Gujarat Board GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 1 Nature and Significance of Management Important Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 1 Nature and Significance of Management
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which are the firms managed by owners themselves?
Answer:
Sole proprietorships and partnership firms.
Question 2.
Define management according to George Terry.
Answer:
Management is such a process which plans and controls men, machine, material, method, money and market. li provides leadership, co-ordination and direction to human efforts which help to, achieve the business objectives.
Question 3.
List down the characteristics of management.
Answer:
- Universal process,
- Goal oriented activity,
- Group activity,
- Continuous process,
- Human process,
- Decision process, and
- Science, Art and Profession.
Question 4.
Why is management known as a universal process?
Answer:
Because management is not only required in industries but can be applied in various social and religious fields and activities like agriculture, army, education etc.
![]()
Question 5.
Why is management known as a human process?
Answer:
Because man is in the centre of management. Management is done by human beings and for the human beings. Other means of production are useless without man.
Question 6.
Why is management known as science?
Answer:
Management is known as science because just like science, management has its own rules and principles.
Question 7.
List down any four importance of management.
Answer:
- Necessary in every field,
- Optimum utilization of resources,
- Useful for the success of business and
- Increase in job opportunities.
Question 8.
Why is it said that profit is the barometer for the efficiency and success of business?
Answer:
Business runs with the motive of profit, Competent and proficient managers, with their insight and proficiency, make the maximum and the most economical ‘ utilization of available resources and earn maximum profit. Hence, profit is…
Question 9.
What are the characteristics to be a professional person?
Answer:
- Requirement of specialized knowledge,
- Increase in knowledge and research,
- professional association,
- implementation of code of conduct, and
- moral responsibility.
Question 10.
State the various levels of management?
Answer:
Top level management, middle level management and bottom level management.
Question 11.
Mention 4 functions of top level management.
Answer:
- To laydown primary and subsidiary objectives of business,
- To take strategic decisions by making long term plans,
- To plan for the enterprise, its implementation and to supervise it and
- To analyze reports of different activities.
Question 12.
Who all are included in middle level management?
Answer:
Departmental officers, divisional officers and experts belonging to production, sale, purchase, finance, personnel, accounts, etc. are included in middle management.
Question 13.
Mention four functions of middle level management.
Answer:
- To focus on functioning of sub-divisions,
- To help the top level management in taking policy decisions,
- To prepare departmental budgets and present in front of top level management, and
- To keep constant touch with other departments and establish coordination.
Question 14.
Who all are included in bottom level management?
Answer:
Supervisors, jobbers and foremen.
![]()
Question 15.
Give five functions of bottom level management.
Answer:
- To supervise function of employees,
- To see that there remains discipline among employees,
- To plan routine
Question 16.
What is the form of authority and responsibility in the various levels of management?
Answer:
In top level management both authority and responsibility are more. In middle level management, authority is comparatively less whereas responsibility is limited to departments only and in bottom level management, least authority is present while responsibility is limited to sub-divisions.
Question 17.
Who is the top level management accountable to?
Answer:
Top level management is accountable to shareholders, creditors, government, departments, and legal provisions.
Question 18.
Define process.
Answer:
A series of functions which is continuously performed for the accomplishment of pre-determined objectives of business is known as process.
Question 19.
State the classification of the functions of management according to Luther Gulick.
Answer:
Gulick classified functions of management as:
- Planning
- Organizing
- Staffing
- Directing
- Co-ordination
- Reporting and
- Budgeting.
Question 20.
List down the classification of functions of management according to Peter Drucker.
Answer:
Drucker classified functions of management as:
- Managing a business
- Managing the managers and
- Managing the workers men and work.
Question 21.
‘Even God cannot change the past, but man can change the future’, this statement relates to which function of management?
Answer:
This statement relates to planning function of management.
Question 22.
Explain planning function of management.
Answer:
Planning means selection of facts for the expected result and to establish inter-relationship between them, as well as observation of necessary activities. Planning is the first step towards efficient management.
![]()
Question 23.
Why is planning known as a function of solotion or preference?
Answer:
In planning, many alternatives are found at the time of defining objectives. Planning becomes useful to select the best, alternative. Hence, planning is ……
Question 24.
What is organization?
Answer:
Organization is a structure for the assignment of authority and responsibility among individuals working for the achievement of common objectives.
Question 25.
Who will have the authority and which function of management?
Answer:
Organization function
Question 26.
‘Planning is considered to be the brain of a business unit.’Explain.
Answer:
Just as a brain in human body takes intellectual decision while its implementation is done by various parts of the body. In the same manner, the function of planning in a business unit is to take intellectual decisions.
Question 27.
What are the different activities involved in staffing?
Answer:
Recruitment, training, transfer, promotions, dismissal, retirement, welfare activities, man-power planning, human resource development and job analysis.
Question 28.
List down some activities included in direction.
Answer:
To direct the subordinates, to supervise the subordinates, to give orders and instructions, to fix the work to motivate ‘ the workers, to provide leadership, etc.
Question 29.
What is controlling as a function of management?
Answer:
Controlling is a function of maintaining balance among efforts, result, resources, and objectives. It is to see whether all the activities are done according to planning or not.
Question 30.
What is co-ordination?
Answer:
Co-ordination is to bring harmony among the different functions – from planning to controlling carried out by different departments in the business unit.
![]()
Question 31.
List down four characteristics of co-ordination.
Answer:
- Success of co-ordination depends on effective communication,
- Optimum utilization of business resources is possible due to co-ordination,
- Co-ordination is required at every level of management, and
- Management , process is not possible without coordination as it is required in all functions – from planning to control.
Question 32.
Mention the functional areas of management.
Answer:
- Marketing management,
- Human resource management,
- Financial management and
- Production management.
Question 33.
What is the main function of financial management?
Answer:
The main function of financial management is to arrange the finance and other related matters to produce the goods as per demand.
Question 34.
List down some activities involved in marketing management.
Answer:
Market research, distributive method, sales promotion, storage, and insurance, price policy, packaging, etc.
Question 35.
What are the functions of marketing management?
Answer:
- Product mix,
- Price,
- Distribution, and
- Promotion.
Question 36.
What does the price decision include?
Answer:
It includes sales policy, credit policy, policy regarding discount, wholesale or retail sale, commission to mediators, etc.
Question 37.
Which function of marketing management includes advertisement, publicity, and means to attract customers?
Answer:
Promotion function
Question 38.
What is known as the live asset in business?
Answer:
Employees of the business are known as the live asset of the business.
Question 39.
Mention four characteristics of human resource management.
Answer:
- Human resource management includes selection, training, promotion and direction to the employees,
- It provides proper training and thus develops personnel for the job,
- Basic function of human resource management is to manage the employees as they are valuable assets of firm, and
- It helps in reduction of labour turnover rate.
Question 40.
What is labour turnover rate?
Answer:
Labour turnover rate is the proportion of a firm’s workforce that leaves during the course of a year.
Question 41.
What is known as the lifeblood of the business?
Answer:
Finance
Question 42.
Mention four functions of financial management.
Answer:
- To estimate the financial needs,
- To prepare budget,
- To allocate funds, and
- To plan for taxes.
![]()
Question 43.
Define production.
Answer:
Process of conversion of naturally available raw material into consumable finished goods with the help of human efforts is known as production.] [Production planning, deciding programmes, maintaining co-ordination, direction and keeping control, are the various activities included in production management.
Question 44.
What are the various activities included in production management?
Answer:
- To have production control,
- To have quality control,
- To select technology and machinery, and
- To introduce variation and simplification in production.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the various important definitions of management.
Answer:
Management:
Management is the process of reaching organizational goals by working with and through people and other organizational resources.
The various definition of management are:
(A) Definition of Koontz and O’Donnell: Management is the art of getting things done through others.
(B) Definition of Livingston: Management is a function of achieving predetermined objectives of a business unit with the use of minimum time and cost as well by making efficient use of available resources.
(C) Definition of George R. Terry: Management is such a process which plans and controls men, machine,
material, method, money and market. It provides leadership, co-ordination and direction to human efforts which help to achieve the business objectives.
Question 2.
Management is both a science as well as art. Explain.
Answer:
- The way science works on its own set of rules and principles, so does management. Hence many experts consider management as a science.
- On the other hand, management focuses heavily on managing man i.e. people.
- Getting work done from man requires proficiency, intelligence, cleverness and insight. So, management is the art of getting the work done.
- Managing people is an art and so management is also considered as an art.
Question 3.
It is a challenging task to manage a labour intensive industry compared to a capital intensive industry. Explain
Answer:
- Capital intensive production requires more machinery, equipment and sophisticated technological production systems in the production process. A capital intensive production process is mostly automated and able to generate a large output of goods and services.
- More automation means better production, faster production, consistent production and lesser labour and their management.
- On the other hand, in a labor intensive industry is most of the production is carried,by workers or employees. It means that the levels of output would be at a much smaller scale.
- Labour intensive industry would require constant training and education of employees, hiring more work to increase production, asking workers to work extra hours, tackling their daily problems, etc. All these would require a lot of management effort as compared to capital intensive industry.
- Hence, it is a challenging task to manage a labour intensive industry compared to a capital intensive industry.
![]()
Question 4.
Write a brief note on management as a science and as an art.
Answer:
Management is a science:
- Knowledge gained by systematic way and by specializing in that area is called science. According to Dr. George Terry, “Science teaches one to know.”
- In science; the rules and principles are derived and cause and effect relationship is established. Similar process is done in management as well.
- Management makes use of gaining systematic knowledge, universality, cause and effect relationship, collection of facts, analysis and experiments, verifying the principles, etc.
- The way science has its own principles and rules, management also has .its own specific principles.
- Management makes use of these principles for co-ordination of human resource, machine, capital, manufacturing methods, etc. Thus, we can rightly . say that management is a science.
Management is an Art:
- The tactful use of skills and expertise gained through theoretical knowledge is called art. According to Dr. George Terry, “Art teaches one to do.”
- The practical application of management makes use of rules and principles, personal skills, insight and cleverness, etc.
- Thus, for proper implementation of knowledge, technical art is also important over and above the theoretical knowledge.
- The theories and principles are challenged and modified by the skilled manager as per the need of the situation. Hence, making use of management is an art.
- From these discussions we can conclude that management is neither only science nor only an art but a combination of both.
Question 5.
What are levels of management? Why there is a need of various levels of management?
Answer:
Need and meaning of levels of management:
1. If a business unit is small, the owner himself can manage it. When the size of unit expands, the number of employees in the business unit increase. Under such a situation, the management has to be divided into different levels for efficient business output.
The owner or the superior officer cannot supervise all his subordinates directly. So, various levels of management are created to delegate the authority. The top management delegates the authority to the people below it, and these people then delegate the management to the next level workers.
2. It should be noted that as the levels of management grows so does the expense, control and co-ordination. Hence, the organization should try to . maintain minimum levels of management without affecting efficiency of business operations.
Basically, there are three levels of management. They are:
- Top Level Management
- Middle Level Management
- Bottom Level Management
Question 6.
State the levels of management and the persons that run each level of management.
Answer:
There are three levels of management. They are:
- Top level management: It consists of Board of Directors, Managing Directors, General Managers, etc.
- Middle level management: This level is controlled by heads of various departments such as production, sales, purchase, personnel (human resource), finance, etc.
- Lower level management: It consists of supervisors, jobbers, foreman, etc.
Question 7.
Write a short note on top level management.
Answer:
top-level management:
- The top level (or higher level) management is the supreme authority for managing the enterprise.
It consists of Board of Directors, Managing Directors (MD), General Manager (GM) and Chief Executive Officers (CEO). - The top management takes important policy decisions for the business unit.
Functions of the top management:
- To lay down primary and subsidiary objectives of business.
- The directors act as the trustees of the business enterprise.
- To select Chief Executive Officer and higher officers and to assign them authority and responsibility.
- To sanction the budget for different departments of the business unit.
- To abide by law and to take care of interest of different stakeholders of the business.
- To take strategic decisions by making long term plans.
- To analyse and resolve complex problems of management as per legal provisions.
- To draft plans for the enterprise, implement them and to supervise them.
- To conduct functions like distribution of profit, dividend, reserve fund, re-investment of profit, etc.
- To analyse reports of different activities and to instruct further activities accordingly.
![]()
Question 8.
What consists of middle management? State the functions of middle management.
Answer:
Middle-level management:
- The middle level of management is an important link between top level and bottom level of management.
- It consists of departmental officers, divisional officers and experts of various fields. For example, production manager, sales head, purchase officer finance manager, human resource manager, accounts head, etc.
- The middle level is also known as Officer’s Level.
Functions:
- To implement the orders and instructions given by Chief Executive Officers.
- Each departmental head prepares the budget for its department and presents it before the top level management for approval.
- To formulate policies, rules and structure for the accomplishing objectives of the enterprise. To decide suitable methods for achieving these objectives, to analyse the methods and also to decide appropriate measures.
- To take necessary steps to increase efficiency and effectiveness of departmental activities.
- To make attempts to motivate the employees of department.
- To keep in constant touch with the officers of the other departments and establish co-ordination.
- To focus on functioning of sub-divisions.
- To supervise the working of the departments, get information, provide
directions and provide information about progress and working of the department to the top level management. - To help the top level management in taking policy decisions.
Question 9.
Write a short note on bottom level of management.
Answer:
Bottom level of management:
- The lowest level of management in an organization is called the Bottom Level or Supervisors’ Level Management.
- The decisions and policies taken by top level management are actually implemented by this level. Hence, this level is also known as Functional/ Operational Level of Management.
- This level of management includes supervisors, jobbers, foremen, etc.
- Supervisors working at this level are actually representatives of management. At this level, management there is more of administrative work rather than managerial functions.
- Although bottom level of management is the lowest level of management, it plays a very important role in the business.
- Efficient and successful performance of this level leads to achievement of business objectives. This then provides support to the entire business.
Functions:
- To supervise function of employees.
- To maintain the discipline and morale of employees.
- To plan routine work of the respective department.
- To perform functions related to employees like transfer, promotion, training, etc.
- To get instructions, orders and programme from the departmental officers to carry out the departmental functions.
- To perform the functions like the layout, repairing and maintenance of machinery.
- To make arrangement for necessary equipment, raw-materials, etc. for the workers.
- To solve the genuine problems of workers.
- To implement decisions and policies decided by top level of management.
- To forward reports of various activities taking place at the bottom level, suggestions and complaints of employees to the middle level of management.
Question 10.
What do you mean by management functions? How have the various management gurus classified the management functions?
Answer:
- Management is the process of reaching organizational goals by working with and through people and other organizational resources.
- The functions done under each process for attaining the objectives of the organization are called management functions.
- Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing and Controlling are the five major functions of management.
- Various thinkers and scholars hold different opinions regarding the functions of management. The classification of management into various functions in the views of some of them is shown in the chart below.
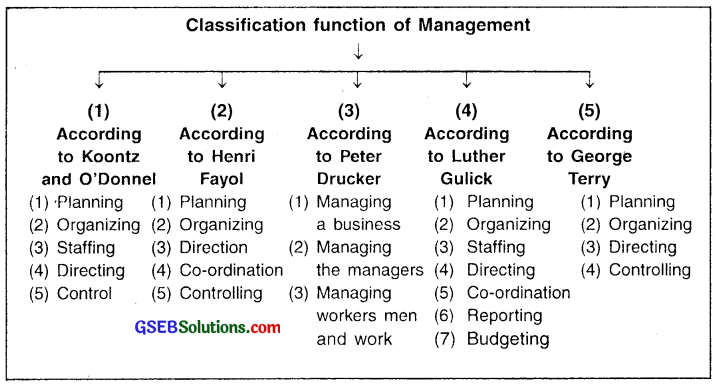
Question 11.
Management is a process and not just an activity. Explain.
Answer:
- An organization sets objectives.
- Efficient management leads to accomplishment of business objectives.
- Now, management involves undertaking various management processes. Several functions are done continuously under these processes to achieve the ultimate business objectives.
- A series of functions which are continuously performed for the accomplishment of pre-determined objectives of business are known as processes.
- To achieve the business goal, various business activities are arranged in chronological and orderly manner.
- Hence, we can say that management is not just an activity but a process.
Question 12.
State and explain in detail the various functions of management.
Answer:
- Planning,
- Organizing,
- Staffing,
- Directing and
- Controlling are the five major functions of management.
1. Planning:
- It is said that ‘even God cannot change the past, but man can change the future through proper planning.
- The process of selecting facts for obtaining the desired results and establishing inter-relationship between them, as well as observing necessary activities for forecasting and anticipating the future of business is called planning.
- Planning is the first step of management.
- Planning consists of deciding well in advance as what work has to be done, who will do what, when, how, to what extent and when will the work be finished for achieving predetermined objectives. Hence, planning is considered as thinking about the future while remaining in the present.
- Planning is extremely important to reduce risk and uncertainties that may arise in future.
- Planning helps to take care of all the business activities in a systematic manner. This helps to accomplish business goals easily.
- Planning helps in systematic selection of the best alternative for the business. Hence, it is said that planning is a function of ‘selection/preference’.
- Planning is also a base for other managerial functions such as organizing, staffing, co-coordinating and controlling.
2. Organizing:
- Organizing or organization is a structure for assigning authority and responsibility among individuals for achieving business objectives.
- Business objectives, policy, programmes, etc. are decided through planning whereas organizing is done for executing the plans.
- Under organizing, various sections and groups of people are allotted various business activities so that the objectives can be fulfilled.
- Organization helps in distribution of authority and responsibility among these sections and groups. The sections and groups get clear cut idea about their roles and responsibility and the structure of the organization. The structure « of organization decides on matters like who will supervise, who will have authority and responsibility of work, inter-relationship among individuals, etc.
- Planning is the brain of a business unit while organization is its physical structure.
- The function of a brain in the human body is to take the intellectual decision
while its implementation is done by various organs of the body. Similarly, the function of planning in a business unit is to take intellectual decisions whereas, implementation of these decisions, distribution of work, delegation of authority and responsibility among the employees of various departments is taken care by organizing.
3. Staffing:
- It is said that “Employees are arms and legs (limbs) of unit.”
- According to Dr. George Terry, “Staffing is concerned with availing and maintaining satisfactory manpower.”
- Every business organization requires staff. Hence, staffing is a very important function of management. An organization without staff is like a mere skeleton. Activities of all businesses depend on their staff.
- The function of staffing is to recruit employees for the right position, at the right time, in the right number, with the right qualification. It also includes selection, training, transfer, promotion, dismissal, retirement and welfare activities of employees.
- This function is carried out by the Human Resource Department of the business organization.
- Staffing also monitors the output of work of each employee. It also listens to the problems of the employees. This helps in maintaining the enthusiasm and zeal of employees. Enthusiasm for work and comfortable and encouraging work environment leads to increase in productivity and efficiency of the organization.
- Today staffing also includes man-power planning, human resource development, evaluation of work, job analysis, etc. It is a highly known fact that a satisfied staff is an invaluable asset of the business.
4. Directing:
- The management function of guiding and to supervising the employees for accomplishing business objectives is called directing.
- Directing is extremely important to supervise employees of an organization effectively in order to achieve the business objectives. All management functions are worthless without direction.
- In a business unit, planning is done after defining objectives. Then an ideal organization structure is formed and raw material, machineries are purchased and staff is appointed. In spite of all these activities, the business can fail to operate if proper direction is not given to the employees or workers.
- The function of directing includes various activities like directing the subordinates, supervising them, giving them orders and instructions, allocating the work, motivating the workers, providing leadership, etc.
- Direction is a continuous process and so it is required at every level of management.
5. Controlling:
- The function of controlling maintains the balance among efforts, result, resources and objectives. Controlling is the last function of management.
- The function of controlling is to make sure that the business activities are conducted as planned.
- As per traditional thought process, controlling refers to putting restriction on the activities of employees, to have a strict approach, punishing or fining the employees in case of mistake, transferring them or withholding their promotion and so on. But this is a negative approach of controlling.
- In modern times, controlling is a oositive concept, it is done as a corrective activity because the function of controlling is not to restrict the activities but to direct them in the right direction.
- It is important to see that the business activities are done as per the planning. Controlling sees to it that the activities take place as per plan so that business objectives are fulfilled.
- The function of controlling is also to see that mistakes made in past are not repeated in future.
![]()
Question 13.
All ends well that’s planned well. Explain.
Answer:
Every activity needs planning. It is the first step of management.
Planning consists of deciding well in advance as what work has to be done, who will do what, when, how, to what extent and when will the work be ‘ finished for achieving predetermined objectives. Hence, planning is considered as thinking about the future while remaining in the present.
Such a forward thinking helps to take care of all the business activities in a systematic manner. This helps to accomplish business goals easily.
Hence, it is said that if things are well planned they also end well.
Question 14.
What major functions are done by the human resource department?
Answer:
- The Human Resource Department of the business organization takes care of the staffing function.
- Under this it recruits employees for the right position, at the right time, in the right number, with the right qualification.
- This department also takes care of selection, training, transfer, promotion, dismissal, retirement and welfare activities of employees.
- Staffing also monitors the output of work of each employee. It also listens to the problems of the employees. Today staffing also includes man-power planning, human resource development, evaluation of work, job analysis, etc.
Question 15.
All management functions are worthless without direction. Explain.
Answer:
- The management function of guiding and to supervising the employees for accomplishing business objectives is called directing.
- Directing is extremely important to supervise employees of an organization effectively in order to achieve the business objectives.
- In spite of all the business activities, the business can fail to operate if proper direction is not given to the employees or workers.
- Hence, all management functions are worthless without direction.
Question 16.
State and define each management function.
Answer:
There are five major management functions. They are:
1. Planning:
- The process of selecting facts for obtaining the desired results and establishing inter-relationship between them, as well as observing necessary activities for forecasting and anticipating the future of business is called planning.
- Planning is the first step of management.
2. Organizing:
- Organizing or organization is a structure for assigning authority and responsibility among individuals for achieving business objectives.
- Under organizing, various sections and groups of people are allotted various ‘ business activities so that the objectives can be fulfilled.
3. Staffing:
- The function of staffing is to recruit employees for the right position, at the right time, in the right number, with the right qualification. It also includes selection, training, transfer, promotion, dismissal, retirement and welfare activities of employees.
- This function is carried out by the Human Resource Department of the business organization.
4. Directing:
The management function of guiding and to supervising the employees for accomplishing business objectives is called directing.
5. Controlling:
- The function of controlling maintains the balance among efforts, result, resources and objectives. Controlling is the last function of management.
- The function of controlling is to make sure that the business activities are conducted as planned.
Question 17.
What is co-ordination? State its characteristics and importance.
Answer:
Co-ordination:
- To task of maintaining co-ordination and harmony among the different functions carried out by different departments in the business unit is called co-ordination.
- Although co-ordination is not a function of management but it is required at each and every stage of management.
- It is necessary right from the planning stage to controlling.
Characteristics of co-ordination:
- Co-ordination is required for all the activities, right from planning to controlling. As a result, none of the management process is possible without co-ordination.
- Co-ordination is required at every level of management.
- Success of co-ordination depends upon effective communication.
- Co-ordination is not possible without co-operation. Co-operation of employees engaged in different activities is necessary to maintain co-ordination among various activities of the organization.
- Co-ordination makes possible optimum utilization of business resources.
- Co-ordination is a part of every activity of management. Therefore co-ordination is considered soul of management.
Importance of co-ordination:
- Co-ordination makes management functions like planning, organizing, directing, controlling, etc. effective.
- Co-ordination makes possible smooth functioning of all the business activities.
- When there is proper co-ordination then neither any work remains incomplete nor any work gets duplicated.
- Co-ordination maintains harmony among various departments of management.
- Co-ordination enables to maintain a balance between order and time of business activities performed by various departments.
- Co-ordination enables accomplishment of pre-decided objectives.
Question 16.
What are functional areas of management?
Answer:
Managing a business requires undertaking several important functions.
On the basis of these functions, we can classify the functional areas of management into –
1. Marketing Management:
Marketing management is the activity or function of providing goods or services from producers to customers. Over and above exchange of goods with money it also includes market research, distributive method, sales promotion, storage, insurance, etc.
2. Human Resource management:
The process which takes into consideration matters like proficiency, knowledge, intelligence, likes and dislikes, personal development, necessity, etc. of employees, integrates them with business objectives and channelizes the business towards the path of success and profitability is called Human Resource Management (HRM).
3. Financial management:
- Financial management is the process of dealing with all the finance related functions of the business.
- The function of acquisition, utilization and allocation of capital is called financial ‘ function or financial management.
4. Production management:
The process which includes planning for production, deciding programmes, maintaining co-ordination, direction, and keeping control is called production management.
Question 17.
State the characteristics of Human Resource Management.
Answer:
Characteristics of Human Resource Management:
- Human resource management includes selection, training, promotion and directing the employees.
Human resource management enables to accomplish business objectives by integrating them with individual objectives business objectives. - Since employees are valuable assets of the business, the basic function of human resource management is to manage them,
- It provides proper training and develops personnel for the job.
- Human resource management evaluates performance of employees and places them at right position.
- Efficient management can reduce labour turnover rate and can maintain skillful employees for a longer period in company.
- As part of human resource management, conducive atmosphere is provided to employees. This boosts their enthusiasm and efficiency. The values of the company are maintained and business objectives are achieved.
![]()
Question 18.
What is financial management? Which functions are included in it?
Answer:
Financial Management:
- Financial management is the process of dealing with all the finance related functions of the business.
- The function of acquisition, utilization and allocation of capital is called financial function or financial management.
- Finance is the lifeblood of business. No activity is possible without finance.
- Finance is required for the establishment, development, expansion and modernization of a business.
Following functions are included in financial management:
- To estimate the financial needs of the business activities
- To make financial plans keeping in mind the time duration
- To prepare budget
- To allocate funds to various departments
- To decide capital structure and to select sources of acquiring capital
- To carry out the procedure for acquiring the finance
- To see that the acquired funds are properly utilized and to keep control over financial activities
- To form financial policy
- To plan for taxes
- To make arrangement of assets
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a problem of business expansion?
(A) Problem of sales
(B) Problem of employees
(C) Problem of infrastructure
(D) Problem of capital
Answer:
(C) Problem of infrastructure
Question 2.
Who gave the definition ‘Management is the art of getting things done through others.’?
(A) Koontz and O’Donnell
(B) Livinstun
(C) George Terry
(D) Peter Drucker
Answer:
(A) Koontz and O’Donnell
Question 3.
Which of the following characteristics of management show that management has its own rules and principles?
(A) Management is a universal process
(B) Management is a human process
(C) Management is a profession
(D) Management is science
Answer:
(D) Management is science
Question 4.
Management is important for which of the following field(s)?
(A) Business
(B) Army
(C) Agriculture
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 5.
Which of the following is the most significant element of management?
(A) Human element
(B) Money element
(C) Group element
(D) Goal element
Answer:
(A) Human element
Question 6.
________ helps to convert a loss making business to profit making business.
(A) Experts
(B) Right Decisions
(C) Efficient management
(D) Good team work
Answer:
(C) Efficient management
![]()
Question 7.
What is known as the barometer for the efficiency and success of business?
(A) Management
(B) Resources
(C) Profit
(D) Wealth
Answer:
(C) Profit
Question 8.
Who said ‘science teaches one to know and art teaches one to do’?
(A) Peter Drucker
(B) Henry Fayol
(C) Dr. George Terry
(D) Livingstun
Answer:
(C) Dr. George Terry
Question 9.
________ is an activity where specialized knowledge in specific field is acquired and is used for welfare of the society.
(A) Science
(B) Art
(C) Management
(D) Profession
Answer:
(D) Profession
Question 10.
Which of the following degree is necessary for management?
(A) MD
(B) MDS
(C) MBA
(D) LLB
Answer:
(C) MBA
Question 11.
Who among the following is not included in top level management?
(A) Managing Director
(B) Departmental heads
(C) General Manager
(D) Board of directors
Answer:
(B) Departmental heads
Question 12.
Who acts as trustees of the business enterprise?
(A) Chief Executive Officer
(B) Directors
(C) General Manager
(D) All of these
Answer:
(B) Directors
Question 13.
Whose function is to distribute the dividend and reserve fund?
(A) Middle level managers
(B) Top level managers
(C) Bottom level managers
(D) None of these
Answer:
(B) Top level managers
Question 14.
What is the other name of middle level management?
(A) Functional level
(B) Worker’s level
(C) Operational level
(D) Officer’s level
Answer:
(D) Officer’s level
Question 15.
Which of the following is included in functional level of management?
(A) Supervisors
(B) Departmental heads
(C) General manager
(D) Directors
Answer:
(A) Supervisors
Question 16.
Which level decisions are least risky in a business?
(A) Top level management
(B) Middle level management
(C) Bottom level management
(D) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(C) Bottom level management
Question 17.
What is a series of functions which are continuously performed for the accomplishment of pre-determined objectives of business called?
(A) Programme
(B) Execution
(C) Process
(D) Management
Answer:
(C) Process
Question 18.
Who gave the functions of management namely planning, organizing, staffing, directing, co-ordination, reporting and budgeting?
(A) George Terry
(B) Luther Gulick
(C) Peter Drucker
(D) Henry Fayol
Answer:
(B) Luther Gulick
Question 19.
First step of management is
(A) Organizing
(B) Coordinating
(C) Staffing
(D) Planning
Answer:
(D) Planning
Question 20.
________ is distribution of authority and responsibility among individuals working for achievement of common objectives.
(A) Planning
(B) Organizing
(C) Staffing
(D) Directing
Answer:
(B) Organizing
![]()
Question 21.
Planning is compared to which part of human body?
(A) Brain
(B) Skeleton
(C) Arms and legs
(D) Blood
Answer:
(C) Arms and legs
Question 23.
Who said ‘staffing is concerned with availing and maintaining satisfactory man-power’?
(A) Henry Fayol
(B) Dr. George Terry
(C) Peter Drucker
(D) Koontz and O’Donell
Answer:
(B) Dr. George Terry
Question 24.
Which of the following function is not a part of staffing?
(A) Training
(B) Transfer
(C) Dismissal
(D) Leadership
Answer:
(D) Leadership
Question 25.
Evaluation of work is a part of which function of management?
(A) Directing
(B) Staffing
(C) Organizing
(D) Controlling
Answer:
(B) Staffing
Question 26.
Directing includes which of the following activities?
(A) Motivating the workers
(B) Job analysis
(C) Evaluation of work
(D) Punishing employees for their mistakes
Answer:
(A) Motivating the workers
Question 27.
Which function of management helps in maintaining balance among efforts, result, resources and objectives?
(A) Staffing
(B) Directing
(C) Controlling
(D) Planning
Answer:
(C) Controlling
Question 28.
Which of the following is the functional area of management?
(A) Production management
(B) Human resource management
(C) Financial management
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 29.
Which functional area of management is an activity of providing goods and services from producers to customers?
(A) Production management
(B) Human resource management
(C) Marketing management
(D) Financial management
Answer:
(C) Marketing management
Question 30.
Which element of marketing management leads to increase in sales of a product?
(A) Product mix
(B) Distribution mix
(C) Production
(D) Promotion
Answer:
(D) Promotion
Question 31.
________ is like the lifeblood of business.
(A) Marketing
(B) Employees
(C) Finance
(D) Planning
Answer:
(C) Finance
Question 32.
Which of the following is a function of financial management?
(A) To select technology and machinery
(B) To undertake activities to control expenditure or cost and increase productivity
(C) To make arrangements of assets
(D) To maintain business prestige
Answer:
(C) To make arrangements of assets
![]()
Question 33.
Deciding programmes and keeping control is a part of ________ management.
(A) Marketing management
(B) Financial management
(C) Production management
(D) Human resource management
Answer:
(C) Production management
Question 34.
Which of the following is the characteristic of management?
(A) National motive
(B) Social benefit
(C) Goal oriented activity
(D) Optimum utilization of resources
Answer:
(C) Goal oriented activity
Question 35.
Who is the supreme authority for the managing an enterprise?
(A) CEO
(B) Board of Directors
(C) General Manager
(D) Chief Operating Officer
Answer:
(B) Board of Directors.