This GSEB Class 12 Economics Notes Chapter 4 Banking and Monetary Policy covers all the important topics and concepts as mentioned in the chapter.
Banking and Monetary Policy Class 12 GSEB Notes
Evolution and Meaning of Bank:
- The word bank means ‘heap’ or ‘mass’.
- In Sanskrit, the word related to bank is ‘bhanda’ which means collection of fund.
- The word ‘bandol’ is derived from ‘bhanda’.
- The word bank originated from the Italian word ‘banca’ or from the French word ‘banque’. Both meant a ‘Bench’ for money exchange.
- European money lenders used to display coins of different countries on benches for the purpose of exchanging various coins. Thus, the word ‘bank’ came into use and is related to collection of fund or money.
- In Spain, the ‘Bank of Barcelona’ is known to be the first real bank established in the world in 1401.
![]()
Meaning of a Bank:
- A bank is an institution authorised to collect peoples’ deposits with the purpose of lending those under the condition of returning the same when the depositor demands.
- A bank is a commercial organization functioning for profit.
- A bank accepts peoples’ deposits and pays interest in return.
- A bank ensures the safety of these deposits and lends money from these deposits by charging interest and invests the surplus deposits in various sectors of economy for the development of the country.
- Banks are instrumental in mobilizing money. Where value of stock of money tends to ‘fall at a future date and value of circulating money tends to increase.
Classification (Types) of Banks: Banks are basically classified into two categories:
- Commercial Bank and
- Central Bank.
1. Commercial Bank:
- Commercial bank is one which transacts the business of banking that is accepting deposits from the people for the purpose of lending or investment, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawble by cheque, draft, pay-order or otherwise.
- Banks undertake the activity of mobilizing peoples’ money in order to make profit and therefore they are commercial institutes.
Functions of Commercial Banks:
- Accepting deposits,
- Providing credit facilities,
- Payments and withdrawal facilities
- Credit creation
- Inter-banking transactions,
- Providing agency and utility services and
- Providing various facilities, like, NEFT; RTGS; CORE banking; etc. with changing times.
Deposits:
Peoples’ savings accepted by banks are deposits. Deposits Eire categorised as:
- Current deposits
- Saving deposits
- Recurring deposits and
- Long-term (Fixed) deposits.
Scheduled Banks in India: The banks which are established according to RBI Act 1934 are called Scheduled Banks.
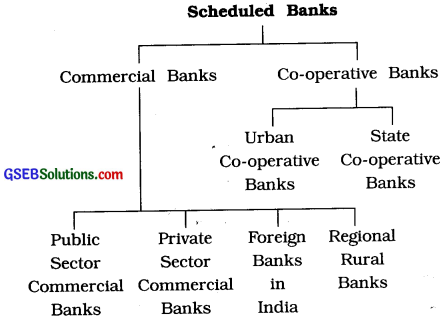
2. Central Bank:
Central bank is the Apex bank of the country whose function is to Eiid, regulate and promote the entire money market and the banking sector as well as to maintain monetEiry stability for overall economic growth of the nation. According to R. P Kent, “Central bank is the institution charged with the responsibility of mEmaging the expansion and contraction of the volume of money in the interest of the general public welfare.”
A central bank assumes the responsi¬bility of mEiintaining economic stability.
- A central bank also provides monetary advice and suggestions to the government.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): RBI is the central bank of India. RBI was established on April 1, 1935 with a private paid up capital of ₹ 5 crores and was nationalized on January 1, 1949.
- RBI is the Apex bEink of India which supervises and regulates the entire banking sector in the country. Also, it formulates monetary policy in India.
![]()
Monetary functions of RBI:
- To issue currency,
- To work as banker to the government,
- To work EIS bankers’ bank
- Lender of last resort,
- To control credit creation and
- To work as custodian of India’s reserves of foreign currencies.
Non-monetary functions of RBI:
- To regulate and supervise the financial and money markets.
- To make efforts to get more and more people under the organized money market.
- To create banking awareness among people.
- To promote setting up of co-operative banks in the interest of people.
- To make continuous efforts in the bEinking sphere and to provide special credit facilities to priority sectors.
- To manage the Prime Minister’s ‘Jan Dhan Yojana’
- To work towards protecting the interest £md rights of customers, and
- To publish sdl types of banking related information and statistics. Also experts’ articles to promote research related to bEinking.
Monetary Policy:
In economic theory, monetary policy is the policy which regulates the demand for money and supply of money.
Instruments of Monetary Policy:
1. Quantitative Measures:
The measures which impact the entire economy in a general or common way Eire called quantitative measures or general measures.
- Bank Rate: The rate at which RBI lends to the commercial banks for long-term is called the bank rate.
- Repo Rate: The rate at which RBI lends to the commercial banks for short-term is called the repo rate.
- Reverse Repo Rate: The rate at which RBI borrows short-term funds from the commercial banks is csilled the reverse repo rate.
- Monetary stability under emergency: In an emergency situation like an acute cash shortage to maintain monetary stability, commercial banks borrow from the RBI at fixed rate of interest. This rate is higher than repo rate.
- Cash Reserve Ratio – CRR: A certain minimum cash which all commercial banks have to keep reserves with the RBI is called Cash Reserve Ratio. It fulfills the need of a comfortable amount of cash reserves with the banking system. It is used to control inflation.
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio – SLR: In addition of CRR, under the Banking Regulation Act 1949, all banks have to maintain 25 % of their total deposits in the form of cash, gold and unencumbered approved securities. This is known as statutory liquidity ratio.
- Open Market Operations – OMOs: Open > market operations refers to sale of or parchase of government securities / bonds by the RBI in the open market. Such operations are undertaken to regulate inflation and depression.
- Sterilization Policy: When there is excessive flow of foreign exchange, then to control this situation the RBI indulges in sale of government securities in open market equal to the amount of inflow of foreign exchange and maintains the balance of monetary system. This is known as sterilization policy.
2. Qualitative Measures:
These measures have unique impact on some sectors and are not meant to impact all sectors similarly. These measures are as follows:
- Security: Banks lend money against some security deposits like jewellery, car, home, land, etc. from the borrowers.
- Margin: An individual is given only a certain percentage as loan of the total value of assets offered as security. This percentage is called margin.
- Ceilling on credit: The RBI prescribes ceilings for credits for different purposes.
- Discriminatory interest rate: RBI suggests different rates of interest for different types of lending. This is called the policy of discriminatory interest rate.