This GSEB Class 12 Commerce Accounts Notes Part 2 Chapter 1 Accounting for Share Capital covers all the important topics and concepts as mentioned in the chapter.
Accounting for Share Capital Class 12 GSEB Notes
Due to the industrial revolution, there is radical changes in Business Trade. Because of limitations to proprietorship concern, concept of partnership firm take place. Company form came into existence due to limitations of partnership firm in carrying out business on a large scale. When huge amount is required to be invested in business and intentions of founders of business are satisfied, then for that purpose company form is more useful. A company has separate entity by the Company Act. The establishment, management and dissolution is done only by law. In the modern era, the company needs large-scale capital. How the company makes capital through shares? In this chapter we will study it as well as related matters and the accounting effects of that respect.
Share and Share Capital:
Capital which can be divided into transferable small denominations and all these divisible units are known as share. Through initial public offer when capital amount is collected, it is known as share capital.
Types of Share:
According to the provision of company act, a company may issue two types of shares :
- Equity (ordinary) share and
- Preference share.
Methods for Issue of Shares:
The company can issue its own share in three ways.
- Issue of shares at Face value or At par.
- Issue of shares at Premium and
- Issue of shares at Discount.
![]()
Share capital Transactions and Its Accounting Effects:
Accounting entry is done in the company’s book for the transaction related to share capital are as under :
| Transaction | Entries |
| 1. Share application money is received | Bank A/c Dr. To Share Application A/c (Being receipt of share application money as per share ₹ ……….. The share application money received) Received amount = Received Applications × Called up amount per share with application |
| 2. When the shares are alloted | Share Application A/c Dr. To Share capital A/c (Alloted share × Call money per share) To Bank A/c (Non-alloted share x Called up amount per share) (Being on the basis of allotment of shares, share application amount transferred to share capital and non-alloted share application money is refunded) |
| 3. When the amount is called up at the time of allotment | Share allotment A/c Dr. To Share capital A/c (Being amount due on allotment on ………… shares at the rate of ₹……. per share) Called up amount = Alloted shares x Amount called per share at the time of share allotment |
| 4. When the amount due on allotement is received | Bank A/c Dr. To Share allotement A/c (Being amount received on allotment on ……………. shares at the rate of ₹ per share) Received Amount = Total amount called up at the time of share allotment – Not received amount of share allotment from shareholders |
| 5. When share instalment amount called up | Share first & final call A/c Dr. To Share capital A/c (Being First/Final call due on……….. shares at the rate of ₹…….. per share) Called up amount = Alloted shares x Amount called up per share the time of shares first/final call. |
| 6. When amount received on call | Bank A/c Dr. To Share first & final call A/c (Being First/Final call due on ……….. share at the rate of ₹……. per share) Amount received = Total amount call up at the time of first & final call – Not received amount on share first & final call from the share holders. |
| 7. When Shares Forfeited : | Share capital A/c Dr. (No. of forfeited shares x Called up amt. per share up to the date of forfeiture) To Share forfeited A/cl To Share Allotment Amount not received To Share first & of forfeited shares final call A/c (Being shares are forfeited for non-payment of allotment/first & final call money) |
| 8. When forfeited share are reissued | Bank A/c Dr. (No. of reissue shares x Amount per share of reissue ) Share forfeiture A/c Dr. (No. of reissue shares x Amount of discount on per share) To Share capital A/c (No. of share reissue x Amount of call money of shares) (Being out of forfeited shares reissued at ₹…………. per share) |
| 9. When share issued at a premium :(A) When amount of Premium called up with the application of share : | (i) Bank A/c Dr. To Share Application A/c (Amount including premium) (Being receipt of share application money on share at ₹……. per share ) |
