Gujarat Board GSEB Class 11 Commerce Accounts Important Questions Part 2 Chapter 4 Bills of Exchange Important Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 11 Accounts Important Questions Part 2 Chapter 4 Bills of Exchange
Answer the following questions in one sentence :
Question 1.
By which other name Is the bill known?
Answer:
Bill of exchange Is also known as letter of exchange.
Question 2.
What is bill receivable?
Answer:
It is a bill receivable for the person who draws the bill. That means it is a bill receivable for the creditor.
Question 3.
The ownership of a bill sent for collection to a bank Ii that of whom?
Answer:
The ownership of a bill sent for collection to a hank Is that of drawer of a bill.
Question 4.
Who bears the noting charges on dishonour of a bill?
Answer:
An acceptor or drawee bears the noting charges on dishonour of a bill.
![]()
Question 5.
Generally, who Is the drawer of the promissory note?
Answer:
Generally, a debtor is the drawer of the promissory note.
Question 6.
What is currency note, which ¡s issued by the Reserve Bank of India?
Answer:
Currency note. which Is issued by Reserve Bank of India. Is a promissory note.
Question 7.
What is bill payable?
Answer:
It Is a bill payable for the person who accepts the bill. That means It is a bill payable for the debtor.
Question 8.
In which type of transactions, grace days are given/allowed?
Answer:
Grace days are given only in transactions of bill of exchange.
Question 9.
What Is meant by dishonour of a bill?
Answer:
Sometimes the acceptor of the bill Is not in a position to pay the money of the bill or not willing to make the payment of the bill. then It is known as dishonour of a bill.
Question 10.
What is accommodation bill?
Answer:
For the internal accommodation of each other, one trader draw a bill on other traders then It Is known as an accommodation bill.
Question 11.
How many main types of the bills are there? Which are they?
Answer:
There are two main types of the bills
- Bills at sight and
- Bill after- dated.
Question 12.
Who Is the drawer of a bill?
Answer:
The drawer of a bill Is the person who draws or makes the bill.
![]()
Question 13.
Who is the drawee of a bill?
Answer:
The drawee of a bill is the person on whom the bill is drawn.
Question 14.
Who Is a payee of a bill?
Answer:
The payee of a bill Is the person to whom the bill is made payable or iii whose favour the bill is drawn.
Question 15.
What is the relationship between the drawer and the drawee?
Answer:
The relationship between the drawer and the drawee is that of the creditor and the debtor.
Question 16.
What is Due date?
Answer:
After adding three days of grace on the maturity date of a bill, a date which comes Is called Due date.
Question 17.
Which account is credited in the books of the drawer when a discounted bill is dishonoured?
Answer:
Bank A/c is credited In the books of the drawer when discounted bill Is dishonoured.
Question 18.
In which type of trade, noting of dishonour of a bill Is compulsory?
Answer:
In foreign trade, noting of dishonour of a bill is compulsory.
Question 19.
What are noting charges?
Answer:
Noting charges are the fees charged by the Notary Public for noting the facts of dishonour on the face of the bill and In his official register.
Question 20.
Who pays the noting charges?
Answer:
The holder of the bill pays the noting charges.
Question 21.
What do you mean by renewal of a bill?
Answer:
Renewal of a bill means cancellation of original bill and drafting a new bill In exchange of that by drawer at the request of drawee.
Pass / Record the necessary journal entries for bills in the books of Drawer and Acceptor :
Question 1.
Write the following transactions in the journal of Shri Sureshbhai:
1. On 2-12-’17, a bill of ₹ 5,000 accepted by Bharati was discounted with the bank at a discount of ₹ 100.
2. On 15-12-’17, a bill of ₹ 8,000 accepted by Jayanti was dishonoured on maturity date and noting charges amounted to ₹ 100.
3. A bill of ₹ 15,000 accepted by us and drawn by Rajesh, was paid by cheque.
4. We endorsed a bill receivable of ₹ 4,500, accepted by Anita, in favour of Hansaben in full settlement of a debt of ₹ 4,600.
Answer:
Journal of Shri Sureshbhai
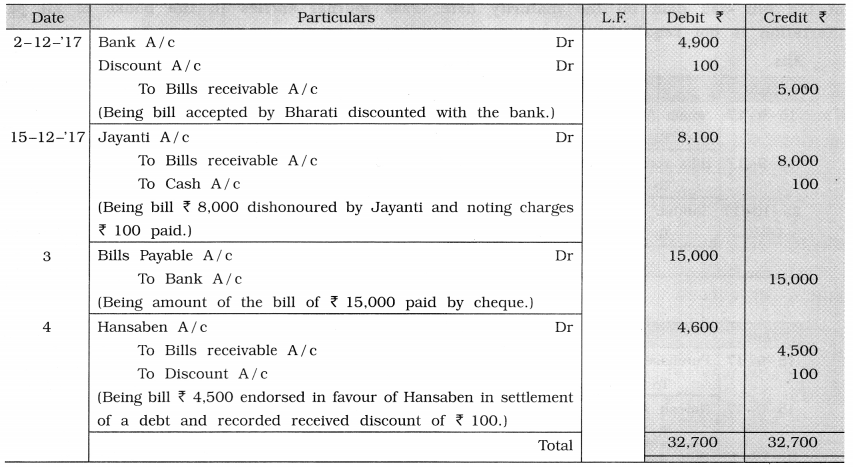
![]()
Question 2.
Paresh sold goods of ₹ 5,000 at 10% trade discount on credit to Rajesh. Paresh drew a bill for the necessary amount for 2 months, which Rajesh accepted and returned. On the same day, Paresh discounted this bill with the bank at a discount of ₹ 100. Rajesh paid the bill on the maturity date. Pass necessary journal entries in the books of both the parties. (Narration is not required.)
Answer:
Journal of Paresh
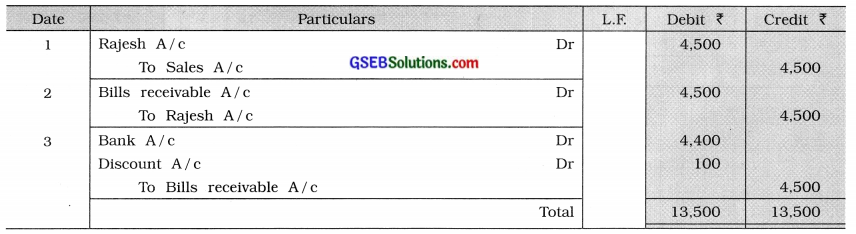
Journal of Rajesh
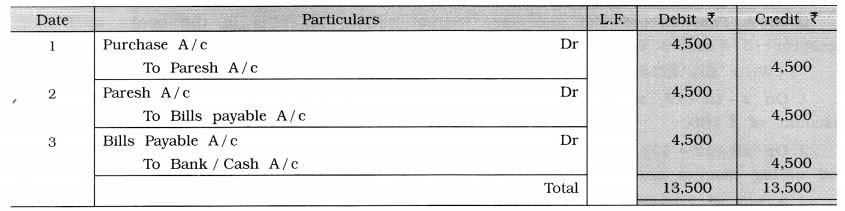
Question 3.
Amish purchased goods of ₹ 75,000 from Naresh at 10% trade discount on 15-9-’17. On the same day, Naresh drew a bill for three months on Amish, which Amish accepted and returned. On 25-10-’17 Naresh endorsed this bill in favour on creditor Shikhar. The amount of the bill was paid on the maturity date. Pass journal entries in the books of all parties. (Narration is not required.)
Answer:
Journal of Naresh
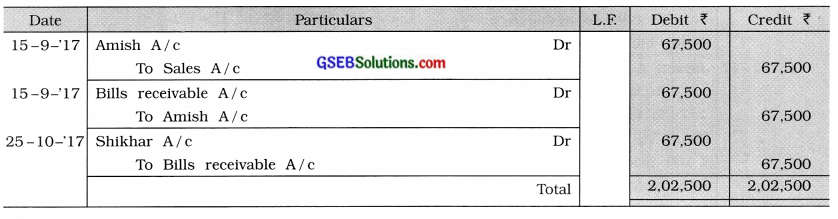
Journal of Amish

Journal of Shikhar

Question 4.
Record the following transactions in the books of Abraham:
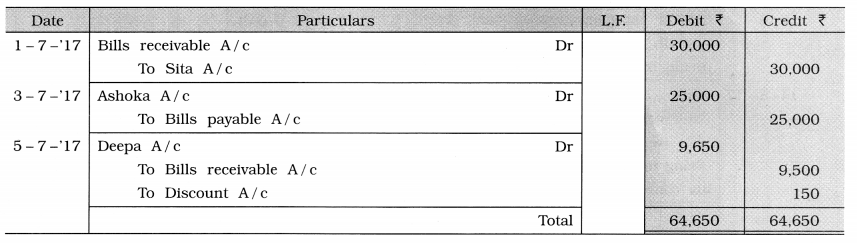
2017
July 1 Drew a bill of ₹ 30,000 on Sita, which she accepted and returned. The period of the bill is of 50 days.
3 Accepted a two months period bill of ₹ 25,000 drawn by Ashoka and returned it. 5 Endorsed a bill receivable of ₹ 9,500 received from Raju to Deepa in full settlement of an account of ₹ 9,650.
(Narration is not required.)
Answer:
Journal of Abraham
![]()
Question 5.
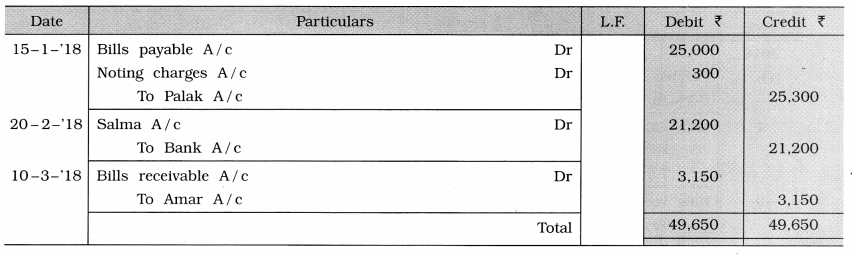
Write the following transactions in the journal of Shri Mukesh:
1. We dishonoured a bill of ₹ 25,000 drawn by Palak on its maturity date (on 15-01-’18). Palak paid noting charges ₹ 300.
2. The bill for ₹ 21,000 accepted by Salma and discounted in bank is returned on the maturity date (20-2-18). Bank has incurred noting charges of ₹ 200.
3. A promissory note of ₹ 3,150, of the period of 60 days, is received on 10-3-’18 from Amar who has written it.
(Narration is not required.)
Answer:
Journal of Mukesh
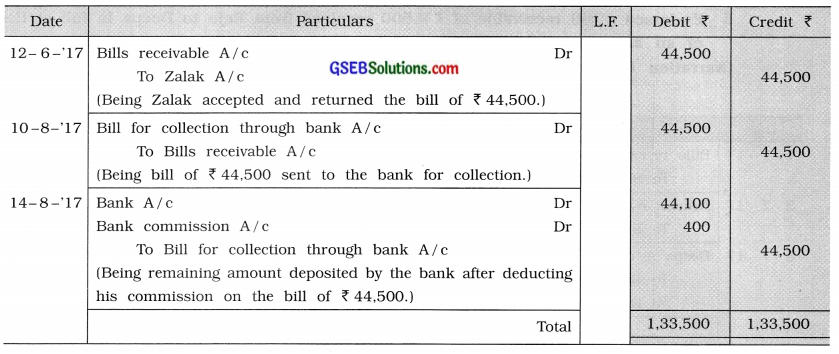
Question 6.
Hasmukh drew a bill of ₹ 44,500 on 12-6-’17 for 2 months on Zalak. Zalak accepted and returned the bill. On 10-08-’17, Hasmukh sent this bill to the bank for collection. The bill was paid by Zalak on the maturity date. The bank debited ₹ 400 to Hasmukh’s account as commission. Pass necessary journal entries in the books of Hasmukh. (Narration is required.) Answer:
Journal of Hasmukh
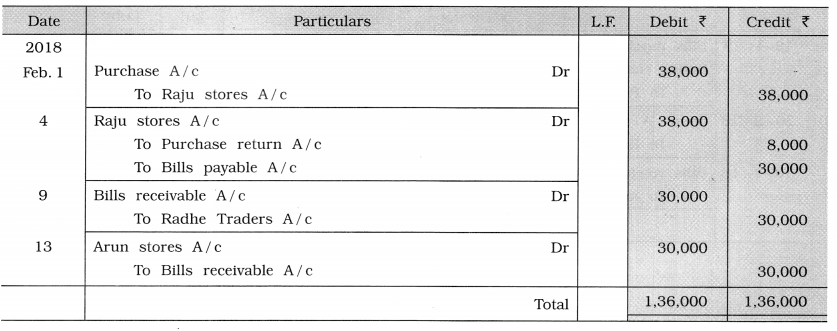
Question 7.
Record the following transactions in the books of Shah Traders:
| 2018 Feb 1 | Purchased goods of ₹ 40,000 at 5 % trade discount from Raju stores. |
| 4 | Returned goods of ₹ 8,000 to Raju stores and sent a Promissory Note for two months period for the remaining amount. |
| 9 | Drew a two months bill of ₹ 30,000 on Radhe Traders which they accepted and returned. |
| 13 | Endorsed the bill accepted by Radhe Traders in favour of Arun stores. (Narration is not required.) |
Answer:
Journal of Shah Traders
Explain the difference between Bill Receivable and Bill Payable.
Answer:
| Points | Bill Receivable | Bill Payable |
| 1. Meaning | After accepting the bill when acceptor of the bill returns the bill to the drawer of the bill then it becomes a bill receivable for drawer of a bill, means for a bill when amount is receivable then the bill is known as bill receivable. | After accepting the bill when acceptor of the bill returns the bill to the drawer of the bill then it becomes a bill payable for acceptor of a bill, means for a bill when amount is payable then the bill is known as bill payable. |
| 2. Amount | For whom the amount is receivable, it is a bill receivable. | For whom the amount is payable, it is a bill payable. |
| 3. Which type of Amount? | It is one kind of receivable amount. | It is one kind of payable amount. |
| 4. Where is it shown? | It is shown on the Assets-Receivables side of a Balance Sheet. | It is shown on the Capital-Liabilities side of a Balance Sheet. |
| 5. Transfer of Bill | Transfer of ownership is possible as bill receivable is an asset. | Generally, transfer of payment of debt is not possible. |
| 6. Creditor or Debtor | Generally, drawer of a bill is a Creditor. | Generally, acceptor of a bill is a debtor. |
Explain the difference between Ordinary (Commercial) bill and Accommodation bill.
Answer:
| Points | Ordinary (Commercial) bill | Accommodation bill |
| 1. Meaning | Ordinary (commercial) bill is written by a creditor on his debtor, then it is known as an ordinary (commercial) bill. | For the internal accommodation of each other, one trader draw a bill on other traders then it is known as an accommodation bill. |
| 2. Consideration | There is consideration in this bill. | Consideration is not apparent in this bill. |
| 3. Relation | There is a relation like creditor and debtor between the parties of this bill. | There is no relation like creditor and debtor between the parties of this bill. Such relation arises after this bill is drawn and duly accepted. |
| 4. Discounted | This bill is not always discounted. | This bill is discounted without fail, (immediately). |
| 5. Purpose | This bill is drawn for the settlement of debts and dues. | This bill is written for the accommodation of each other. |
| 6. Bill dishonoured | If this bill is dishonoured, legal steps can be taken against the acceptor and amount can be collected through the court of law. | If this bill is dishonoured, then amount cannot be collected through the court of law. |
Write the correct option from those given below each question :
Question 1.
What Is legal maturity date of a bill, which Is drawn on 23- 10- ‘17 for three months?
(a) Dt. 23-01-18
(b) Dt. 25-01-18
(c) Dt. 26-01-18
(d) Dt. 27-01-18
Answer:
(b) Dt 25-01-’18
Question 2.
A bill of 10.000 Is drawn on 01 -01 -‘18 for 4 months. which is discounted with the bank at 12% on 04-04—18, then what Is
the net value of a bill?
(a) 9.900
(b) 9,700
(c) 9.600
(d) 8,800
Answer:
₹ 9,900
![]()
3. The ownership of a bill sent for collection to a bank is that of ……………….. .
(a) Drawer
(b) Acceptor
(c) Bank
(d) Government
Answer:
(a) Drawer
Question 4.
How many parties are there in a promissory note?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) One
(d) Four
Answer:
(a) Two
Question 5.
Who has Lo bear the noting charges incurred on a dishonoured bill at last?
(a) Drawer
(b) Acceptor
(c) Payee
(d) Bank
Answer:
(b) Acceptor
Question 6.
Bill of exchange is also called as …………………….. .
(a)Letter of exchange
(b) Request letter
(c) Cashbook
(d) Bankbook
Answer:
(a) Letter of exchange
Question 7.
How is a bill?
(a) Written
(b) Oral
(c) Request type
(d) Conditional
Answer:
(a) Written
Question 8.
How Is the noting of dishonour of a bill?
(a) Voluntary
(b) Compulsory
(c) Advisable
(d) Unavoidable
Answer:
(c) Advisable
Question 9.
How many parties are there In a bill?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Five
Answer:
(b) Three
Question 10.
If a bill falls due on 15th August. payment on It must be made on ……………………. .
(a) 14th August
(b) 16th August
(c) 13th August
(d) 15th August
Answer:
(a) 14th August
![]()
Question 11.
A person to whom a bill of exchange is endorsed is called …………………… .
(a) endorsee
(b) drawer
(c) endorser
(d) payee
Answer:
(a) endorsee
Question 12.
A bill of exchange is required to be ……………………. by drawee.
(a) drafted
(b) discounted
(c) accepted
(d) endorsed
Answer:
(c) accepted
Question 13.
What Is called the person to whoni the amount of the life is made?
(a) Endorsee
(b) Drawer
(c) Drawee
(d) Payee
Answer:
(d) Payee
Question 14.
How many types of Bills are there?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Five
Answer:
(a) Two
Question 15.
How many alternatives are available to the person possessing the bill for the disposal or use of the bill?
(a) Two
(b) Three
(c) Four
(d) Five
Answer:
(c) Four
Question 16.
What type of account is Bill of exchange?
(a) Personal
(b) Nominal
(c) Real
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Real
Question 17.
Fdllity of grace days ¡s availahl only in ………………….. .
(a) Bills
(b) Promissory note
(c) Credit note
(d) Debit note
Answer:
(a) Bills
![]()
Question 18.
In which type of Bill, endorsement of the bill is not possible?
(a) Bill at sight
(b) Bill after dated
(c) Accommodation bill
(d) Bills payable
Answer:
(c) Accommodatíon bill
Question 19.
A one month’s hilt drawn on 31st January. 2018 will mature on ……………………… .
(a) 3rd March. 2018
(b) 28th February. 2018
(cl 27th February. 2018
(d) 2nd March 2018
Answer:
(a) 3rd March 2018
Question 20.
Which type of document is a bill?
(a) Transferable
(b) Non-transferable
(c) Reftindable
(d) Non-refundable
Answer:
(a) Transferable
Question 21.
In foreign trade, noting of dishonour of a bill is ………………….. .
(a) voluntary
(b) compulsory
(c) advisable
(d) cssential
Answer:
(b) compulsory
Question 22.
Renewal of a bill is also known as …………………… .
(a) Change of bill amount
(b) Change of bill date
(c) Change of bill period
(d) Change of bill type
Answer:
(c) Change of bill period