Gujarat Board GSEB Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 10 International Trade Important Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 10 International Trade
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the definition of foreign trade given by Thomas.
Answer:
According to Thomas, ‘Exchange of product of one country with another country is called foreign trade.
Question 2.
State few advantages of foreign trade,
Answer:
- Benefit of labour distribution and specialization,
- Development of less developed countries,
- Maximum utilization of resources,
- Maintain price level, etc.
Question 3.
How less developed countries can develop themselves through international skills trade?
Answer:
Less developed countries lack specialized scientific technology research and other resources. These countries can import technology and processes, modern administrative methods, research knowledge, advanced products, etc. and develop themselves.
Question 4.
How can a country make maximum utilization of resources through foreign trade?
Answer:
A country can import modern technology, machineries and process and improve the efficiency of its resources. Similarly, it can export excess production to earn foreign currency and hence utilize its resources fully.
Question 5.
How trade related services gets benefit by foreign trade?
Answer:
When a trader enters into foreign trade he needs services of insurance, banking, ports, warehouses, etc. and so these industries get benefit.
Question 6.
How does foreign trade help in stabilizing prices?
Answer:
A country producing excess can export to other countries and prevent price of that product from falling below a level in local market. In case if the price of a product/service rises drastically, the country can import it to control its price.
Question 7.
How does foreign trade improves standard of living?
Answer:
By foreign trade international goods enter various countries. As a result, people of that country can enjoy a variety of innovative foreign goods that too at reasonable prices. This improves standard of living.
Question 8.
Give an example through which you can say that foreign trade improves standard of living.
Answer:
Availability of foreign clothing brands in Indian malls, presence of food chains like McDonalds, Domino’s, presence of footwear brands such as Nike, Reebok, etc. shows that by using all these our standard of living has gone up.
Question 9.
How can foreign trade be helpful in natural calamities?
Answer:
During natural calamities like flood, drought, tsunami, etc. a country can get food grains, medicines, etc. from other countries either free of cost or at very nominal prices. This becomes quite helpful for the victim country.
Question 10.
How does foreign trade makes the whole world a market?
Answer:
Industrially developed and wealthy nations use very advanced technologies and scientific methods which results in very large scale production that too with precision and less time. Such countries are always in search of countries where they can sell their excess production. This results in trade with various countries and so whole world becomes a market.
Question 11.
What do you mean by incentives for export trade?
Answer:
An incentive or say benefit that a country provides to an exporter to encourage him export goods or services is called incentive for export trade.
Question 12.
Why are trade agreements signed between nations?
Answer:
Countries sign trade agreements in order to assure that they will trade with each other. This boosts their import and export trade and economy.
Question 13.
State two financial and economic encouragements that government provides to exporters.
Answer:
Give exemption or collect very less sales tax and income tax on exported products. Give partial or full exemption of income-tax for income earned through export.
Question 14.
State two non-financial facilities that an exporter gets as a form of export encouragement?
Answer:
- Government provides information on export opportunities, procedures and benefits,
- Train people for producing goods that can be exported.
Question 15.
What is special economic zone?
Answer:
A special economic zone (SEZ) refers to certain fix area of a country which enjoys special economic regulations and liberal economic laws compared to other parts of the country.
![]()
Question 16.
When was SEZ set-up in India?
Answer:
In 2005, government of India passed law for SEZ in the parliament and brought it in force from 10th February, 2006.
Question 17.
State the types of zones that come under SEZ.
Answer:
Special economic zones contain several types of zones like:
(a) Export processing zone,
(b) Free trade zone (FTZ),
(c) Free ports and
(d) Industrial zone
Question 18.
State the aim of SEZ and benefits one gets under it.
Answer:
SEZ is set-up with the aim of attracting direct local and foreign capital investment. Under SEZ the government provides part or full exemption of custom duty, central excise, service tax, central sales tax, security transaction tax, etc. on products produced in SEZ.
Question 19.
What is an export processing zone?
Answer:
Indian government has established export processing zones or say free processing zones to encourage export trade. In such zones exporttio can import goods, re-process them if needed, manufacture goods and export them without interference of custom authorities. This helps in bringing more foreign earnings to our country.
Question 20.
State locations of SEZ in India.
Answer:
Kandla, Santa Cruz (Mumbai), Falta (West Bengal), Noida, Cochin, Chennai, Vishakhapattannam, Kosindra (near Dwarka) and Dahej (near Bharuch)
Question 21.
When does an importer need to contact trade director?
Answer:
If an importer wants to import items that are not mentioned in the Government list then he needs to apply for the license to comptroller of import trade.
Question 22.
What is quota certificate?
Answer:
If government has set a limit on importing only a fix quantity of particular goods then it is said that the government has decided quota on that product. In such a case, government issues a quota certificate to the importer which states the maximum quantity of the listed product an importer can import.
Question 23.
Why does an importer needs foreign exchange?
Answer:
When goods are imported from a foreign country the payment has to be made in the currency from which he is importing. For this the importer needs to raise necessary foreign currency or say foreign exchange.
Question 24.
How can an importer raise/obtain foreign exchange?
Answer:
The importer has to submit an application in the prescribed form along with import license to a bank that deals with foreign exchange. The bank then forwards the application to RBI. RBI scrutinizes the application and then sanctions the release of foreign exchange. The importer can then obtain the sanctioned foreign exchange from the bank.
Question 25.
Define indent.
Answer:
The order that the importer places for importing the goods is called ‘indent’. He places the indent to the exporter. Indent contains details regarding quantity of goods, price, packaging, insurance, name of transporter, etc
Question 26.
Why does an exporter demands letter credit from importer?
Answer:
Generally, foreign traders are not acquainted to each other and so before the exporter exports the goods he wants to make sure he will receive his payment. Hence, he demands ………
Question 27.
What is letter of credit?
Answer:
A letter of credit is a document from a bank guaranteeing that the seller will receive full payment at specified time if cell the delivery conditions are fulfilled by the seller.
Question 28.
What is documentary bill?
Answer:
Various documents such as bill of lading, invoice, consular invoice, shipping order, insurance policy of goods, etc. sent to the foreign exchange bank of importer by the exporter are together called documentary bill
Question 29.
State the types of documentary bill.
Answer:
There are two types of documentary bills. They are – (i) D/A i.e. Documents against acceptance bill and (ii) D/P Bill i.e. Documents against payment bill.
Question 30.
Define bill of lading.
Answer:
A bill of lading is a legal document between the shipper (i.e. exporter) of the goods and the carrier i.e. the transporter. If contains details like quantity of goods, destination, etc. It is issued by the carrier to the exporter.
Question 31.
How many copies of bill of lading are made? How are they distributed?
Answer:
The shipping company prepares three copies of bill of lading. It keeps one copy and gives the other two to the exporter. The exporter sends the third copy to the importer.
Question 32.
What procedure does an importer need to follow if he is liable to pay partial import duty?
Answer:
If at all the importer has to pay only partial duty i.e. lesser than actual then he needs to fill a form called ‘bill of entry form’. The form contains the details of name of the ship, name of the port of the country from where goods were loaded, name of exporter, name and address of importer and complete details of the goods. Based on this form the excise department decides the amount of duty to be paid by the importer.
Question 33.
What procedure does an importer need to follow if he is to obtain exemption import duty?
Answer:
If the importer is exempted from import duty from he need to present consular invoice and the certificate of origin of goods (from the exporter) and obtain a certificate of exemption of import duty from the excise department.
![]()
Question 34.
With respect to goods, what is a dock?
Answer:
A place where goods are kept once they arrive is called a dock.
Question 35.
What are dock charges? Which charges are included in it?
Answer:
The charges that an importer/exporter need to pay for using the facilities of the dock such as loading/unloading goods in ship, transporting them to a specific place in dock, storing them, equipment used for these activities, etc. are all included in dock charges.
Question 36.
Why does RBI keep regulation on foreign exchange?
Answer:
So that RBI can come to know the foreign money that comes to our country and the foreign currency that goes out of our country.
Question 37.
What is charter party agreement?
Answer:
If the exporter wants to rent whole ship for sending the goods it is called ‘charter’. The agreement between the shipping company and the exporter to rent the whole ship is called Charter party agreement’.
Question 38.
What procedure is to be done by exporter if the products he wish to export are duty-free?
Answer:
If a product comes under duty-free category then the exporter needs to fill a form containing public notification certifying that the goods are duty-free and submit it to the duty . officer. The duty-officer than gives certificate to the exporter for exemption of duty.
Question 39.
Why is it necessary to insure goods in international trades?
Answer:
International trade poses various risks to the good. Moreover the goods are mainly transported through sea which is quite risky. Hence to protect the goods from damage due to humid atmosphere of sea, sinking of sea, attacks of pirates, etc. goods must be insured.
Question 40.
What is carting order?
Answer:
Carting order is the final clearance given by the customs department to either load the goods or to transport the goods after import clearance.
Question 41.
What is a foul receipt or dirty chit?
Answer:
If the captain finds that the goods are not packed properly and hence not suitable for transportation he makes a mark in the mate’s receipt. Such receipt is called ‘foul receipt’ or ‘dirty chit’.
Question 42.
Why was GATT established?
Answer:
GATT was established to regulate world trade so that harmony could be attained among countries and economies of countries affected in Second World War could be improved.
Question 43.
What were the main objectives of GATT?
Answer:
The main aim of GATT agreement was to remove barriers from international trade by reducing tariffs, boost international trade and encourage distribution of regional labour.
Question 44.
What is demurrage?
Answer:
When importers/exporters do not remove their goods from the ship within the specified time limit it means they have breached the time clause and so they need to pay penalty to the shipping company.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How does the need of international trade arise?
Answer:
- Man depends on natural resources for his survival and development. All natural resources are not concentrated in one part of the world but are distributed unequally among different countries. Hence, man has to depend on other countries for availing natural resources of other countries.
- No country in this world is self-sufficient. It has to depend on other countries to fulfill its needs. No country can produce all the resources in enough quantity to fully satisfy the needs of its entire population. In such situation it procures those resources from countries that produce such resources in excess quantities through international trade. For example, Africa is one of the largest producers of gold in the world. Many countries obtain gold from Africa.
- Moreover, due to several reasons like cheap labour advanced technology, etc. a country may produce a resource in quite less quantity. In such cases the country can sell its resources to other country through international trade. For example, China is one of the biggest manufacturing hubs of the world due to cheap labour, efficient production processes, etc.
- Yet in another example, if a developed country possesses industries and scientific technology to produce things but does not have raw material, it can import if from countries producing necessary raw material.
- These and several other reasons give rise to international trade. It is impossible to imagine the world without international trade.
Question 2.
What do you mean by incentive for export trade? List the various incentives.
Answer:
Incentive for export trade:
- An incentive or say benefit that a country or say its government provides to an exporter to encourage him export goods or services is called incentive for export trade.
- A country cannot do without importing items necessary for its economic development and security. When a country imports it has to pay in the currency of seller country. Thus, the buyer (importing) country loses its foreign currency.
- To balance the lost foreign currency and to stabilize its economy the country then needs to export its products/services and earn foreign currency. To do so it needs to provide certain motivations or say incentives to exporters to export their products. All such incentives are called incentives for export.
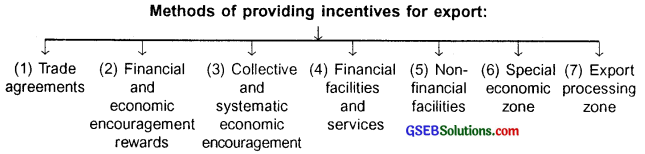
Question 3.
Define foreign trade and explain its meaning.
Answer:
International (foreign) trade:
- When individuals, business units or government of a country trades i.e. either buys or sells with individuals, business units or government of another country it is called international or foreign trade.
- The one who buys from foreign country is called the importer of goods/services whereas the one who sells is called the exporter.
- According to Thomas, ‘Exchange of product of one country with another country is called foreign trade.
Question 4.
How does a country obtains benefit of distribution of labour and specialization through foreign trade?
Answer:
Benefit of division of labour and specialization:
- A country may not be producing all the needed resources that too in sufficient quantity.
- It may also not have enough labour or specialized skills to produce such resources.
- Under such situations a country can easily obtain those resources from another country. For example, India has a very large population that specializes in farming that too at very low labour rates, whereas this is not the case with America. So, America can import agricultural products from India.
- A country may also not have suitable weather, government policies, skilled people, etc. for production of a specific resource and so it can obtain it through foreign trade.
Question 5.
How foreign trade is beneficial to less developed countries?
Answer:
Development of under developed countries:
- Under developed countries lack specialized skills, scientific technology research and other resources.
- These countries can import technology and processes, modern administrative methods, research knowledge, advanced products, etc. and develop itself.
- Government of under developed countries can enter into various trade agreement with other countries and uplift their own countries.
![]()
Question 6.
Exports lead to maximum utilization of resources. Give reason.
Answer:
Maximum utilization of resources:
- A country imports technology, machinery, human labour, business processes, etc.
- It then deploys these resources and makes best possible use of resources available in the country. For example, importing a highly advanced printing machine may reduce the printing time by half. The printer can then make use of remaining time in other printing jobs.
- Thus, people living in various countries can enter into foreign trade and improve their production efficiencies and processes and make maximum utilization of their resources. Moreover, excess production resulting out of improved efficiency can be exported.
Question 7.
How can international trade help in maintaining prices?
Answer:
Maintains price stability:
- A country producing excess can export to other countries and prevent price of that product from falling below a level in local market.
- In case if the price of a product/service rises drastically, the country can import it to control its price.
Question 8.
How can foreign trade help in improving standard of living?
Answer:
Improves standard of living:
- international trade results in competition among countries. Each country tries to produce high quality and technologically advanced products that too at lowest possible price.
- By doing so it can compete international producers and increase its exports and earn revenues. On the other hand such approach improves the standard of living of people because they get better and better products at lower prices.
Question 9.
How export help in turning the entire world into market?
Answer:
World as a market:
- Industrially developed and wealthy nations use very advanced technologies and scientific methods which results in very large scale production that too with precision and less time.
- Such countries are always in search of countries where they can sell their excess production. This gives rise to international trade.
- As a result many countries fall in the network of international trade and so world itself becomes a market.
Question 10.
Which type of financial and economic encouragement does government gives to exporters?
Answer:
Financial and economic encouragement reward:
Exporters are provided several financial and economic benefits to encourage them for producing and/or exporting. These encouragements include:
- Give some pre-decided reward directly to the exporter.
- Give exemption or collect very less sales tax and income tax on exported products.
- Give partial or full exemption of income-tax for income earned through export. Provide land, raw material, electricity, equipment, etc. at cheaper rates for producing goods/services for export.
Question 11.
Government provides several non-financial facilities to exporters. Explain.
Answer:
Non-financial facilities:
Exporters are also provided several non-financial facilities and services for motivation. They are:
- Provide information on export opportunities, procedures and benefits.
- Train people for producing products that can be worth exporting.
- Arranging competitions among exporters and rewarding highest exporter.
- Provide information about export market i.e. international market.
- To lock-out or create strike in factories that produce export items illegally
Question 12.
Write a short note on SEZ.
Answer:
Special economic zone (SEZ):
- A special economic zone (SEZ) refers to certain fix area of a country which enjoys special economic regulations and liberal economic laws compared to other parts of the country.
- In 2005, government of India passed law for SEZ in the parliament and brought it in force from 10th February, 2006.
- Special economic zones contain several types of zones like:
(a) Export processing zone
(b) Free trade zone (FTZ)
(c) Free ports
(d) Industrial zone - SEZ is set-up with the aim of attracting direct local and foreign capital investment.
- Under SEZ the government provides part or full exemption of custom duty, central excise, service tax, central sales tax, security transaction tax, etc. on products produced in SEZ.
Question 13.
Write a short note on export processing zone.
Answer:
Export processing zone:
Indian government has established export processing zones or say free processing zones to encourage export trade. In such zones exporters can import goods, re¬process them if needed, manufacture goods and export them without interference of custom authorities. This helps in bringing more foreign earnings to our country.
- Excise duties, financial transaction regulations and some labour laws are liberal in these zones.
- Government assures people that it will provide all basic facilities such as roads, electricity, water, communication, transportation, facility to procure high quality raw material, etc. to industries set-up in such zones.
- Government also provides information on export procedures, international market, demand of products for export, political conditions favorable export, etc. to people interested in export business.
- Under its economic policy India has developed various free trade zones (FTZ) in places like Kandla, Santa Cruz (Mumbai), Falta (West Bengal), Noida, (Cochin, Chennai, Vishakhapattannam, Kosindra, (Near Dwarka) and Dahej (near Bharuch), etc.
Question 14.
Explain procedure to obtain import license.
Answer:
Obtaining import license:
Open General License (OGL):
If an importer wants to import those items/services which are listed in government list, he needs to obtain Open General License (OGL) which is quite easy.
License from trade director:
- If an importer wants to import items that are not mentioned in the government list then he needs to apply for the license to comptroller of import trade.
- The importer needs to provide various details in the application like his name, address, complete detail of goods to be imported, financial records of the importer, name of the exporter and exporting country, etc.
- If and only if the assessing officers are thoroughly satisfied with all the details, they will provide the import license to the importer.
- If the government has set some quota for importing only a specific quantity of goods than the importer is given a quota certificate. As per the quota certificate, the importer can import only upto the maximum quantity mentioned in the certificate.
Question 15.
How can an importer obtain foreign exchange?
Answer:
Obtaining foreign exchange:
- When goods are imported from a foreign country the payment has to be made in the currency from which he is importing. For this the importer needs to raise necessary foreign currency or say foreign exchange.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) controls the foreign exchange in India.
- The importer has to submit an application in the prescribed form along with import license to any bank that deals with foreign exchange. The bank than forwards the application to RBI. RBI scrutinizes the application and then sanctions the release of foreign exchange.
- The importer can then obtain the sanctioned foreign exchange from the bank. The applicant needs to mention the amount he needs in American Dollar as per the prevailing currency rate.
Question 16.
What do you mean by placing an indent? Explaining.
Answer:
Placing the indent or order:
- The order that the importer places for importing the goods is called ‘indent’. He places the indent to the exporter.
- The importer first collects information of different manufacturers and exporters of the exporting country. He collects information regarding the details of goods, price and other conditions and then gives the indent to the exporter he selects.
- Indent contains details regarding quantity of goods, price, packaging, insurance, name of transporter, etc.
![]()
Question 17.
Explain the procedure of paying import duty.
Answer:
Paying import duty or say excise:
- Goods are not allowed to bring out of port unless duty is paid on them.
- If the importer is exempted from import duty he can collect the goods without paying it.
- If the importer is exempted from import duty he need to present consular invoice and the certificate of origin of goods (from the exporter) and obtain a certificate of exemption of import duty from the excise department.
- If the importer is liable to pay full import duty then he needs to pay it to possess the goods.
If at all the importer has to pay only partial duty i.e. lesser than actual then he needs to fill a form called ‘bill of entry form’. The form contains the details of name of the ship, name of the port of the country from where goods were loaded, name of exporter, name and address of importer and complete details of the goods. - Based on this form the excise department decides the amount of duty to be paid by the importer. Once the importer pays the duty, the excise officer endorses the ‘bill of entry’ and hands it to the importer.
Question 18.
Explain the process of paying dock charges and releasing goods.
Answer:
Payment of dock charges:
- A place where the goods are kept once they arrive is called a dock. Since goods of importer are unloaded from the ship and handled and stored by dock employees the importer needs to pay dock charge for theses dock services he received. Dock charges also include charges on equipment and facilities that were used for the goods in the dock.
- Dock charge is to be paid irrespective of the mode of arrival of goods i.e. airway, waterway, roadway or railway.
- After paying the dock charges the importer gets a dock receipt.
Obtain possession of goods:
- After completing all the formalities the importer can then obtain possession of the goods.
- The importer needs to take the goods from the bonded warehouse where they are stored by the customs department within the specified time. If the importer does not collect the goods on time, he will have to pay demurrage along with the additional rent.
Question 19.
Write following short notes from exporter/s point of view.
Answer:
1. Obtaining export license
- The exporter then needs to obtain an export license so that he can export the goods. The exporter needs to obtain license which comes under Imports and Exports Control Act.
- An exporter can easily obtain a general license for those goods/services whose list is published by the government of India.
- Items not mentioned in the list can also be freely exported but one needs to apply for a specific license to the trade department of government.
- Along with the license form the exporter needs to provide clear identity of the exporter, detail of exporter, assurance of regular payment of income tax and other tax.
2. Foreign exchange activity of an exporter.
- Importer’s make payment to exporters in exporter’s currency or in American dollars. However, the exporter does not get the money directly.
- Although many controls related to foreign exchange have been liberalized after economic corrections of 1991, still the export needs to follow some. To keep a watch on export income, it is compulsory for the exporter to apply to RBI and ask it to convert the foreign exchange it received in his local currency.
- The exporters provide complete details about how much foreign exchange he will obtain from importer.
- The exporter needs to submit a copy of this application to the bank or institution through which he will perform this financial transaction.
3. Obtaining shipping order.
- When an exporter instructs a shipping company to deliver goods to the importer the shipping company provides a copy called shipping order’ to the exporter. To obtain a shipping order the exporter writes an application to the shipping company asking it to deliver the goods at a certain date. The application contains all the details of goods such as quantity, weight, sending date, cost, etc. based on the application the shipping company prepares a shipping order and gives it to the exporter.
- If the exporter wants to rent whole ship for sending the goods it is called ‘charter’. The agreement between the shipping company and the exporter to rent the whole ship is called ‘Charter party agreement’.
4. Procedure for paying excise duty.
- Excise duty is levied on products manufactured in India.
- The exporter prepares a shipping bill that contains details such as name and address of importer, price of goods, quantity, weight, name of the port where goods will be boarded, name of ship and the shipping company, etc.
- Based on these details and inspection of goods if necessary the excise officer calculates the amount of duty.
- Once the exporter pays the excise duty he gets permission to bring the goods on the port.
- If a product comes under duty-free category then the exporter needs to fill a form containing public notification certifying that the goods are duty-free and submit it to the excise officer. The excise-officer than gives certificate to the exporter for exemption of duty.
5. Packing and marking goods for export.
- The exporter needs to properly pack and mark the goods before shipping.
- The goods in long distance transit should be properly packed to prevent their damage in moist air of the sea. An exporter also needs to follow any specific packing instruction mentioned by the importer.
- Based on the size, weight and other factors the shipping company decides its shipping charge.
- The exporter also marks important details like name and address of importer and exporter, name of destination port, weight of goods, etc. on the goods.
6. Obtaining carting order.
- Carting order is the final clearance given by the customs department to either load the goods or to transport the goods after import clearance.
- To obtain carting order the exporter needs to make an application to the port authority informing them the location from where the goods are to be exported. The exporter in this application mentions all the details of the shipping bill and also details of payment of excise.
- The exporter then pays port related expenses such as bringing the goods at the port, boarding them on the ship, etc. and obtains carting order.
7. Mate-receipt.
Mate receipt:
- The chief officer of the ship or representative of the captain of the ship is called ‘mate’. Mate checks whether the goods loaded on the ship are as per the shipping bill or not. If details and packing of goods are proper the captain or his representative issues ‘mate-receipt’ certifying that they accept the goods.
- If the captain finds that the goods are not packed properly and hence not suitable for transportation he makes a mark in the mate’s receipt. Such receipt is called ‘foul receipt’ or ‘dirty chit’. The exporter then settles the matter and obtains a ‘clean chit’ to export the goods.
8. Obtaining bill of Lading.
Obtaining bill of lading:
- A bill of lading is a legal document between the shipper (i.e. exporter) of the goods and the carrier i.e. the transporter. If contains details like quantity of goods, destination, etc. It is issued by the carrier to the exporter.
- The exporter when produces mate receipt to the shipping company, the company provides him the insurance of the goods during transport through the document called ‘Bill of Lading’.
- The bill of lading contains details like name of exporter, name of ship, fare, details of goods, price, weight, name of exporting port, terms and condition of export, etc.
- The shipping company makes three copies of bill of lading. It keeps one copy and gives the other two to the exporter. The exporter sends one copy to the importer to enable him obtain the goods.
9. Obtaining certificate of origin.
- A certificate obtained by exporter certifying that the products to be exported are wholly procured or produced or manufactured in India is called the certificate of origin.
- Various countries have made agreements to provide concession on import excise. An exporter must have certificate of origin in order to get concession under this agreement.
- The exporter can obtain this certificate from Trade’ Association, Chamber of Commerce or Government.
10. Consular invoice.
- When goods reach to the importer, he needs to pay excise on the goods.
- To simplify the payment of excise some countries demand consular invoice.
- Consular invoice is a document certifying shipment of goods and shows details of exporter, importer, quantity of goods and their price, etc. calculating and collecting excise becomes easy on the basis of this invoice.
- The exporter can obtain consular invoice from the consular of importing country located in exporting country.
Question 20.
Why does an exporter demand a letter of credit from importer?
Answer:
Obtaining letter of credit:
- To make sure that the importer is financially capable to make payment, the exporter demands a letter of credit from the importer before exporting the goods. The importer gets this from his bank.
- Sometimes, if the bank of exporter has its branch in importer’s country then the exporter’s bank may ask that branch to provide the letter of credit of the importer.
Question 21.
Why and how does an exporter insures his goods?
Answer:
Taking insurance of goods:
- To protect goods against the possible risks in the sea like cyclone, damage due to weather getting robbed by pirates, sinking of ship, etc. the goods must be insured.
- The exporter approaches an insurance company, pays the said premium and obtains a cover-note from the company. Based on the cover-note the insurance company then issues insurance policy to the exporter.
Question 22.
How does an exporter obtain his money?
Answer:
Collection of money
- The exporter advises his bank to collect money from the importer. The exporter then writes Bill of Exchange for the amount mentioned in the export invoice.
- This bill of exchange may be of the type
- Document against acceptance i.e. D/A bills or
- Document against payment i.e. D/P bills.
- If the Bill of Exchange is a D/A bill, then the documents of title of goods are released to the drawee i.e. importer only when he accepts the D/A bill.
- If it is a D/P bill, the documents of title of goods are given to the drawee i.e. importer only when he makes full payment.
- The bank collects money on behalf of exporter as per the maturity date of the D/A bill. In case of D/P bill the bank sends the amount to the exporter.
Question 23.
Why did the world feel of establishing a trade organization to control world trade after Second World War?
Answer:
After the Second World War, the political and economical system of the world was highly disturbed. Countries involved in the war became quite weak financially.
- Under such situations it became necessary to establish an organization that would regulate the world trade so as to create harmony in the world and help in economic recovery.
- Owing to these reasons General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was implemented in 1548. GATT provided rules for conducting world trade.
![]()
Question 24.
The benefits of international trade lures a country so much that it cannot resist jumping into it. Give reason.
Answer:
No country is self-sufficient. It needs a very large number of resources, goods and services that too in huge quantity to keep the economy running smoothly. This cannot be possible if the country just deals with internal trade.
- International trade contributes heavily in making optimum use of resources, obtaining resources from other countries, and selling excess produce of country.
- A country can also stabilize its prices, improve its standard of living and above all get a lot of help from other countries in times of natural calamities.
- Owing to these reasons it is impossible for a country not to get lured by foreign trade.
Question 25.
Special Economic Zones boost the morale of traders and hence the economy. Give reason.
Answer:
- Although international trade is highly profitable it comes with several risks and hassles. This demotivates traders and they fear entering foreign trade.
- Creation of special economic zone or SEZ is one very effective way to encourage businessman for international trade.
- Linder SEZ government provides several benefits to people. Cheap land, cheap raw material and electricity, partial or full exemption of excise duty, income tax, sales tax, etc. are all advantages a businessman gets in SEZ.
- Moreover, government also assures all facilities like road, water, communication, etc. to people who conduct foreign trade through SEZ.
- Owing to so many benefits under SEZ, the morale of businessman increases and he dares to trade internationally.
Question 26.
International trade is not as easy as internal trade. Give reason. OR An importer/exporter needs to undergo several processes before he can start trading internationally. Give reason.
Answer:
International trade requires various administrative formalities to be fulfilled.
- One may be trading without a license but in case of international trade one needs to obtain a separate import/export license.
- One needs to find out an overseas trader with whom without physical meet, trade can be conducted.
- One also needs to obtain various documents like letter of credit, bill of lading, shipping orders, consular invoice, etc. while trading internationally.
- One needs to deal with excise and customs department, dock or port trust office, foreign exchange, etc.
- Compared to these, internal trade requires very less activities. So, one can surely say internal trade requires a lot of processes.
Question 27.
GATT and WTO have played a vital role in world economy. Give reason.
Answer:
- Both GATT and WTO aimed at increasing trade, encouraging businessman and government and bring them on common platform of foreign trade.
- They aimed at removing barriers to foreign trade and encourage free-trade and globalization.
- Under these objectives several countries including India signed numerous trade agreements with each other and traded enormously.
- All the‘sectors namely primary, manufacturing and service sectors made unprecedented progress due to these trade agreements.
- As a result, GATT and WTO both have played a vital role in world economy.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Who gave definition of international trade?
(A) Gates
(B) Thomas
(C) Anderson
(D) Lehman
Answer:
(B) Thomas
Question 2.
Benefit of distribution of labour and specialization is achieved due to ________
(A) Unequal distribution of natural resources
(B) Less development of nations
(C) Economic and political policies
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(A) Unequal distribution of natural resources
Question 3.
Unreasonable price rise of a commodity in a country can be managed by ________
(A) Export
(B) Both
(C) Import
(D) None
Answer:
(C) Import
Question 4.
Which of the following is not a feature of international trade?
(A) Maximum utilization of resources
(B) High standard of living
(C) Divisions of labour and specialization
(D) Lesser taxes and duties
Answer:
(D) Lesser taxes and duties
Question 5.
Who makes international trade agreements?
(A) Politicians
(B) Businessman
(C) Industrialists
(D) Custom and excise departments
Answer:
(A) Politicians
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a direct financial or economic encouragement to exporter?
(A) Partial or full exemption of excise
(B) Provide raw materials at lower rates
(C) Land at cheaper prices
(D) Establishment of economic zones
Answer:
(D) Establishment of economic zones
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a non-financial facility for exporter?
(A) Assisting exporter for same day clearance of his export-bill
(B) Arrange seminars for awareness of global market
(C) Declaring lock-out of factory producing export products illegally
(D) None of these
Answer:
(A) Assisting exporter for same day clearance of his export-bill
Question 8.
A special economic zone is where ________
(A) No economic laws of the nation are to be followed
(B) All export duties are waived off
(C) Special concessions and laws are provided
(D) Government aims to attract local investment
Answer:
(C) Special concessions and laws are provided
Question 9.
When was law for SEZ implemented?
(A) 2 January 2005
(B) 10 February 2006
(C) 1 January 1995
(D) 3 March 2004
Answer:
(B) 10 February 2006
Question 10.
The main aim of SEZ is to ________
(A) Attract local and foreign investment
(B) To give excise relief
(C) To bring exporters on a common platform
(D) To protect exporters against undue changes in foreign exchange rates.
Answer:
(A) Attract local and foreign investment
Question 11.
In which of the following places, SEZ is not present?
(A) Dahej
(B) Falta
(C) Cochin
(D) Banswada
Answer:
(D) Banswada
Question 12.
An importer or exporter needs OGL in case ________
(A) The items to be import/exported are not mentioned in government list.
(B) Items to be imported/exported are mentioned in government list.
(C) Import/exporter is dealing in duty free goods.
(D) Importer/exporter is not operation from SEZ.
Answer:
(B) Items to be imported/exported are mentioned in government list.
Question 13.
For importing items not published in government list one needs to apply for license to ________
(A) Customs officer
(B) Port authority
(C) Excise department
(D) Comptroller of import trade
Answer:
(D) Comptroller of import trade
Question 14.
The importer is issued a ________ in case government has set a limit on import.
(A) Quota certificate
(B) Fix quantity certificate
(C) Limited license
(D) Restricted license
Answer:
(A) Quota certificate
Question 15.
One needs to mention amount equivalence in ________ and submit it to RBI for obtaining foreign exchange.
(A) Local currency
(B) British pounds
(C) American dollars
(D) Both B and C
Answer:
(C) American dollars
Question 16.
The order for import is also called ________
(A) Consul
(B) Indent
(C) L/C
(D) Bill of lading
Answer:
(B) Indent
Question 17.
The exporter demands ________ from importer to assure his financial capability.
(A) Bill of lading
(B) Consular invoice
(C) Letter of credit
(D) Quota certificate
Answer:
(C) Letter of credit
Question 18.
DIP stands for ________
(A) Dock charges to pay
(B) Documents against payment
(C) Duty at rate of payment
(D) Delivery against payment
Answer:
(B) Documents against payment
Question 19.
How many copies of bill of lading are made?
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 1
Answer:
(C) 3
Question 20.
To obtain exemption of import duty one needs to present ________ to the excise department.
(A) Bill of lading
(B) Quota certificate
(C) Bill of entry
(D) Consular invoice
Answer:
(D) Consular invoice
Question 21.
If an importer is liable to pay lesser duty he needs to prepare ________
(A) Bill of entry
(B) Bill of lading
(C) Consular invoice
(D) Duty-free form
Answer:
(A) Bill of entry
Question 22.
An amount paid by importer for using the service of unloading the goods at a place and maintaining them for sometime is called ________
(A) Bill of lading
(B) Consular charge
(C) Port fees
(D) Dock charge
Answer:
(D) Dock charge
Question 23.
If an importer keeps his goods for extra time than mentioned he need to pay ________
(A) Rent
(B) Demurrage
(C) Import hold fee
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Question 24.
Office of professionals who specialize in exporting goods of merchants is called______
(A) Exporter’s dock
(B) Export specialist
(C) Export house
(D) Export consultancy
Answer:
(C) Export house
Question 25.
In which year did India underwent major economic reforms?
(A) 1991
(B) 1995
(C) 2001
(D) 2005
Answer:
(A) 1991
![]()
Question 26.
Shipping order means ________
(A) Instruction given to the shipping company
(B) Receipt of shipping given to exporter
(C) Receipt of shipping given to importer
(D) Instruction of shipping given to the importer
Answer:
(A) Instruction given to the shipping company
Question 27.
An exporter is permitted to bring the goods to the port only after ________
(A) He presents consular invoice
(B) Pays import duty
(C) Generates bill of lading
(D) He prepares shipping order
Answer:
(B) Pays import duty
Question 28.
An exporter gets a cover-note on ________
(A) Generating shipping order
(B) Showing consular invoice
(C) Paying insurance premium
(D) Exchanging mate receipt
Answer:
(C) Paying insurance premium
Question 29.
An order to board the goods on the ship is called ________
(A) Carting order
(B) Charter order
(C) Shipping order
(D) Dock off-loading order
Answer:
(A) Carting order
Question 30.
Mate receipt refers to ________
(A) Loading the goods on the ship
(B) Certification of approval of goods by the captain
(C) Exemption from payment of import duty
(D) Confirmation of bill of lading
Answer:
(B) Certification of approval of goods by the captain
Question 31.
A foul receipt or a dirty receipt means ________
(A) Goods are loaded without paying duty
(B) A breach of shipping agreement by shipping company
(C) Goods for shipping are packed improperly
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(C) Goods for shipping are packed improperly
Question 32.
From where can one obtain certificate of origin?
(A) Chamber of commerce
(B) Government
(C) Merchant association
(D) Any of these
Answer:
(D) Any of these
Question 33.
Consular invoice ________
(A) Simplifies excise payment
(B) Increases import duty
(C) Is mandatory for shipping
(D) Is a necessary document for obtaining mate receipt
Answer:
(A) Simplifies excise payment
Question 34.
GATT was established in ________
(A) 1955
(B) 1948
(C) 1995
(D) 1986
Answer:
(B) 1948
Question 35.
An agreement was made among nations in Geneva for establishing GATT.
(A) 17
(B) 23
(C) 58
(D) 104
Answer:
(B) 23
Question 36.
How many nations signed an agreement to support establishment of WTO?
(A) 17
(B) 23
(C) 58
(D) 104
Answer:
(D) 104
Question 37.
When did WTO start its work?
(A) 2nd December 1948
(B) 10th February 1961
(C) 1st January 1995
(D) 8,h September 1986
Answer:
(C) 1st January 1995