Gujarat Board GSEB Solutions Class 10 English Second Language Chapter 8 Our Feathered Friends Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 10 English Textbook Solutions Chapter 8 Our Feathered Friends (Second Language)
GSEB Class 10 English Our Feathered Friends Text Book Questions and Answers
1. Know the words for the body parts of a bird.

2. Make a list of ten small-sized birds and write about their characteristics (at least two).
| No. | Name of the bird | Characteristics |
| (1) | house sparrow | It lives around humans. It is one of the noisiest birds. |
| (2) | parrot | It has a red, curved beak. It can imitate human sounds. |
| (3) | cuckoo | It is usually seen during monsoon. The male is greenish-black and the female is brownish. |
| (4) | mynah | It can reproduce human sounds. It nests in holes. |
| (5) | woodpecker | It has a strong, pointed beak. It has a very long beak. |
| (6) | green-bee-eater | It is found around wheat fields. It nests inside the ground. |
| (7) | dov | It has very short legs. It has a powerful flight and its wings create a whirring sound. |
| (8) | black drongo | It is fully black. It has a unique forked tail. |
| (9) | babbler | It is always found in small groups of 6-10 birds. It is a social bird. |
| (10) | tailor bird | It has a long tail. It is often heard, but very difficult to see. |
![]()
3. Read this excerpt on Salim Ali.
Salim Ali is one of the foremost names in the field of Ornithology (scientific study of birds) and Natural History in the entire world. He was an Indian, born on 12th November, 1896. He is often referred to as the ‘Birdman of India’. He was among the first Indians to conduct systematic bird surveys and has written a number of bird books.

He spent a major part of his life in camping in jungles and staying in tents for studying birds. His ten volumes of ‘Handbook of The Birds of India and Pakistan’ is an authentic reference book for bird lovers and researchers. Due to his contribution only, Ornithology became popular in India. After Independence, he became a key figure behind the Bombay Natural History Society.
He was instrumental in the establishment of Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary (Keoladeo National Park). He was awarded the Padma Bhushan in 1958 and the Padma Vibhushan in 1976. A number of bird species and a couple of bird sanctuaries and institutions have been named after him. He passed away on 20th June, 1987.
Vocabulary
1. Replace the underlined words / phrases with the words having the similar meanings from the text. Write that word in the blank.
(1) Chandani was tempted by the low price of the dress.
Chandani was fascinated by the low price of the dress.
(2) A rabbit’s dwelling is a hole.
A rabbit’s home is a hole.
(3) Colour of the female birds is naturally dull to protect them from the destroyers.
Colour of the female birds is naturally dull to protect them from the hunters.
(4) Arya has a longing for trekking in the Himalayas.
Arya has a passion for trekking in the Himalayas.
(5) The Grey Hornbill collects mud-globes to build its nest.
The Grey Hornbill collects mud-pellets to build its nest.
![]()
(6) Vultures are called scavengers as they clean our environment by eating flesh.
Vultures are called scavengers as they clean our environment by eating rotten dead bodies.
(7) Birds travel from Siberia and the chilly countries of Europe to Asia every year.
Birds migrate from Siberia and the chilly countries of Europe to Asia every year.
2. State whether these expressions are of happiness, wonder, sadness, curiosity or excitement. Write the appropriate word.
Question 1.
How beautiful!
Answer:
wonder
Question 2.
That’s great!
Answer:
happiness
Question 3.
What a design of nature!
Answer:
curiosity
Question 4.
Wow! It’s cool.
Answer:
excitement
Question 5.
What a caring dude!
Answer:
happiness
Question 6.
Poor boy!
Answer:
sadness
Question 7.
What a painful experience!
Answer:
sadness
![]()
Question 8.
Oh! That is miserable!
Answer:
sadness
3. Follow the instructions to find the words.
Example :
It is risky to face a bull with sharp corns in a narrow street. (Change one letter)
It is risky to face a bull with sharp horns in a narrow street.
(1) Have you ever observed a mill of the parrot? It’s curved. (Change one letter)
Have you ever observed a bill of the parrot ? It’s curved.
(2) In my courtyard, a block of sparrows is fed every day. (Change one letter)
In my courtyard, a flock of sparrows is fed every day.
(3) Some animals in the jungle feed on carrier.(Change two letters)
Some animals in the jungle feed on carrion.
(4) The habit of the cheetah is open fields. (Add two letters)
The habitat of the cheetah is open fields.
![]()
(5) His chief at school brought him a suspension letter and scolding too. (Add three letters)
His mischief at school brought him a suspension letter and scolding too.
(6) Your compassion to meet your favourite ? actor will be fulfilled one day. (Remove three letters)
Your passion to meet your favourite actor will be fulfilled one day.
4. Tick mark the correct options.
(1) Children don’t like if their parents make their compromise / comparison (✓) with others.
(2) India is the second largest country in (✓) population / pollution in the world.
(3) There is a dangerous (✓) curve / cross at the Crescent Road. Be careful while driving.
(4) If you happen to pass through a jungle, you will surely hear noise / chirping (✓) of birds.
(5) The idea of setting up a language lab in our school was (✓) abandoned / absent so we were very unhappy.
(6) Some birds come from other countries to Gujarat. They are travelling / migratory (✓) birds.
5. Choose the correct words from the box that matches the definitions.
carcasses, grassland, chirp, scavenger, carrion, characteristics, zoology, perch
(1) An open field full of grass.
Answer:
grassland
(2) The flesh of dead animals.
Answer:
carrion
(3) Dead bodies of animals or men.
Answer:
carcasses
(4) A branch of science that studies animals and their behaviour.
Answer:
zoology
![]()
(5) To make a short, high-pitched sound.
Answer:
chirp
(6) An animal or a bird that feeds on dead plant, animal or refuse.
Answer:
scavenger
(7) Special qualities of a person or a thing.
Answer:
characteristics
6. Make meaningful sentences using all the words.
(1) eagle – endangered – species – world
The eagle is the most endangered species in the world today.
(2) stomach-ache – Saloni – suffer – cure – doctor
Saloni is suffering from a stomach-ache and she must go to a doctor for a cure.
(3) dude – get – pleasant – surprise
That dude will get a pleasant surprise when he sees his friend.
(4) fascinated – robot – little boy – fair
The little boy was fascinated to see a robot at the fair.
(5) government – supply – necessities
It is the duty of the government to supply the necessities in times of floods.
(6) grassland – rosy pastor – flock
A flock of rosy pastors flew into the grassland.
7. A. homophone is a word that sounds like another word but has a different meaning and spelling.
Example : We go to a shop to buy things.
When we leave, we say bye.
Tick mark the correct words in the bold print to make the sentences meaningful.
We all no / know (✓) that our freedom was won through non-violence. Many of our freedom fighters sacrificed there / their(✓) lives four / for (✓) the noble cause of making our country free.
They (✓) said / sad, “India is over / our (✓) country so we (✓) won’t / want let them rule over us anymore. We will (✓) send / sand them (✓) back / bake to their country.” Now we are a free country but it is /also quite (✓) / quiet right that if we are divided / into (✓) pieces / peaces, our nation will become / week / weak (✓).
Now use these homophones in your own sentences.
(1) peace / piece
People of different religions live in peace in India.
Can I have a piece of that cake ?
(2) son / sun
Raj is Mr Sharma’s son.
The sun always rises in the east.
(3) write / right
Amit will write a letter to his grandmother.
What is the right answer ?
![]()
(4) dear / deer
Jay is a dear friend of mine.
Look at that deer grazing in the field.
Comprehension
1. Name five birds you like. Classify the information of the birds in the table. Work in pairs. One is done for you.
| Name of the Bird | Habitat | Size | Colour | Special Information |
| Tailor bird | Lives around us. | Medium | Yellowish, rust | Stitches its nest with green leaves and fibres of trees. |
| Grey Hornbill | Lives in the wild, as well as urban areas, especially in large trees. | Medium | Grey | Its beak has an extra portion which looks like a horn.
It nests in hollows of tall trees. |
| Weaver bird | Lives in grasslands, cultivated areas and scrubs. | Small | Yellowish, grey | Weaves its nest with long, thread-like grass leaves. |
| Vulture | Lives in forest areas. | Large | Grey | It keeps our surroundings clean by eating dead animals.
It has a sharp, curved beak. |
| House Sparrow | Lives around human beings. | Small | Grey | We have destroyed their homes, so we get to see very few sparrows now. |
| Rosy Pastor | Lives in cold regions like Europe. Migrates to India in June/ July. | Small | Dull brown and pink | It flies in a flock.
It takes the help of the sun to find its way. |
2. Write True or False.
Question 1.
Because of our carelessness, the population of vultures is decreasing.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Birds should be fed with grains and farsart.
Answer:
False
![]()
Question 3.
Prey birds like vultures hunt smaller birds for their food.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
The weaver bird and the tailor bird are the same birds.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Birds can travel anywhere without the help of a map.
Answer:
True
Question 6.
The migratory birds generally travel in larger groups or flocks.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
The Grey Hornbills are generally not found S in the Indian subcontinent.
Answer:
False
Question 8.
Male sughari weaves more than one nest in the nesting season.
Answer:
True
3. Tick mark the most appropriate options.
Question 1.
Shubhangi saw tailor bird.
A. a smaller
B. a female
C. a male
D. a yellowish
Answer:
B. a female
Question 2.
The vultures prove to be the best friends for human being because they….
A. clean our surroundings
B. are hunters
C. are non-vegetarians
D. are bird-friendly
Answer:
A. clean our surroundings
![]()
Question 3.
Who, according to you, is responsible for a half-completed nest ?
A. the male weaver bird
B. the females
C. the would-be mother
D. the maker itself
Answer:
B. the females
Question 4.
It is observed that the female in almost all species is….
A. larger and attractive looking
B. smaller and dull in look
C. as good looking as the male
D. dull in comparison with the male
Answer:
D. dull in comparison with the male
4. Frame questions to get the under- lined words as answers.
Example:
The female in most of the species looks duller in comparison to the male.
How does the female in most species look in comparison to the male ?
(1) We find two types of birds : birds of prey and small birds.
(i) How many types of birds do we find ?
(ii) Which are the two types of birds that we find ?
(2) The male hornbill takes care of the female and the new-born babies.
Who takes care of the female and the new-born babies ?
(3) Shubhangi saw a number of nests of the weaver birds on the babool trees.
(i) How many nests of the weaver birds did Shubhangi see on the babool trees ?
(ii) Where did Shubhangi see a number of nests of the weaver birds ?
![]()
(4) The male weaver bird invites the female bird to observe the half-completed nest.
(i) Whom does the male weaver bird invite to observe the half-completed nest ?
(ii) Why does the male weaver bird invite the female bird?
(5) Vultures are known as scavengers.
What are the vultures known as?
(6) The beak of a vulture is designed to tear the flesh from the dead bodies.
How is the beak of the vulture designed?
(7) We should observe the colour, size, shape and the length of a bird while watching it.
What should we observe while watching a bird
5. Answer these questions in one line.
Question 1.
What does Devangi study ? Where ?
Answer:
Devangi studies zoology in M.S. University in Vadodara.
Question 2.
What is Shubhangi interested in ?
Answer:
Shubhangi is interested in birds.
Question 3.
What did Shubhangi want to know from Devangi ?
Answer:
Shubhangi wanted to know about birds from Devangi.
Question 4.
What do the birds of prey do ?
Answer:
Birds of prey hunt small birds for food.
Question 5.
Why has nature made the female birds smaller and duller ?
Answer:
Nature has made the female birds smaller and duller to hide them from hunters.
Question 6.
How is the beak of a Hornbill ?
Answer:
The beak of a Hornbill has an extra portion like a horn.
![]()
Question 7.
Where does Nazmin live ?
Answer:
Nazmin lives in the Polo forest.
6. Answer these questions in two or three sentences each.
Question 1.
In what way are the birds very useful to us ?
Answer:
Birds eat insects that are harmful to crops. They also help in spreading seeds. They entertain us with their sweet chirping.
Question 2.
Have you observed a tailor bird ? How does it build its nest ?
Answer:
Yes, I have observed the tailor bird. It stitches its nest with green leaves and fibres of trees.
Question 3.
Which are the basic tips for bird – watching ?
Answer:
While bird watching, you should observe the colour and size of the bird. You should notice the shape and length of its bill and tail. You should also see where it is perched-on a tree or a wire, in a water body, open ground or grassland.
Question 4.
What does the weaver bird or sughari use to build the nest ?
Answer:
The weaver bird or sughari uses long, thread-like grass leaves to build the nest.
Question 5.
Why are vultures not seen in the sky ?
Answer:
Nowadays, people use a medicine called diclofenac to cure sick cattle. When these cattle die, the vultures feed on them. After eating such a flesh, a vulture dies within a few days. This is because diclofenac is very harmful to vultures.
Question 6.
Why are birds like sparrows disappearing from human habitats ?
Answer:
Birds like sparrows are disappearing from human habitats because we have destroyed V their homes. We design our houses in such a way, that the sparrows cannot enter into them. We do not allow them to nest in our homes.
![]()
Question 7.
From where do the rosy pastors migrate ? What is the speciality in their migration ?
Answer:
Rosy pastors migrate from the cold regions of Europe. They take the help of the sun to find their way. When they come, they travel in the morning, and during their return migration, they travel in the evening.
Question 8.
How can we help the birds ?
Answer:
We can help birds by offering them grains and water. We can prepare sparrow nests with the help of cardboard boxes.
7. Write short notes with the help of the given points.
Question 1.
The House Sparrow
colour – size – friendly – make atmosphere alive – importance – less numbers at present – faulty design of our houses – the bird cannot enter – we keep them away from our premises – feel safety in co-existence -prepare sparrow nests – feeding them – saving them from extinction.
Answer:
The house sparrow is a small bird. The male sparrow is a brightly coloured bird with gray head, white cheeks and black bib. The female sparrow is plain brown in colour. The house sparrow is a very friendly bird. It makes the atmosphere alive by its constant chirping. It likes to live around human beings. It feels safe in living with us.
![]()
But we have destroyed its home. We design our houses in such a way that a sparrow cannot enter into our house. We keep sparrows away from our premises. As a result, we see less number of sparrows now. We can prepare sparrow nests with cardboard boxes and feed them with grains and water. This will attract sparrows to live among us. It will save the house sparrows from extinction.
Question 2.
The nest-building procedure of sughari size – colour – appearance – weaver bird is gifted with the skill of weaving nests-it prefers long thread-like grass leaves to build
the nests – male weaver birds build nests – the male invites the female for pairing when the nest is half-complete – female approves – they (make a pair-if disapproves, the nest is sabandoned-a beauty and wonder of nature
Answer:
The weaver bird, known as sughari in Gujarati, is a small bird. Both, males and females are brownish in colour. But the male has a bright yellow crown, with yellowish neck. The sughari has been gifted with the skill of weaving its nests. It prefers long thread-like grass leaves to build its nest, The male weaver bird builds the nest.
It takes nearly 18 days to complete nest building. When the nest is half-completed, the male invites the female for pairing by its song. If she accepts the nest, both of them finish the nest. If she doesn’t, the nest is abandoned. Therefore a male often makes many nests during nesting season. It is a beauty and wonder of nature.
Question 3.
Bird migration
thousands of birds migrate from Europe,Siberia and other cold countries – pelicans, cranes, various ducks and rosy pastors travel thousands of kilometres to fly to India – they take help of the sun to find their way-these birds fly in different patterns
Answer:
Every year, thousands of birds migrate to India from the cold regions of Europe, Siberia and other countries. Birds like pelicans, cranes, various ducks and rosy pastors travel thousands of kilometres to fly to India. The migratory birds take help of the sun to find their way. While coming, they travel in morning and during their return migration they fly in the evening. Migratory birds fly in different patterns. Birds like cranes, ducks and geese fly in a formation of ‘V’ shape. Certain ducks, warblers and flycatchers travel in groups.
8. Give your views. You may use your mother tongue. (Classroom / Individual Activity)
(1) Along with your friends, prepare a list of, birds found in your surroundings. Mention their chief characteristics.
(2) Save birds. Suggest a few steps to save the birds that we find around, (work in pairs)
(3) Reflect and give your ideas on ‘Birds are our best friends’.
Language Practice
Read the conversation.
Vismay: I watched a nice movie Bhag Milkha Bhag.
Sharan : What is it about ?
Vismay: You really don’t know ? It is about the life of Milkha Singh. He is a former Indian track and field sprinter.
Sharan : Oh, he is an athlete!
Vismay: Yes, but originally he was in the Indian Army and participated in sports through it.
Sharan: He must have set many records.
Vismay:Yes. He won gold medals in 1958 and 1962 Asian Games. He also represented India in the Summer Olympics at Melbourne, Rome and Tokyo. But his 1960 Olympic 400 m race will always be remembered. He was fourth but set Indian National Record and held it for 41 years.
Sharan:Wow, what a man!
![]()
I Vismay: Indeed, he is. He is known as ‘The Flying Sikh’.
Now read this news report on Milkha Singh and notice the underlined parts.
Bhag Milkha Bhag is a biographical movie by Rakesh Mehra, starring Farhan Akhtar as the famous athlete Milkha Singh.
(1) Milkha Singh, who is a former track and field sprinter, is known as ‘The Flying Sikh’.
(2) He was born in Govindpur which is in Pakistan after the partition of India.
(3) The young boy, whose parents were killed in riots after partition, came to India and joined the Indian Army as a sepoy.
(4) The sepoy who participated in a race at the army camp was noticed by an officer.
(5) He is famous for the record that he set at the Rome Olympics in 400 m race by completing it in 45.73 seconds.
(6) The Flying Sikh who brought glory to the country was also awarded the Padma Shri, the Padma Shri, ktdias fourth-highest civilian honour.
2. Complete the table using sentences numbered 1 to 6 in the above news report on Milkha Singh.
|
Sentence no. |
Talked about who | What | Connector | What is said |
| 1. | Milkha Singh | is a former track and field sprinter | who | is known as the Flying Sikh |
| 2. | He | is in Pakistan after the partition of India | which | was born in Govindpur |
| 3. | The young boy | parents were killed in riots after the partition | whose | came to India and joined the Indian Army as a sepoy |
| 4. | The sepoy | participated in a race at the army camp | who | was noticed by an officer |
| 5. | He | he set at the Rome Olympics in 400 m race by completing it in 45.73 seconds | that | is famous for the record |
| 6. | The Flying Sikh | brought glory to the country | who | was also awarded the Padma Shri, India’s fourth-highest civilian honour |
3. (A) Join the sentences using ‘who’.
(1) The man is from Jamaica. He won 9 Gold Medals.
The man, who won 9 gold medals, is from Jamaica.
(2) Nelson Mandela became the President of South Africa. He spent 27 years in jail.
Nelson Mandela, who spent 27 years in jail, became the President of South Africa.
(3) Kailash Satyarthi is an Indian activist. He won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2014.
Kailash Satyarthi, who won the Nobel Peace Prize in 2014, is an Indian activist.
(B) Join the sentences using ‘whose’.
(1) I met a man in London. His brother works in Ahmedabad.
I met a man, whose brother works in Ahmedabad, in London.
(2) A woman is on the phone. Her name is Sharon.
A woman, whose name is Sharon, is on the phone.
![]()
(3) The man is a doctor. His TV show is popular.
The man, whose TV show is popular, is a doctor.
(C) Join the sentences using ‘which / that’.
(1) Our house is on M.G. Road. We rented it.
Our house, which we rented, is on M.G. Road.
(2) Let’s go for dinner in the hotel. The hotel is close to our home.
Let’s go for dinner in the hotel that is close to our home.
(3) The shop is in Tower – II of the Crescent Arcade. Tower – II is towards the river side.
The shop is in Tower – II, which is towards the riverside, of the Crescent Arcade.
4. Add information given in the s brackets using who, whose, which or that.
Example:
She worked for a man (the man used to, be an athlete).
She worked for a man who used to be an athlete.
(1) That man is from Sri Lanka (the name of that man is Tilakaratne Dilshan).
That man, whose name is Tilakaratne Dilshan, is from Sri Lanka.
(2) Lucknow is the capital of Uttar Pradesh (the capital of Uttar Pradesh is famous for its culture, tahezib (mannerism) and food).
Lucknow, which is famous for its culture, tahezib (mannerism) and food, is the capital of Uttar Pradesh.
(3) Usain Bolt is a Jamaican athlete (the Jamaican; athlete is known as the ‘Fastest Man on the Earth’ with 9 Olympic gold medals).
Usain Bolt, who is known as the ‘Fastest Man on the Earth’ with 9 Olympic gold medals, is a Jamaican athlete.
(4) Is that the man? (the man lives near your society)
Is that the man who lives near your society
(5) Ahmadabad is famous for the River Front- Project (the project is on the banks of the river Sabarmati).
Ahmedabad is famous for the River Front Project which is on the banks of the river Sabarmati.
(6) Dr Arpit Bindra is a businessman (the businessman’s son won the Olympic gold medal in Rifle Shooting).
Dr Arpit Bindra, whose son won the Olympic gold medal in Rifle Shooting, is a businessman.
(7) Jaipur is the capital town of Rajasthan (the town is known as the Pink City).
Jaipur, which is known as the Pink City, is the capital town of Rajasthan.
5. Read the paragraph and underline the parts that add information about a person or place. One is done for you.
The town of Dalhousie, which is situated at the height of about 6700 feet, is the perfect place for summer holidays, and the Hotel Pirpanjal View, which faces the snow covered mountain range, is the perfect place to stay. Two artist brothers, who bought this hotel premises 30 years ago, is a famous accommodation now.
![]()
In addition to the view that the hotel offers, Vicky, whose cooking is one of the reasons why the Hotel Pirpanjal View is so popular in Dalhousie. The guests, whom the hotel staff treat as family members, are always delighted to stay there. Shri Subhash Chandra Bose, who once stayed in the hotel, recovered from serious illness after spending time in Dalhousie.
6. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate options from the list and read the paragraph aloud. You may just write the appropriate number from the table and read the complete paragraph.
1. whose shouts were heard at a distance
2. who was hurt by the fall
3. whose mangoes were stolen
4. which were in his pockets
5. that the boy had plucked.
6. in which a bicycle could not go
7. which were just beginning to ripe
8. whose pockets had grown big
9. which was five feet high
10. who was the owner of the farm
The boy who had come away from school went to a mango orchard. He jumped over the hence, which was five feet high, and reached a mango tree. He plucked many mangoes, which were just beginning to ripe, and put them in his pockets.
As he was trying to jump the fence while coming out, he slipped and fell, and some of the mangoes, which were in his pockets, rolled away. Rahimbhai, who was the owner of the farm, realized that someone has entered the farm. He immediately jumped on his bicycle and rode towards the boy. But the boy, who was hurt by the fall, ran off along a very narrow lane, in which a bicycle could not go. The farm owner, whose mangoes were stolen, was chasing the boy.
![]()
But the boy could reach the school. The boy, whose pockets had grown big with the mangoes was spotted by a teacher. The farm owner, whose shouts were heard at a distance, also reached the school. The farm owner complained the teacher. The teacher asked the boy to apologize and return the mangoes that the boy had plucked.
7. Follow the examples of sentence parts in L. 6 starting with who, whose and which. Replace the word/s in the brackets and complete the sentences.
The farm owner, who was very fat (very fat), soon became breathless. His bicycle was too difficult to ride. He jumped off his bicycle, which was very old (very old) and hid it behind bushes. He ran along the path, which was narrow (narrow). The boy, who was hiding : behind a tree (hide behind a tree), watched the man go past.
The boy now ran back and took the bicycle that was hidden behind the bush (hide behind the bush). The man had forgotten to lock his bicycle. The boy, who was now very tired (now very tired), got on the bicycle and rode off. When he reached a place that was near the school (near the school), he left the bicycle there and went away. The cycle, which was left there (left there), was later found by l the farm owner.
Writing
Question 1.
You found a seriously injured pigeon in your compound on the day of Uttarayan. Use the mixed up clues given in the brackets and write what you did to help and save the bird. You can add your own ideas also.
Answer:
(wound – string – corn -pull out- give – from its wings – helpline for birds – wash – telephone)
First of all I kept the pigeon at a safe place. I made sure there were no other birds or animals around. Then I carefully pulled out the string from its wings.
I took cotton and gently cleaned its wound with water. Later I made the bird comfortable by covering it with a soft cloth. I also gave it some grains to eat and water to drink. Mean while I called up the bird help line and told them about the injured bird. Soon they came and took it away.
![]()
Question 2.
Spandan attended a lecture on ‘Save the Birds’ given by a famous bird watcher Shri Lalsinh Raol. He has made notes of what he heard. Read the notes and in groups of 3, prepare your own speech on
Answer:
‘Save the Birds’. Importance of Birds: important part of nature – help maintain the eco-system – beautify surroundings.
Reasons of decreasing number of birds:
concrete buildings with no nesting site – cell phone radiation – unleaded petrol and insecticides – increasing noise of automobiles – cutting of trees – chemical fertilizers – excessive use of – wireless devices.
Remedies to save the birds: bird-boxes and bird feeders outside houses and gardens-a bowl of fresh water every day-growing plants and fences to encourage some of the common birds to come back-big bowls with cool water to bathe in – broken rice in open space for birds to feed on
Answer:
Save the Birds
I will begin my speech by taking about the importance of birds in our lives. Birds are a very important part of nature. They are help to maintain the balance in the eco-system. Besides this, they also beautify surroundings and enliven the atmosphere by their sweet chirping.
Birds are very useful to us. Some birds eat the insects that are harmful to the crops. Some birds also help in spreading seeds. Vultures ( keep our surroundings clean by eating the carcasses. The peacock is called the harbinger (indication) of rains. All of us are fascinated when the peacock spreads its feathers and dances. But today, most of the birds have become endangered species.
Why is it so ? Well, we are majorly responsible for creating this imbalance in / the eco-system. For example, we rarely see the house sparrow now. What happened to them? Well, we human beings have destroyed their homes. We have designed our houses in such a way that sparrows cannot enter into them. They do not find safe places to build their nests.
![]()
We have started cutting trees for concrete buildings. The birds have lost their homes and food. Another important reason for decline in the number of birds, especially sparrows, is the radiation from the cell phone towers. Excessive use of wireless devises is also a danger to the birds.
We use unleaded petrol, chemical fertilizers and insecticides. This is harmful to the birds. There is a lot of noise pollution, air pollution and water pollution. As a result, we see less and less number of birds in cities. Are there any remedies to save the birds ? Yes,there are. Let us all bring the birds back into our lives. We should keep bird-boxes and bird feeders outside our houses and in thegardens. We should feed them with grains and keep a bowl of fresh water for them.
If there is enough space, we can keep big bowls of cool water for them to bathe in. We should plant trees to encourage some of the common birds to come back. Let us all work hard to have these beautiful birds all around us. Thank you for listening to me.
Question 3.
Homework + Project work : Here are some samples of bird feeders made from worn out and scrap materials. Make a bird feeder of your choice using worn out or scrap materials. For example, you can use a five litre empty oil jar, or an empty water bottle and plates, spoons etc. (Classroom / Individual Activity)
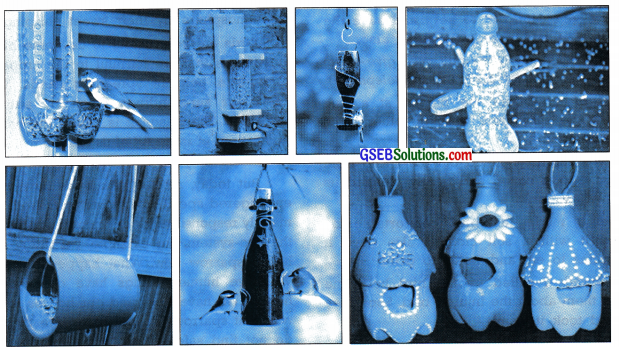
Now narrate the process of building a bird feeder. You can use these points if you wish.
(things required-a hole in the side of the bottle to allow a free flow of seeds-pass ice cream spoons through the holes-few small holes at the bottom-fill with seeds-hang on a wire)
Question 4.
Write a paragraph on ‘My Favourite Feathered Friend’ with help of the given clues. Draw / Paste the picture of that bird in your notebook.
(types of birds-your favourite bird-name – habitat – habits – special features – food – shape – size – usefulness – colour – reason for liking -places where you see it-your feelings when you see it)
Answer:
There are so many types of birds around us. But my favourite bird is the peacock. The peacock is our national bird. It is a very beautiful bird. It has a long and slender neck. It has a crest on its head. It has long, beautiful and colourful feathers. The peacock has a very charming walk. It is called the harbinger of rains. We can hear its sweet call during the rainy season.
![]()
It spreads out its colourful feathers like a fan and dances in the rain. It is a great pleasure to see it dancing. The peacock lives on trees. It is usually found in fields and forests. It feeds on grains, insects and worms. It also catches snakes and eats them up.
Therefore, the peacock is called an enemy of snakes. The peacock cannot fly very high. It has a slow but graceful walk. It struts about majestically. The female peacock is called a peahen. The peahen does not have colourful feathers. It does not look beautiful. It is a plain bird.
The feathers of the peacock are used to make many decorative items. Children love peacock feathers. They like to keep its feathers in their books. It is also said that Lord Krishna wore a crown made of the peacock feathers. We can see the peacock in a zoo.
Exam-Oriented Study Material
1. Read the extracts and answer the questions.
(1) It is a fresh and pleasant morning. Birds are chirping and the wind is cool and , calm. Shubhangi, with her family, is having tea and breakfast in their garden. Devangi, Shubhangi’s sister Mitra’s friend, has come to stay for a couple of days. Devangi is a student of second year zoology in M. S. University, Vadodara. Shubhangi, fascinated by the call of a bird exclaims, ‘What a beautiful sparrow it is !’ Devangi promptly corrects her, “My dear, it is not a sparrow. It is a tailor bird. See its colour is yellowish green and it is smaller than a sparrow.”
Shubhangi :You are right, didi. But the day before yesterday when I saw it, its colour was rust.
Devangi: Look, Shubhu, this one is a male and the rust was a female.
Question 1.
What is Shubhangi doing in the garden ?
Answer:
Shubhangi is having tea and breakfast with her family in the garden.
Question 2.
Describe the atmosphere.
Answer:
The morning is fresh and pleasant, birds are chirping and the wind is cool and calm.
Question 3.
Who is Devangi ?
Answer:
Devangi is Shubhangi’s sister’s friend.
Question 4.
What does Devangi study? Where?
Answer:
Devangi studies zoology in the M. S. University in Vadodara.
Question 5.
What does Devangi tell Shubhangi about the tailor bird?
Answer:
Devangi tells Shubhangi that the tailor bird is yellowish green in colour and is smaller than a sparrow.
![]()
Question 6.
What does Devangi tell Shubhangi about the tailor bird’s colour?
Answer:
Devangi tells Shubhangi that the male tailor bird is yellowis green in colour and the female is rust in colour.
(2) Shubhangi: Why is it so ? I have observed the female in almost all the species is dull in comparison with the male.
Devangi: It seems that you have keen interest in birds.
Shubhangi: Oh yes, didi. See, Mitra didi is always busy with her projects. Will you, please, tell me more about birds ?
Devangi: It is my interest and not Mitra’s.
I will be happy to talk about birds. Mitra, will you, please, bring a book I from my bag titled ‘Birds of India’ by Salim Ali?
Question 1.
Who has a keen interest in birds ?
Answer:
Shubhangi has a keen interest in birds.
Question 2.
The female in all the species is
Answer:
The female in all the species is dull in comparison with the male.
Question 3.
Name the book written by Salim Ali.
Answer:
Birds of India.
Question 4.
What did Shubhangi want to know from Devangi ?
Answer:
Shubhangi wanted to know about birds from Devangi.
(3) Devangi: Listen, Shubhangi, there are jungle birds, water birds and birds that live near human habitats. This tailor bird is a bird of our surrounding. It stitches its nest with green leaves and fibres of trees. That’s why it is called a tailor bird.
Shubhangi: That’s great! But why do the female and the male have different colours We have same colours.
Devangi: Oye chulbul! There are two major types of birds : birds of prey and small birds. Birds of prey hunt small birds for food. The female bird should be dull to hide itself from hunters as it is supposed to continue generations.
Shubhangi: Wonderful! What a design of Nature!
![]()
Question 1.
What are the different kinds of birds?
Answer:
The different kinds of birds are: jungle birds, water birds and birds that live near human habitats.
Question 2.
Which bird is a bird of our surrounding ?
Answer:
The tailor bird is a bird of our surrounding.
Question 3.
The tailor bird stitches its nest
Answer:
The tailor bird stitches its nest with green leaves and fibres of trees.
Question 4.
How does the tailor bird get its name ?
Answer:
The tailor bird stitches its nest with green leaves and fibres of trees and so it is called a tailor bird.
Question 5.
Name the two major types of birds.
Answer:
The two major types of birds are birds of prey and small birds.
Question 6.
What do the birds of prey do ?
Answer:
The birds of prey hunt small birds for food.
Question 7.
Why is the female bird dull in colour ?
Answer:
The female bird is dull in colour so that it can hide itself from hunters l as it is supposed to continue generations.
(4) Devangi: Birding is my passion, Mitra. Look, Shubhangi! Here is a picture of a tailor bird’s nest.
Shubbangi :Wow ! It’s cool.
Devangi: Let’s talk about another interesting bird. Look this is the Indian Grey Hornbill. This bird is common in the Indian subcontinent. It has grey feathers all over the body with light grey and dull belly.
Shubhangi :Yup didi, Where does it live ?
Devangi: Its habitat is both in the wild as well as urban areas, especially large trees.
Question 1.
What is Devangi passionate about ?
Answer:
Devangi is passionate about birding.
Question 2.
Where is the Indian Grey Hornbill usually found?
Answer:
The Indian Grey Hornbill is usually found in the Indian subcontinent.
Question 3.
Describe the Grey Hornbill.
Answer:
The Grey Hornbill has grey feathers all over the body with light grey and dull belly.
Question 4.
Where does the Grey Hornbill live ?
Answer:
The Grey Hornbill lives in large trees in both the wild as well as urban areas.
(5) Shubhangi: Its beak is quite strange, isn’t it?
Devangi :Yes, dear. Its beak or bill has an extra portion like a horn and that’s why it is called hornbill. One more interesting thing is that it nests in hollows of tall trees. The female enters the nest hollow and seals it by the using mud-pellets supplied by, the male. The male takes care of the female and its new-born chicks. It supplies food to the mother and chicks.
Shubhangi :What a caring dude
Devangi: Such a difficult task to feed the whole family For the whole day, it has to collect food. For its caring behaviour for female, it is called vahu ghelo in some areas of our state, meaning one who takes extra care of his wife.
![]()
Question 1.
How does the hornbill get its name?
Answer:
The hornbill’s beak or bill has an extra portion like a horn and so it is called hornbill.
Question 2.
Where does the hornbill build its nest?
Answer:
The hornbill builds its nest in the hollows of tall trees.
Question 3.
What does the female hornbill do?
Answer:
The female hornbill enters the nest hollow and seals it by the using mud-pellets supplied by the male.
Question 4.
What does the male hornbill do ?
Answer:
The male hornbill takes care of the female and its new-born chicks by supplying food to them.
Question 5.
What does Shubhangi call the male hornbill ?
Answer:
Shubhangi calls the male hornbill ‘a caring dude’.
(6) Shubhangi: When I visited my friend Nazmin’s home in the Polo forest, I saw many nests of weaver birds on babool trees. So beautiful! How do they build their nest ?
Devangi: Look at this picture in the book.
It is a weaver bird. The bird is known as sughari in Gujarati, meaning one who builds a beautiful house. Almighty has gifted us different skills and the weaver bird is gifted with the skill of weaving its nests. Weaver birds prefer long thread-like grass leaves to build their nests.
Question 1.
Where does Nazmin live?
Answer:
Nazmin lives in the Polo forest.
Question 2.
What did Shubhangi see in the Polo forest ?
Answer:
Shubhangi saw many nests of weaver birds on babool trees in the Polo forest.
![]()
Question 3.
What is the weaver bird called in Gujarati ?
Answer:
The weaver bird is called sughari in Gujarati.
Question 4.
Sughari means
Ans .
Sughari means one who builds a beautiful house.
Question 5.
Which skill is the weaver bird gifted with ?
Answer:
The weaver bird is gifted with the skill of weaving its nest.
Question 6.
What does the weaver bird use to weave its nest ?
Answer:
The weaver bird uses long thread – like grass leaves to build its nest.
(7) Shubhangi: Didi, who builds a nest, the male bird or the female bird?
Devangi: Male weaver birds build nests.
It takes nearly 18 days to complete nest building. When the nest is half completed, the male invites the female for pairing by its song. If she accepts the nest, both of them finish the nest. If she doesn’t, the nest is abandoned.
Shubhangi: Then it must be very difficult for the male to build more than one nests.
Devangi :Yes, absolutely right. A male often makes many nests during the nesting season.
Question 1.
Who builds the weaver bird’s nest ?
Answer:
A male weaver bird builds its nest.
Question 2.
How long does it take to complete the nest ?
Answer:
It takes nearly 18 days to complete the nest.
Question 3.
What does the male do when the nest is half-completed ?
Answer:
When the nest is half completed, the male invites the female for pairing by its song.
Question 4.
If the female weaver bird accepts the nest.
Answer:
If the female weaver bird accepts the nest, both of them complete the nest.
Question 5.
What happens if the female weaver bird does not accept the nest ?
Answer:
If the female weaver bird does not accept the nest, it is abandoned.
Question 6.
A male often makes
Answer:
A male often makes many nests during the nesting season.
(8) Devangi: Shubhangi, the birds are not only our friends, but they also help us in many ways. You know the vulture. Generally people do not like vultures as they eat carcasses or dead animals. But they are called scavengers as they clean our surrounding by eating the rotten dead bodies.
Observe its beak in the picture. It is designed to tear the flesh from dead bodies.
Shubhangi :Yes, the curve of the beak is very sharp. Didi, I have ? not seen any vulture soaring in the sky for last so many 5 months. What is the reason?
Devangi: At present people use medicine to cure sick cattle. When that cattle dies, vulture eats its body. Diclofenac is very harmful for the vulture, After eating such flesh, it slowly dies within a few days. Nearly 97 % of vulture s population is lost.
Question 1.
People do not like vultures because
Answer:
People do not like vultures because they eat carcasses or dead animals.
Question 2.
Why are vultures called scavengers ?
Answer:
Vultures are called scavengers because they clean our surrounding by eating the rotten dead bodies.
Question 3.
The beak of the vulture
Answer:
The beak of the vulture is designed to tear the flesh from dead bodies.
Question 4.
Why are vultures not seen in the sky?
Answer:
People use a medicine called diclofenac to cure sick cattle and when these cattle die, the vultures feed on them and die within a few days as diclofenac is very harmful to them.
(9) Shubhangi: It simply means that we, the human beings, are very selfish. We do not care for other living beings on the earth. Why are we not doing anything to save the birds How can we help the birds ?
Devangi :You can offer grains and water to birds. Nowadays, we get to see very few sparrows, right ? Where have they gone ? What does Shubhangi say about human beings
Answer:
Shubhangi says that human beings are very selfish because they do not care for other living beings on the earth.
Question 2.
How can we help the birds?
Answer:
We can help the birds by offering them grains and water.
Question 3.
Which birds are not to be seen nowadays ?
Answer:
The sparrows are not to be seen nowadays.
![]()
(10) Devangi:They have left us because we have destroyed their homes.
Shubhangi: How ? I haven’t done that mischief.
Devangi: No, sweetheart. Actually we have designed our houses in such a way that the birds cannot enter into the house. We do not allow them to nest in our premises. They feel safe living with us. That’s why we call them the house sparrows.
Shubhangi :Well, I want them back and I am sure my friends will also help me.
Devangi: Ok. You can prepare sparrow nests with the help of cardboard boxes. Do not feed birds ganthiyas, as it is very harmful to their stomach. Put some grains like rice, millet etc. and water in a dish.
Question 1.
Why have the sparrows left us ?
Answer:
The sparrows have left us because we have destroyed their homes.
Question 2.
We have designed our houses in such a way that
Answer:
We have designed our houses in such a way that the birds cannot enter into the house and make nests.
Question 3.
The house sparrows feel safe
Answer:
The house sparrows feel safe living with us.
Question 4.
What does Devangi ask Shubhangi to prepare ?
Answer:
Devangi asks Shubhangi to prepare sparrow nests with the help of cardboard boxes.
Question 5.
What should we offer to the birds ?
Answer:
We should offer grains like rice and millet and some water in a dish to the birds.
Question 6.
We should not feed ganthiyas to the birds because
Answer:
We should not feed ganthiyas to the birds because it is harmful to their stomach.
(11) Shubhangi: Please tell me about migratory birds.
Devangi :Well Shubhu, every year we have thousands of birds as our guests from Europe, Siberia and other cold countries. Birds like pelicans, cranes, various ducks and rosy pastors travel thousands of kilometres to fly to India.
Shubhangi: Rosy pastor ! This name sounds sweet. What is that ?
Devangi: It is a bird like our myna. Rosy pastor is vaiya in Gujarati. Its colour is dull brown and pink.
Shubhangi: It is the same one I see during winter, flying in the flock.
Devangi: Good observation. This bird arrives in India in June / July from Europe and returns in March / April.
Question 1.
What are migratory birds?
Answer:
Birds that travel to India every year from other cold countries are called migratory birds.
Question 2.
From where do the migratory birds come ?
Answer:
Migratory birds come from Europe, Siberia and other cold countries.
Question 3.
Name some migratory birds that come to India.
Answer:
Some migratory birds that come to India are pelicans, cranes, various ducks and rosy pastors.
Question 4.
What is the rosy pastor called in Gujarati ?
Answer:
The rosy pastor is called vaiya in Gujarati.
Question 5.
What colour is the rosy pastor ?
Answer:
The rosy pastor is dull brown and pink.
![]()
Question 6.
When does the rosy pastor arrive in India ? When does it return ?
Answer:
The rosy pastor arrives in India in June / July from Europe and returns in March/April.
(12) Shubhangi: How do they travel without any map ?
Devangi: They take help of the sun to find their way. While they come, they travel in the early morning and during return migration they fly in the evening.
Shubhangi: Do they all use the same pattern for migration ?
Devangi: Of course not. Migratory birds fly in different patterns. Birds like cranes, ducks and geese fly in a formation of ‘V’ shape.
Certain ducks, warblers and flycatchers travel in groups.
Question 1.
How do the migratory birds travel without any map ?
Answer:
The migratory birds take help of the sun to find their way
Question 2.
When the migratory birds come, they travel
Answer:
When the migratory birds come, they travel in the early morning.
Question 3.
When the migratory birds go, they fly
Answer:
When the migratory birds go, they fly in the evening.
Question 4.
In which pattern do cranes and geese fly?
Answer:
Cranes and geese fly in a V shape formation.
Question 5.
Which birds travel in groups ?
Answer:
Certain ducks, warblers and flycatchers travel in groups.
(13) Shubhangi: Oh god! How can I remember all the details ?
Devangi: That’s easy. Remember these steps while birding.
1. See the colour of the bird
2. Observe its size.
3. Notice the shape and length of the bill and tail.
4. Place of sight like perched on a tree or wire, in water body, open ground, grassland or sky. Apart from these tips, you can ‘give your close friend’s name to that bird whose nature or any characteristic matches with the friend.
Question 1.
What things should you observe while birding ?
Answer:
While birding, we should observe the colour and size of the bird, the shape and length of its bill and tail and where it is perched.
Question 2.
You can give your close friend’s name to that bird
Answer: You can give your close friend’s name to that bird whose nature or any characteristic matches with the friend.
(14) Mitra : Remember, Shubhu ! We need birds on the earth as they eat up insects harmful to our crops. They are also helpful in spreading of seeds. They entertain us with their sweet s calls. Take care of birds; they are the true indicators of a healthy environment.
Question 1.
How are birds useful to us ?
Answer:
Birds eat up insects that are harmful to our crops, spread seeds and entertain us with their sweet calls.
Question 2.
Birds are the true indicators of
Answer:
Birds are the true indicators of a healthy environment.
2. Frame sentences using the given set of words. You may change the forms of the words.
(1) fascinate – chirping
Mohini was fascinated by the chirping of birds in the garden.
(2) comparison – observe
Please observe the birds carefully and compare their colour and size.
(3) difficult task – collect
It is a difficult task to collect a huge fund in such a short time.
![]()
(4) gift – skill
God has gifted each one of us with ‘f different skills.
(5) selfish – care – destroy
We are so selfish that we destroy trees
and do not care about environment.
(6) harmful – spread
Dirty water is harmful as it spreads
mosquitoes that cause malaria.
3. Fill in the blanks selecting the correct words from the brackets.
(1) (information, discussion, prepare, collected)
The meeting was held to prepare a plan for the festival of Diwali. The secretary gave all the information about the funds collected by the society. The plan was finalized after a long discussion.
(2) (promptly, introduced, explained, invited)
The host of the quiz invited the teams on the stage and introduced the participants. He then explained the rules. In the first round, the team that knows the answer has to ring the bell promptly and give the answer.
(3) (return, pleasant, nature, healthy)
Going for an early morning walk on a pleasant winter morning is a good way to be healthy. Every morning, I go for a walk at 5 o’clock and return home by 6 o’clock! I really enjoy the beauty of nature in the morning.
(4) (reason, keen, passion, observes)
Mitali has a keen interest in birds. She observes birds wherever she goes. Birding is her passion. That is the reason she often visits the nature parks.
(5) (patterns, travel, shape, formation)
Migratory birds fly in different patterns. Birds likes geese fly in a formation of ‘V’ shape. Some birds travel in groups.
(6) (remember, surroundings, destroys, environment)
Cutting trees destroys our environment. We must remember that trees are not only useful to us, but they also make our surroundings beautiful.
(7) (selfish, wild, hunted, species)
Wild animals living in jungles are hunted by selfish people, who do not care about preservation of wildlife. As a result, many species of birds and animals are becoming extinct.
(8) (accepts, prefers, abandoned, gifted)
The weaver bird is gifted with the skill of weaving its nest. It prefers long thread like grass leaves to build its nest. If the female accepts the nest, both of them l finish the nest. If she doesn’t, the nest is abandoned.
(9) (task, strange, caring, behaviour)
The teacher found that the behaviour of the new student was quiet strange. In spite of her caring attitude, the boy continued to behave rudely. Improving his behavior seemed to be an impossible task for the teacher.
(10) (spread offered, arrived, supply)
Many diseases have spread after floods. A team of doctors has arrived in the village to help the flood-affected people. The government has offered to supply free medicines to the poor.
4. Write short notes using the given questions/ points.
Question 1.
The House Sparrow
(size – small bird – make atmosphere alive-live around human beings-feels safe – destroyed its home-design of our houses-the bird cannot enter-we keep them away from our premises-so less in number – prepare sparrow nests-feed them-save them from extinction)
Answer:
The house sparrow is a small bird. It is a very friendly bird. It makes the atmosphere alive by its constant chirping. It likes to live around human beings. It feels safe in living with us. But we have destroyed its home. We design our houses in such a way that a sparrow cannot enter into our house. We keep sparrows away from our premises.
![]()
As a result, we see less number of sparrows now. We can prepare sparrow nests with cardboard boxes and feed them with grains and water. This will attract sparrows to live among us. It will save the house sparrows from extinction.
Question 2.
The Weaver Bird’s Nest
(what it is called in Gujarati – small bird – gifted with the skill of weaving nests – prefers long thread-like grass leaves to build the nests-male weaver birds build nests – the male invites the female for pairing when the nest is half- complete – female approves – they complete the nest-if female disapproves, the nest is abandoned)
Answer:
The weaver bird, known as sughari in Gujarati, is a small bird. It is gifted with the skill of weaving its nests. It prefers long thread-like grass leaves to build its nest. The male weaver bird builds the nest. It takes nearly 18 days to complete nest building.
When the nest is half- completed, the male invites female for pairing by its song. If she accepts the nest, both of them finish the nest. If she doesn’t, the nest is abandoned. Therefore a male often makes many nests during nesting season.
Question 3.
Migratory Birds
(thousands of birds migrate from Europe, Siberia and other cold countries – pelicans, cranes, various ducks and rosy pastors – take help of the sun to find their way-fly in different patterns)
Answer:
Every year, thousands of birds migrate to India from the cold regions of Europe, Siberia and other countries. Birds like pelicans, cranes, various ducks and rosy pastors travel thousands of kilometres to fly to India. The migratory birds take help of the sun to find their way.
While coming, they travel in morning and during their return migration, they fly in the evening. Migratory birds fly in different patterns. Birds like cranes,ducks and geese fly in a formation of I- ‘V’ shape. Certain ducks, warblers and flycatchers travel in groups.
Question 4.
The Vulture
(Why do people not like the vultures ?-Why : are they called scavengers ?-How does it use its heak ? – Why do we see very few ; vultures now ? – How is diclofenac harmful ; to vultures ?
Answer: People do not like vultures as they eat ; carcasses or dead animals. But they clean our surrounding by eating the rotten dead bodies. And so they called scavengers.
A vulture has a sharp beak. It is designed to tear the flesh from l dead bodies. But today, we see very few vultures. People use a medicine called diclofenac to cure sick cattle. When that cattle dies, the vultures eat its body. Diclofenac is very harmful to them. So after eating such flesh, they slowly die within a few days. Nearly 97 % of vulture population is lost in this way.
Question 5.
The Indian Grey Hornbill
(common in Indian subcontinent – grey feathers with light grey and dull belly-lives in the wild and urban areas-beak has an extra portion like a horn – nests in hollows of tall trees-female enters the nest – seals it with mud-pellets – male takes care-called ‘vahu ghelo’ for his caring behaviour)
Answer:
The Indian Grey Hornbill is common in the Indian subcontinent. It has grey feathers all over the body with light grey and dull belly. Its habitat is both in the wild as well as urban areas, especially large trees. Its beak or bill has an extra portion like a horn and that’s why it is called hornbill.
The hornbill nests in the hollows of tall trees. The female enters the nest hollow and seals it by the using mud-pellets supplied by the male. The male takes care of the female and its new-born chicks. It supplies food to them. For his caring behaviour for the female, it is called vahu ghelo in Gujarati.
5. Select the title of the Read related with each sentence.
(Note: Important sentences of this Read are given here.)
(1) Shubhangi is fascinated by the call of a bird
(2) See its colour is yellowish green and it is smaller than a sparrow.
(3) This one is a male and the rust was a female.
(4) I have observed the female in almost all the species is dull in comparison with the male.
(5) It stitches its nest with green leaves and fibres of trees.
(6) Why do the female and the male have different colours ?
(7) The female bird should be dull to hide itself from hunters as it is supposed to continue generations.
(8) What a design of Nature !
(9) Its habitat is both in wild as well as urban areas, especially large trees.
(10) Its beak or bill has sin extra portion like a horn.
(11) The female enters the nest hollow and seals it by the using mud-pellets supplied by the male.
(12) It supplies food to the mother and chicks.
(13) For its caring behaviour for female, it is called vahu ghelo in some areas of our state.
(14) It takes nearly 18 days to complete nest building.
(15) If she accepts the nest, both of them finish the nest.
(16) A male often makes many nests during the nesting season.
(17) They are called scavengers as they clean our surroundings by eating the rotten dead bodies.
(18) It is designed to tear the flesh from dead bodies.
(19) They have left us because we have destroyed their homes.
(20) We have designed our houses in such a way that the birds cannot enter into the house.
(21) How do they travel without any map?
(22) They take help of the sun to find their way.
(23) While they come, they travel in the early morning and during return migration they fly in the evening.
(24) They are also helpful in spreading of seeds.
(25) They are the true indicators of a healthy environment.
6. Fill in the blanks selecting the correct words from the brackets.
(painted, buy, Wow, piece, How beautiful)
“Look at this picture,” said Manoj. “How beautiful it is !” said Pratik, praising the lovely colours in the picture. “Did you buy it ?” he asked. “Oh, no,” said Manoj. “I painted it myself.” “Wow!” said Pratik. “It’s a wonderful piece of art.”
![]()
7. Write the correct question to get the underlined word / words as answers.
Question 1.
There are three types of tulips.
A. Which are the three types of tulips?
B. How many types of tulips are there ?
C. Where are the three types of tulips ?
D. Who has the three types of tulips?
Answer:
(B) How many types of tulips are there?
Question 2.
Mita saw a cuckoo in the neem tree.
A. How did Mita see a cuckoo in the neem tree ?
B. When did Mita see a cuckoo ?
C. Where did Mita see a cuckoo ?
D. Who saw a cuckoo in the neem tree?
Answer:
(C) Where did Mita see a cuckoo ?
Question 3.
Ramji looks after our garden.
A. Who looks after our garden?
B. What does Ramji do ?
C. Where does Ramji look after the garden ?
D. When does Ramji look after the garden ?
Answer:
(A) Who looks after our garden?
Question 4.
Our team is known as the Lions of Gujarat.
A. Who is known as the Lions of Gujarat ?
B.Why is our team known as the Lions of Gujarat ?
C. How is our team known as the Lions of Gujarat?
D.What is our team known as?
Answer:
(D) What is our team known as?
Question 5.
The teacher will call the students who have registered their names.
A. Whom will the teacher call?
B. Why will the teacher call the students ?
C. How many students will the teacher call ?
D. Where will the teacher call the students ?
Answer:
(A) Whom will the teacher call?
8. Complete the sentences using the functions given in the brackets.
(1) We have sold the house that was build by my grandfather, (describing place)
(2) The lady who is wearing a pink sari is our teacher, (describing person)
(3) This is the girl whose purse was stolen. (describing person)
(4) The Akshardham Temple, which is in Gandhinagar, is a beautiful structure.(describing place)
(5) Mount Abu, which is in Rajasthan, is a famous hill station, (describing place)
(6) Sakshi is the girl who won the medal in wrestling, (describing person)
(7) This is the boy whose parents have come to meet the principal. (describing person)
(8) Patan is the place that is famous for the Rani ki Vaav. (describing place)
9. Complete the dialogue using the functions given in the brackets
Pooja : Ali, who is that man ?
Ali: That is the man who has bought a flat in our building, (describing person)
Pooja :What does he do ?
Ali: He has a shop near the Town Hall on
M.G. Road, (specifying location)
Our Feathered Friends Summary in Gujarati
ખુશનુમા સવાર છે. પક્ષીઓનો કલરવ અને શીતલ, શાંત પવન. શુભાંગી તેના કુટુંબ સાથે તેમના બગીચામાં ચા-નાસ્તો કરી રહી છે. શુભાંગીની બહેન મિત્રાની બહેનપણી દેવાંગી (તેમની સાથે) બે દિવસ રહેવા આવી છે. દેવાંગી વડોદરાની એમ. એસ. યુનિવર્સિટિમાં પ્રાણીશાસ્ત્રની બીજા વર્ષની વિદ્યાર્થિની છે. એક પક્ષીના અવાજથી મંત્રમુગ્ધ શુભાંગી આશ્ચર્યથી કહે છે, “કેટલી સુંદર ચકલી છે!” દેવાંગી તરત જ તેને સુધારે છે, “તે ચકલી નથી. તે દરજીડો છે. જો, તેનો રંગ પીળાશપડતો લીલો છે અને તે ચકલી કરતાં નાનું છે.” શુભાંગી: તારી વાત સાચી છે, દીદી. પણ પરમ દિવસે મેં તેને જોયું ત્યારે તેનો રંગ બદામી હતો. દેવાંગીઃ જો, શુભ. આ નર છે અને બદામી રંગની માદા હતી. શુભાંગીઃ એવું કેમ? મેં જોયું છે કે (પક્ષીઓની) લગભગ બધી જ
જાતમાં નરની સરખામણીમાં માદાનો રંગ ઝાંખો હોય છે. દેવાંગી એમ લાગે છે કે તને પક્ષીઓમાં ઊંડો રસ છે. શુભાંગી : હા, દીદી. જો મિત્રાદીદી હંમેશાં તેના પ્રજેક્ટમાં વ્યસ્ત હોય છે. તું મને પક્ષીઓ વિશે વધારે જણાવીશ, પ્લીઝ? દેવાંગી એ મારો રસનો વિષય છે, મિત્રાનો નહીં. પક્ષીઓ વિશે વાતો કરતાં મને આનંદ થશે. મિત્રો, મારી બૅગમાંથી સલિમ અલીનું પુસ્તક “બડ્ઝ ઑવ ઈન્ડિયા’ લઈ આવીશ, પ્લીઝ?
![]()
મિત્રો કેમ નહિ? જરૂર. માતા-પિતા બાળકો, તમે ચર્ચાની મજા માણો. અમારે હવે જવું પડશે.
દેવાંગીઃ સાંભળ, શુભાંગી. વન્ય પક્ષીઓ, જલપક્ષીઓ અને માનવોના રહેઠાણ નજીક રહેતાં પક્ષીઓ હોય છે. આ દરજીડો એ આપણી આસપાસ રહેનારું પક્ષી છે. તે લીલાં પાંદડાં અને ઝાડના રેસાથી તેનો માળો ગૂંથે છે.
તેથી જ તેને ટેલર-બી (દરજીડો) કહેવામાં આવે છે.
શુભાંગીઃ વાહ! પણ નર અને માદાના રંગો શા માટે જુદા જુદા હોય છે? આપણે તો સરખા રંગ હોય છે. દેવાંગી એય, ચુલબુલ! પક્ષીઓ મુખ્યત્વે બે પ્રકારનાં હોય છે: શિકારી પક્ષીઓ અને નાનાં પક્ષીઓ. શિકારી પક્ષીઓ ખોરાક માટે નાનાં પક્ષીઓનો શિકાર કરે છે. શિકારીઓથી પોતાને છુપાવવા માટે માદાનો રંગ ઝાંખો હોવો જોઈએ કારણ કે તેણે વંશ ચાલુ રાખવાનો હોય છે. શુભાંગી અદ્ભુત! કુદરતની કરામત કેવી છે! મિત્રા દેવાંગી, આ રહ્યું તારું પુસ્તક. તેમાં પક્ષીઓ વિશે ખૂબ રસપ્રદ માહિતી આપવામાં આવી છે.
દેવાંગી: પક્ષીઓ વિશે જાણકારી મેળવવી, એ મારો શોખ છે, મિત્રા. જો શુભાંગી! આ ચિત્ર દરજીડાના માળાનું છે.
શુભાંગીઃ ઓહ! સુંદર છે. દેવાંગી ? ચાલ, આપણે એક બીજા રસપ્રદ પક્ષી વિશે વાત કરીએ. જો, આ ઇન્ડિયન ગ્રે હૉર્નબિલ છે. આ પક્ષી ભારતીય ઉપખંડમાં જોવા મળે છે. તેના આખા શરીર પર રાખોડી રંગનાં પીછા છે અને પેટ ઝાંખા રાખોડી રંગનું છે.
શુભાંગી હા, દીદી. તે ક્યાં રહે છે? દેવાંગી : તેનું રહેઠાણ જંગલમાં તેમજ શહેરી વિસ્તારમાં, ખાસ કરીને મોટાં વૃક્ષોમાં – એમ બંને જગ્યાએ હોય છે. શુભાંગી તેની ચાંચ વિચિત્ર છે, નહીં? દેવાંગી હા. તેની ચાંચ પર શિંગડા (horn) જેવો એક વધારાનો
ભાગ હોય છે અને તેથી જ તેને હોંનબિલ (શિંગડા જેવી ચાંચ) કહેવામાં આવે છે. બીજી રસપ્રદ વાત એ છે કે તે ઊંચાં વૃક્ષોની બખોલમાં માળો બાંધે છે, માદા માળાના પોલાણમાં પ્રવેશ કરે છે અને પછી નર દ્વારા આપવામાં આવતી માટીની ગોળીઓથી તેને (માળાને બંધ કરી દે છે. નર, માદાનું અને નવા જન્મેલાં બચ્ચાંનું ધ્યાન રાખે
છે, તે મા અને બચ્ચાંને ખોરાક પહોંચાડે છે. શુભાંગી : કેટલો પ્રેમાળ નર! દેવાંગી : આખાય કુટુંબને ખોરાક પહોંચાડવાનું કામ કેટલું અઘરું !
![]()
આખોય દિવસ તેણે ખોરાક એકઠો કરવો પડે છે. માદા પ્રત્યે આટલા પ્રેમાળ વર્તન માટે આપણા રાજ્યના કેટલાક વિસ્તારોમાં તેને વહુ-ધેલો – એટલે કે જે પોતાની પત્નીની વધારે પડતી કાળજી લેતો હોય – પણ કહેવામાં આવે છે. શુભાંગી : વાહ ! સરસ. મારા શિક્ષક પણ કહે છે કે આપણે બીજાને મદદરૂપ થવું જોઈએ. શું હું હજી એક પ્રશ્ન પૂછી શકું? દેવાંગી : અવશ્ય. શુભાંગી : જ્યારે હું પોલોના જંગલમાં મારી બહેનપણી નાઝમિનના
ઘરે ગઈ હતી, ત્યારે મેં બાવળના ઝાડ પર સુગરીના કેટલાય માળા જોયા. કેટલા સુંદર ! તેઓ તેમના માળા
કેવી રીતે બાંધતા હશે? દેવાંગી : પુસ્તકમાં આ ચિત્ર જો. આ સુગરી છે, ગુજરાતીમાં તેને સુગરી કહે છે, એટલે કે એ, જે સુંદર ઘર બાંધે છે. ઈશ્વરે આપણને વિવિધ કૌશલ્યોની ભેટ આપી છે. અને સુગરીને તેના માળા બાંધવાનું કૌશલ્ય ભેટમાં મળ્યું છે. માળા બાંધવા માટે સુગરી લાંબા દોરા જેવા ઘાસના તાંતણા પસંદ કરે છે. શુભાંગીઃ દીદી, માળો કોણ બાંધે છે? નર કે માદા? દેવાંગીઃ નર સુગરી માળા બાંધે છે. માળો બાંધવાનું કામ પૂર્ણ
કરતાં આશરે 18 દિવસો લાગે છે, જ્યારે માળો અધ્ધ બંધાઈ જાય છે, ત્યારે નર તેના ગીત દ્વારા માદાને રહેવાનું આમંત્રણ આપે છે. જો તે (માદા) માળો પસંદ કરે, તો બંને સાથે મળીને માળો પૂર્ણ કરે છે. જો તે (માળો પસંદ) ન કરે, તો માળો ત્યજી દેવામાં આવે છે. શુભાંગી તો નર માટે એકથી વધુ માળા બનાવવાનું બહુ અઘરું
દેવાંગી : હા, સાવ સાચી વાત. માળા બાંધવાની સતુમાં નર ઘણા માળા બાંધે છે. શુભાંગી : બિચારો! દીદી, મને યાદ છે, મેં કેટલાય અપૂર્ણ માળા
પણ જોયા હતા. દેવાંગી શુભાંગી, પક્ષીઓ આપણા મિત્રો તો છે, પણ તેઓ આપણને ઘણી રીતે મદદ કરે છે, તું ગીધને તો જાણે છે, સામાન્ય રીતે, લોકોને ગધ ગમતા નથી, કારણ કે તેઓ મૃત પ્રાણીઓ ખાય છે, પણ તેમને અંગ્રેજીમાં) ઑવિંજ (સફાઈ કરતા પક્ષીઓ) કહેવામાં આવે છે, કારણ કે સડેલાં મડદાં ખાઈને તેઓ આપણી આસપાસનો વિસ્તાર સાફ રાખે છે. તેના ચિત્રમાં તેની ચાંચ ધ્યાનથી જો.
મડદાંમાંથી માંસ ચીરીને કાઢી શકે તેવી તેની રચના છે, શુભાંગી : હા, ચાંચનો વળાંક ખૂબ તીણ છે. દીદી, છેલ્લા કેટલાય મહિનાઓથી મેં એક પણ ગીધને આકાશમાં ઊડતું જોયું નથી. તેનું કારણ શું? દેવાંગ : આજકાલ માંદાં પ્રાણીઓને (ઢોરને) સાજાં કરવા માટે લોકો દવાનો ઉપયોગ કરે છે. જ્યારે તેના પ્રાણીઓ મરે છે, ત્યારે ગીધ તેમને ખાય છે. Diclofenac ગીધ માટે ખુબ જ હાનિકારક છે. આવું માંસ ખાધા પછી તે (ગીધ) ધીમે ધીમે થોડા દિવસોમાં મરી જાય છે. આ
રીતેં) લગભગ 97 % ગીધની વસ્તી નાશ પામી છે. શુભાંગી તેનો અર્થ એ કે આપણે, માનવજાત, ખૂબ જ સ્વાર્થી
છીએ. પૃથ્વી પરના અન્ય જીવોની આપણે પરવા કરતા નથી. પક્ષીઓને બચાવવા આપણે કેમ કંઈ કરતા નથી?
આપણે પક્ષીઓને કઈ રીતે મદદ કરી શકીએ?
દેવાંગી : તમે પક્ષીઓને ઘણા અને પાણી આપી શકો છો. આજકાલ આપણને બહુ ઓછી ચકલીઓ જોવા મળે છે, નઈં ? તે ક્યાં ગઈ? શુભાંગી હું… કદાચ તેઓ રજામાં તેમના મામાના ઘરે ગઈ હશે. દેવાંગીઃ (તો પછી) બાકીના દિવસોનું શું? શુભાંગી મને ખબર નથી. શું તું મને સમજાવીશ, પ્લીઝ? દેવાંગીઃ તેઓ આપણને છોડી ગઈ, કારણ કે આપન્ને તેમનાં ઘર નષ્ટ કર્યો. શુભાંગી : કેવી રીતે? મેં તો એવું કોઈ તોફાન કર્યું નથી.
![]()
દેવાંગી : ના, વહાલી. ખરેખર તો આપણે આપબ્રાં ઘરોની રચના એવી રીતે કરી છે કે પક્ષીઓ ઘરમાં આવી ન શકે, આપણે આપણાં ઘરમાં તેમને માળો બાંધવા દેતા નથી. આપણી સાથે રહેવામાં તેમને સલામતી લાગે છે, તેથી જ કે આપણે તેને હાઉસ સ્પેરો (ધરની ચકલી) કહીએ છીએ. શુભાંગીઃ વારુ, મારે તે પાછી જોઈએ છે અને મને ખાતરી છે
કે મારા મિત્રો પણ મને મદદ કરશે. દેવાંગ સારુ. પૂંઠાની પેટીઓ વડે તમે ચક્લીના માળા બનાવી
શકો છો. પક્ષીઓને ગાંઠિયા ખવરાવશો નë, કારણ કે તે તેમના પેટ માટે હાનિકારક છે. ચોખા, બાજરી, વગેરેના દાણા (આપો) અને રકાબીમાં પાણી મૂકો. તમારી સાથે રમવા તેઓ જરૂર આવશે. પછી તું અને તારા મિત્રો એક ગીત ગાઈ શકશો :
“ચકીબહેન, ચકીબહેન, મારી સાથે રમવા આવશો કે નહીં. આવશો કે નહીં?” શુભાંગીઃ હજુ એક પ્રશ્ન, દીદી. દેવાંગી: ઓહ, જરૂર. શુભાંગી : મને પ્રવાસી પક્ષીઓ વિશે કહે, પ્લીઝ. દેવાંગી : જો શુભ, દર વર્ષે યુરોપ, સાઇબિરિયા અને બીજા ઠંડા
દેશોમાંથી હજારો પક્ષીઓ આપણા મહેમાન બની આવે છે. પેલિકન, સારસ, વિવિધ બતકો અને રોઝિ પાસ્ટર જેવાં પક્ષીઓ હજારો ક્લિોમીટરનો પ્રવાસ કરી ભારતમાં ઊડી નાવે છે, શુભાંગી: રોઝિ પાસ્ટર! આ નામ સાંભળવામાં મીઠું છે. તે શું છે? દેવાંગીઃ એ આપણી મેના જેવું એક પક્ષી છે. ગુજરાતીમાં રોઝિ
પાસ્ટરને વૈયા કહે છે. તેનો રંગ આછો બદામી અને ગુલાબી હોય છે. શુભાંગીઃ તે એ જ પક્ષી છે, જેને શિયાળામાં હું ટોળામાં ઊડતા જોઉં છું. દેવાંગીઃ સારું નિરીક્ષણ છે. આ પક્ષી જૂન-જુલાઈમાં યુરોપથી ભારત આવે છે. અને માર્ચ-એપ્રિલમાં પાછા ફરે છે. શુભાંગીઃ કોઈ નકશા વિના તેઓ કેવી રીતે પ્રવાસ કરે છે?
દેવાંગીઃ તેઓ સૂર્યની મદદથી તેમનો માર્ગ શોધે છે. તેઓ આવે ત્યારે વહેલી સવારે પ્રવાસ કરે છે અને વળતા પ્રવાસમાં તેઓ સાંજે ઊડે છે. શુભાંગીઃ શું બધાં પક્ષીઓ એકસરખી રીતે ઊડીને પ્રવાસ કરે છે? દેવાંગી : જરાય નહીં. પ્રવાસી પક્ષીઓ જુદી જુદી રીતે પ્રવાસ કરે છે.
સારસ, બતક અને હંસ જેવાં પક્ષીઓ v આકારની ગોઠવણીમાં ઊંડે છે. અમુક બતકો, વૉબ્લર અને મમ્મીમાર જેવાં પક્ષીઓ સમૂહમાં ઊડે છે. શુભાંગી : હે ભગવાન! આટલી બધી માહિતી હું કઈ રીતે યાદ રાખી શકું? દેવાંગી : સહેલું છે, પક્ષીઓને ઓળખવા માટે આ મુદ્દા યાદ રાખો.
- પક્ષીનો રંગ જુઓ.
- તેના કદનું નિરીક્ષણ કરો.
- તેની ચાંચ અને પૂંછડીનો આકાર અને લંબાઈ જુઓ.
- દેખાયા હોય તે સ્થળ, જેમ કે, ઝાડ અથવા તાર પર બેઠા હોય, પાણીમાં, ખુલ્લા મેદાનમાં, ઘાસમાં
અથવા આકાશમાં હોય.
આ મુદ્દાઓ ઉપરાંત, જે પક્ષીનો સ્વભાવ કે કોઈ લક્ષણ તમારા નજીકના મિત્ર સાથે મળતા હોય, તો તે મિત્રનું નામ તેને આપી શકો છો. શુભાંગી ઃ સાચી વાત છે. પક્ષીઓની રંગીન દુનિયા સાથે મારો પરિચય કરાવવા બદલ આભાર, દીદ. દેવાંગીઃ હા, મારા બ્રેનફીવર પક્ષી ! મિત્રાઃ તે વળી શું છે? દેવાંગી : શુભાંગી જેવું એક પક્ષી, શુભ, તે પક્ષી વિશે માહિતી મેળવ. મિત્રાઃ શુભ, યાદ રાખજે !
![]()
પૃથ્વી પર આપણને પક્ષીઓની જરૂર છે, કારણ કે તેઓ પાકને નુકસાન કરતાં જંતુઓ ખાઈ જાય છે. બીજ ફેલાવવામાં પણ તેઓ મદદરૂપ થાય છે. તેમના મીઠા કલરવથી તેઓ આપણું મનોરંજન કરે છે. પક્ષીઓની સંભાળ લો; તેઓ સ્વસ્થ વાતાવરણના ખરા , સૂચક છે. શમાંગીઆભારે, દા.
Word Meanings



Idioms And Phrases
(1) to be fascinated by
The little girl was fascinated by the colourful flowers.
(2) in comparison with
Tinas ran goli looks duil in comparison with Divya’s ran golf.
![]()
(3) to be busy with
Father was busy with his office work, when his friends came to meet him.
(4) to talk about
Mrs Pandya is going to talk about the importance of discipline in life.
(5) to hide from
The little boy is hiding from his mother, who is angry with him.
(6) supposed to
All the students are supposed to wear white uniform for the Sports Day.
(7) as well as
Geeta can sing as well as dance.
(8) to take care of
Mitali takes care of her little sister.
(9) at present
How many students are there in the school at present ?
(10) to enter into
Since it was raining, many people entered into my shop for shelter.
(11) to match with
Do these bangles match with my new dress ?
![]()
I feel… (Classroom / Individual Activity)
(1) How do you feel when you hear a bird chirping / singing ?
(2) Make a list of birds that you see around you.
(3) What will you do if you find somebody hunting or teasing birds ?
(4) Do you find house sparrows in your area ? What will you and your friends do to save the sparrows ?
(5) Underline the sentences that show Shubhangi’s curiosity to know more about birds.