Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Commerce Accounts Part 1 Chapter 2 Dual Effect of Transactions and Types of Accounts Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Accounts Part 1 Chapter 2 Dual Effect of Transactions and Types of Accounts
GSEB Class 11 Accounts Dual Effect of Transactions and Types of Accounts Text Book Questions and Answers
1. Write the correct option from those given below each question:
Question 1.
Which of the following characteristic is not applicable to economic transaction ?
(a) Cash transaction
(b) Credit transaction
(c) External transaction
(d) Transaction without monetary value
Answer:
(d) Transaction without monetary value
Question 2.
Rent paid ₹ 10,000. What type of transaction is it?
(a) Cash transaction of asset
(b) Non-cash transaction of service
(c) Cash transaction of service
(d) Cash transaction of liability
Answer:
(c) Cash transaction of service
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following transactions is a transaction of special nature ?
(a) Goods purchased of ₹ 5,000
(b) Goods of ₹ 5,000 purchased from ‘B’
(c) Goods of ₹ 5,000 purchased through cheque
(d) Goods destroyed by fire ₹ 5,000
Answer:
(d) Goods destroyed by fire ₹ 5,000
Question 4.
Which transaction disclosed relation of debtor and creditor ?
(a) Goods purchased of ₹ 8,000
(b) Goods of ₹ 8,000 purchased from ‘B’
(c) Good of ₹ 8,000 purchased through cheque
(d) Goods destroyed by fire ₹ 8,000
Answer:
(b) Goods of ₹ 8,000 purchased from ‘B’
2. Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
What is dual effect ?
Answer:
Dual effect means first effect is debit and second effect is credit. In short, every business transaction is recorded with at least two effects or aspects.
Question 2.
What is cash transaction ?
Answer:
A transaction because of which cash or bank balance of the business gets affected (increases or decreases) is known as cash transaction.
Question 3.
Explain credit transaction.
Answer:
Purchase-sale of goods, asset, service are made in present but their money is payable or receivable in future. These transactions are recognized as credit transactions.
Question 4.
Give illustration of cash transaction of goods.
Answer:
Purchased goods of ₹ 20,000 for cash. Sold goods of ₹ 24,000 on cash.
![]()
Question 5.
Give illustration of cash transaction of service.
Answer:
Paid salary of ₹ 15,000 to employee. (Salary is a service). Received commission of ₹ 12,000. (Work of commission is a service).
Question 6.
Give illustration of credit transaction of goods.
Answer:
Purchased goods of ₹ 21,000 from Bhavna Stores on credit. Sold goods of ₹ 9,000 to Eshita.
Question 7.
Give illustration of credit transaction of service.
Answer:
Rent of ₹ 4,500 is receivable from Dhara. Brokerage of ₹ 6,000 is payable to Kailash.
Question 8.
Which transaction is called noneconomic transaction?
Answer:
Non-economic transaction is that transaction whose value cannot be measured in terms of money.
3. Answer the following questions in two or three sentences:
Question 1.
Distinguish between Cash transaction and Credit transaction.
Answer:
Cash transaction
- A transaction in which an exchange of cash takes place is known as Cash transaction.
- In such a transaction, one account is definitely related to Cash /Bank.
- In such transaction specifies that it is for cash or there is no mention about cash or name of person.
- Cash transaction is recorded in Cash book or Petty cash book.
- Cash account or Cash book is prepared to keep record of cash transactions and cash balance can be known at the end of the given period.
- No debt is created due to cash transaction.
Credit transaction
- A transaction in which no exchange of cash takes place is known as Credit transaction.
- In such a transaction, one account affected Is of a person.
- In such transaction, there is only name of person without specifying that it is for cash.
- Credit transactions are recorded in Purchase book, Sales book, Goods-returns book or in Journal proper.
- Debtors and Creditors accounts are prepared from credit transactions and amount payable to creditors as well as total amount receivable from debtors can be known from these accounts.
- A debt is created due to credit transaction.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between Economic transaction and Non-economic transaction.
Answer:
Economic transaction
- A transaction which can be measured in terms of money is known as Economic transaction.
- Economic transactions have effect on business from accounting view point.
- Economic transactions are recorded in the books of accounts of business.
- Economic transactions can be classified into three types :(1) Cash transactions, (2) Credit transactions and (3) Exchange transactions.
- Illustration : Purchased goods worth ? 24,000 for cash.
Non-economic transaction
- A transaction which has no monetary value or in a transaction where money is not involved are known as Non-economic transaction.
- Non-economic transactions have no effect on business from accounting view point.
- Non-economic transactions are not recorded in the books of accounts of business.
- Non-economic transactions cannot be classified.
- Illustration: Received an order for supply of goods of ? 6,000 from Kushal.
Question 3.
Explain internal and external transaction.
Answer:
Internal transaction : These type of transactions would take place within business. In certain transactions of business, there is no need of other parties. That is why, these transactions are called Internal transactions, e.g., Loss in business due to natural calamity, depreciation on asset, asset became out of dated, etc. Internal transactions are all economic transactions but are non-cash transactions. These transactions are recorded in the books of accounts.
External transaction : When transactions are taken place between the business and other parties, then these transactions are called External transactions, e.g., purchased goods from traders, cash withdrawn from bank, amount paid for insurance premium, paid salary to employees, purchase of asset, payment of interest on B.O.D. to bank, etc. External transactions are all economic transactions, which are recorded in the books of accounts.
Question 4.
Explain other transactions.
Answer:
The transactions, which are neither cash nor credit transactions, but they are real or actual transactions, these transactions are called special or other transactions.
Theft of goods, goods destroyed in fire, goods given for donation, received goods against old furniture, asset turned defective or useless, etc. are special or other transactions, which are recorded in the books of accounts.
4. To which account, the following transactions will be debited and credited in the books of Nilima? Describe with reason :
Questions
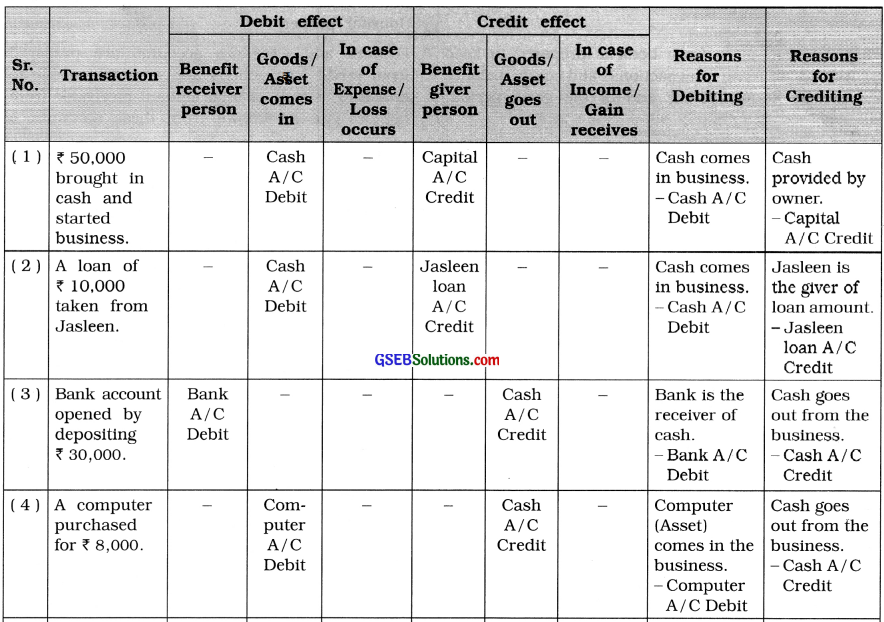
(1) ₹ 50,000 brought in cash and started business.
(2) A loan of ₹ 10,000 taken from Jasleen.
(3) Bank account opened by depositing ₹ 30,000.
(4) A computer purchased for ₹ 8,000.
(5) Stationery purchased ₹ 1,000.
(6) Purchase made of ₹ 20,000.
(7) Purchase is made of ₹ 30,000 from Raman.
(8) Goods of ₹ 15,000 sold on cash for ₹ 28,000.
(9) Goods of ₹ 8,000 sold to Nila for ₹ 15,000.
(10) Goods returned to Raman of ₹ 2,000.
(11) Goods returned by Nila of ₹ 1,500.
(12) Paid ₹ 500 for carriage.
(13) Goods of ₹ 200 destroyed by fire.
(14) Commission received ₹ 5,000.
(15) ₹ 2,000 paid for salary.
Answer:
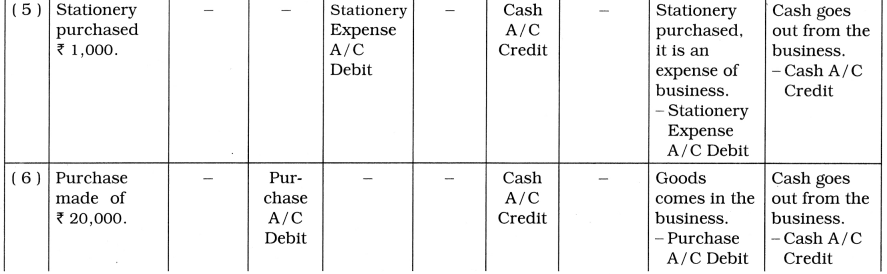
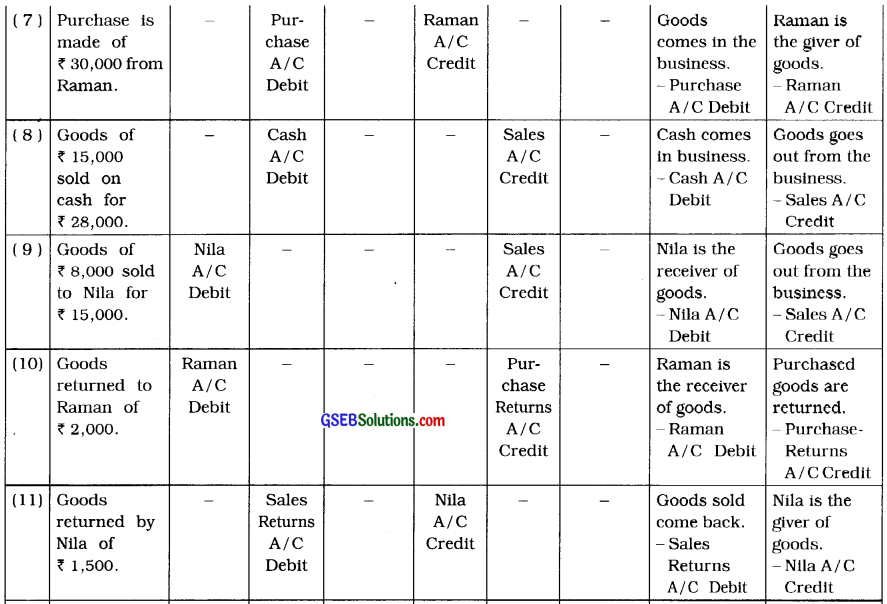
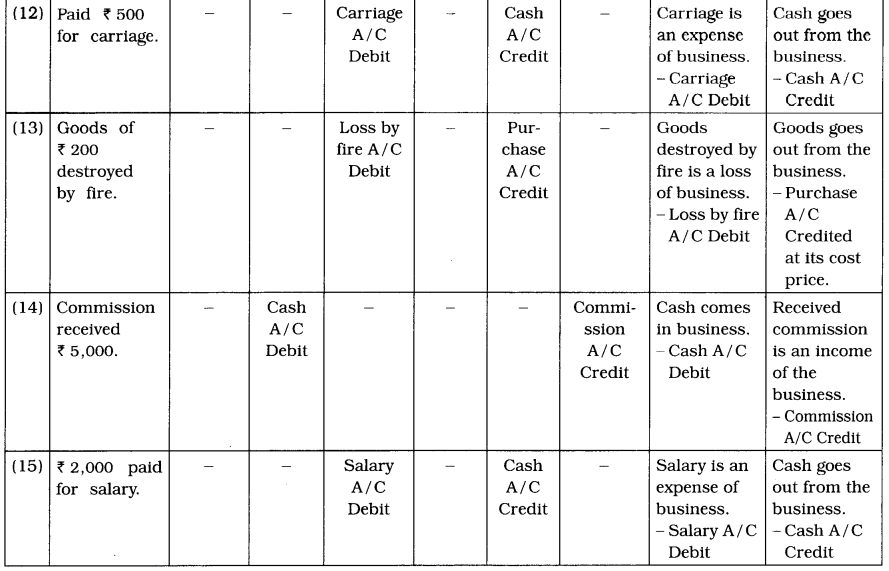
![]()
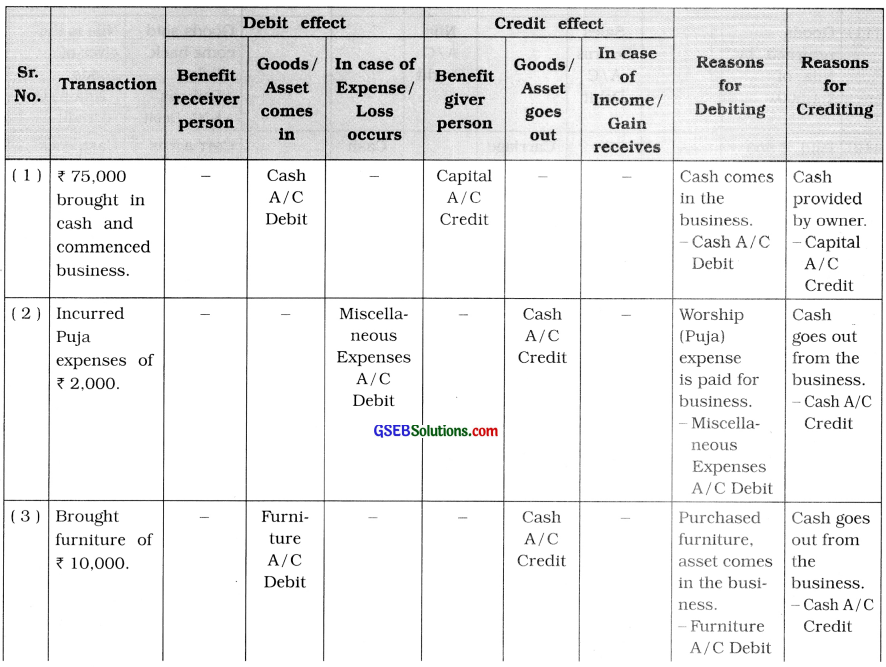
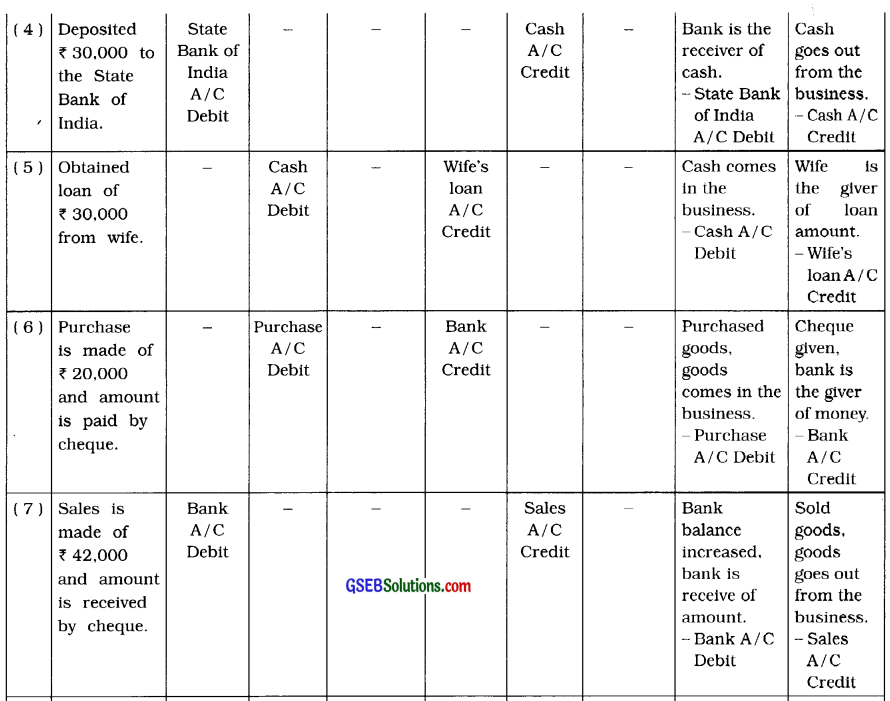
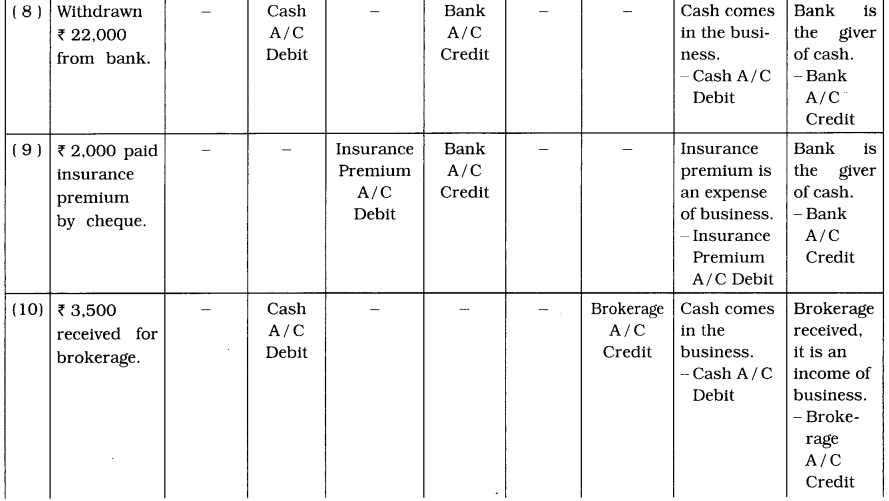
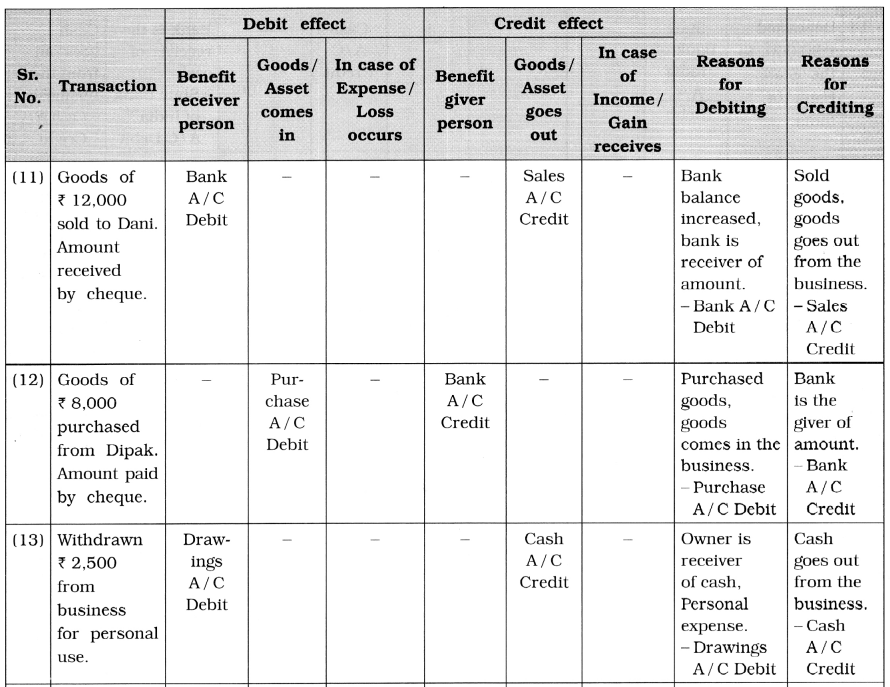
5. To which account, the following transactions will be debited and credited in the books of Ganesh ? Describe with reason:
Questions
(1) ₹ 75,000 brought in cash and commenced business.
(2) Incurred Puja expenses of ₹ 2,000.
(3) Brought furniture of ₹ 10,000.
(4) Deposited ₹ 30,000 to the State Bank of India.
(5) Obtained loan of ₹ 30,000 from wife.
(6) Purchase is made of ₹ 20,000 and amount is paid by cheque.
(7) Sales is made of ₹ 42,000 and amount is received by cheque.
(8) Withdrawn ₹ 22,000 from Bank.
(9) ₹ 2,000 paid insurance premium by cheque.
(10) ₹ 3,500 received for brokerage.
(11) Goods of ₹ 12,000 sold to Dani. Amount received by cheque.
(12) Goods of ₹ 8,000 purchased from Dipak. Amount paid by cheque.
(13) Withdrawn ₹ 2,500 from business for personal use.
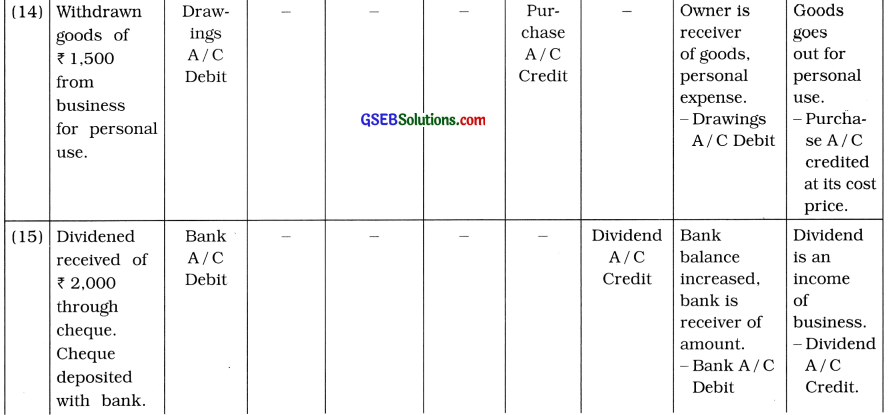
(14) Withdrawn goods of ₹ 1,500 from business for personal use.
(15) Dividend received ₹ 2,000 through cheque. Cheque deposited with bank.
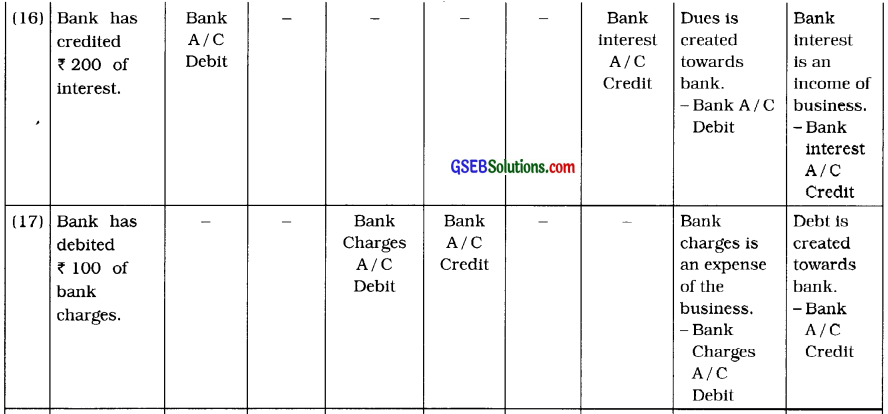
(16) Bank has credited ₹ 200 of interest.
(17) Bank has debited ₹ 100 of bank charges.
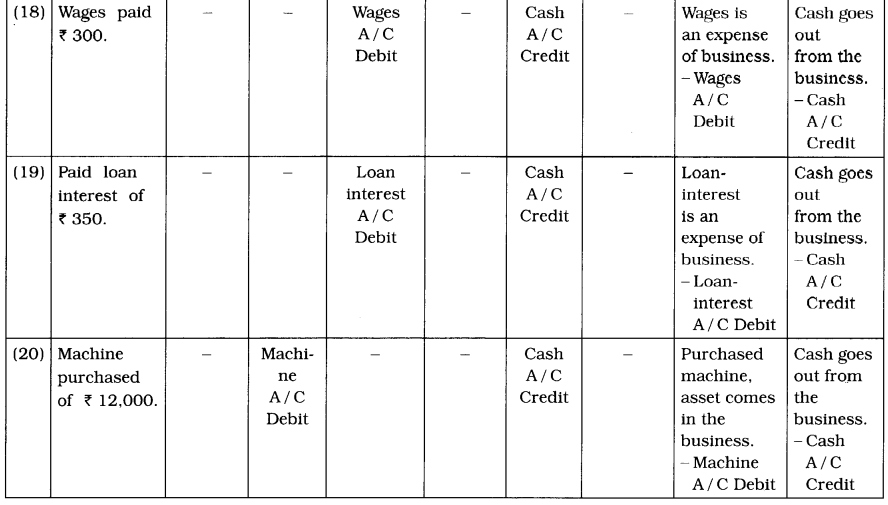
(18) Wages paid ₹ 300.
(19) Paid loan interest of ₹ 350.
(20) Machine purchased of ₹ 12,000.
Answer: