Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Commerce Accounts Part 1 Chapter 8 Journal Proper Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Accounts Part 1 Chapter 8 Journal Proper
GSEB Class 11 Accounts Journal Proper Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the correct option from those given below each question :
1. Transactions which are not recorded in other subsidiary books are recorded in ………………. .
(a) Journal
(b) Journal proper
(c) Cash book
(d) Other book
Answer:
(b) Journal proper
2. ……………….. is not included in subsidiary book.
(a) Sales book
(b) Petty cash book
(c) Ledger
(d) Debit note
Answer:
(c) Ledger
![]()
3. Why is it necessary to write adjustment entry at the end of the year for closing stock?
(a) To rectify the error
(b) To find true profit or loss
(c) To transfer the account
(d) To close the account
Answer:
(b) To find true profit or loss
4. Wages of ₹ 1000 paid for the installation of a new machine is debited to wages account. Which account will be affected while rectifying this error?
(a) Wages A/c and Machine A/c
(b) Only Machine A/c
(c) Only Wages A/c
(d) Cash A/c
Answer:
(a) Wages A/c and Machine A/c
Question 2.
Explain journal proper with illustration.
Answer:
Journal proper: The transactions which are not recorded in the other subsidiary books, are recorded in one special subsidiary book which is known as Journal proper.
Explanation: When the business transactions are limited, only one book of account is to be prepared known as Journal. With the development of business, number of business transactions also increased considerably. In this situation, from one book of accounts to get all the information in time or whenever necessary, is not possible. Therefore subsidiary books are maintained in the business. Thus, the transactions which are not to be recorded in purchase book, sales book, purchase return book, sales return book, cash book, petty cash book, bills receivable book, bills payable book, that type of the transactions are recorded in one other subsidiary book which is known as Journal proper.
Format: Format of the journal proper is just like the format of journal, in which five columns are like this: Date, Particular, Ledger Folio (L. F.) Number, Debit Amount (₹), Credit Amount (₹).
Illustration : To commence a business, Sagar has brought furniture of ₹ 16,000 and stock of goods of ₹ 9,000 in the business on 1 – 4 -’19.

Utility: This book is useful for the limited types of transactions, e.g., (1) Opening journal entry of the year, (2) Transactions of inter-account transfer, (3) Closing entries, (4) Adjustment entries, (5) Rectification entries and (6) Transactions which are not included in other subsidiary books.
Question 3.
Explain the classifications of the transactions recorded in the journal proper.
Answer:
Classification of the transactions which are necessary to be recorded in journal proper is as follows :
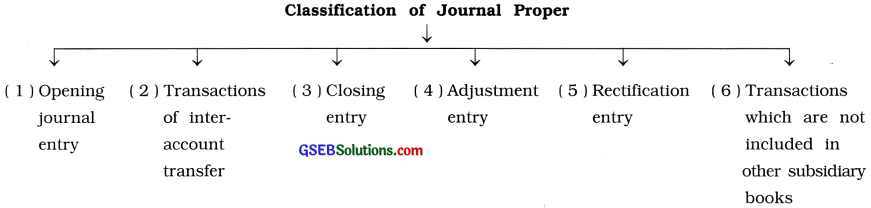
Explanation :
( 1 ) Opening journal entry: At the time of commencement of business, proprietor of the business brings some assets in the business. This transaction is recorded in the journal proper through a special journal entry in the books of the business, e.g., To commence a business Hashmukh has bro„ught cash ₹ 9,000, stock of goods of ₹ 6,000 and debtors of ₹ 5,000 in the business on 1-4-’19.

[Note: As other subsidiary books are maintained by the business, cash ? 9,000 brought by the proprietor should have been recorded in the cash book, therefore in the journal proper the effect of this cash transaction will not be shown.]
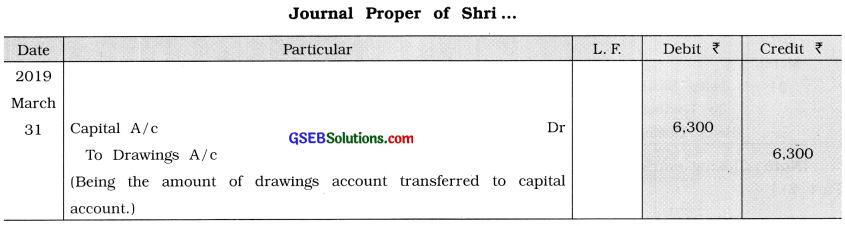
(2) Transactions of inter-account transfer : Due to certain reason, if the amount is to be transferred from one account to another account or if the total amount is to be transferred to another account by closing that account, one entry is to be passed which is known as Inter-account transfer entry, e.g., Receivable amount transfer from one account to another account, or to close the drawings account or entry of depreciation of an asset are known as inter-account transfer entry.
e.g., The balance of the drawings account ? 6.300 as on 31 – 3- ’19 is to be transferred to capital account. This will be recorded in journal proper as under :
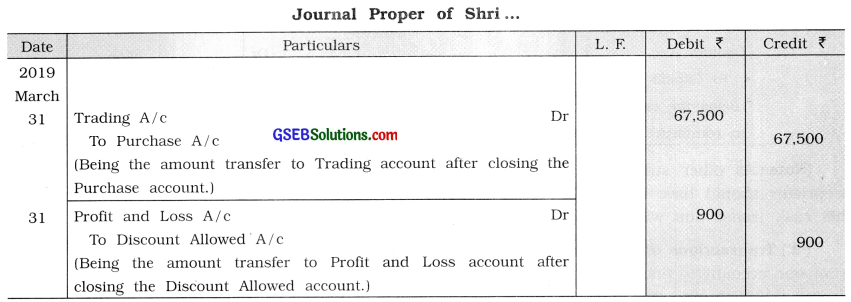
(3) Closing entry: At the end of the year, accounts relating to goods and incomes-expenses will be closed by transferring them either to trading account or to profit and loss account. Accounts related to the goods and accounts related to purchase expenses will be closed by transferring them to trading account. While accounts related to other than purchase expenses and incomes will be closed by transferring them to profit and loss account. Entries will be passed for transferring the gross profit or gross loss to profit and loss account and net profit or net loss to capital account. All these entries are known as Closing entry. In short, closing entry means entry passed for closing the account.
e.g., Closing balance of purchase account is ₹ 67,500 and of discount allowed account is ₹ 900 on 31 – 3- ’19. The entry for closing these accounts will be as follows:
![]()
(4) Adjustment entry: Final accounts are prepared with an intention to know the true and fair financial position and result of the business. For this, adjustment entry is necessary for the adjustment.
e.g., On 31 – 3 – ’19, closing stock was of ₹ 42,000. Entry for which will be as follows:

[Note : Closing entries and adjustment entries are discussed in detailed in the final account chapter (Part 2).]
(5) Rectification entry: Mistakes made at the time of preparing accounts are kept as it is, instead of erasing it or cancelling it. To rectify these errors, an entry is to be passed which is known as Rectification entry.
e.g., On 31 – 3 -’19, salary amount ₹ 2,500 paid to Munim (accountant) Shri Mafatbhai, is debited to Mafatbhai account. The rectification entry of this error will be as follows:

[Note : Rectification entry is discussed in detail in the. Chapter 1 Rectification of Errors (Part 2).]
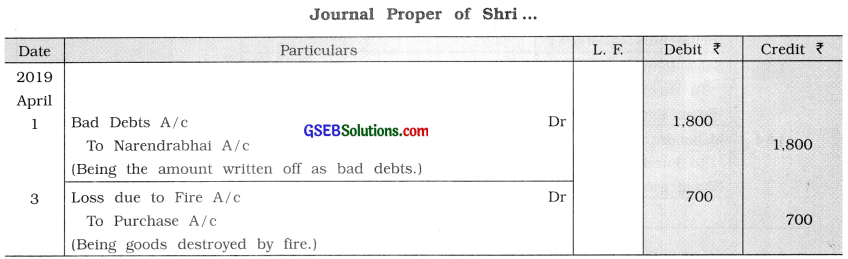
(6) Transactions which are not included in other subsidiary books: We studied earlier, how the transactions are recorded in the different subsidiary books. The transactions which cannot be recorded in other subsidiary books are recorded in the journal proper, e.g., Transactions related to bad debts, endorsment of bills, goods destroyed by fire, or by an accident, goods given as charity or goods goes out by any means, dishonour of bills, assets purchased on credit, etc. e.g.,
2019
April 1 Receivable amount of ₹ 1,800 from Narendrabhai is to be written off.
3 Goods of ₹ 700 burnt in fire.
Entries for these transactions are as follows :
![]()
★ Practical Examples:
Question 4.
Dhrumil Kamani starts business with following assets and liabilities on Dt. 1 – 1 -’15. Write opening journal proper.
Cash ₹ 18,000; Bank balance ₹ 12,000; Furniture ₹ 15,000; Stock of goods ₹ 20,000; Personal debtors ₹ 5,000 and 12 % Loan from Mayaben ₹ 10,000.
Note: Record cash and bank balance in cash book.
Answer:
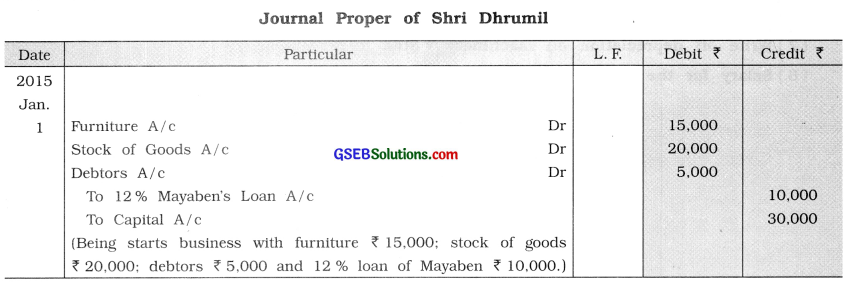
Question 5.
Shri Gujarat Stores does not maintain separate subsidiary books for transactions of bill receivable, bill payable, purchase returns and sales returns. Record the following transactions in the journal proper:
(1) Drew a bill of ₹ 8,000 on Ramnik which he accepted and returned.
(2) Accepted a bill of ₹ 3,000 drawn by Vijay and returned to him.
(3) Bill receivable of Ramnik endorsed to Ramesh.
(4) Goods of ₹ 3,000 returned by Paresh to us.
(5) Goods of ₹ 1,500 returned to Mahendra.
Answer:
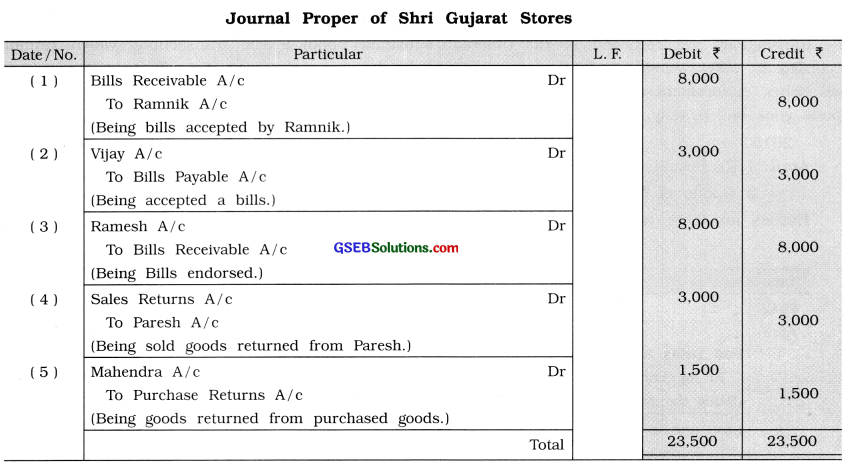
![]()
Question 6.
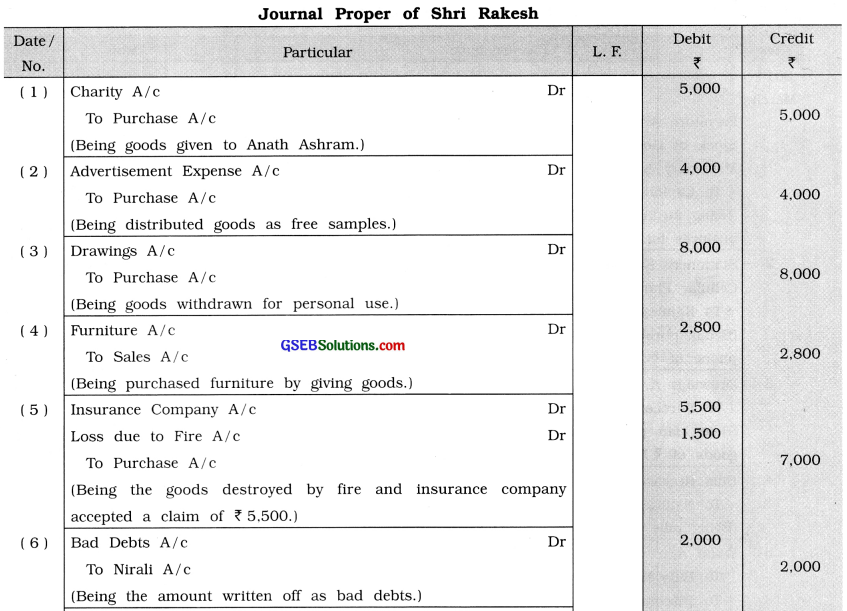
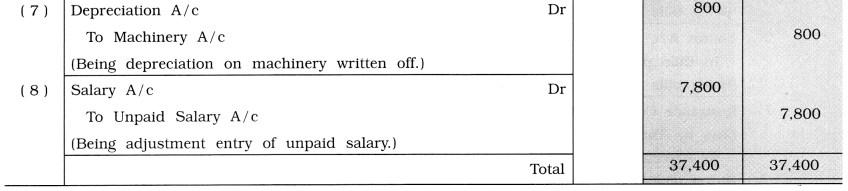
Record the following transactions in the journal proper of Rakesh:
(1) Gave goods of ₹ 5,000 to Anath Ashram.
(2) Distributed goods of ₹ 4,000 as free samples.
(3) Withdrew goods of ₹ 8,000 from the business for the personal use.
(4) Purchased furniture of ₹ 3,000 by giving goods of ₹ 2,800.
(5) Goods of ₹ 7,000 were destroyed by fire, for which the insurance company accepted a claim of ₹ 5,500.
(6) An amount of ₹ 2,000 is receivable from Nirali, which cannot be received now.
(7) Write off depreciation on machinery ₹ 800.
(8) Salary for the month of March is unpaid ₹ 7,800.
Answer:
![]()
Question 7.
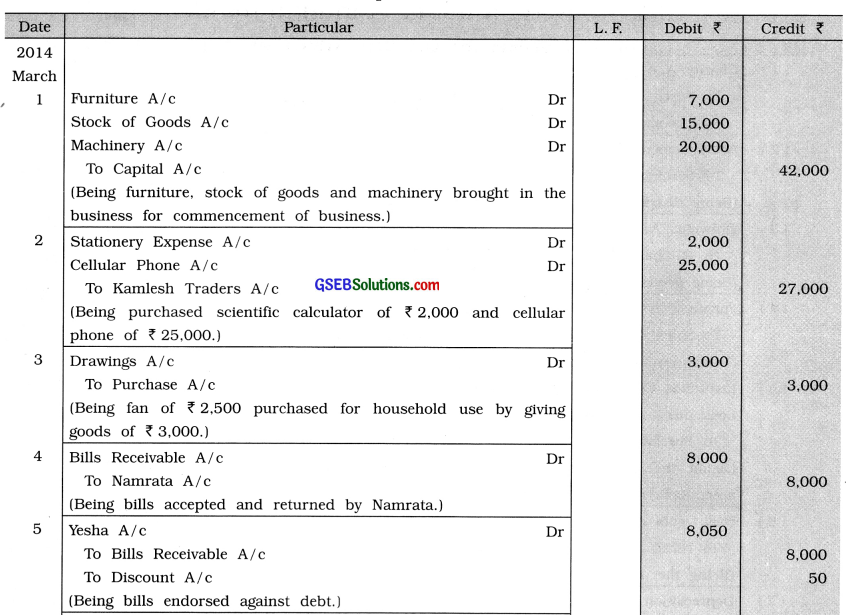
Record the following transactions in the Journal Proper of Shri Ekta:
2014
March 1 Brought furniture of ₹ 7,000, goods of ₹ 15,000 and machinery of ₹ 20,000 to start the business.
2 Scientific calculator of ₹ 2,000 and cellular phone of ₹ 25,000 purchased from Kamlesh Traders.
3 Fan of ₹ 2,500 purchased for household use by giving goods of ₹ 3,000.
4 Drew a bill of ₹ 8,000 on Namrata, which she accepted and returned.
5 Bill of Namrata endorsed to Yesha against her debt of ₹ 8,050.
6 A bill of ₹ 6,000 drawn by Bharat accepted by us and returned to him.
7 Goods of ₹ 8,000 were stolen away from the godown, for which the insurance company accepted a claim of 75 % of the amount.
8 An amount of ₹ 8,000 is receivable from Nirav and ₹ 8,200 is payable to Nalin. The account of Nalin was settled by Nirav accepting to pay ₹ 8,000.
9 Cash received from Rajendra for bad debt recovered ₹ 2,000.
10 ₹ 300 is payable to Manoj for interest.
Answer:
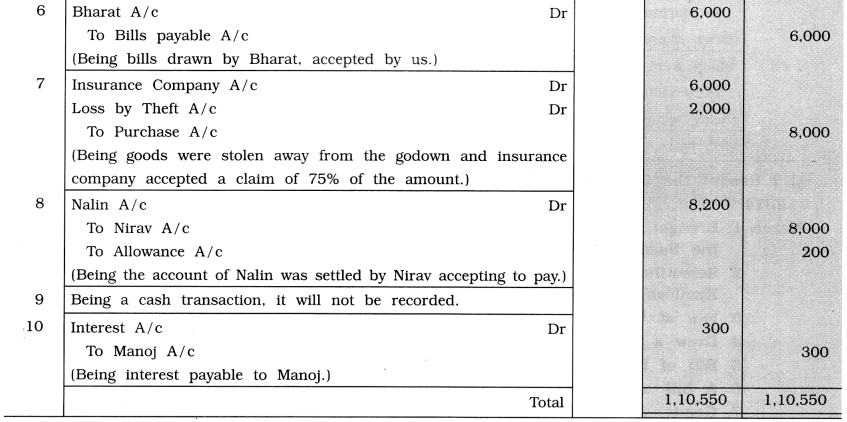
Note: Date 9 Cash transaction, it will be recorded in cash book.
Date 10 Manoj name is given in the transaction, so Manoj A/c will be credited instead of ‘Unpaid Interest A/c’.
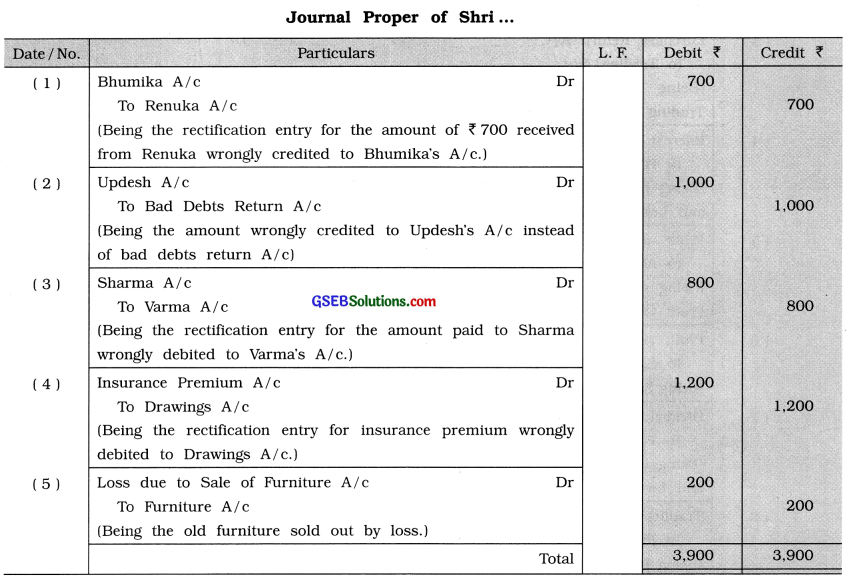
Question 8.
Pass journal entries for the following transactions in journal proper:
(1) ₹ 700 received from Renuka is recorded in Bhumika’s account.
(2) ₹ 1,000 received from Updesh for bad debt written off in past, which is credited to Updesh’s account.
(3) ₹ 800 paid to Sharma is debited to Varma’s account.
(4) ₹ 1,200 paid for insurance premium is debited to drawings account.
(5) Old furniture of ₹ 6,000 of business sold for ₹ 5,800.
Answer:
![]()
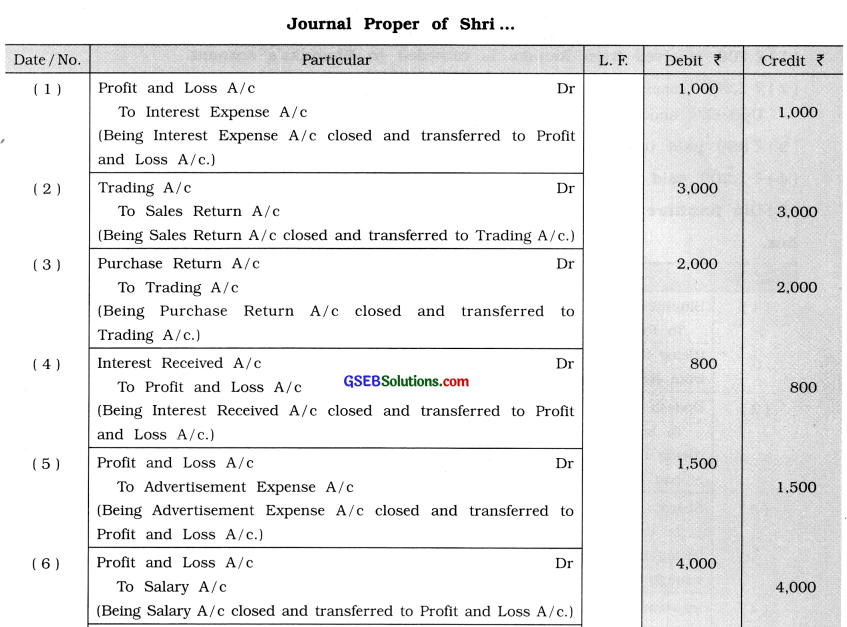
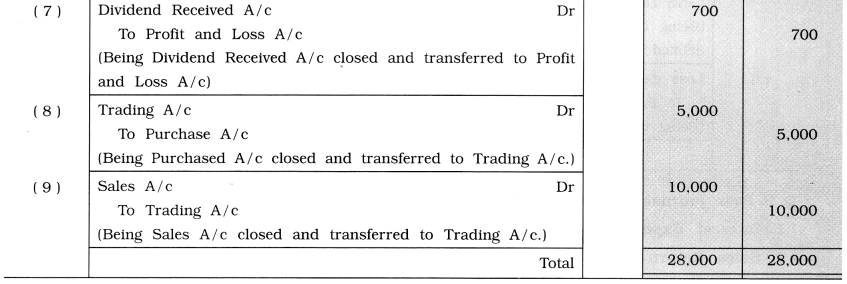
Question 9.
Pass journal entries for closing the following account:
(1) Interest Expense account ₹ 1,000
(2) Sales Return account ₹ 3,000
(3) Purchase Return account ₹ 2,000
(4) Interest Received account ₹ 800
(5) Advertisement Expense account ₹ 1,500
(6) Salary Account ₹ 4,000
(7) Dividend Received account ₹ 700
(8) Purchase account ₹ 5,000
(9) Sales account ₹ 10,000
Answer: