Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Gujarat Board Class 9 Science The Fundamental Unit of Life InText Questions and Answers
Page – 59
Question 1.
Who discovered cells, and how?
Answer:
Robert Hooke discovered the cells in 1665. He used a primitive microscope to observe the cells in a thin slice of cork. He observed that cork resembles the structure of a honeycomb consisting of many little compartments.
![]()
Question 2.
Why the cell is called the structural and functional unit of life?
Answer:
The body of all living organisms is composed of one or more cells, so cell is called the structural unit of life. Also, the various life processes like digestion, respiration, excretion, etc. are performed by the cells, so cell is called the functional unit of life.
Page – 61
Question 3.
How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer:
The substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell on the basis of their concentration by the process of diffusion or osmosis respectively. If the concentration of CO2 is more inside the cell, then the diffusion of CO2 occurs from inside to the outside of the cell.
If the concentration of CO2 is less inside the cell, then CO2 diffuses from outside to inside of the cell. If the concentration of water is more inside the cell, then osmosis of water occurs from inside to the outside of the cell. If the concentration of water is less inside the cell, then osmosis of water occurs from outside to the inside of the cell.
Question 4.
Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Answer:
Plasma membrane allows the entry and the exit of only certain selected molecules through the cells and prevents the movement of other substances across the cell. So, plasma membrane is called a selectively permeable membrane.
Page – 63
Question 5.
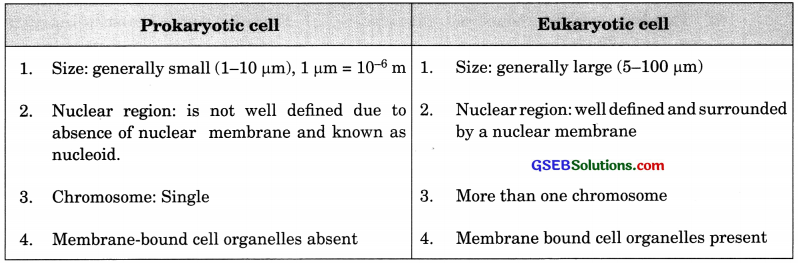
Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.

Answer:
Page – 65
Question 6.
Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer:
Mitochondria and chloroplast are the two cell organelles that contain their own genetic material.
Question 7.
If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer:
The various functions of the cell are performed by its cell organelles. If the organisation of the cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, these functions will not be performed by the cell and ultimately the cell will die.
Question 8.
Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer:
Lysosomes are single membrane bound cell organelles which contains hydrolytic enzymes. If the lysosomes burst open, the enzymes released by it digest their own cell organelles. So, lysosomes are called suicidal bags.
Question 9.
Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer:
The site of proteins synthesis in the cell are the ribosomes
![]()
In-Text Activities Solved
(Textbook Page 46)
Activity 5.1
Answer:
(a) The peel is used like a thin slice to observe the cells of onion.
(b) We observe closely packed several units called cells which are compactly arranged. Yes, we can draw the structures that we see through the microscope, on an observation sheet. Yes, it looks like the figure given below.
(Textbook Page 58)
Activity 5.2
Answer:
(a) Yes, all cells look alike in terms of shape and size
(b) Yes, all cells look alike in structure
(c) Yes, the cells from different parts of a plant body are different as the type of cell depends on the function they perform.
(d) Cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm and nucleus are present in all the cells.
(Textbook Page 60)
Activity 5.3
Answer:
(a) The egg swells because water passes into it by osmosis (as the solution inside the egg is more concentrated).
(b) Water passes out of the egg solution into the salt solution because the salt solution is more concentrated (i.e., the solution outside the egg is more concentrated).
(Textbook Page 60)
Activity 5.4
Answer:
(a) Reason. The raisins or apricots swell up as water moves inside them from outside because the water concentration is less inside the cell as compared to the solution outside. Hence, water moves inside the cell by endosmosis.
(b) Reason. The raisins or apricots shrink as water moves outside from them because the water concentration is more inside the cell as compared to the solution outside. Hence, water moves out of the cell by exosmosis.
(Textbook Page 61)
Activity 5.5
Answer:
A normal compound microscope uses light to get a magnified image of the object. Electrons are used in an electron microscope to get a highly magnified image of the object and that too with a higher resolving power than a compound microscope.
(Textbook Page 61)
Activity 5.6
Answer:
(a) We observe that the cell undergoes plasmolysis due to the shrinking of the protoplasm. This occurs as the water moves outside the cell due to a more concentrated solution present outside the cell.
(b) No effect of the strong solution of sugar or salt will be seen if the leaves are boiled for a few minutes. So, plasmolysis does not occur in them as the cell die in boiling water. This proves that only living cells undergo shrinking or swelling of their protoplasm during the movement of water outside the cell or into the cell respectively. The phenomenon does not occur after boiling the leaves as the plasma membrane does not remain selectively permeable after it.
(Textbook Page 61)
Activity 5.7
Answer:
(a) We observe the cheek cells. The shape of the cheek cells is: Flat, polygonal have irregular boundaries. The diagram of cheek cells is shown below:
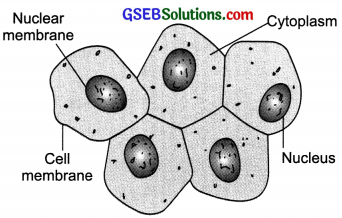
(b) Yes, a darkly coloured, spherical or oval, dot-like structure called the nucleus is present near the centre
of each cheek cell. The similar structures are seen in onion cells too but not in the centre because a large central vacuole occupies the centre of onion cell and nucleus is present at its periphery.
Gujarat Board Class 9 Science The Fundamental Unit of Life Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer:
Plant Cell:
- Cell wall is present.
- Plastids are present.
- A large central vacuole is present.
- Centrioles are absent.
Animal Cell:
- Cell wall is absent.
- Plastids are absent.
- Vacuoles are either absent or are very small.
- Centrioles are present.
Question 2.
How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer:
Prokaryotes:
- Organisms whose cells lack a well-defined nuclear membrane.
- They lack membrane bound cell organelles.
- Size is generally small (1-10 pm)
- Have a single chromosome
Eukaryotes:
- Organisms with cells having a well-defined nulear membrane.
- They have membrane bound cell organelles.
- Size is generally large (5-100 pm)
- Have more than one chromosome
Question 3.
What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer:
The plasma membrane regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell. So, if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down the regulation of substances would get affected, the contents of the cell will ooze out of the cell and ultimately the cell would die.
Question 4.
What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer:
If there was no Golgi apparatus, then the following processes carried out by it would get affected:
- The storage, modification and packaging of products in vesicles.
- The packaging and dispatch of the material synthesised near the ER to various targets inside and outside the cell.
- The formation of lysosomes.
- The formation of cell plate during cell division.
So, in the absence of the Golgi apparatus, most of the functions of the cell would get disrupted.
![]()
Question 5.
Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer:
Mitochondria are called as the powerhouse of the cell as they are the storehouse of energy synthesised by the cells during respiration. Energy is stored in the mitochondria in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which is released when cell needs it.
Question 6.
Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer:
The lipids are synthesised by the smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The proteins are synthesised by the ribosomes which are attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
Question 7.
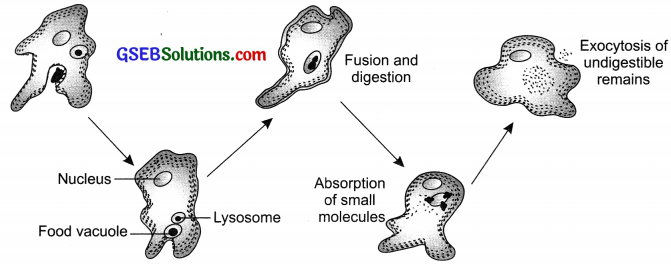
How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer:
The Amoeba takes in food with the help of finger like extensions called pseudopodia by the process called endocytosis. Pseudopodia help to engulf the food which gets enclosed in a food vacuole. The complex particles of the food get broken down into simpler substances inside the food vacuole and diffuse into the cytoplasm of Amoeba. The undigested food particles are removed from the cell by exocytosis.
Question 8.
What is osmosis?
Answer:
The movement of water from a region of its high concentration to a region of its low concentration through a semi-permeable membrane is called as osmosis.
Question 9.
Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoop each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water.
Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D.
Answer:
(i) Water gathers in the hollow portion of B and C because the concentration of water is more in the trough than in the hollowed portion of B and C. The plasma membrane of the potato cells acts as a semi-permeable membrane through which the water enters by the process of osmosis.
(ii) Potato A acts as a control for the experiment which helps us to infer the changes which occur during the course of the experiment.
(iii) Water does not gather, in cup A because it is empty, so osmosis does not occur. In cup D, the semi- permeable nature of the cell membrane is lost after boiling, so, the process of osmosis does not occur.