| (ii) Share Application A/c Dr. To Share capital A/c To Securities premium A/c (Being transfer of shares application money in respect of……… equity shares alloted to share capital account and…….. ₹ to securities premium A/c) |
|
| (B) When amount of premium called up with the allotment of share : | (i) Share allotment A/c Dr. To Share capital A/c To Securities premium A/c (Being allotment money of ₹………. per share on share capital and ?……. per share on premium is due on………. equity share alloted) |
| (ii) Bank A/c Dr To Share allotment A/c (Being receipt of amount of equity share allotment money on …………. shares at ₹………. per share) |
|
| (C) When the amount of premium is called with share call money | (i) Share cedi A/c Dr. To Share capital A/c To Securities Premium A/c (Being call of ?…… (including premium of ₹……… per share due on………… shares) |
| (ii) Bank A/c Dr To Share call A/c (Being receipt of share call amount on ………………. shares) |
|
| (D) When share issued with Premium are forfeited | Share capital A/ c Dr. (No. of forfeited share x per share called up money) Securities premium A/c Dr. (No. of forfeited shares x per share called up but not received premium amount) To Share forfeiture A/c (Amount received on forfeited share except premium) To Share allotment A/c To Share first/final call A/c (Not received amount on forfeited shares) • If the premium amount has been received on the forfeited shares then donot make any note of it, but if there is a nominal premium on such a share then the securities premium account will be debited at the time of forfeiture) |
| 10. If all the forfeited shares are reissued & the balance of share forfeiture account is transferred to capital reserve account. | Share forfeited A/c Dr. To Capital reserve A/c (Being balance of the share forfeited account will be transferred to capital reserve account) |
Issue of Shares for Consideration Other Than Cash:
The circumsances and the accounting entries related to issue of shares for consideration other than cash are as follows :
1. When company issued share against purchase of any assets or business :
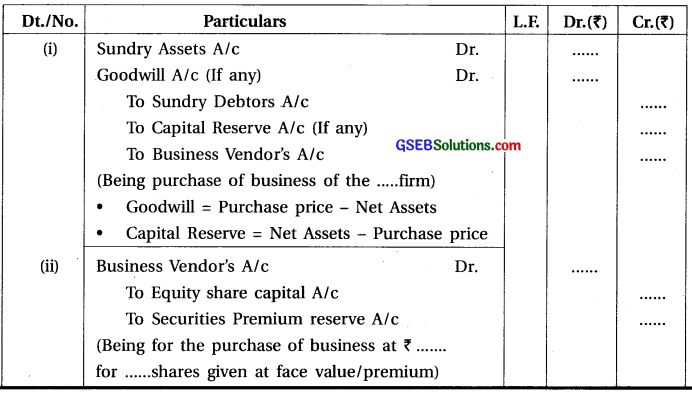
2. When company may issue shares as remuneration to promoter or others who render their service :
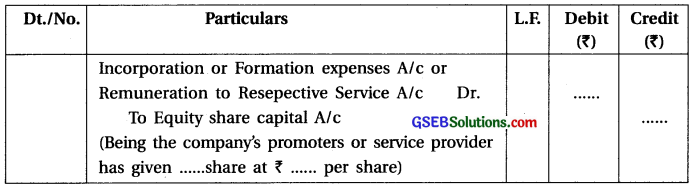
3. When the underwriters are given shares in exchange for commission :
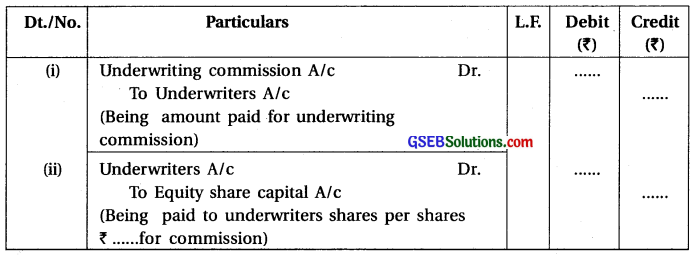
4. When bonus share are given to company’s existing shareholders :
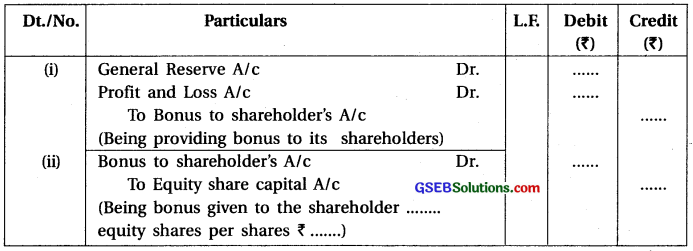
![]()
When share application & share allotment A/c keep combined (joint) in place of separate:
1. On receipt of application money :
Bank A/c Dr.
To Share application and allotment A/c
(No. of share applied x Application money per share)
2. On transfer of application money to share capital and allotment money due :
Share application and allotment A/c Dr.
To Share capital A/c
(No. of Share alloted x Application money per share + Allotment money per share)
3. On refund of money to applicants on rejected applications :
Share applications and allotment A/c Dr.
To Bank A/c
(No. of Rejected shares x Application money per share)
4. On receipt of allotment money :
Bank A/c Dr.
To Share application and allotment A/c
(Actual amount received from share holders on allotment)
Pro-Rata Allotment of Shares:
If applications are received for more number of shares than the shares issued for public subscription is known as oversubscription. In this situation, the shares are approved by the company through proportional allocation to the share applicants. In this situation, the excess amount received on application from applicants is utilised towards the amount due on allotment and towards share calls. If still any surplus amount remains, then it will be refunded to share applicants.
At the time of recording accounting entries regarding share capital transactions:
1. If you get an application for a lesser share of the shares issued by company then keep in mind the number of share application received and accordingly record the transactions.
2. If applications are received for more mumber of shares than issued for public subscription then excess application money are refunded to share applicants and regarding received amount it should be debited to Share application A/c and credited to Bank A/c. Then after all the accounting treatments are given keeping in mind the allotted shares.
3. If company has issued both equity shares as well as a preference share, then while calculation put the equity and preference word before the word share in the accounting notes.
4. When the shareholder do not pay the share allotment or share call money in time :
- Transfer the amount not received from sharefolder to Calls in arrears A/c and credited to Share allotment A/c or Respective call A/c.
- In future if these amount is reveived then debit to Bank A/c and credit to Call in arrears A/c.
- If these amount is not received and these share are forfeited then at the time of forfeiture, credit to Calls in arrears A/c and account has been closed.
- Sometimes amount not received from shareholder has been transferred to Share allotment or Share calls A/c instead of Calls in arrears A/c with actual received amont. In future if this amount received then it debited to Bank A/c and credited to Share allotment A/c or Respective call A/c. If this amount is not received then these shares has been forfeited.
5. If any share holders pay advance amount towards allotment or call then in that circumstances :
- Amount received in advance for share allotment will be credited to Share allotment A/c and amount received in advance for call will be credited to Calls in advance A/c.
- When actual amount of call is received then it will be debited to Calls in advance A/ c and credited to Respective call A/c.
6. When shares are issued at premium has been forfeited;
- If amount of premium is received on forfeited shares then no entry will be given.
- If amount of premium is not received on forfeited shares then at the time of forfeiture, this ‘ not received amount is debited to Securities premium A/c.
7. If forfeited shares are reissued with premium then amount of premium will be credited to securities premium A/c. If forfeited share are reissued at discount then amount of discount will be debited to Share forfeiture A/c.
8. The maximum discount can be given on reissue of forfeited shares is equal to the amount forfeited on capital account which was received on these shares.
9. If some of the forfeited shares are re-issued then the proportion of the forfeited share is found out by the following formula :
- Proportional Balance of Forfeited Shares = Total amount of Forfeited Shares \(\frac{\text { Reissue of Shares }}{\text { Total Forfeited Shares }}\)
- If these shares are issued by discount then total amount of discount will be debited to Share forfeited account and remaining share forfeiture amount will be transferred to capital reserve account.
10. When company purchases any business and shares are issued for consideration then if value of issued shares is higher than the net assets of business, the amount of difference is transferred to Goodwill Account, but if the value of issued shares is less than the net assets of business, the difference is transferred to Capital Reserve Account.
![]()
Following are some important points to be kept in mind :
1. In India, the management of company is done according to the Company Act of 1956. However, the new Companies Act, 2013 has been implemented by making necessary changes.
2. The name of a private company ends with the words, Private limited and the name of a public company ends with the words Limited.
3. The maximum number of members in the private company is 200. In the public company there is no limit for the maximum No. of members but must have at least 7 members in the public company.
4. After the implementation of Companies Act, 2013, company limited by shares does not issue irredeemable preference shares.
5. According to the SEBI guidelines, company must get share application money for at least 90% of the amount called up by the public subscription. This minimum amount of subscription should be received within 30 days from the issue of prospectus.
6. According to the current provision of the Companies Act face value of equity share should be at least ? 1.
7. According to the section-39 of Companies Act 2013, application money on shares should be minimum of 5% of face value of shares.
8. It is necessary (mandatory) to open demat account for dematerialisation of shares between the company and the share buyer. In which the purchase and sale transactions of the shares are recorded.
9. As per section-53 of Companies Act, 2013, companies would no longer be premitted to issue share at discount. But as per section-54 of Companies Act, 2013, the only shares that could be issued at a discount are sweat equity wherein share are issued to employees or directors in lien of their services.
10. If the amount called on share by company is not paid then these unpaid up calls are shown by deducting from Called up share capital while preparing balance sheet.
11. The company if authorised by its Articles of Association may change interest at the specific rate on calls in arrears from the due date to the date of payment.
In case the Articles of Association is silent, table-F of the Companies Act, 2013, shall apply which provides for interest at 10% p.a. However, the directors have the right to waive the interest on calls-in-arrears.
12. Balance of calls-in-advance on share is shown in the equity and liabilities side of the balance sheet under the head current liabilities and sub-head other current liabilities.
13. It is compulsory to pay interest on calls-in-advance from the date of receipt till the date when the call is due for payment as per rate specified in the articles of the company. However if the articles do not contain such rate, table-F of schedule I of the Companies Act, 2013 shall be applicable, which leaves the matter to directors of company subject to a maximum rate of 12% p.a. The interest on calls-in-advance is payable compulsorily even if there is no profits.
14. There is no legal restriction for determining the amount of premium on the share.
15. Unless the forfeited shares are reissued the balance of the forfeited shares account is added to paid up capital under subscribed share capital in the note to accounts on share capital.
16. Share issued for consideration other than cash has to be shown separately in balance sheet of company under the heading ‘Share Capital.
17. A company may issue sweat equity shares as per section-54 of Companies Act 2013. This shares cannot be resold by their holders within period of 3 years from the date of shares received. It is called lock-in-period.
18. ASBA is an application containing an authorization to block the application money in the bank account for subscribing to an issue.