless if there are differences in the interests of leader and his subordinates.
8. Effect of situation:
The success of a leader depends on certain circumstances. If there is change in situation, leader does not get the success.
Question 9.
Explain communication as an element of directing.
Answer:
Communication:
- Communication is the process of exchange of words, letters, instructions and opinions.
- As per New Mann and Summer, “Communication is an exchange of facts, ideas, opinions or emotions by two or more persons.”
- Communication is an important part of management and an element of directing.
- Communication is a process of exchanging words, letters, instructions, thoughts, opinions etc.
- Manager must have on time and correct information of various departments of the unit. For this, the bottom level staff has to send information to the upper level in the form of report.
- The process of providing information is known as reporting whereas communication includes giving orders and instructions, receiving reports, attending complains and solving them, etc.
- Modern world is growing very fast in the field of science and communication. As a result, the communication has become very fast, efficient and of a large variety.
Question 10.
Classify the various forms of communication with the help of a chart.
Answer:
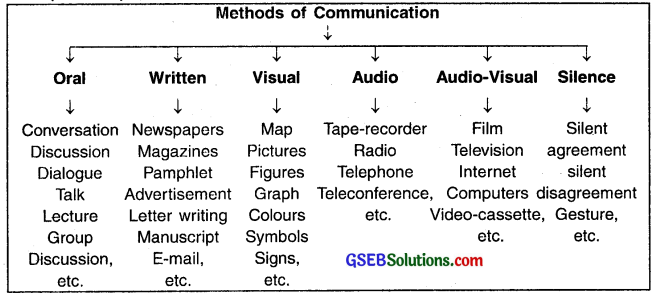
Question 11.
State the main types of communication. Name and define them.
Answer:
There are two types of communication. They are :
1. Formal communication :
Communication that depends on the structure of an organization and its rules and regulations and is implemented for the accomplishment of business objective is called formal communication.
2. Informal communication:
Communication which depends on human relations and friendship among employees of an organization is known as informal communication.
![]()
Question 12.
Write a short note on formal communication.
Answer:
Formal communication:
- Communication that depends on the structure of an organization and its rules and regulations and is implemented for the accomplishment of business objective is called formal communication. Generally, formal communication is in writing.
- This type of communication has a formal link between the superior and the subordinate. Its objective is to control and co-ordinate.
- Formal communication is clear and easy to understand.
- Here, who will send information to who is decided before communicating. Moreover, the form of information is also pre-decided.
Example:
- Notice or Memo is given as warning to the employees who are irregular and remaining absent without prior permission.
- A letter given by superior to subordinate for his transfer or promotion.
Characteristics:
- In formal communication, superior and subordinates are formally related
- Its main objective is control and co-ordination
- Formal communication is generally in written form
- This type of communication system is accepted as policy of organization
- It is based on organization structure
- Formal organization is formed for the accomplishment of business objectives
- It is easy and clear to understand
Question 13.
Write a short note on informal communication.
Answer:
Informal Communication:
- Any communication which depends on human relations and friendship among employees of an organization is known as informal communication.
- Informal communication is flexible and simple in nature.
- There is no need for control and order informal communication.
- It can be explained orally or even in a symbolic language i.e. through signs. -> Informal organization provides co-ordination and credibility to the organization. Example:
- Industrial manager instructs the labourer to work
- Sales manager gives information and suggestions regarding presentation to the salesman in an easy going manner
Characteristics:
- It depends on human relations
- Control or order is not required in informal communication
- It can be explained orally or through symbolic language
- Depends on human and friendly relations
- It is flexible and easy
- Process is not important in this communication
- It gives more co-ordination and credibility to the organization
- Informal communication is not. supplementary but complementary to the formal communication
Question 14.
State differences between reporting and communicating (or communication).
Answer:
| Reporting | Communication |
| 1. Reporting is only upward transmission of information. | 1. Communication is both downward and upward transmission of information. |
| 2. Report is prepared by the Management Accountant. | 2. The communication is forwarded by a responsible officer or the section supervisor. |
| 3. Report is only a written document. | 3. Communication may be in oral too. |
| 4. The function of reporting starts when accounting information comes to an end. | 4. Communication is a continuous process. |
| 5. A report consists of draft, schedules statements, charts, graphs and any other statistical presentation. | 5. Communication mainly consists of sentences |
| 6. The reports may be sent weekly, monthly, quarterly or yearly i.e. reports are time bound. | 6. Communication is not time bound. It keeps on following as and when required |
Question 15.
Differentiate between written communication and oral communication.
Answer:
| Basis of comparison | Written Communication | Oral Communication |
| Meaning | Communication done in written form is called written communication | Communication done orally is called oral communication |
| Ways of communication | Letters, circulars, notices, e-mails, bulletins, etc. | Meetings, telephone, conference, Audio-Video conference, etc. |
| Record | It always has permanent record | It does not have any permanent record |
| Time taken | It takes more time to draft written communication | It takes less time to transmit oral communication |
| Reliability | It is fully reliable | It is not reliable |
| Legal status | It is a legal evidence | It is not a legal evidence |
| Effectiveness | Written communication may or may not be very effective | Communication done orally is more effective |
| Formality | It maintains a formal format | It may or may not maintain a formal format |
Question 16.
Directing is like strategizing for the war. Explain.
Answer:
Just like the war, directing is a very crucial act which has to be performed flawlessly.
- Any mistake in guiding or providing instruction can lead to havoc. It may affect production, productivity, quality, etc.
- Just like the war, directing also uses several tools, techniques and manpower.
- Direction takes special care of points at which special efforts are to be put.
- At the same time, the leaders continuously need to motivate the employees to keep their morale high so that they accomplish their work as desired.
- Hence, directing is like strategizing for the war.
Question 17.
Incentives help the industries in several ways. Explain.
Answer:
- Incentive incites action into employees.
- They increase the enthusiasm of workers and motivate them to over-achieve organizational targets.
- In lieu of incentives the employees remain loyal to their works and organization. This in turn reduce labour turnover.
- Thus, incentives help industries in several ways.
![]()
Question 18.
An efficient leader is the key to successful directing. Explain.
Answer:
- Leadership is the art and skill of creating the desire in others, for achieving objectives.
- A leader is an influential person of the group who without any pressure provides guidance and inspiration and thus gets the expected work willingly done.
- Several people work in industrial units. Even after paying wages and incentives and motivating them, the desired results may not be obtained if they are not led well. A good leader can lead the unit and extract work smoothly.
- An efficient leader with his attitude and behaviour channelizes the efforts of the group members in a proper direction. He provides guidance to achieve decided targets, motivates to achieve objectives, inspiration, faith, etc.
- Thus, an efficient leader is the key to success directing.
Question 19.
A leader should have balance of mental, physical and psychological abilities. Explain.
Answer:
- The main job of the leader is to inspire people and make them walk on the path he suggests.
- This can be done only by the one who has some special abilities to inspire.
- Leader should have a good health and cheerful outlook.
- He should have good knowledge about things, intellect and awareness to deliver the talk and guide people.
- People also wish that the one who leads them should have good emotional quotient so that the leader can understand emotional needs and problems of the followers.
- Thus, a leader should have a balance of mental, physical and psychological abilities.
Question 20.
Neither all communication can be written nor can all communication be oral. Explain.
Answer:
- Written communication is very formal way of communicating whereas oral is mostly informal.
- Communication is a human based activity.
- Irrespective of the size, structure and discipline of the organization, all written communication cannot solve the purpose. Communication is not only ordering, setting rules on paper and expecting people to follow. Employees need to constantly be reminded about the rules and regulations communicated in written form.
- Although it must be well communicated in written form, employees need to be continuously inspired by guiding them, explaining them and making them follow the written formats.
- Similarly, if communication is just in oral form, it can create several confusions, lack of discipline and arguments.
- Hence, neither all communication can be written nor can all communication be oral.
Question 21.
Man buys several insurance plans. Explain.
Answer:
- Insurance is a tool to safeguard against risk of losing assets, life, etc.
- When a person insures something he feels safe and secure that even if he loses the insured things, he will get the insurance money to buy the new ones, or will leave money for family in case he dies.
- This is actually a safety need as per Maslow’s hierarchy of needs.
- Once, man’s physiological needs such as food, clothing and shelter are over he moves towards securing his physiological needs.
- This makes him open a savings and fixed deposit account, buy insurance, etc.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Direction is the exclusive function of guiding and observing sub-ordinates who gave this definition?
(A) Peter Drucker
(B) Koontz and O’Donnell
(C) Mann and Summer
(D) Maslow
Answer:
(B) Koontz and O’Donnell
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of directing?
(A) Communication
(B) Flow of direction
(C) Motivation
(D) None of these
Answer:
(D) None of these
Question 3.
Direction is not needed at
(A) Bottom
(B) Top
(C) Middle
(D) None of these
Answer:
(D) None of these
Question 4.
What is the flow of direction?
(A) Top to bottom
(B) Bottom to top
(C) Across
(D) All of these
Answer:
(A) Top to bottom
Question 5.
Direction has wider scope because
(A) It is used at all levels
(B) It has top-bottom approach
(C) It also makes people understand about business decisions and encourage them for implementation
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(C) It also makes people understand about business decisions and encourage them for implementation
Question 6.
The main motive for direction is
(A) Reducing stress
(B) Making employees happy
(C) Cut on costs and work at lower remuneration
(D) Encouraging employees
Answer:
(D) Encouraging employees
Question 7.
Directing as motivation to employees include
(A) Removal of work related confusions
(B) Repetition of same work
(C) Explaining rules and policies
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Question 8.
Motivation (Find the odd one out)
(A) Makes work interesting
(B) Increases enthusiasm
(C) Makes employees better problem solves
(D) Helps better communication
Answer:
(D) Helps better communication
Question 9.
What is true for supervision?
(A) It is an interval process
(B) It is mainly needed for lower level
(C) It encourages optimal usage of resources employees
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 10.
Who looks after the work of jobbers?
(A) Supervisor staff
(B) Departmental heads
(C) Top level managers
(D) Senior jobbers
Answer:
(A) Supervisor staff
Question 11.
_______ is the connecting link between top level and workers.
(A) Planners
(B) Supervisor
(C) Directing staff
(D) Manager
Answer:
(B) Supervisor
Question 12.
The process of stimulating people to perform action and to make it possible to have maximum satisfaction is called
(A) Direction
(B) Supervisor
(C) Motivation
(D) Leadership
Answer:
(C) Motivation
![]()
Question 13.
Who gave the definition about motivation which talks about stimulating someone?
(A) Koontz
(B) Morgan
(C) Drucker
(D) Jucious
Answer:
Question 14.
Abraham Maslow was a
(A) Management Guru
(B) Psychologist
(C) Management consultant
(D) Production engineer
Answer:
(B) Psychologist
Question 15.
‘Principal of Human motivation’ was released in
(A) 1927
(B) 1936
(C) 1943
(D) 1951
Answer:
(C) 1943
Question 16.
How many principles did Maslow give?
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Answer:
(C) 5
Question 17.
Which of the following needs is not given in Maslow’s theory?
(A) Social needs
(B) Physiological needs
(C) Economic needs
(D) Self-esteem needs
Answer:
(C) Economic needs
Question 18.
Safety needs include
(A) Opening savings account
(B) Gathering food
(C) Earning enough to get clothing and shelter too
(D) Getting love and affection as security
Answer:
(A) Opening savings account
Question 19.
An aspiring star aiming to become as popular as Shah Rukh Khan is trying to fulfill his _______ need.
(A) Social
(B) Self-actualization
(C) Physiological
(D) Safety
Answer:
(B) Self-actualization
Question 20.
Incentives are of _______ types.
(A) Two
(B) Three
(C) Five
(D) Several
Answer:
(B) Three
Question 21.
‘Advisor’ as an incergive means
(A) Electing worker in the advisory committee
(B) Advising the worker patiently
(C) Talking advice of worker
(D) Appointing a manager as advisor of the union
Answer:
(C) Talking advice of worker
Question 22.
Influencing people to work willingly for realization of specific goals is
(A) Directing
(B) Leadership
(C) Supervising
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(B) Leadership
Question 23.
_______ is the pre-requisite for an effective leader.
(A) Good personality
(B) Good appearance
(C) Good health
(D) All of these
Answer:
(C) Good health
Question 24.
Which of the following is not a psychological need of a leader?
(A) Zeal
(B) Tact
(C) Posture
(D) Work interest
Answer:
(C) Posture
Question 25.
_______ decides the human needs.
(A) Economy
(B) Mental status
(C) Social status
(D) Man’s current situation
Answer:
![]()
Question 26.
The need of leadership arise when
(A) People work in groups
(B) When workers do not care
(C) When workers have political backing
(D) When workers are illiterate
Answer:
(A) People work in groups
Question 27.
Leadership is the for an efficient organization.
(A) Base
(B) Need
(C) Process
(D) Way
Answer:
(A) Base
Question 28.
Which of the following is not a characteristic of communication?
(A) Goal oriented process
(B) Related to administration
(C) Many equipment
(D) None of these
Answer:
(D) None of these
Question 29.
There are methods of communication.
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Answer:
(D) 6
Question 30.
Which of the following is not communication?
(A) Video-cassette
(B) Silence
(C) Manuscript
(D) None of these
Answer:
(D) None of these
Question 31.
We can classify communication into types.
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 6
Answer:
(A) 2
Question 32.
The objective of formal communication is
(A) Supervise and guide
(B) Control and direct
(C) Administer and control
(D) Control and co-ordinate
Answer:
(D) Control and co-ordinate
Question 33.
Informal communication can be
(A) Written only
(B) Gesture
(C) Oral
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Question 34.
Which of the following is not a barrier for effective communication?
(A) Unclear assumption
(B) Distrust and fear
(C) Time shortage
(D) Over excitement
Answer:
(D) Over excitement