Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Commerce Accounts Part 1 Chapter 11 Bank Reconciliation Statement Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Accounts Part 1 Chapter 11 Bank Reconciliation Statement
GSEB Class 11 Accounts Bank Reconciliation Statement Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the correct option from those given below each question :
1. Bank reconciliation statement is prepared by …………….. .
(a) bank
(b) trader
(c) bank and trader both
(d) auditor
Answer:
(b) trader
2. Bank reconciliation statement is …………………. and not ……………….. .
(a) an account, a statement
(b) a subsidiary book, a journal proper
(c) a statement, an account
(d) part of cashbook, part of passbook
Answer:
(c) a statement, an account
![]()
3. Passbook is ……………….. .
(a) abstract of trader’s account in the book of bank.
(b) abstract of transactions with bank in the book of trader.
(c) part of bank reconciliation statement.
(d) subsidiary book prepared by trader.
Answer:
(a) abstract of trader’s account in the book of bank.
4. Main objective of bank reconciliation statement is to reconcile difference between ……………….. .
(a) opening and closing balance of cashbook.
(b) opening and closing balance of passbook.
(c) closing balance as per passbook and cashbook for respective period.
(d) opening balance as per passbook and cashbook for respective period.
Answer:
(c) closing balance as per passbook and cashbook for respective period.
5. ………………….. can be known by preparing bank reconciliation statement.
(a) Errors committed in passbook
(b) Errors committed in cashbook
(c) Transactions not recorded in passbook and cashbook
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d)All of the above
6. A statement of transaction with bank is sent by ………………. to ………………. .
(a) trader, customer
(b) trader, bank
(c) bank, trader
(d) customer, trader
Answer:
(c) bank, trader
7. Bank balance as per cashbook means …………………… balance.
(a) debit
(b) credit
(c) debit or credit
(d) debit and credit
Answer:
(a) debit
8. Bank overdraft as per cashbook means ……………….. balance.
(a) debit
(b) credit
(c) debit or credit
(d) debit and credit
Answer:
(b) credit
![]()
9. Credit balance as per passbook means ………………. .
(a) bank overdraft
(b) bank balance
(c) balance on which bank charges interest from a trader
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(b) bank balance
10. Debit balance as per passbook means ……………….. .
(a) bank overdraft
(b) bank balance
(c) balance on which bank gives interest to a trader
(d) both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(a) bank overdraft
Question 2.
Answer the following questions in one sentence :
(1) By whom and when the bank reconciliation statement is prepared?
Answer:
Bank reconciliation statement is prepared by’a trader for a certain time or on a date.
(2 ) What is the main objective of preparing a bank reconciliation statement?
Answer:
Main objective of bank reconciliation statement is to reconcile different between closing balance as per passbook and as per cashbook for respective period.
(3) Which transactions are recorded in a bank reconciliation statement?
Answer:
A transaction, because of which the difference arises between the bank balance as per cashbook and balance as per passbook, those transactions are recorded in a bank reconciliation statement.
![]()
(4) Which transactions are not recorded in a bank reconciliation statement?
Answer:
A transaction because of which the difference does not arise between the bank balance as per cashbook and balance as per passbook, those transactions are not recorded in a bank reconciliation statement.
(5) If total of debit column in passbook and total of credit side in cashbook is more, what is it?
Answer:
If the total of debit column exceeds, total of a credit column in a passbook, the difference is known as a bank overdraft. If the total of credit side is more, total of a debit side in a cashbook, the difference is known as a Bank overdraft.
(6) What is the other name of bank reconciliation statement ?
Answer:
The other name of bank reconciliation statement is bank reconciliation.
(7) Give the reason for bank balance means credit balance as per passbook and debit balance as per cashbook.
Answer:
Bank balance is receivable for the business hence it shows debit balance. The same are payable for the bank hence it shows credit balance for bank.
Question 3.
Answer the following questions in two or three sentences : OR Answer in short as asked :
(1) What is Bank Reconciliation Statement ?
Answer:
On a specified date, after finding out the reasons of difference between the bank balance as per cashbook and as per passbook, a statement which is prepared to tally the two balances is called a Bank reconciliation statement.
![]()
(2) State three reasons for difference between balance as per cashbook and passbook.
Answer:
Following are the three reasons for differences in the balance as per cashbook and as per passbook :
- Cheques deposited / paid into bank but not credited.
- Cheques drawn / issued but not paid by bank.
- Transactions recorded in passbook but not recorded in cashbook.
(3) Explain the rule of debit and credit to record the difference in the bank reconciliation.
Answer:
Both the sets of books, i.e., cashbook and passbook will be verified and differences will be found out. In actual entry passed, if this difference is debited, then in bank reconciliation statement it will be recorded in the credit column and if the difference is credited in the actual entry, then, in bank reconciliation statement it will be recorded in the debit column.
(4) Cashbook of Ramesh shows bank balance of ₹ 10,000 on 31 – 3 – ’16. On 31 – 3 -’16 cheques received from customers of ₹ 5,000 are yet to be deposited with bank while cheques of ₹ 7,000 drawn on 31 – 3 – ’16 are not presented for payment. A cheque of ₹ 8,000 was deposited with bank on 29 – 3 -’16 which is dishonoured, which is yet to be recorded in cashbook. What
is the bank balance as per passbook on 31 – 3 -’16?
Answer:
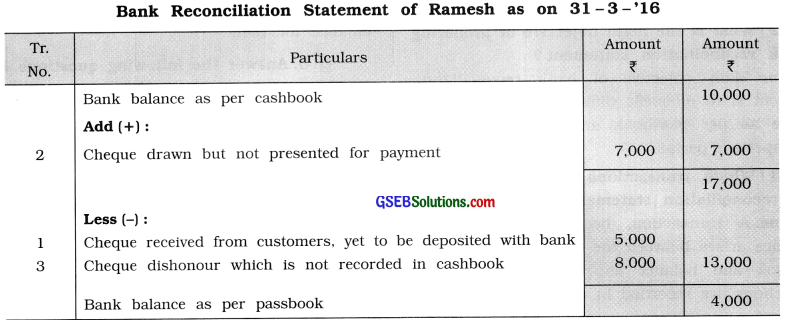
(5) Passbook shows debit balance ₹ 6,000 on 30 – 4 -’16. During April 2016, interest allowed by bank ₹ 200 and bank charges of ₹ 50 collected by the bank are not recorded in cashbook, while cheques of ₹ 4,000 are drawn but not presented for payment. A bills receivable of ₹ 7,000 maturing on 2 – 5 -’16 was sent for collection to bank on 29 – 4 -’16. What is the balance as per cashbook on 30 – 4 -’16?
Answer:
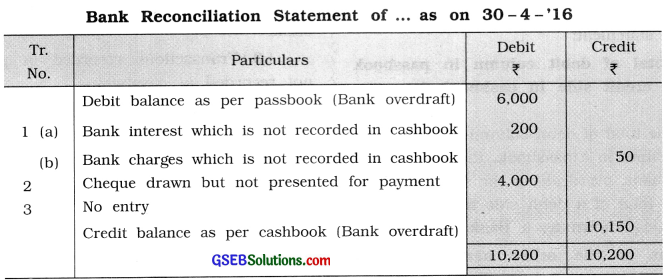
(6) Cashbook shows bank balance ₹ 3,000 on 1 – 1 -’16 while on 31 – 1 -’16 cashbook shows bank overdraft of ₹ 1,000. Passbook shows bank balance of ₹ 4,000 on 1 – 1 -’16. The bank reconciliation statement prepared for the month of January 2016 will start by which balance and why ?
Answer:
As bank reconciliation statement is to be prepared for the month of January, it can be started with the bank overdraft of ₹ 1,000 as per cashbook on 31-1-’16. One thing is remembered, if the opening and the closing balance of a particular time period are given then in such circumstances, take the closing balance only for preparing the bank reconciliation statement.
![]()
Question 4.
Cashbook of Shiri Sudhir shows bank balance of ₹ 5,000 on 31 – 12 – ’15. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement from the information given below :
(1) A cheque of ₹ 8,000 was deposited with bank on 29 – 12 -’15, but this cheque is not credited in passbook by bank till 31 – 12-’15.
(2) A cheque of ₹ 6,000 was sent for collection to bank on 30 – 12 -’15 which is not collected by bank till 31 – 12 – ’15.
(3) A cheque of ₹ 3,000 was issued on 28 – 12 – ’15 for payment of electricity bill, which is not debited by bank in passbook till 31 – 12 – ’15.
(4) A cheque of ₹ 2,000 was drawn on 27 – 12 – ’15 and given to creditor but it is not presented for payment till 31 – 12 -’15.
(5) Interest of ₹ 80 credited in passbook by bank, which is not debited in cashbook.
(6) Bank debited ₹ 100 in passbook for bank charges, which is not credited in cashbook.
Answer:
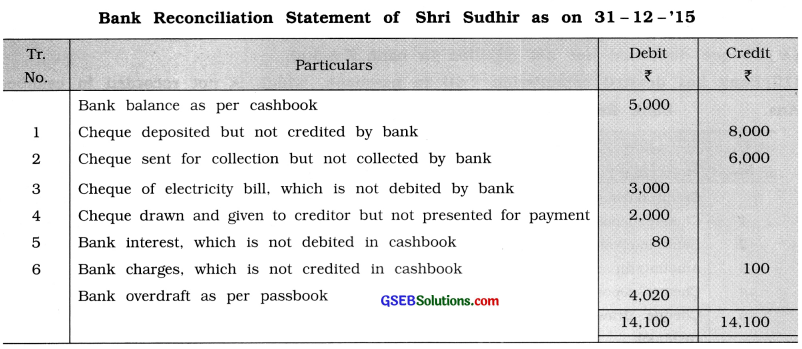
Explanation :
Transaction No.
(1) Cheque is not credited in passbook, therefore write the transaction in credit column of bank reconciliation statement.
(2) Cheque is sent for collection to bank, which is not collected by bank therefore write the transaction in credit column of bank reconciliation statement.
(3) Cheque is issued for payment of electricity bill, which is not debited by bank in passbook, therefore write the transaction in debit column of bank reconciliation statement.
(4) Cheque is drawn and given to creditor but it is not presented for payment, therefore write, the transaction in debit column of bank reconciliation statement.
(5) Interest credited by bank is income for the trader which is not debited on the bank column of cashbook, therefore write the transaction in the debit column of the bank reconciliation statement.
(6) Bank charges debited by the bank is expense for the trader which is not credited in the cashbook. Therefore, write the transaction in credit column of the bank reconciliation statement.
Question 5.
Cashbook of Naresh shows credit balance of bank ₹ 12,000 as on 31 -3 -’16, which does not tally with the balance as per passbook. Following information is obtained while comparing the passbook and cashbook. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement.
(1) A cheque of ₹ 10,000 was deposited with hank on 28-3-’16 which is not yet recorded in passbook by bank.
(2) Interest credited by bank ₹ 160 on 30 – 3 – ’16 is not recorded in cashbook.
(3) A customer has deposited ₹ 10,000 directly in bank account, which is not known till 31 -3-’16.
(4) Cheque deposited with bank, but not recorded in cashbook ₹ 8,000.
(5) Cheque drawn and paid by bank but not recorded in cashbook ₹ 6,000.
(6) A bill receivable of ₹ 3,000 discounted with bank is dishonoured and bank has recorded
the amount in passbook including noting charges of ₹ 40, which is not known to Naresh.
(7) Total of receipt side of cashbook cast short by ₹ 2,000.
(8) cheque drawn but not present for payment ₹ 1,000.
(9) Cheque deposited but not credited in bank ₹ 1,500.
(10) Bank has debited commission ₹ 80 in passbook, which is not recorded in cashbook.
Answer:
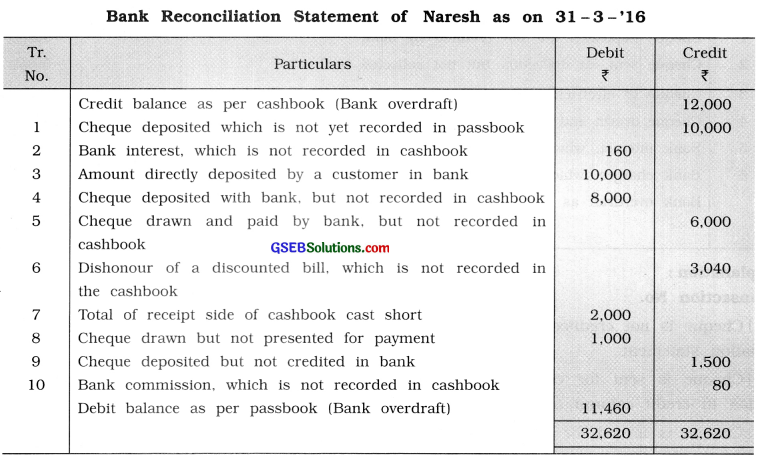
![]()
Question 6.
Bank balance as per passbook of Gaurang on 31 – 3 -’16 was ₹ 10,000 which does not tally with the bank balance as per cashbook. Following information is obtained while comparing the passbook and cashbook. Prepare a bank reconciliation statement.
( 1) A cheque of ₹ 7,000 is drawn and recorded in cashbook but not given to creditor.
(2) A cheque of ₹ 12,000 was deposited with bank on 29 – 3 – ’16, which is credited by bank on 1 – 4- ’16.
(3) Bank has paid ₹ 6,000 for insurance premium, which is known to Gaurang on 1 – 4 – ’16.
(4) A customer has deposited directly with bank ₹ 5,000, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(5 ) Bank has credited interest ₹ 200 and recorded in passbook, but not recorded in cashbook.
(6) A cheque of ₹ 6,700 deposited with bank is dishonoured, of which the information is received on 1 – 4 – ’16.
(7) Cheques drawn for ₹ 18,000 but out of these cheques of ₹ 6,000 were presented for payment till 31 – 3 – ’16.
(8) Cheques of ₹ 32,000 were deposited with bank, out of which cheques of ₹ 7,000 are credited in passbook till 31 – 3 -’16.
(9) A cheque of ₹ 1,800 was deposited with bank, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(10) Bank has debited ₹ 20 in passbook for bank charges, which is not recorded in cashbook.
Answer:

Question 7.
Cashbook of Aditya shows bank balance of ₹ 9,000 on 31 – 10 – ’15, which does not tally with the bank balance as per passbook. Prepare Aditya’s bank reconciliation statement from the information given below:
(1) Cheques of ₹ 51,000 were deposited, out of which cheques of ₹ 41,000 were credited in bank till 31-10-’15.
(2) A cheque of ₹ 2,300 is drawn and recorded in cashbook but not yet given to creditor.
(3) Bank has paid ₹ 1,700 for insurance premium through electronic clearing service, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(4) A customer has deposited ₹ 3,200 directly in Aditya’s bank account, which is known to him on 2 – 11 – ’15.
(5) Bank charges recorded by bank ₹ 70, is recorded twice in cashbook by mistake.
(6) A cheque of ₹ 6,750 deposited with bank on 27 – 10 -’15 is dishonoured, the information of which is received by Aditya on 1 – 11 – ’15.
(7) Cheques of ₹ 4,780 were drawn out of which cheque of ₹ 1,770 was presented in bank on 2- 11 -’15.
(8) A cheque of ₹ 1,320 was deposited in the bank but it is not recorded in the cashbook. This cheque is not collected by bank till 31 – 10 -’15.
(9) Bank has credited ₹ 130 for interest and debited ₹ 60 for bank charges in passbook, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(10) Total of receipt side of cashbook is over cast by ₹ 900.
(11) Bills receivable of ₹ 1,200 discounted with bank, is dishonoured on 28 – 10 -’15 and bank debited this amount with the noting charges of ₹ 20 but entry for dishonour is not made in cashbook till 31 – 10-’15.
(12) Bills payable of ₹ 700 maturing after one month was retired by bank under rebate of ₹ 30 on 30 – 10 -’15, which is not recorded in cashbook.
Answer:
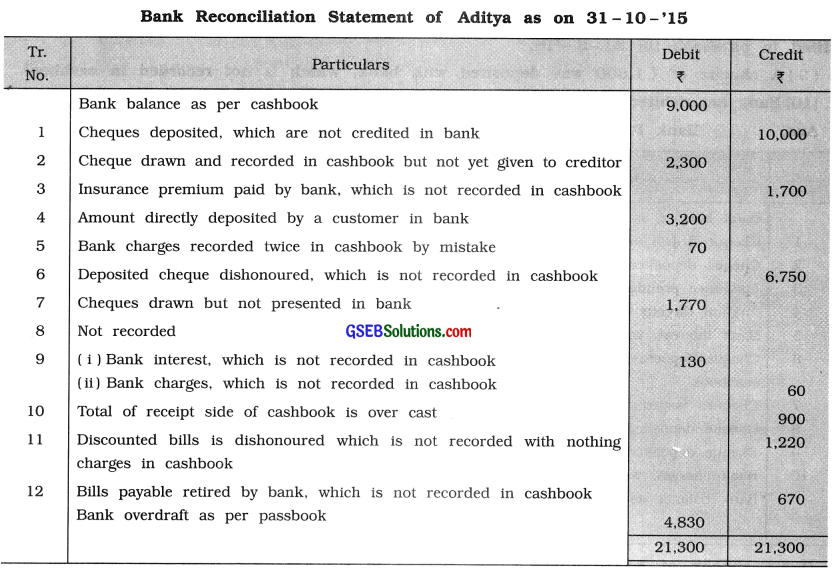
![]()
Question 8.
Prepare a bank reconciliation statement of Priyal for December, 2015 from the information given below:
(1) Bank overdraft as per cashbook (Dt. 31 – 12 – ’15) ₹ 710.
Bank overdraft as per passbook (Dt. 1 – 12- ’15) ₹ 261.
(2) Information of cheques deposited and credited in passbook is as under:
| Amount ₹ | Date of cheque deposited in Bank | Date of cheque credited in Passbook |
| 2,300 | 15 – 12 – ’15 | 18 – 12 – ’15 |
| 7,200 | 17 – 12 -’15 | 17 – 12 -’15 |
| 4,600 | 27 – 12 – ’15 | 1 – 1 – ’16 |
| 1,500 | 30 – 12 -’15 | 2 – 1 -’16 |
(3) Information of cheques drawn and presented in hank is as under:
| Amount ₹ | Date of cheque drawn | Date of cheque presented in Bank |
| 8,200 | 26 – 12 – ’15 | 28 – 12 -’15 |
| 9,300 | 28 – 12 – ’15 | 1 – 1 – ’16 |
| 7,100 | 29 – 12 -’15 | 31 – 12 – ’15 |
| 1,300 | 31 – 12 -’15 | 2 – 1 – ’16 |
(4) Interest ₹ 400 credited by bank in passbook is recorded on payment side in cashbook by mistake.
(5) Barak has collected dividend of ₹ 360 on behalf of Priyal which is not recorded in cashbook.
(6) Bank has recorded interest on overdraft ₹ 120 in passbook but this transaction is no recorded in cashbook.
(7) Sales made by cheque ₹ 2,300 recorded by bank in personal account of Priyal.
(8) Bank has reversed bank charges of ₹ 380 on request of Priyal, which is not recorde in cashbook.
(9) Signature is forgotten in cheque drawn and hence the cheque of ₹ 2,000 is returned by bank.
(10) Bank has collected bill of ₹ 3,000 sent to bank for collection and charged ₹ 100 for the same, this transaction is not recorded in cashbook.
Answer:
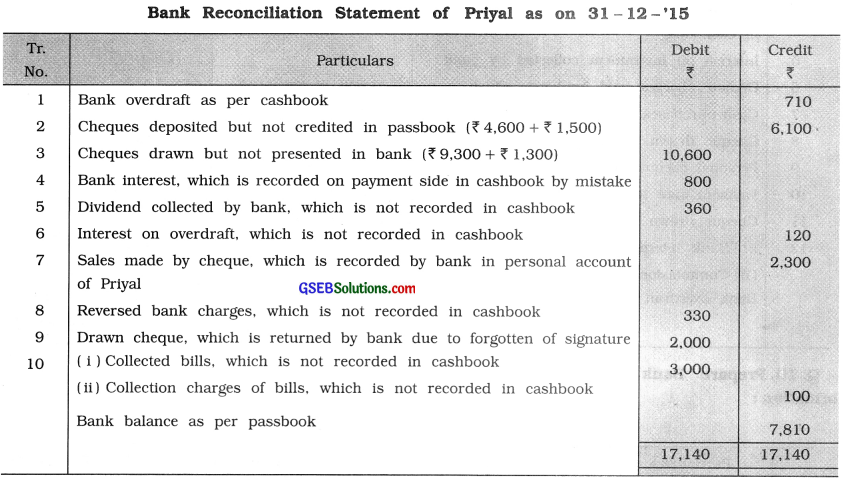
Question 9.
Prepare bank reconciliation statement of Dharamsinh as on 29 – 2 – ’16:
(1) Cheque deposited but not collected ₹ 5,200.
(2) Cheque drawn but not presented in bank, ₹ 37,000.
(3) Cheque received is recorded in cashbook but not sent for deposit in bank, ₹ 9,900.
(4) Cheque deposited with bank is dishonoured, which is not recorded in cashbook, ₹ 1,650.
(5) Interest on investment collected by bank ₹ 1,900.
(6) Demate charges paid by bank ₹ 1,320 as per instruction of Dharamsinh, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(7) Cash purchase, recorded on payment side of cashbook in bank column, ₹ 8,300.
(8) Cheque drawn but not given to creditor ₹ 4,160.
(9) Cheque drawn by Dharamsinh from his personal account, debited by bank in business bank account ₹ 3,340.
(10) Payment side of bank column in cashbook is overcast ₹ 1,180.
(11) Cheque drawn ₹ 6,400 dishonoured ora technical ground, dishonour of cheque is not recorded in cashbook.
(12) Interest credited by bank ₹ 1,240 and commission debited by bank ₹ 1,160, not recorded in cashbook.
Passbook of Dharamsinh showed overdraft of ₹ 4,000 on 29 – 2 – ’16.
Answer:
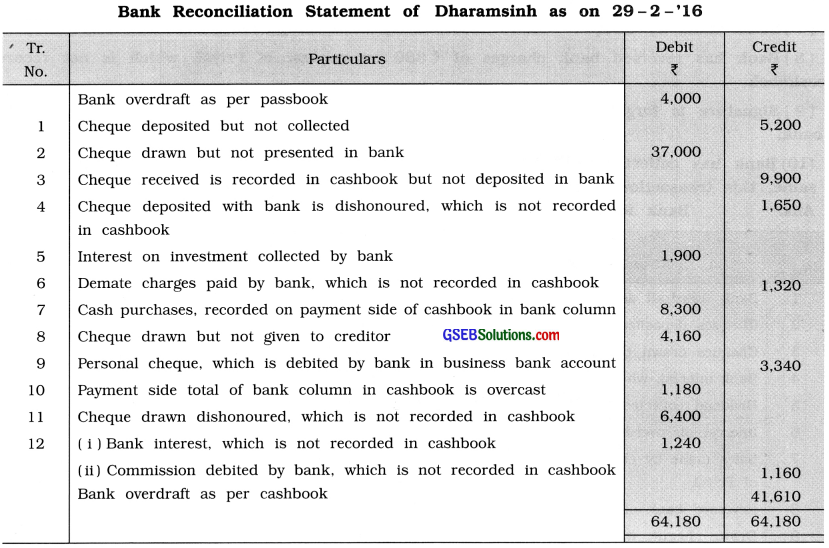
![]()
Question 10.
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement of Mecwan for May, 2016 from following information :
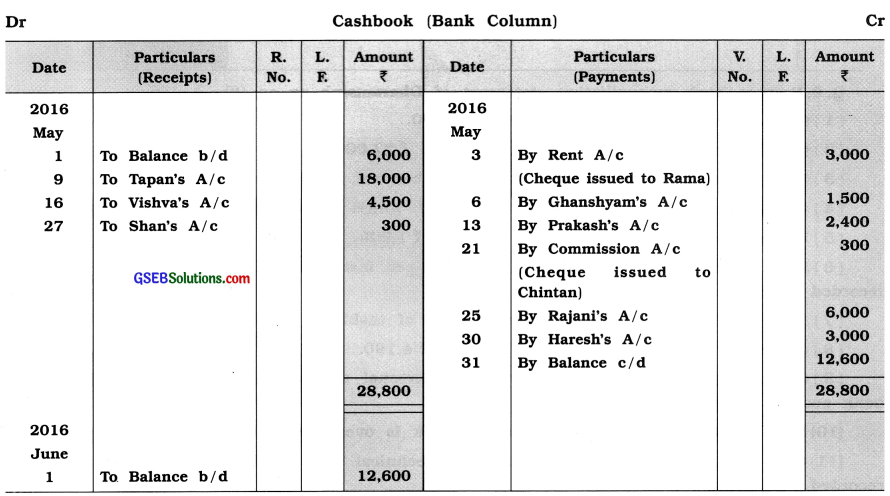
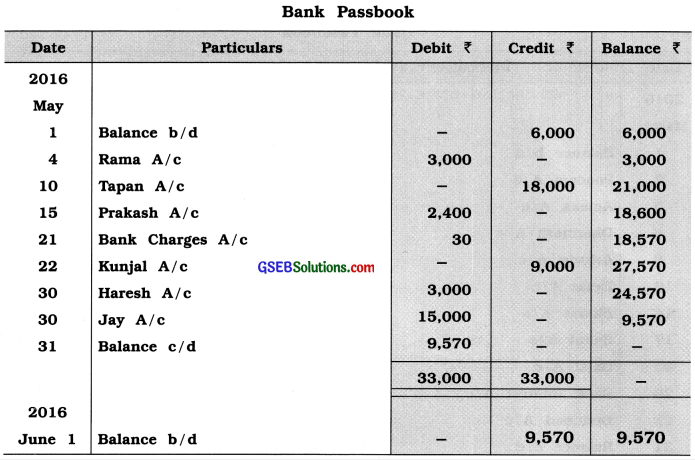
Answer:
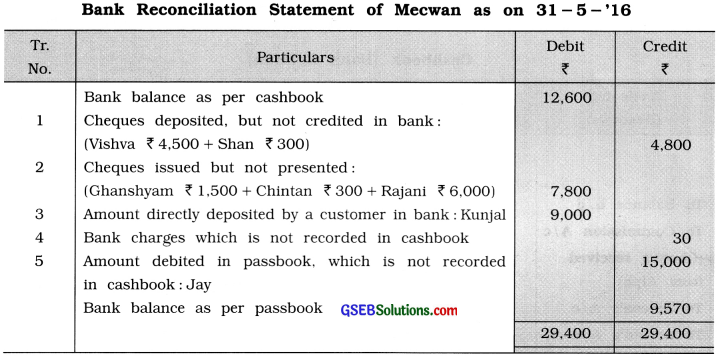
![]()
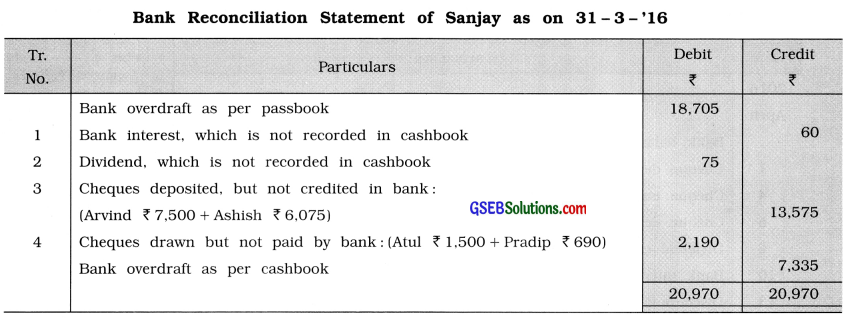
Question 11.
Prepare Bank Reconciliation Statement of Sanjay from following information:
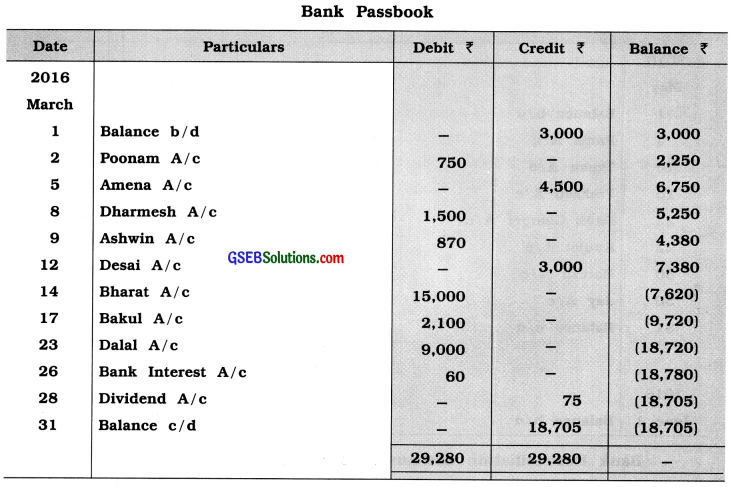
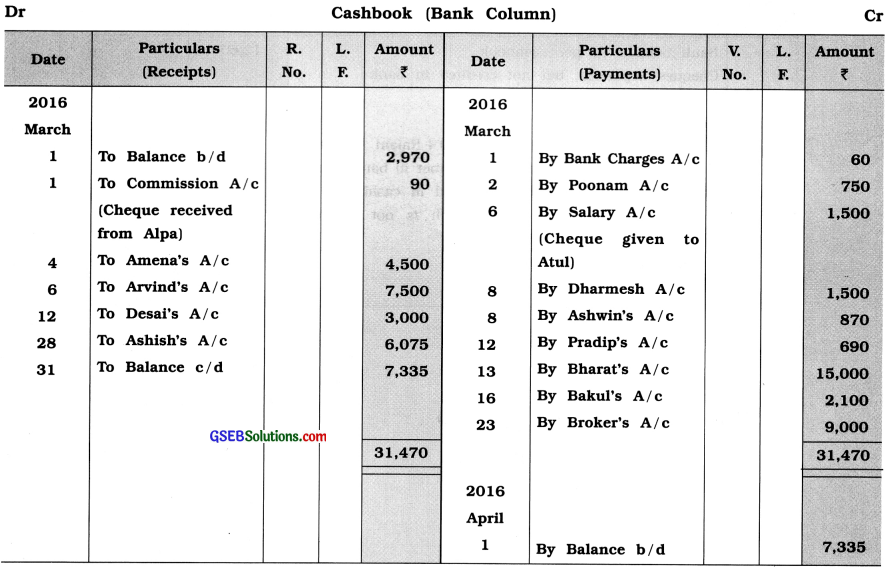
Answer:
![]()
Question 12.
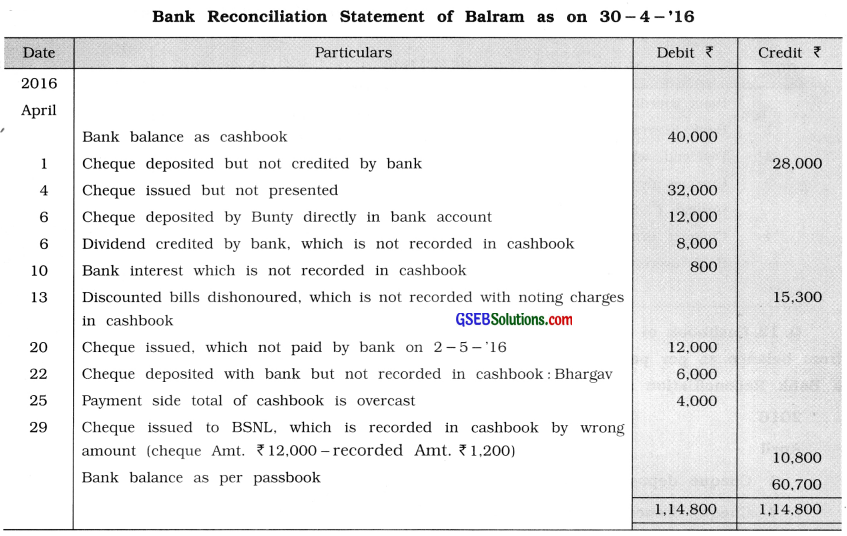
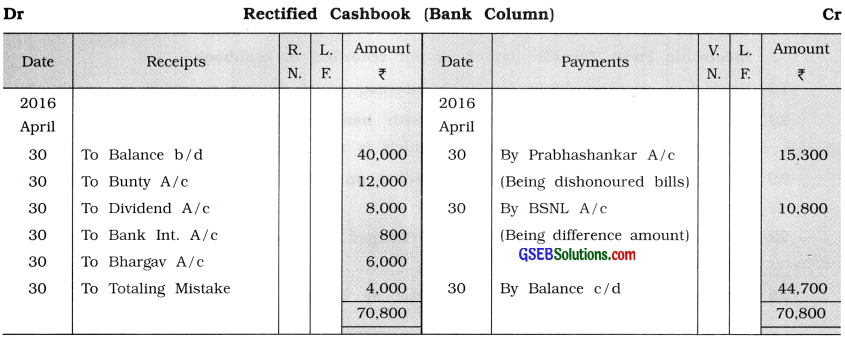
Cashbook of Balram shows debit balance of ₹ 40,000 on 30 – 4 – ’16, which is different from balance as per passbook. From the following information prepare a Rectified Cashbook and a Bank Reconciliation Statement as on 30 – 4 – ’16:
2016
April
1 Cheque deposited but not credited by bank ₹ 28,000.
4 Cheque issued but not presented ₹ 32,000.
6 Cheque deposited by Bunty directly in bank account ₹ 12,000.
6 Company has credited dividend of ₹ 8,000 in Balram’s bank account through National Electronic Fund Transfer, which is not recorded in cashbook.
10 Bank has credited ₹ 800 for bank interest, which is not recorded in cashbook.
13 Bills of Prabhashankar discounted with bank is dishonoured and bank has debited ₹ 15,300 including noting charges which is not known to Balram.
20 A cheque of ₹ 12,000 issued to Seema on 28-4-’16, which is paid by bank on 2 – 5 – ’16.
22 A cheque of ₹ 6,000 received from Bhargav is deposited with bank but not recorded in cashbook.
25 Payment side of cashbook was overcast by ₹ 4,000 while carry forwarding the balance of cashbook on next page.
29 A cheque of ₹ 12,000 was issued to BSNL for telephone bill, which was paid by bank, on 30 – 4 – ’16 but it is recorded in cashbook by ₹ 1,200.
Answer:
![]()
Question 13.
Ambica Electronics is having two accounts with Bank of Baroda. Account no. 100 and account no. 101. Cashbook of account no. 100 shows balance of ₹ 9,000, while cashbook of account no. 101 shows bank overdraft of ₹ 6,000 on 31 – 3 – ’16. Prepare bank reconciliation statement of Ambica Electricals for account no. 100 for the month of March, 2016.
(1) A cheque of ₹ 10,000 in account no. 100 and cheque of ₹ 8,000 in account no. 101 were deposited. Bank has credited amount of account no. 100 in account no. 101 and the amount of account no. 101 in the account of no. 100 by mistake.
(2) A cheque of ₹ 3,000 was issued on account no. 101 which is not yet presented for payment in bank.
(3) Cheques totalling ₹ 9,000 were deposited in account no. 100 out of a cheque of ₹ 2,500 was credited by bank in account no. 101 by mistake.
(4) A cheque of ₹ 2,600 was issued on account no. 101, payment of which is debited by bank in account no. 100.
(5) A customer has deposited directly ₹ 2,000 and ₹ 800 in account no. 101 and account no. 100 respectively, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(6) Bank has debited ₹ 300 for bank charges in account no. 100 and credited ₹ 170 for bank interest in account no. 101, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(7) Cheques of ₹ 7,000 were issued on account no. 100, out of which cheques of ₹ 1,200 are not yet presented for payment.
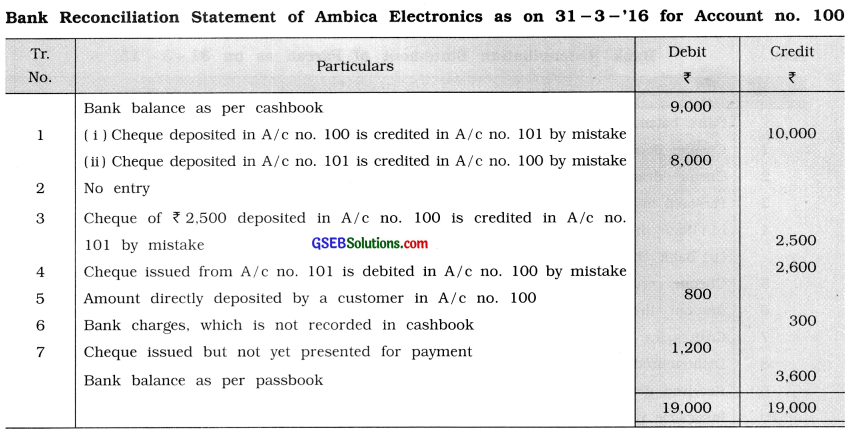
Explanation :
(1) Transaction no. 2 will not be recorded because it is issued from A/c no. 101, whereas this is a B.R.S. for A/c no. 100.
(2) Similarly, in transaction no. 6, interest credited by bank in A/c no. 101 will not be taken into consideration for the preperation of a B.R.S. of A/c no. 100.
![]()
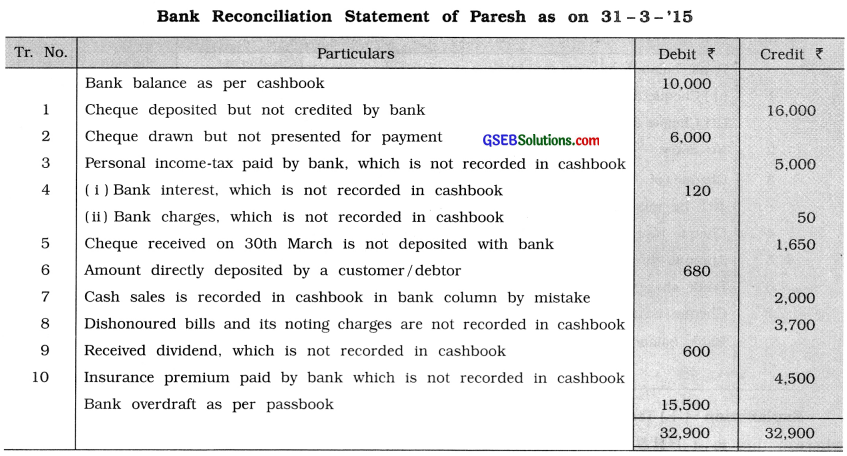
Question 14.
Cashbook of Paresh shows bank balance of ₹ 10,000 on 31 – 3 – ’15. This balance does not tally with bank balance as per passbook. From the following information prepare bank reconciliation statement for March, 2015 :
(1) Cheques of ₹ 30,000 were deposited in bank during the month of March out of which cheques of ₹ 16,000 were credited in bank on 2nd April.
(2) Cheques of ₹ 16,000 were drawn during the month of March out of which a cheque of ? 10,000 was presented for payment till 31st March.
(3) During the month of March, bank paid ₹ 5,000 for personal income tax out of bank account of business, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(4) On 31st March, bank has credited ₹ 120 for interest and debited ₹ 50 for bank charges, which are not recorded in cashbook.
(5) A cheque of ₹ 1,650 received on 30th March is not deposited with bank.
(6) A debtor has directly deposited ₹ 680 in bank, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(7) Cash sales of ₹ 2,000 is recorded in cashbook in bank column.
(8) A bills of ₹ 3,600 discounted in February 2015 was dishonoured on maturity date during the month of March and bank has recorded the same in passbook including noting charges of ? 100, which is not recorded in cashbook.
(9) ₹ 600 received for dividend on shares is recorded in passbook but not recorded in cashbook.
(10) Bank has paid ₹ 4,500 for insurance premium as per instruction of Paresh, which is not recorded in cashbook.
Answer:
![]()
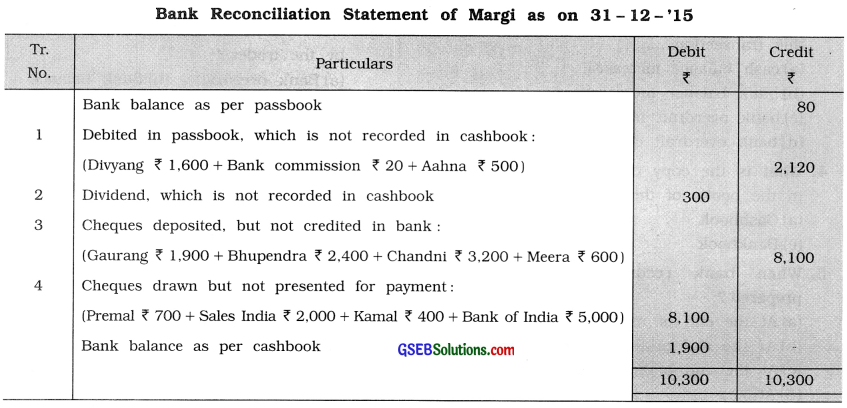
Question 15.
From the following information, prepare bank reconciliation statement of Margi :
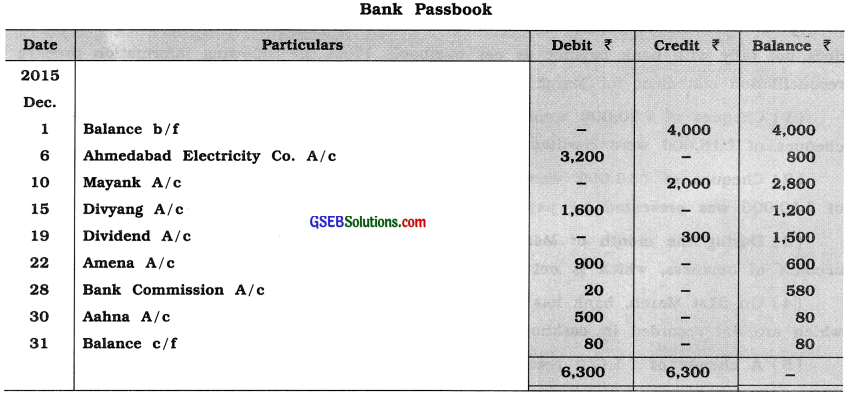
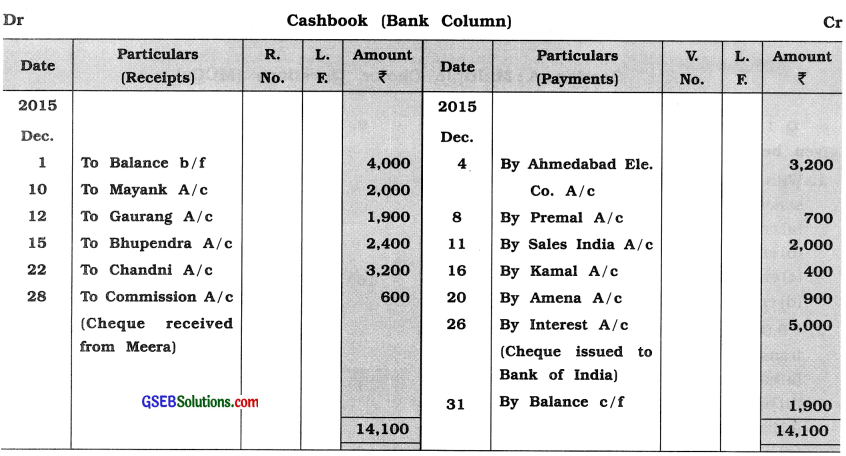
Answer: