Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Chapter 7 Public Sector, Private Sector and Global Enterprises Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Chapter 7 Public Sector, Private Sector and Global Enterprises
GSEB Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Public Sector, Private Sector and Global Enterprises Text Book Questions and Answers
1. Select the correct alternative and write answers to the following questions :
Question 1.
Which is not a type of public sector?
(A) Government department
(B) Individual ownership
(C) Public corporation
(D) Government company
Answer:
(B) Individual ownership
Question 2.
In which of the following types, the employees are governed by government rules?
(A) Government department
(B) Public corporation
(C) Government company
(D) Private company
Answer:
(A) Government department
Question 3.
Which of the following is considered the oldest form of business?
(A) Public enterprise
(B) Private enterprise
(C) Global enterprise
(D) Public-Private partnership
Answer:
(B) Private enterprise
Question 4.
Which of the following statement is wrong for private global enterprise?
(A) Active at international level
(B) Massive size and scales
(C) Direct control of Parliament/Legislative Assembly
(D) Political supremacy exists due to strong economic capability
Answer:
(C) Direct control of Parliament/Legislative Assembly
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following is incorrect for public-pnvate partnership?
(A) Necessary land is to be purchased by them from the government
(B) For a prescribed period fee is collected from t.he beneficiaries .
(C) Creation of infrestructural facility from their o’/vn investment
(D) After the stipulated time period the infrastructure set up will have to be handed over to the government.
Answer:
(A) Necessary land is to be purchased by them from the government
2. Answer the following questions in one sentence each :
Question 1.
Define public enterprises.
Answer:
When a business is managed by an individual or group of individual with the objective of earning profit it is known as a private sector enterprise or private sector or even private enterprise.
Question 2.
Give name of types of public sector.
Answer:
Government department, government company and public corporation.
Question 3.
How much is the minimum share proportion of the government in government companies?
Answer:
51 %
Question 4.
In whose name shares are held in Government company?
Answer:
State government or central government or government of more than one state’s government or of more than one states government and central government.
Question 5.
Which is the oldest form of business?
Answer:
Sole proprietorship i.e. private sector enterprise.
Question 6.
State the meaning of global enterprise.
Answer:
A business enterprise operating in various countries is called a global enterprise. Global or transnational enterprises produce, sell and invest across the world. Global enterprises are highly organized companies which make use of factors of production of the world and global wealth to earn profit from the world market. Coca-Cola, Pepsi, Cadbury, Nestle, Ford, Hyundai, Tata, Birla, etc. are all very strong global enterprises.
Question 7.
What is public private partnership?
Answer:
Public-private partnership is a new arrangement initiated by Indian government between public and private enterprises. Under the PPP arrangement government combined public i.e. government sector with private sector for together raising infrastructure in the country.
3. Answer the following questions in short.
Question 1.
Give a list of various types of business unit.
Answer:
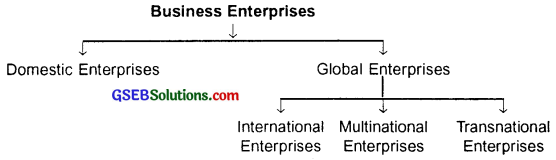
Question 2.
How can balanced regional development be achieved through public sector enterprises?
Answer:
- Public sectors have objectives of social welfare, raising employment and then earning profit.
- To provide balanced development to all the citizens government puts industries in several regions. This also includes setting up industries and other avenues of employment in backward areas or rural areas.
- Production and processing takes place in these plants.
- On the other hand government set-ups administrative offices of public sectors in urban areas. This helps in generating employment in urban areas In this sense, government tries to all the regions of a country through public sector and achieves regional development.
![]()
Question 3.
What is government department? Explain with an example.
Answer:
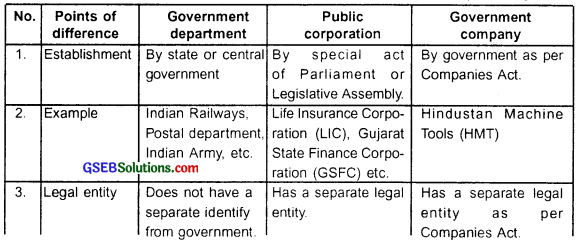
Government department:
- A public sector unit run and managed either by state or central government as per the laws, rules and regulations of either state or central government or both is called a government department. The employees working in these units are called government employees.
- For example, Postal department, Railway etc. are government departments.
Characteristics of government department:
1. Financial allocation:
Government allocates budget for government departments and industry and so these departments need to manage their expenses and administration from the allotted budget. Income earned by these departments is deposited in government treasury.
2. Maintenance of accounts:
The maintenance of account of government department is done by the respective department. The accounts are audited by CAG i.e. The Comptroller and Auditor General.
3. Appointment of employees:
The employees of the government departments are considered as government employees. So, the process of appointing them, their work conditions, rules and regulations are all set by government.
4. Government management and control:
The civil service officers of respective government enterprises, as well as the minister of concerned department, directly controls the administration.
5. Responsibility:
The responsibility of running the unit lies with the departmental heads. They are directly answerable to the Member of Parliament or Vidhan Sabha (Legislative Assembly) for the progress and status of the department.
Question 4.
“The only objective of private enterprise is to earn profit” – Discuss
Answer:
- Private enterprises are owned and managed by individuals or group of individuals.
- Individuals set-up private enterprises to earn a living raise their standard of living and maximize wealth.
- For achieving these objectives they focus on profit. Higher the profit higher the fulfillment of their objectives.
- Private enterprise is not concerned with national objectives of regional development or providing employment.
- Thus the only objective of private enterprise is to earn profit.
Question 5.
State the importance of private enterprises in the economy.
Answer:
In 1991, India adopted the policy of liberalization, privatization and globalization. As a part of these policies due importance was given to the private sector. Also, foreign countries were allowed to enter into Indian market.
- Private sector expanded in all the areas in which they were allowed to operate. They invested huge capital in all the possible industries that too in all the parts of the country. As a result Indian economy grew drastically. Millions of people got employment and their living standards improved.
- Though public sector was given an opportunity due to weaknesses of public sector, they took Indian economy to great heights and left public sector far behind.
- Today, private sector boasts of a very high economic contribution in India’s growth. It holds a lion’s share in Indian economy. Although private sector can be considered as old as mankind but its role and importance has been evergrowing. Realizing the contribution and overall development that the private sector has made, the government makes continuous efforts to motivate and strengthen this sector.
Question 6.
What is the importance of global enterprise in the Indian economy?
Answer:
- Before 1991 the presence of global enterprises was quite less in India. Moreover, owing to the political condition of India that time it was quite difficult for foreign companies to enter Indian market.
- In 1991, India adopted the policies of liberalization and globalization. These policies changed the entire form of Indian market. These polices led to faster entry and expansion of global enterprise in India.
If we wish to prepare a list of global companies present in India we can divide them in two parts. They are:
1. Companies of other countries present in India
2. Indian companies present in countries outside India.
- It is quite obvious that there are much more foreign companies present in India than presence of Indian companies in foreign countries.
- Coca-Cola, Pepsi, McDonalds, Nokia, Sony, Samsung, Ford, General Motors etc. are all global enterprises of foreign origin present in India.
- In recent years companies of Indian origin such as Infosys, Reliance, Maruti, Wipro, ONGC, Tata Steel, Asian Paints, Royal Enfield, etc. have also spread their business in other countries.
- The number of Indian based companies spreading their wings in foreign countries is constantly increasing. These Indian enterprises now turned into global enterprises are supplying products and services to several countries.
- Global enterprise companies of both foreign and Indian origin have boosted Indian economy to many folds. These companies have revolutionized the Indian economy. Today, they hold a very strong hold in Indian finance, economy and politics.
- The sales and income of global enterprise are much higher than that of domestic industries. Global enterprises are proving to be more effective in contributing to, Indian economy and employment because of their mammoth capital, very high reputation, use of modern technology, very aggressive marketing and highly efficient administrative systems. For example, McDonalds, a global enterprise is able to sell a burger for as low as ₹ 27 Sony and Samsung till date rule the Indian electronics market.
4. Answer the following questions in brief :
Question 1.
What is departmental management? state its features.
Answer:
Question 2.
After giving the meaning of public corporation explain its features.
Answer:
Public corporation:
Public corporation is a corporation which comes into existence through a special Act of Parliament or Legislative Assembly i.e. Vidhan Sabha. The authority to run these units, the powers, duties, rights and responsibility, service rules and relationship with government department are all mentioned in this special Act passed in the Parliament.
For example, Life Insurance Corporation (LIC) of India, Food Corporation of India, Gujarat State Text Book Board, etc. are all public corporations.
Characteristics of public corporation:
1. Establishment:
- Public corporation is a corporation which comes into existence through a special act of Parliament or Legislative Assembly i.e. Vidhan Sabha. The authority to run
- these units, the powers, duties, rights and responsibility and labour laws are all as per the special act passed in the Parliament.
2. Ownership:
- Government makes provisions for raising capital for these units. So, the ownership is either with the central or state government or both.
- Government decides ways and strategies of making these units profitable. The loss made by these units becomes burden on the government.
3. Capital accumulation through government:
The government provides capital to these corporations. Public corporations can also borrow from government’s budget or from public if needed.
4. Separate identity:
Public corporations have a special legal identity and they enjoy and command all the facilities and rights available to a company.
5. Managerial autonomy:
Though public corporations are owned by the government, they enjoy complete autonomy in management. Politicians cannot interfere in the day to day activities of the corporation. The corporation gets enough freedom to take even important decisions and implement them.
6. Service rules:
- The employees of public corporations are not bound by the rules similar to that of government employees.
- The rules and regulation and laws applicable to the employees of corporation are determined by the concerned corporation. The employees then need to adhere to them.
- At times, government deputes its officers in these corporations for management.
7. Management through Board of Directors:
Public corporations are managed by the Board of Directors. Government appoints the president of Board of Directors from eminent personalities, prominent industrialists, expert professionals, celebrities, etc. The Board of Directors formulates policies to take care of the day to day activities.
8. Answerable to parliament /legislative assembly:
Public corporations work using public money. Hence the government expects them to make profit and questions them if they make loss. The corporations need to submit financial reports to the Parliament/Legislative Assembly and face them for any loss they make.
![]()
Question 3.
Define government company and write a note on its features.
Answer:
Government Company:
- A company established as per the Company Act and in which minimum 51% stake is with State or Central Government or both together is called a government company. Since the government owns the largest stake of shares in such companies they are called government companies. Due to major stake, government can exercise its control and supremacy in government company.
- The share of government in government company lies in the name of the president of India.
- The objective of government company is purely to do business, make profit and compete with private companies.
- Hindustan Machine Tools (HMT), Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd., etc. are examples of government companies.
Characteristics of government company:
1. Establishment:
These companies are established as per the Indian Companies Act.
2. Separate identity:
A government company has an independent legal identity and hence it can sue or can be sued as individuals in the court of law. Just like any other company it can also own property or enter into contract with any individual or company.
3. Capital:
Government brings and owns at least 51 % share capital of these companies.
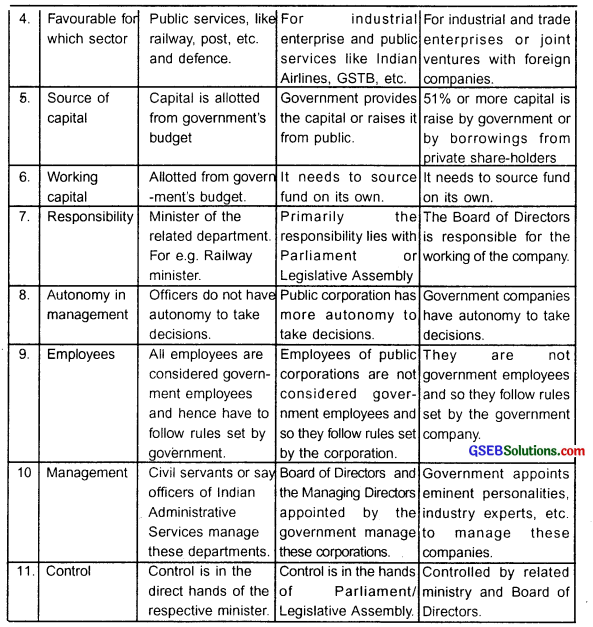
4. Administration:
Just like any other company the administration of a government company is also done as per Companies Act.
5. Appointment of workers:
The workers of these companies are appointed on the basis of rules and regulations of the company.
6. Appointment of members of Board of Directors:
The Board of Directors and its members are appointed by the government.
7. Appointment of auditors:
When it comes to maintenance of accounts and auditing the company, the government companies are exempted from the rules and regulations of Company Act. However, government appoints auditors who submit annual report of the company in the Parliament/Legislative Assembly.
8. Arrangement of capital accumulation:
Based on the requirement government companies accumulate capital from the shares of government and private shareholders. They can also sell shares to the private individuals.
9. Policy decisions:
The policy decisions of the government companies are taken by the respective ministers.
Question 4.
State the changing role of public enterprise.
Answer:
1. When India became independent it planned to establish and expand industries in public sector. The era of 1950-1990 was quite important for public sector. It was expected that public sector would play a major role in fulfilling the important objectives of Indian economy.
2. It was also expected that public sector would create facilities and infrastructure necessary for the development of key industries which form a base for economic development.
3. For example, areas such as railways, custom department i.e. building of ports and its management, etc. needed a huge investment with a very low return on investment. Private sectors were not at all willing to venture into such high risk industries.
4. These set-ups were then purely on the shoulder of public sector. It was also expected from public sector to produce or procure for such heavy industries, process them and provide service. Owing to poor economic conditions and weak political system India was not in a position to deliver expected results via. public sector.
5. In 1991, India adopted the policy of liberalization, privatization and globalization.
This transformed the role and scenario of public sector.
- As a part of these policies due importance was given to the private sector. Also, foreign countries were allowed to enter into Indian market. The, public sector then started competing with private sector. Just like private sectors, the public sectors also started giving importance to profit rather than just providing service.
- Loss making public sector units started making structural changes to convert themselves into profit making units. Those units who made severe losses which could not be recovered by any new strategies were closed. Certain public enterprises were dissolved and their equity shares were distributed to the shareholders where as some were sold to private companies.
- Government appointed various committees to develop strategies for converting non-performing public sector units into profitable units.
- Today, private sector boasts of a very high economic contribution in India’s growth. It holds a lion’s share in Indian economy. Although private sector can be considered as old as mankind but its role and importance has been ever growing.
Question 5.
State the points of difference between public and private sector.
Answer:
| Point of difference | Public sector | Private sector |
| Ownership | Ownership lies with either state government or central government or both | Owned by individuals or group of individuals |
| Control | It is owned by government and so it is also controlled by the government | Individuals or group of individuals who owns the unit controls it as per government laws |
| Main objective | Main objective is social and economic welfare of the citizens | Main objective is to earn profit |
| Profitability | The profit is quite less because the objective is not to maximize profit but welfare | Private sector earns high profit and is keen for profit maximization |
| Nature/Form | Government department, public corporations and government companies are the various foruis | Sole proprietorship, partnership, co-operative society joint stock company, etc. are its various forms |
Question 6.
After giving the meaning of global enterprises, state its characteristic features.
Answer:
1. Domestic (local) enterprise :
An enterprise which operates within the political boundaries of a country is known as a domestic or a local enterprise. The business policies of domestic enterprises are framed by the country as per the business and social environment of the country.
2. Global enterprise:

A business enterprise operating in various countries is called a global enterprise. Coca-Cola, Pepsi, Cadbury, Nestle, Ford, Hyundai, Tata, Birla, etc. are all very strong global enterprises.
Characteristics of a global enterprise:
1. Business in more than one country:
Global enterprises work on a very large scale at international level. They conduct business in different countries in different manners.
2. Priority:
Global enterprises give priority to regional aspects, while making investment, and production and distribute their resources accordingly in each country.
- They understand that different countries have different religions, culture and social and economic set-up.
- They also are very well aware about the behavioral patterns and mindset of people of each region.
- Based on their rich knowledge and research they plan separate strategies for each country and even state and expand their business. For example, McDonalds have highly changed their product range and taste as per the taste and preference of Indians.
3. Size and sales:
The size and sales of global enterprise is extremely huge. In most cases the annual income of these companies is more than national income of some small countries.
4. Economic capability:
Global enterprises are very strong financially. Many times they can even afford to operate at very low profits or even losses that too for a very long period in order to penetrate into the market of a country. Since they are very sound financially they can produce and sell at a massive scale.
5. Political supremacy:
Due to their very strong economic (financial) power, they also enjoy political
supremacy. Global enterprise invests very heavily in a country and so in return the country has to compromise with some of its rules, regulation and policies. In many cases they can even influence the economic policy of the country by influencing the political leaders.
6. Loyalty:
Global enterprises do business with a number of countries and make huge profits. But when it comes to loyalty, they are majorly loyal only to their native countries.
7. Emergence in developed countries:
Global enterprises mainly belong to economically developed countries whereas their business mostly exists in developing and under developed countries of the world.
8. Massive expenditure on Research and Development (R&D):
Global enterprises spend huge amount of money on R&D and strengthen their knowledge and strategies. They spend a huge amount of their income for research and development and develop new products, services, processes, modern technology and administrative strategies. Owing to massive finance they have they are able to invest in capital intensive technologies.
9. Brings life style changes:
To develop their products and services Global enterprise brings changes in the life style of the people the countries in which these companies operate. For example, global enterprises have changed the way we eat. Due to their marketing strategies and options we now eat burgers and pizza and drink coffee in cafe quite frequently.
5. Answer the following questions in details :
Question 1.
What is public sector? explain in detail their characteristics.
Answer:
Public sector:
- An enterprise, which is owned, managed and controlled by government is called a public sector enterprise. For example, Postal department, Indian Railways, LIC of India, Indian Airlines, etc. are all examples of public enterprise.
- The ownership of such units is either partially or fully in the hands of central government or state government. Such units can be either government department or part of it could be set up through the act of parliament
Characteristics of public sector:
1. Aims at establishing basic industries:
- The basic objective of establishing units in public sector is to provide base for accelerating those industries which require huge investment. Post-independence it was quite important for India to attain growth in industrialization to improve its economic condition.
- Basic industries require huge investment for their set-up in the initial stage. However returns in initial years are quite low compared to the capital invested. As a result, private sectors were not much interested in setting up heavy industries.
- Government invests in such industries with an objective to achieve faster economic growth.
2. Elimination of monopoly:
By owning basic industries government can stop private units from creating monopoly.
3. Balanced regional development:
Private enterprises are not interested in investing in backward areas whereas government can set-up industries in such areas and play an important role in developing them. For example, government established iron and steel industries in Rourkela, Bokaro, Bhilai etc. and developed these backwards areas.
4. Objective of social welfare:
- Generally, the objective of private sector is to maximize profit whereas public sector aims at achieving social welfare along with profit.
- Moreover, all sections of society without any discrimination receive benefits from public sector. Speeding up industrialization leads to faster establishment of basic industries which ultimately welfares the entire society.
5. Low profit:
- When public sectors were first set-up they either made very less profit or loss.
- However, government continued industries set-up in public sector. After 1991, government changed its policies and aimed at converting such industries into profit making units along with social welfare.
6. Maintenance of national interest:
Public sector units also aim at interest of the nation. For example, the production of defence equipment is done by the government via. its public sector units. Since defence is a very confidential and sensitive issue, production of its equipment can be done only through government units.
7. Generation of employment opportunities:
Countries like India which are developing and highly populated too need to provide employment to its population. Investment in public sectors boosts industrial growth and solves the problems of unemployment.
8. Increase in economic development of the country:
Public sector industries create a base for industrialization which leads to economic development.
9. Social and economic justice:
The management of public sector is in the hands of the government and hence public sector industries need to compulsorily follow government policies and regulations. Due to this reason we can see positive trend of providing free or concessional services, job security, better working conditions, importance to labour laws, priority to women, etc. in public sector units. This forces public sector units to provide social justice to the society.
10. Ideal wages and facilities for employees:
As the ownership of public sectors rests with the government they pay decent wages to the workers. Employees of public sector get quite good facilities like conveyance, paid holidays, pension, etc. compared to private sector employees.
![]()
Question 2.
Compare the three types of public enterprise.
Answer:
Question 3.
Prepare a note on meaning and characteristics of private enterprise.
Answer:
Private sector enterprise:
- When a business is managed by an individual or group of individual with the objective of earning profit it is known as a private sector enterprise or private sector or even private enterprise.
- Sole proprietorship, Partnership, Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), Co-operative society, Joint stock companies, etc. are all private sector enterprise.
Characteristic of private sector enterprise:
1. Oldest form of business:
Private sector is the oldest form of business. We can also say that the concept of business started with private sector. Today private sector is a very important characteristic and a special entity of our economy.
2. A big share in our economy:
Private sector occupies a strategic place in India’s economy. It is difficult to imagine our economy without private sector.
3. Need based changes:
From the time of its inception private sector has been open to adapt itself as par the demand of market and time.
4. Acceptance priority to profit and of social responsibility:
- Although the main objective of private sector is profit, it has also accepted and fulfilled responsibilities in various areas.
- For example, private sector has played a very active role in fulfilling social and environmental responsibilities. Along with this it has also taken care of women empowerment, literacy, etc.
5. Exists in all countries:
- Private sector exists in one form or the other in all the countries of the world.
- Every city, town and village has private sector enterprise.
- Although the laws governing these private sectors may be different in different countries but all the countries have accepted private sector existence and cannot do without it.
6. Inclusion of Multinational Corporation (MNC):
- Any business activity undertaken by a firm in more than one country is known as multinational corporation (MNC).
- Multinational companies started gaining pace in 19*h century. This increased the presence of private sector in many countries that too in large scale. Many MNCs started producing and selling in more than one country which increased the standard of living of people across the world.
7. Employment generation:
- Maximum people around the world are employed in private sector rather than government sector.
- Private sector has expanded leaps and bounds which has resulted in employing a very large population. This in turn has increased people’s income and standard of living.
Question 4.
Give a detailed explanation of meaning and characteristcs of joint enterpises.
Answer:
Joint venture:
When two or more business units join with each other to conduct the business activities together it is called a joint venture. Units joining hands can be private enterprises, government-owned or global enterprises.
Joint venture between countries:
- If joint venture occurs between enterprises of two different countries then it is called joint venture between two enterprises of two countries. Under such joint ventures, both the enterprises must compulsorily follow rules framed by their countries.
- In, India, there are no separate laws for joint ventures. Companies listed in India are considered as domestic company and Indian laws are applicable to them.
- Global enterprises who wish to undergo joint venture with Indian enterprises or Non-resident Indians (NRIs) who wish to invest in Indian industries must follow specific procedures and must have all the approvals from Indian government.
Such approvals must adhere to the policies of the Reserve Bank of India or foreign investment promotion board.
- A joint venture is generally done for a very long period. Business units of any size can join with each other under joint venture with an objective of fulfilling and safe guarding mutual interests.
- Joint venture aims at making maximum use of resources and expertise available with both the enterprises to expand the business, share and enjoy the profits jointly and also jointly bear the risk and loss.
- The main objective of creating joint venture is to expand business, develop new products and create and expand new markets. In recent times several industrial units have created joint ventures with other industrial units. These joint ventures have started utilizing their full capacities to develop distribution channels, improve production techniques, expand market and achieve higher financial goals.
Characteristics of joint venture:
1. Mutually beneficial for both parties:
Joint venture proves to be beneficial for both parties. Both parties compliment each other due to their individual capabilities, resources and strategies. Together they expand the market which then benefits both.
2. More resources and capabilities:
Enterprises forming joint venture share their resources and capabilities to increase their mutual benefits. Thus the associated resources and capabilities bring several – opportunities for the joint venture.
3. New technology:
Both enterprises have their own set of technological expertise and applications. Through joint venture they can utilize the technologies in the joint venture and produce new, improvised products at faster rate with better technology and more effectiveness. This overall reduces time and money and increases productivity.
4. Development of new market:
When a business unit undergoes joint venture with a business unit of a foreign country the market expands and even a new market may emerge. For example, when an Indian company enters into a joint venture with a foreign country, the market expands in India due to the new products, services, brand and strategies that the foreign country offers.
Many companies who have already established market in their countries, after saturation join hands with enterprises of other countries for entering into new market and making profit.
5. Innovation:
Through joint venture new and innovative products are placed in the market. Foreign partners often bring products that are based on new and advanced technologies. This adds innovation to the products and processes existing in the market.
6. Low production cost:
Use of modern technology results in large scale production. This reduces cost of production. As a result products can be sold at cheaper prices which in turn increase their demand.
7. Increase in business credit:
When companies join hands under joint venture, the news spread in market. This also increases credit i.e. reputation of their individual businesses. Sometimes under joint venture a foreign company may even allow an Indian partner to use its brand name.
Question 5.
What is public utility? Explain its features.
Answer:
Public utility:
- Basic facilities like water, electricity, transportation, communication, cooking gas, sewage, etc. that are needed by people on a daily basis are called public utilities.
- Public utilities form a part of basic infrastructure of any nation. A nation needs to provide these utilities to every city, town and village.
- Every citizen has a right to avail and use these utilities irrespective of his caste, sex or income.
- Government tries to provide public utilities at nearest locations to each citizen.
- For example, we have bus-stands near our house, we get clean water to drink, electricity, sewage facilities, etc.
- Any deterioration in the quality of these services can affect human health and life badly. To see that these facilities are available to all on a continuous basis government joined hands with private sectors. Private companies like Torrent ‘ Power supplies electricity in few cities of Gujarat, Adani gas provides cooking
gas lines, etc. - It is quite possible that private sectors can monopolize the market if strict regulations and policies are not framed and observed by the government. Hence, government takes several measures to safeguard the interests of citizens and protect them from exploitation of private sectors.
- Similarly, monopoly existed at government level too. In olden times, government owned few sectors and so the customers suffered due to monopoly of the government.
- Later, by a law of parliament other private companies were also allowed to operate and hence the market became open. For example, more than one company and even private companies were allowed to provide services of telecom. This led to better, faster and cheaper telecom services in the nation.
However, government keeps a control over these companies to see that customers are not exploited.
- At local level the public utility services are raised and managed by village panchayat, taluka panchayat, zilla panchayat, nagar-palika or mahanagar-palika.
- The state government company or corporations takes care of utilities like transportation, electricity, health centres, etc.
- At national level, the central government, companies or corporations provide utilities like Post and Telegraph, Railway, Telecommunication, etc. to the entire nation.
Question 6.
“Public-private partnership is an arrangement due to the need of time.” – Explain,
Answer:
Public-Private Partnership (PPP):
1. Public-private partnership is a new arrangement initiated by Indian government between public and private enterprises.
2. In 1991, the Indian government adopted the policy of liberalization, privatization and globalization. Owing to the policy of globalization many foreign companies entered into Indian market. They brought several products and services which were earlier not available in India.
3. International companies were invited to make investment in India, set-up factories and establish market. However, India did not have modern and sufficient infrastructure to give proper platform to these companies. For example, India did not have very good roads, good connectivity within various regions through roads ahd communication, airports, bridges, dams, electricity, etc. Unless these infrastructural facilities are raised, foreign countries cannot be lured to India.
4. Generating such infrastructure in the country required massive investment. For example, for providing air services we need airport and other allied services. For new and modern foreign cars to be introduced in Indian market a good roads are must. For all these infrastructural development, government needed massive investments which was not possible for the government.
5. It was possible that private sector which was capable of such high investments be given the task of raising the required infrastructure in the country. But at the same time governments feared the private sector would become economically very strong and dominate the country. Hence, the India government thought of a middle way out. It proposed a new arrangement of Public-Private Partnership.
6. Under the PPP arrangement government combined public i.e. government sector with private sector for together raising infrastructure in the country. For example, government (public sector) gave land to private enterprise for developing infrastructure. The private enterprise would then put its own money raise the infrastructure as per government’s specifications. To recover its investment, the private enterprise would be allowed to collect fee from the beneficiaries of that services for a fixed duration. For example, Ahmedabad-Vadodara express highway is built under PPP arrangement. The private enterprise built it and now it collects a toll fee from the passers. Once the investment is recovered the private enterprise will take away its stake from the express highway.