Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy Textbook Questions and Answers, Additional Important Questions, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
Gujarat Board Class 10 Science Sources of Energy InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is a good source of energy?
Answer:
The energy which is easily available, cheap, does not produce pollution is said to be a good source.
Question 2.
What is a good fuel?
Answer:
A good fuel is one that is cheap, easily available, easy to handle, transport, has proper ignition temperature, and high calorific value.
Question 3.
If you could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use, and why?
Answer:
If sun’s heat is accessible then solar cooker or else CNG.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
Answer:
Disadvantages of fossil fuels are:
(a) They are non-renewable resources
(b) They cause pollution which can lead to
- Acid rain
- Smoke
- Greenhouse effect due to CO2
- Fly ash suspended in air.
Question 5.
Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy?
Answer:
The sources of energy we are using now is fossil fuel i.e., petrol and petroleum products, and coal which are exhaustible and non-renewable. The demand of energy is increasing due to increased population and better technology that has added many machines, appliances to add comfort to lifestyle. Hence the demand for energy is increasing day by day. To overcome this problem we are looking for alternate sources of energy.
Question 6.
How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience?
Answer:
- The traditional use of water energy has been modified and we have built dams, turbines and dynamos to generate electricity with the help of the flow of water.
- Wind energy is used to rotate the windmills, turbines, and generate electricity by constructing wind fans.
Question 7.
What kind of mirror – concave, convex or plain – would be best suited for use in a solar cooker? Why?
Answer:
Concave mirror would be best suited for use in solar cooker. As it is a converging mirror and would converge sun’s heat radiation at one focussed point.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the limitations of the energy that can be obtained from the oceans?
Answer:
The limitations of ocean energy are:
- Few limited sites/places where this wave, tidal or ocean thermal energy can be obtained.
- The cost of construction of plants is very high.
- The efficiency of producing energy is also low.
Question 9.
What is geothermal energy?
Answer:
The heat energy obtained in the form of steam from under the earth’s crust is called geothermal energy
Question 10.
What are the advantages of nuclear energy? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
The advantages of nuclear energy are:
- A very small amount of radioactive material can produce large amount of energy which can be controlled and converted into usable form e.g.,1 kg Uranium = 25 thousand tonnes of coal.
- It does not release any smoke or harmful gases in the ait: Hence it can curb the global warming that is caused due to the greenhouse effect.
Question 11.
Can any source of energy be pollution-free? Why or why not?
Answer:
Yes, there can be a source of energy that can be pollution-free in using it. e.g., sun’s energy that is used in a solar cooker, solar water heater, solar cell panels.
Question 12.
Hydrogen has been used as rocket fuel. Would you consider it a cleaner fuel than CNG? Why or why not?
Answer:
Hydrogen is a cleaner fuel than CNG because hydrogen on burning/combustion form water whereas CNG that contain methane burns to produce carbon dioxide.
![]()
Question 13.
Name two energy sources that you would consider to be renewable. Give reasons for your choices.
Answer:
- Solar energy – it will not get exhausted it can be used for multipurpose – heating, burning and producing electricity It will not cause any pollution, it is cheap and easily available.
- Energy from water – Energy can be obtained from water in various form i.e., for producing electricity without pollution.
Question 14.
Give the names of two energy sources that you would consider to be exhaustible. Give reasons for your choices.
Answer:
Petroleum and coal are the exhaustible sources of energy as they are once used up, cannot be renewed.
In-Text Activities Solved
Activity 14.1
- List four forms of energy that you use from the morning. When you wake up, until you reach the school.
- From where do we get these different forms of energy?
- Can we call these ‘source’ of energy? Why or why not?
Answer:
- Electrical energy – To iron clothes, lightning.
- Muscular energy – to brush, take bath etc.
- Heat energy – For cooking food, room heater, etc.
- Chemical (food) energy – From breakfast (respiration, digestion etc.)
Sources:
- Electrical energy – From power plants.
- Muscular energy – Energy stored in our body due to the food we eat.
- Heat – From fuel
- Chemical energy – From breakfast
- All these are sources of energy
Activity 14.2
- Consider the various options we have when we choose fuel for cooking our food.
- What are the criteria you would consider when trying to categorize something as a good fuel?
- Would your choice be different if you lived
(a) in a forest?
(b) in a remote mountain village or small island?
(c) in New Delhi?
(d) lived five centuries ago? - How are the factors different in each case?
Answer:
- To choose fuel for cooking our food:
(a) It should have higher calorific value. .
(b) It should have a proper ignition temperature.
(c) It should not produce any smoke, no ash.
(d) It should be easily available, easy to handle, and transport. - Our choice will be different in the following condition:
(a) If one lives in forest – fuel would be wood.
(b) In a remote mountain village or small island – dry leaves, dry twigs, wood, - cow dung cakes.
(c) In New Delhi – L.PG, CNG.
(d) Lived five centuries ago – wood. - Availability is the main factor in choosing fuel.
Activity 14.3
- Take a table tennis ball and make three slits into it.
Put semicircular fins cut out of a metal sheet into these slits.
fins cut out of a metal sheet into these slits. - Pivot the tennis ball on an axle through its center with a straight metal wire fixed to a rigid support. Ensure that the tennis ball rotates freely about the axle.
- Now connect a cycle dynamo to this.
- Connect a bulb in series.
- Direct a jet of water or steam produced in a pressure cooker at the fins.
Observation: The bulb gets lighted.
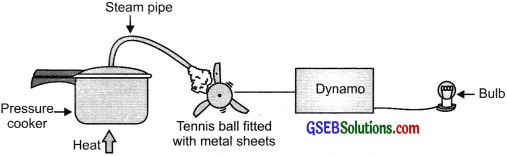
A model to demonstrate the process of thermoelectric production
Activity 14.4
- Find out from your grandparents or other elders –
(a) how did they go to school?
(b) how did they get water for their daily needs when they were young?
(c) what means of entertainment did they use? - Compare the above answers with how you do these tasks now.
- is there a difference? If yes, in which case more energy from external sources is consumed?
Answer:
(a) Our grandparents used to walk, use cycle, tonga to go to school.
(b) They used to get water from wells, boring, rivers.
(c) Fairs, group games, dance etc. were sources of entertainment for them. Whereas today we
(a) go to school on the school bus or in car.
(b) get water using submersible pumps.
(c) are glued to TV mobile phones, computers most of the time. Obviously, today more energy is consumed
![]() .
.
Activity 14.5
- Take two conical flasks and paint one white and the other black. Fill both with water.
- Place the conical flask in direct sunlight for half an hour to one hour.
- Touch the conical flasks, measure the temperature of the water in the two conical flasks with a thermometer.
- Can you think of ways in which this finding would be used in your daily life?
Observation: Conical flask with black paint will have water with more temperature. In daily life, we use this property by wearing light-colored clothes in summers which reflect light, and dark-colored clothes in winters, which absorb heat.

Measuring temperature In both the conical flasks.
Activity 14.6
- Study the structure and working of a solar cooker and/or a solar water heater, particularly with regard to how it is insulated and maximum heat absorption is ensured.
- Design and build a solar cooker or water.heater using low-cost material available and check what temperatures are achieved in your system.
- Discuss what would be the advantage and limitations of using the solar cooker or water heater.
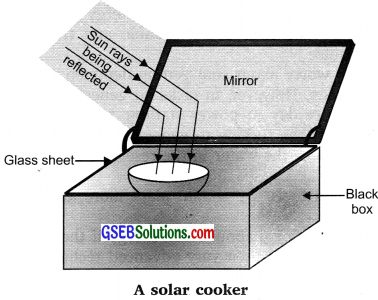
Construction and Working
Black box – To absorb heat.
Glass sheet – To create a greenhouse effect
Mirror – To reflect the sun’s heat into the box.
Advantages of solar cooker:
(a) It is cheap and easy to handle.
(b) It does not need any fuel for cooking food.
(c) It is pollution-free.
Disadvantages of solar cooker:
(a) It is very slow, takes a long time for cooking.
(b) It is dependent on the sun’s light, cannot work on a cloudy day.
(c) The reflectors position need to be monitored so as it reflects the sunlight at the center focused point of the solar cooker.
Yes – the places where the sun’s energy is not sufficient, the use of solar cookers would be limited
Activity 14.7
- Discuss in class the question of what is the ultimate source of energy for biomass, wind, and ocean thermal energy.
- Is geothermal energy and nuclear energy different in this respect? Why?
- Where would you place hydroelectricity and wave energy?
Answer:
The ultimate source of energy for biomass, wind, and ocean thermal energy is solar energy Le., Sun. Because sun is only a source of energy for the earth.
- Geothermal energy is obtained inside the earth due to heat and pressure. Nuclear energy is obtained due to the nuclear reaction of radioactive substances.
- Hydroelectricity and wave energy can be placed under Sun’s energy as both of them are caused and formed due to the sun’s heat energy.
![]()
Activity 14.8
Gather information about various energy sources and how each one affects the environment.
Debate the merits and demerits of each source and select the best source of energy on this basis.
Answer:

Activity 14.9
- Debate the following two issues in class.
(a) The estimated coal reserves are said to be enough to last us for another two hundred years. Do you think we need to worry about coal getting depleted in this case? Why or why not?
(b) It is estimated that the Sun will last for another five billion years. Do we have to worry about solar energy getting exhausted? Why or why not? - On the basis of the debate, decide which energy sources can be considered (i) exhaustible, (ii) inexhaustible, (iii) renewable, and (iv) non-renewable. Give your reasons for each choice.
Answer:
(a) We need not to worry about coal getting depleted and it would last for another two hundred years. However, in order to generate electricity a large amount of coal is burnt every day in power stations to heat up water to produce steam which further runs the turbine to generate electricity.
But we have other options too, i.e., water. Since the water in the reservoir would be recharged each time it rains. To replace coal as fuels, we should plant more and more trees so that we can use wood as fuels.
(b) We do not have to worry about solar energy if the sUn will last for another five billion years because till then very advanced technology would be developed to
trap and store solar energy. Moreover, we will have other options to for this purpose.
- Exhaustible – petrol, coal are examples of exhaustible sources of energy as they will one day last.
- Inexhaustible – Sun and water are examples of an inexhaustible source of energy as solar and water are renewable.
- Renewable: Sun and water are renewable sources of energy as they are renewed.
- Non-renewable: Petrol and coal are non-renewable sources of energy as they are once used up cannot be renewed.
Gujarat Board Class 10 Science Sources of Energy Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on
(a) a sunny day.
(b) a cloudy day.
(c) a hot day.
(d) a windy day.
Answer:
(b) a cloudy day.
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following is not an example of a bio-mass energy source?
(a) wood
(b) gobar-gas
(c) nuclear energy
(d) coal
Answer:
(c) nuclear energy
Question 3.
Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the Sun’s energy?
(a) geothermal energy
(b) wind energy
(c) nuclear energy
(d) bio-mass
Answer:
(c) nuclear energy
Question 4.
Compare and contrast fossil fuels and the Sun as direct sources of energy.
Sun:
- It is renewable source of energy
- It does not cause pollution.
- It is cheap, easily available for most of the time and at most of the places.
Fossil fuels:
- It is a non-renewable source of energy
- It causes pollution in the environment.
- It is expensive, not easily available any time and anywhere.
![]()
Question 5.
Compare and contrast bio-mass and hydroelectricity as sources of energy.
Answer:
Biomass as Energy Source:
- It causes pollution.
- It is cheap and easily available.
- Initial cost for building the bio-gas plant is very cheap and its maintenance is also cheap.
Hydroelectricity as Energy Source:
- It does not cause pollution.
- it is expensive and not easily available.
- The initial cost of building the power plant is expensive, its maintenance is also expensive.
Question 6.
What are the limitations of extracting energy from:
(a) the wind?
(b) waves?
(c) tides?
Answer:
(a) The Wind
- It can be extracted only at limited sites where the wind blows most of the time in a year.
- The minimum speed of wind should be 15 km/h.
- A large area is required to build the wind farm/windmills which is an expensive affair.
- Efficiency is low and maintenance is high.
(b) Waves
- The place and time is limited when the waves are strong.
- Initial setup cost is expensive.
- Efficiency is low.
(c) Tides
- The areas where tidal energy can be harnessed is less.
- The efficiency is very low.
- The plants are not cost-effective.
Question 7.
On what basis would you classify energy sources as
(a) renewable and non-renewable?
(b) exhaustible and inexhaustible? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Both (a) and (b) options are same:
Renewable/Inexhaustible:
- They are also called inexhaustible
- The energy sourëe that will not finish and can be renewed or made again and again is called renewable sources of energy e.g., sun, wind, water.
Non-renewable/Exhaustible:
- they are also called as exhaustible.
- The energy source that will finish and will get exhausted and cannot be made very soon or takes millions of years for its formation e.j., fossil fuels—petrol, coal.
Question 8.
What are the qualities of an ideal source of energy?
Answer:
The ideal source should have the following qualities:
- It should be cheap, easily available and easy to handle.
- It can be transported easily.
- It should have high calorific value.
- It should have a proper ignition temperature.
- It should not cause any environmental pollution.
Question 9.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a solar cooker? Are there places where solar cookers would have limited utility?
Answer:
- Study the structure and working of a solar cooker and/or a solar water heater, particularly with regard to how it is insulated and maximum heat absorption is ensured.
- Design and build a solar cooker or water.heater using low-cost material available and check what temperatures are achieved in your system.
- Discuss what would be the advantage and limitations of using the solar cooker or water heater.
Construction and Working
Black box – To absorb heat.
Glass sheet – To create a greenhouse effect
Mirror – To reflect the sun’s heat into the box.
Advantages of solar cooker:
(a) It is cheap and easy to handle.
(b) It does not need any fuel for cooking food.
(c) It is pollution-free.
Disadvantages of solar cooker:
(a) It is very slow, takes a long time for cooking.
(b) It is dependent on the sun’s light, cannot work on a cloudy day.
(c) The reflectors position need to be monitored so as it reflects the sunlight at the center focused point of the solar cooker.
Yes – the places where the sun’s energy is not sufficient, the use of solar cookers would be limited

![]()
Question 10.
What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy?
What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption?
Answer:
- Due to the increasing demand for energy, the available sources of energy are depleting at a fast rate.
- The use of fuels on large scale is releasing lot of gases and unwanted particles in the air. The gases like SO2, NO2 are causing acid rain that is destroying monuments, iron articles, bridges, etc.
- The CO2 released in air is causing a greenhouse effect that is leading to global warming which will melt the ice and sea-level will increase submerging coastal areas and islands.
- To reduce energy consumption we should look for alternative sources of energy which can help us to overcome all these problems.
Gujarat Board Class 10 Science Sources of Energy Additional Important Questions and Answers
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is energy?
Answer:
Energy is the capability to do work.
Question 2.
What is a source of energy?
Answer:
A source of energy is one which is capable of providing an adequate amount of useful energy
Question 3.
What is a good source of energy?
Answer:
A good source of energy must be convenient. It should be capable of delivering the desired quantity of energy at a steady rate over a long period of time.
Question 4.
What is a fuel?
Answer:
Fuel is a substance which on burning produces usable energy Examples of fuels are wood, coal, petrol, diesel, kerosene, CNG, LPG, etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What are fossil fuels?
Answer:
Fuels that are formed from the fossil remains of plants and animals and are obtained from under the earth’s crust are called fossil fuels, for example, coal, petroleum and normal gas.
Question 6.
What is biomass?
Answer:
The matter contained in living organisms is called bio-mass.
Question 7.
What does bio-gas consist of?
Answer:
Biogas consists of 75% of methane.
Question 8.
What are the conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
Fossil fuels like coal and petroleum are conventional sources of energy These are the regular sources of energy that we use.
Question 9.
What are alternative or non-conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
To save the conventional sources of energy like the fossil fuels, scientists are trying to develop technology to tap new sources of energy like the solar energy wind energy, etc., these sources of energy are called the alternative source of energy
![]()
Question 10.
Which is the ultimate source of energy?
Answer:
Sun is the ultimate source of energy
Question 11.
What is geothermal energy?
Answer:
The heat energy obtained in the form of steam from under the earth’s crust is called geothermal energy
Question 12.
Name the renewable sources of energy
Answer:
Solar, wind, and water are some renewable sources of energy
Question 13.
Name some non-renewable sources of energy
Answer:
Coal and petroleum are non-renewable sources of energy
Question 14.
Name any two materials that are used for making solar cells.
Answer:
Silicon, germanium and selenium are used for making solar cells.
![]()
Question 15.
Name some gadgets where solar cells are used.
Answer:
Solar cells are used in traffic lights, artificial satellites, solar calculators etc.
Question 16.
What is the minimum wind velocity required for obtaining electric power with a windmill generator?
Answer:
15 km/h.
Question 17.
What is the range of temperature that can be obtained in a box-type solar cooker?
Answer;
100°C – 140°C.
Question 18.
What fraction of solar energy reaches the earth’s surface?
Answer:
47 % approximately.
Question 19.
What is the value of solar constant on earth?
Answer:
It is 1.4 kW / m2.
Question 20.
What is the age of the sun?
Answer:
The sun is 5 billion years old and will live for another 5 billion years.
Question 21.
Name some devices that can harness solar energy
Answer;
Solar cooker, solar cells, solar water heater.
Question 22.
Name one liquid and one gaseous fossil fuel.
Answer:
Petrol and natural gas.
![]()
Question 23.
Name the process that produces such a large amount of energy in the sun.
Answer:
Nuclear fusion.
Question 24.
What is a renewable source of energy?
Answer:
A source of energy that can be obtained on a regular basis even after using it continuously is called a renewable source of energy like solar; wind and water energy
Question 25.
What is a non-renewable source of energy?
Answer:
A source of energy that is present in a fixed form and takes millions of years to get replenished is called a non-renewable source of energy like fossil fuels, coal, and petroleum.
Question 26.
Name a device used to harness wind energy.
Answer:
Windmill.
Question 27.
What is wind energy farm?
Answer:
A large compact area where a large number of windmills are erected and their energy outputs are coupled together is called a wind energy farm.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What raw materials can be used in a biogas plant to produce biogas?
Answer:
The raw materials that can be used for the production of bio-gas are cow dung, vegetable waste, sewage, and agriculture waste.
Question 2.
What is the use of the slurry left behind in the biogas plant?
Answer:
The slurry left behind after the production of the biogas is used as manure as it is very rich in nitrogen and phosphorus.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the places where nuclear reactors are located in India.
Answer:
The nuclear power reactors are located in the following places in India:
- Tarapur (Maharashtra)
- Narora (U.P)
- Kalpakkam (Tamil Nadu)
- Kota (Rajasthan)
- Kakrapar (Gujarat)
- Kaiga (Karnataka)
Question 4.
How much energy needs of our country and the world is being fulfilled by nuclear power?
Answer:
In India only 3% of the total electric generation comes from nuclear power plants while in the industrialized countries around 30% of their electric power is met from nuclear power plants.
Question 5.
Why are fossil fuels classified as non-renewable sources of energy?
Answer:
Fossil fuels took millions of years to be formed under the earth’s crust so there is a fixed amount of these fuels (like coal and petroleum) under the earth. If we go on using them at this rate soon we will run out of energy. Since they can not be renewed at a fast pace, therefore, they are called non-renewable sources of energy.
Question 6.
What is the principle of solar cookers? Name two types of solar cookers.
Answer:
Solar cookers use the solar heat energy It works on the principle of producing the greenhouse effect with the help of black surfaces and the glass plate when kept in the sun. The two types of solar cookers are: the box type and concentrator type.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the output of a solar cell?
Answer:
A typical solar cell develops a voltage of 0.55 – 1 V and can produce about 0.7 W of electricity when exposed to the sun.
Question 8.
Name the different constituents of biogas.
Answer:
Biogas is a mixture of 75% methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulfide.
Question 9.
How does a solar panel light up a bulb at night when there is no solar energy?
Answer:
The electricity generated by a solar panel during day time is utilized to charge the storage batteries. The batteries operate on the inverter system during night time and the inverter supplies alternating current to light up the bulb.
Question 10.
Why is bio-gas called a clean fuel?
Answer:
Bio-gas is called a clean fuel because:
- It burns leaving no ash.
- It can be used directlÿ for heating, lighting, etc.
- It does not produce poisonous gas.
Question 11.
Give reasons why hydrogen can not be used as a domestic fuel?
Answer:
Hydrogen cannot be used as a domestic fuel in spite of its high calorific value because it is explosive in nature and is difficult to store and transport.
Question 12.
Name the commonly used forms of energy
Answer:
The commonly used forms of energy are thermal energy (from cow dung, firewood, coal, natural gas etc.) and electrical energy (formed by thermal power plants, hydroelectric power plants, nuclear power plants).
![]()
Question 13.
What are the different types of energies obtained from the sea?
Answer:
The different types ‘of energies obtained from the sea are:
- Tidal energy: The energy possessed by the rising and falling water of high and low tides.
- Wave energy: The energy possessed by the wavës.
- Ocean thermal energy: The energy obtained due to the difference in temperature at the surface and lower layers of seawater.
Question 14.
What are the disadvantages of using a solar cooker?
Answer:
The disadvantages of using a solar cooker arc:
- The cooking is slow.
- It can be used only when sunlight is there.
- No flying can be done in it.
Question 15.
Describe a simple activity to demonstrate the working of a turbine generator. How does it produce electricity?
Answer:
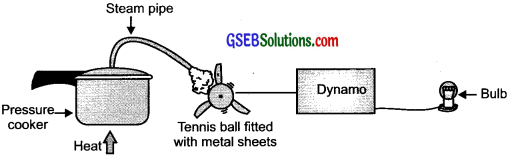
A model to demonstrate the process of thermoelectric production
A turbine consists of a moving rotor-blade assembly. The moving fluid acts on the blades to spin them and imparts energy to the rotor. When the fan moves the rotor blade with speed, it turns the shaft of the dynamo and converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy
Question 16.
Explain the working of a hydroelectric power plant to produce electricity
Answer:
In order to produce hydroelectricity; high rise dams are constructed on the river to obstruct the flow of water and thereby collect water in very large reservoirs. The water from a high level in the dam is carried through pipes, to the turbine, at the bottom of the dam. The turbines are connected to the generator.
Rotation of the turbines makes the generator produce electricity Water when stored at a height in the dam has a large amount of potential energy which gets converted into the kinetic energy of flowing water when it is allowed to fall on the turbines it gets converted into mechanical energy of the turbine and finally gets converted into the electric energy by the generator.
![]()
Question 17.
Describe how a solar cell is fabricated? Name two elements used for fabricating it. What is a solar cell panel?
Answer:
For solar cells take a set of semiconductors like arsenic and silicon.
Fix silicon sheets on arsenic and connect them with silver wires.
Two elements used – selenium and germanium or Arsenic and silicon.
Solar cell panel – It consists of many cells connected together to produce a large amount of electricity
Question 18.
Draw a diagram and explain the construction and working of a box-type solar cooker.
Answer:
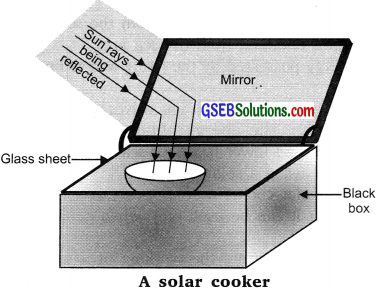
Construction:
- Take a metal box – paint it black.
- Place a glass sheet on the top of the box.
- On the lid of the box fix a concave mirror.
Working:
The black box absorbs the heat.
- The mirror reflects the sun’s radiations at a focused point in the box.
- The glass sheet creates the greenhouse effect by allowing all the heat radiation after reflection to enter the box. But once
- they enter the box, these radiations do not escape and thereby increase the temperature in the box.
Question 19.
Write three advantages of nuclear energy
Answer:
Nuclear energy has three advantages:
(a) It has very high efficiency; a small amount of nuclear fuel can produce a large amount of heat energy which can be controlled and used.
(b) It does not release any harmful gases like SO2, CO2, NO2, etc. in the air which may cause acid rain or greenhouse effect.
(c) Once the reaction is initiated it can go on automatically for decades unless we want to stop it.
![]()
Question 20.
Name three forms in which energy from the ocean is made available for use. What are the OTEC power plants? How do they operate?
Answer:
Energy from the ocean can be obtained as:
- wave energy
- tidal energy and
- ocean thermal energy
OTEC – It is. Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion. These plants can operate if the temperature difference between water at the surface and water at depths up to 2 km is 293 K (20°C) or more. The warm surface water is used to boil a volatile liquid like ammonia. The vapor of the liquid is then used to run the turbine. The cold water from the depth is pumped up and condense vapor again to liquid.
Question 21.
The current generation should focus on making of all the devices and equipment which shall work only on renewable sources of energy Explain why.
Answer:
- The global warming is at its peak, the environmental conditions are changing.
- The fossil fuels are depleting and the need for alternative fuel is a must.
- Most of the developed countries have already shifted to the renewable source of energy
- The efficiency of solar panels, windmill sand biogas has increased due to advancement in technology
Question 22.
What are the initiatives taken by our government in encouraging people to use alternative sources of energy?
Answer:
The government has given a lot of subsidies for encouraging people to make use of the alternative source of energy It has also eased imports.
![]()
Question 23.
Name a few states that have mum installation f solar panels in India.
Answer:
Few states that has lot of solar panels are: Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
Question 24.
The use of technology can solve the problems of global warming. Justify this statement.
Answer:
The technology if used correctly to research and find the most efficient renewable energy sources and devices will certainly cut down the use of fossil fuels and the release of carbon dioxide gas will cut down. This may lead to reduced emission of greenhouse gases and the issue of global warming can be addressed.
Question 25.
The very poor air quality of Delhi during winters is due to the burning of agricultural waste as one of the reasons. Explain how this problem can be addressed.
Answer:
The small initiative by the local community and the government can resolve this problem by educating the villagers about the biogas making of the waste. The government can install some biogas plants for the farmers or they may pay farmers for this waste. Use the waste to make biogas.
Question 26.
India has the potential of producing a large amount of energy -from renewable sources of energy Justify
Answer:
India is a country with a large coastal line where most of the states get 365 days of sunlight. The coastal line can be used to install the tidal power plants, the wind -blows well due to coast and the wind farms can also be installed in many locations.
As the country receives sunlight all day the solar panels can be very effective in the making of renewable sources of energy. We also have nuclear resources which can also be used in nuclear power plants to produce electricity.
Question 27.
“I want to use alternative sources of energy but when I go to the market I don’t easily get the solar lamps, solar cookers, and solar water heaters.” This is what citizens in India said when I asked about the switching to alternative sources of energy Give the solutions to this issue.
Answer:
Yes, it is true that the devices that work on alternative sources of energy are not that easily available. The youth of India should take the start-up to make these resources available at the doorsteps of the people and the manufacturing units should be installed and at the same time, the youth should be trained with the skills to make and maintain these devices which work on renewable source of energy This may also bring a lot of job opportunities to our countrymen.
![]()
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the structure and working of a fixed dome biogas plant.
Answer:
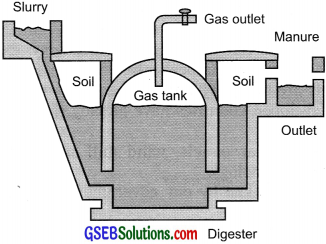
Schematic diagram of a biogas plant
The biogas plant has a dome-like structure built with bricks. A slurry of cow dung and water is made in a mixing tank and then fed into the depositor – which is a closed underground tank. The digester is a sealed chamber in which there is no oxygen.
Anaerobic microbes break down the complex compounds of the slurry. This generates a mixture of gases that consists of methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and hydrogen sulfide. The bio-gas is stored in the gas tank above the digester from which it is drawn through pipes for use.
Question 2.
(a) What is nuclear energy?
(b) What are the main hazards of nuclear power generation?
(c) What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
Answer:
(a) Nuclear energy is the energy produced by nuclear fission or nuclear fusion process.
(b) The main hazards of nuclear power generation are the deposition of the spent fuels as the uranium keeps on decaying and producing harmful radiations. Improper nuclear waste storage and disposal results in environmental contamination.
(c) The advantages of nuclear energy are that a small amount of nuclear fuel releases a tremendous amount of energy the self-sustaining nuclear fission reaction can be controlled to release the required amount of energy
![]()
Question 3.
Answer the following questions on the basis of the diagram of a bio-gas plant given
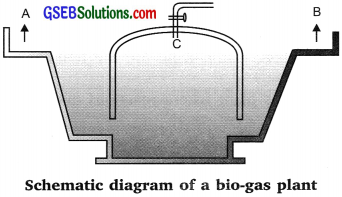
(a) What is biomass? How is biogas obtained from biomass?
(b) Why is bio-gas considered an ideal fuel?
(c) Name the parts labeled A, B, and C in the diagram.
Answer:
(a) Bio-mass – The matter contained in living organisms is called bio-mass.
Biogas can be obtained from the biomass by anaerobic fermentation.
(b) Biogas is considered as an ideal fuel because:
- It bums leaving no ash.
- It can be used directly for heating, lighting, etc. It is easily available.
- It does not produce any poisonous gas, and it is a renewable source of energy
(c) A → Slurry → bio-mass + water 50% each
B → Spent slurry → can be used as manure.
C → Bio-gas.
![]()
Questions On Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots)
Question 1.
A person ‘X’ rolled up the glasses of his black car and parked it in sun for one hour. Another person ‘Y’ rolled up-te glasses of a white car and parked it in sun for one hour. ¡n which car will the temperature inside the car be more and why?
Answer:
In the black car because the black color absorbs heat and the glass causes the greenhouse effect, which increases the temperature.
Question 2.
Suggest any three ways to contribute to saving LPG/CNG at home.
Answer:
- Soak dais, rice in water before cooking, so that it takes less time and fuel for cooking.
- Use a pressure cooker most of the time.
- Cover the lid of the container while cooking.
Question 3.
A student wants to design a car which can run on any alternative source of energy Suggest any two sources of energy and give its advantages.
Answer:
- Solar cells panel – can be installed on the rooftop of the car. It can change the sun’s energy into electrical energy charge the battery of the car and run the vehicle.
- Use water as a fuel that can split into H2 and O2 gas and the H2 gas produced can be burnt to run the engine.
![]()
Question 4.
During summers the houses on the top floor get heated, even the classes on the top floor get equally heated. Suggest a few methods by which you can overcome this problem.
Answer:
- The use of insulators like thermocol can be fixed on the ceiling of the room which acts as an insulator and does not allow the external heat to come into the room.
- If the windows have transparent glasses it should be coated with sun film reflector.
- On the rooftop trap the air by keeping inverted pots or planting saplings all over the roof.
Question 5.
Do you have to design a hydroelectric power plant model in which you have to produce electricity How will you complete this project?
- Name the fuel/source of energy you will use to produce electricity.
- Name any 4 parts/things you will need to do the same.
Answer:
In order to design a power plant model to produce electricity, we have to use
- water
- generator, turbine, pipes, water running with speed.