Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Commerce Accounts Part 2 Chapter 1 Rectification of Errors Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Accounts Part 2 Chapter 1 Rectification of Errors
GSEB Class 11 Accounts Rectification of Errors Text Book Questions and Answers
1. Write the correct option from those given below each question:
Question 1.
When a transaction is left unrecorded in primary books, the error is known as …………………… .
(a) Errors of compensatory
(b) Errors of omission
(c) Errors of principle
(d) Not carry forward to Suspense A/c
Answer:
(b) Errors of omission
Question 2.
An error arises because of non-compliance of accounting principles is known as ………………………. .
(a) Errors of compensatory
(b) Errors of omission
(c) Errors of principle
(d) Not carry forward to Suspense A/c
Answer:
(c) Errors of principle
Question 3.
An error arises because of debiting or crediting a wrong account with correct amount on the correct side is known as ………………. .
(a) Errors of compensatory
(b) Errors of omission
(c) Errors of principle
(d) Errors of recording to a wrong account
Answer:
(c) Errors of principle
Question 4.
When trial balance does not tally, it is tallied temporarily with the help of …………………….. .
(a) Trading A/c
(b) Suspense A/c
(c) Profit and Loss A/c
(d) Balance Sheet
Answer:
(b) Suspense A/c
![]()
Question 5.
By opening Suspense account, which of the following accounts brings effect on ‘Profit and Loss Account?
(a) Error in Personal A/c
(b) Error in Assets A/c
(c) Error in both Personal A/c and Assets A/c
(d) Error in Goods A/c and Nominal A/c.
Answer:
(d) Error in Goods A/c and Nominal A/c
2. Answer the following questions in one sentence:
Question 1.
State the types of accounting errors.
Answer:
Accounting errors are classified into two parts, based on whether they affect the trial balance or not.
- Errors which do not affect the trial balance.
- Errors which affect the trial balance.
Question 2.
State the errors not affecting the trial balance.
Answer:
Following are the different types of errors which do not affect the trial balance:
- Errors of omission
- Errors of principle
- Errors of recording to a wrong account
- Errors committed at the time of recording in primary books
- Compensatory errors.
Question 3.
State the errors affecting the trial balance.
Answer:
Following are the different types of errors which affect the trial balance :
- Errors regarding posting
- Errors regarding balance of an account
- Errors in totalling the subsidiary books
- Errors committed at the time of preparing the trial balance
Question 4.
When is the Suspense A/c used?
Answer:
When the trial balance does not tally in spite of repeated efforts, then the Suspense account is used for tallying the trial balance. In short Suspense A/c is used for rectification of errors.
Other than rectification of errors, Suspense A/c is also useful for various other purposes such as, When it is not possible to decide the account head or account to be debited or account to be credited, Suspense A/c is used.
Suspense A/c is used in a journal entry when trader/businessman does not want to disclose the name of the party.
![]()
Question 5.
When does the accounting errors affect the profit?
Answer:
When the accounting errors affects the accounts of goods and the accounts of income- expenses, then these errors affect the profit of the business.
Question 6.
When does the accounting errors do not affect the profit?
Answer:
When the accounting errors affect the assets accounts or personal accounts, then these errors do not affect the profit of the business.
3. Answer the following questions in detail:
Question 1.
What is errors of omission? How to rectify these errors? Explain with illustration.
Answer:
Meaning: When a transaction is totally omitted to be recorded in the journal or the subsidiary books or the ledger, such an error is known as an error of omission. The trial balance will tally even though error of omission is committed because posting is omitted on both credit and debit side.
How to rectify these errors?
Errors of omission take place at two stages :
1. A transaction is totally omitted to be recorded in the journal or the subsidiary books or the ledger.
e.g., Goods sold to Rajan for ₹ 12,000 is not recorded in the books. This transaction is not recorded in journal or in subsidiary book. As a result, the Rajan’s account is not debited by ₹ 12,000 and sales account is not credited by ₹ 12,000. Thus, on debit side and on credit side error is there with an equal amount and therefore trial balance will tally. For this, rectification entry is passed as follows :

2. A transaction is totally recorded in the journal or the subsidiary books or the ledger but posting of both accounts are omitted.
e.g., Washing machine purchased on credit from Sales India off 35,000 is recorded in journal proper, but it is forgotten to be posted in the accounts of Washing machine and Sales India in ledger.
To rectify this error there is no need to record journal entry in journal proper but the error will be rectified by debiting Washing machine A/c and crediting Sales India A/c in ledger.
Question 2.
What is errors of principle? How to rectify these errors? Explain with illustration.
Answer:
Meaning: Error of principle means, while writing the books of accounts, the basic principles of accounts are violated. These types of errors do not affect the trial balance. Because the amount of the transaction is same but instead of one account any other account is debited or credited.
How to rectify these errors?
In such types of errors, capital expenditure is treated as revenue expenditure or capital income is treated as revenue income and recorded in the books accordingly.
e.g., Old machine of ₹ 6,000 sold to Sunder Patel which is recorded in the sales book. Here machine is an asset of the business, so it should not be credited to sales account (should be credited to machine account) which is recorded in the wrong account and therefore principle is violated. Though this type of the error is there, trial balance will get tally, because the debited and credited amount are same. So rectification entry is passed as follows :

Question 3.
What is compensatory errors ? How to rectify these errors ? Explain with illustration.
Answer:
Meaning: In the books of accounts when more than one error exists but because of their nullifying effects on both debit and credit sides, the trial balance tallies, such errors are known as compensatory errors.
In this type of error, the effect of error (or errors) on one side is removed by the effect of error (or errors) on another side. Means, the error on the amount on debit side, with the same amount if an error is there on the credit side, then the effect of error in totalling will be removed and trial balance will get tally.
How to rectify these errors?
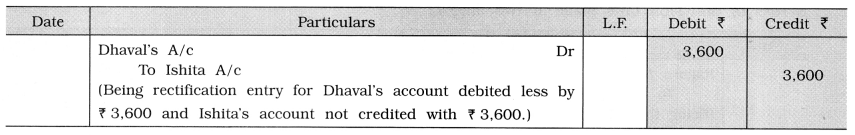
e.g., Goods of ₹ 4,000 sold to Dhaval which is debited to his account as f 400, while received ₹ 3,600 from Ishita, which is not posted to her account. Here Dhaval’s account is debited less by ₹ 3,600 which is compensated with the error of ₹ 3,600 received from Ishita and not credited to her account, and therefore the trial balance will get tally. And so rectification entry is passed as follow :
![]()
Question 4.
Write note on Suspense Account.
Ans. Meaning: When the trial balance does not tally because of some accounting errors and it requires more time to prepare final accounts after detection and rectification of such errors, but there is an urgency for preparing final accounts, temporarily the difference in the trial balance is transferred to one account, in order to get it tallied and that account is known as a ‘Suspense Account’.
If in the debit column of trial balance the amount is written then Suspense Account has debit balance and if in the credit column of trial balance the amount is written then Suspense Account has credit balance. While preparing the final accounts, this balance is shown in the Balance Sheet. If the balance of Suspense Account is a debit balance then, it will be written on Assets – Receivables’ side and if the balance is a credit balance then it will be shown on ‘Capital – Liabilities’ side.
Suspense Account is opened on temporary basis and therefore after detecting the errors in the next year, with the help of rectification entries, errors are rectified. Here effected accounts are to be passed on debit or credit side while the other effects are to be recorded in the Suspense Account.
Illustration: Received f 100 from ‘A’ is not posted to his account. In this error, A’s account is not credited therefore debit the Suspense Account and credit the A’s account. In this way, after all errors are rectified, the Suspense Account should not have any balance, means it should be closed automatically, but still if there is balance in Suspense Account it means that some errors still remains undetected and unrectified or it may be possible that some new errors, took place while making rectification. Other uses of Suspense Account: Other than rectification of errors, Suspense Account is useful for various other purposes, such as,
- When it is not possible to decide the account head (name) or account to be debited or account to be credited, Suspense A/c is used.
- Suspense A/c is used in a journal entry when trader/businessman does not want to disclose the name of the party.
![]()
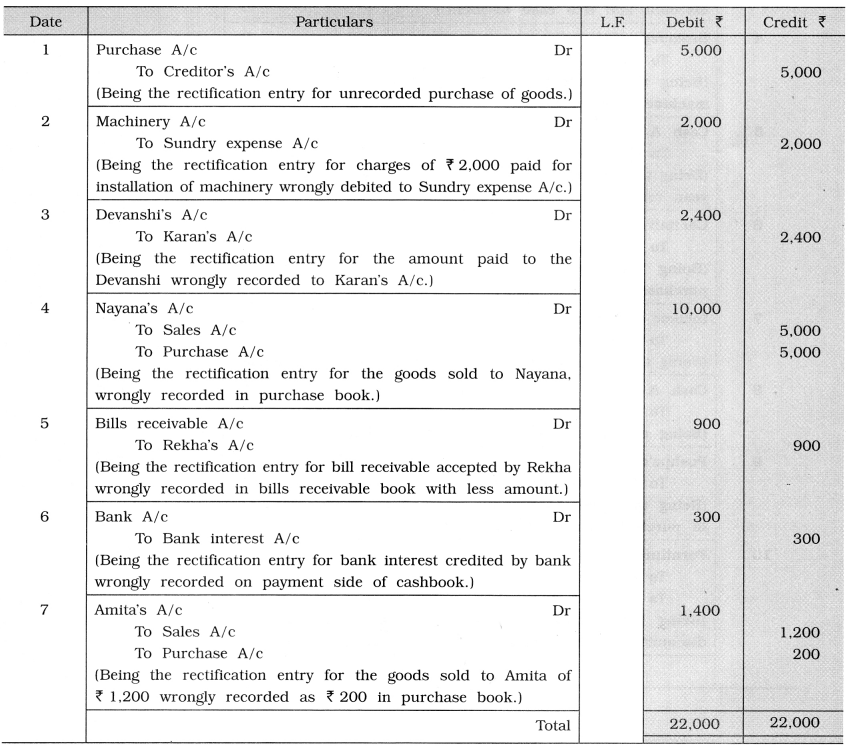
4. Prepare rectification entries to rectify the following errors detected while preparing final accounts of Shri Balram as on 31-03-’15:
(1) Purchase of goods ₹ 5,000 is left to be recorded.
(2) Installation charges paid ₹ 2,000 on purchase of machinery is debited to Sundry expense account.
(3) ₹ 2,400 paid to Devanshi is recorded to Karan’s account by mistake.
(4) Goods of ₹ 5,000 sold to Nayana is recorded in purchase book by mistake.
(5) Our bill receivable off 1,900 accepted by Rekha is recorded in bills receivable book by ₹ 1,000.
(6) ₹ 150 credited by bank as interest in passbook recorded on payment side of cashbook.
(7) Goods of ₹ 1,200 sold to Amita is recorded in purchase book by ₹ 200.
Answer:
Rectification Entries of Shri Balram
Question 5.
Pass necessary rectification entries to rectify the following journal entries written by Ishwarlal:
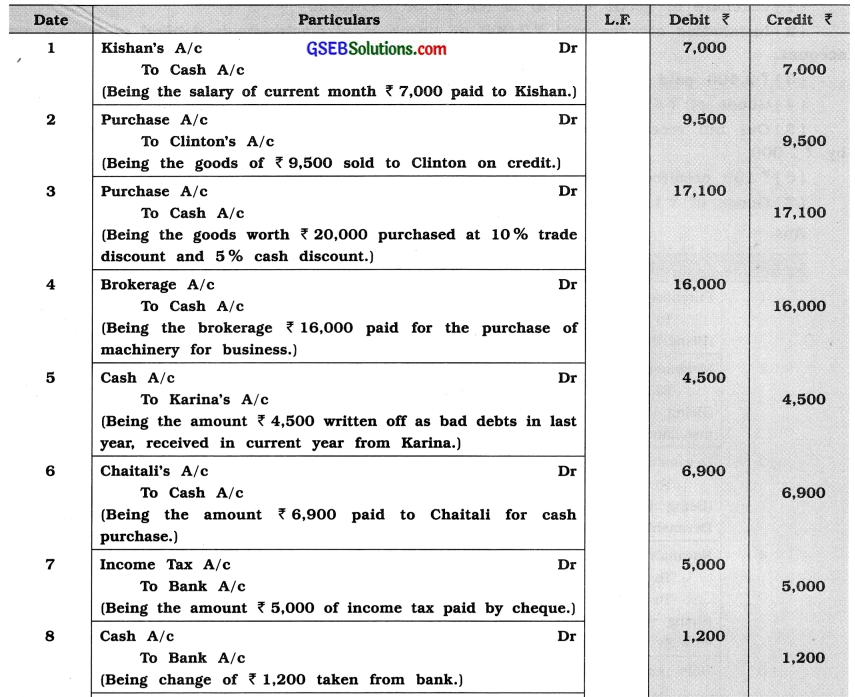
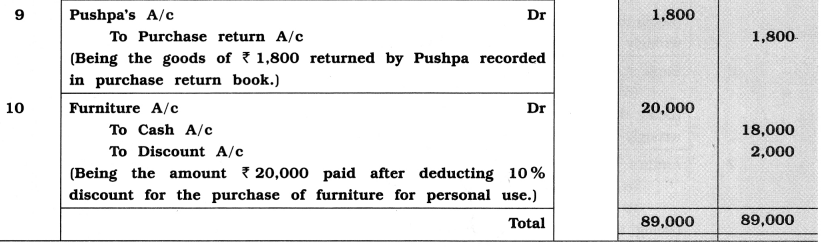
Answer:
Rectification Entries of Shri Ishwarlal
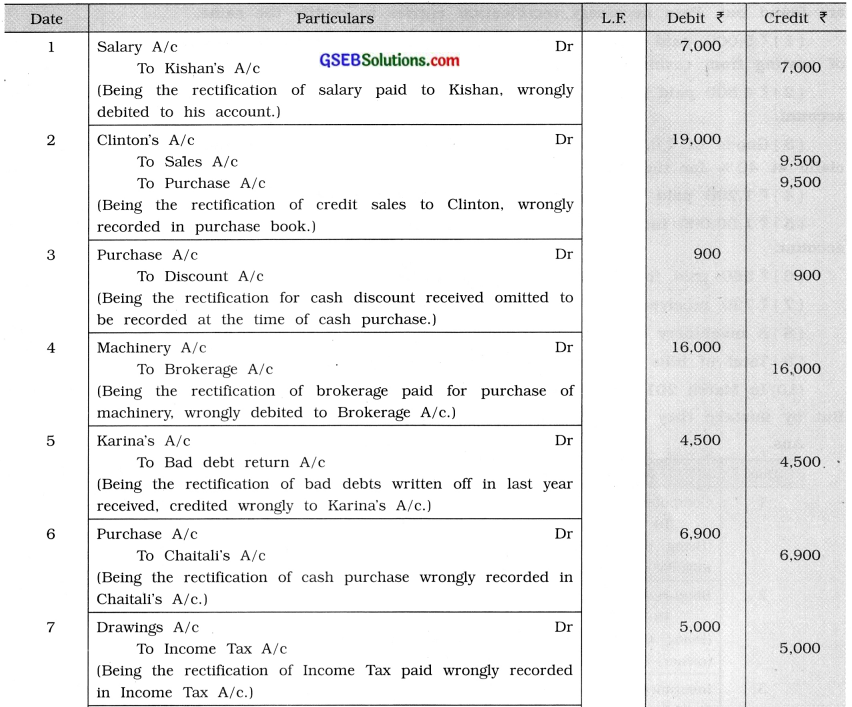
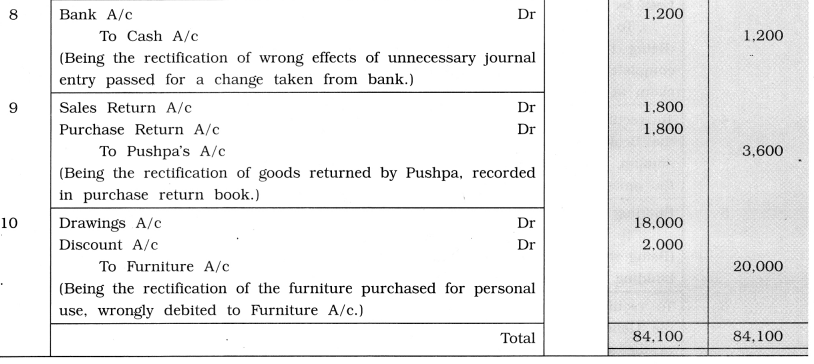
Question 6.
At the time of preparing final accounts of Vivek as on 31-3-’15, the following errors are found out. Pass necessary rectification entries to rectify the same.
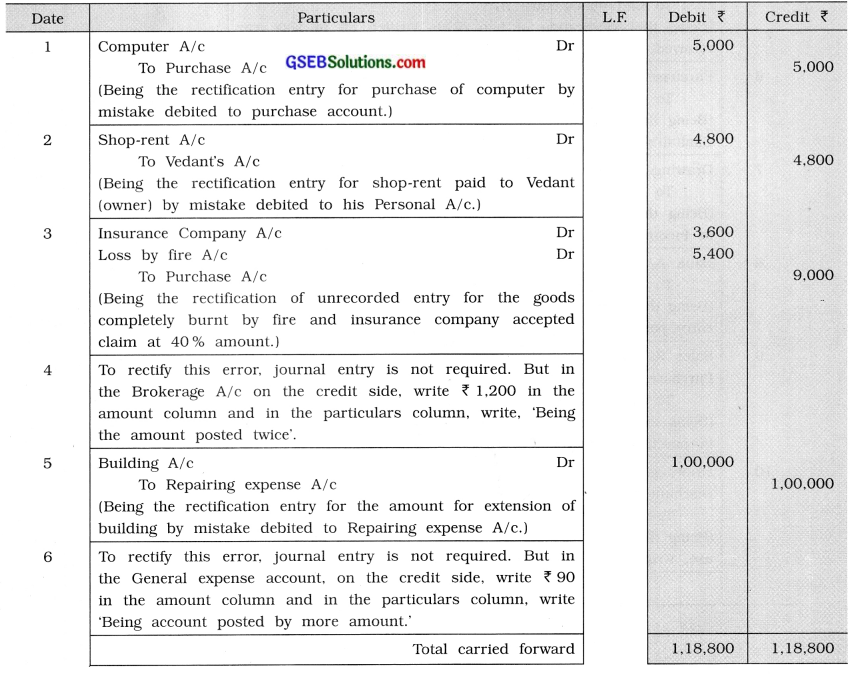
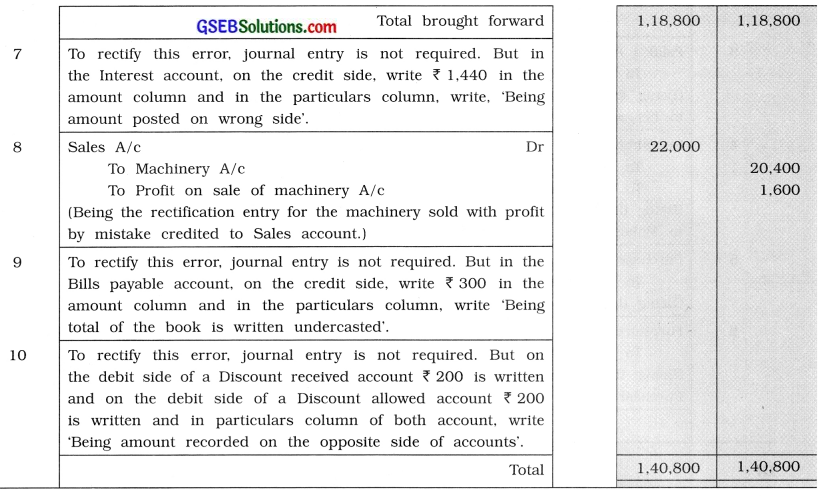
(1) ₹ 5,000 paid for purchase of a computer is debited to Purchase account at the time of posting from cashbook.
(2) ₹ 4,800 paid for rent to Vedant, an owner of shop, by mistake is debited to his Personal
account.
(3) Goods of ₹ 9,000 are completely burnt by fire and insurance company has accepted a claim at 40 % for the same, which is unrecorded by mistake.
(4) ₹ 1,200 paid for brokerage is posted twice in Brokerage A/c.
(5) ₹ 1,00,000 incurred for extension of building, by mistake, is debited to repairing expense account.
(6) ₹ 560 paid for general expense is posted to that account as ₹ 650.
(7) ₹ 720 received towards interest is posted to interest account on debit side.
(8) A machinery of ₹ 20,400 is sold for ₹ 22,000. It is recorded in sales book by ₹ 22,000.
(9) Total of bills payable book is undercast by ₹ 300.
(10) In March 2015, discount received and discount paid are ₹ 3,400 and ₹ 3,600 respectively. But by mistake they are recorded on their opposite sides.
Answer:
Rectification Entries of Shri Vivek
Question 7.
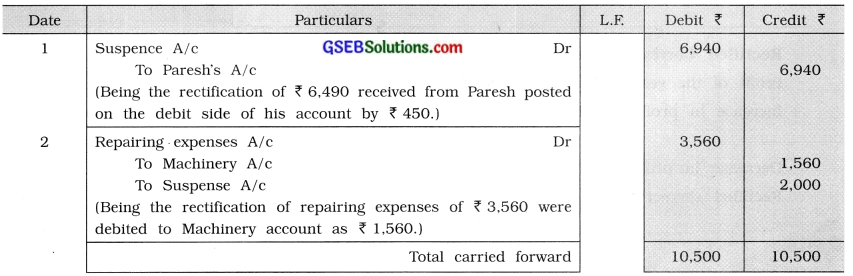
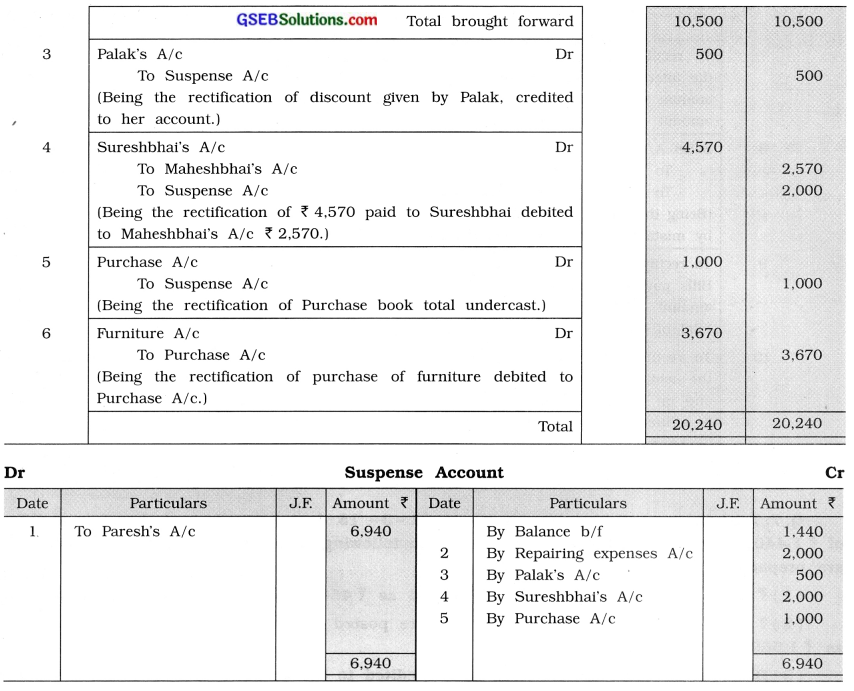
Trial balance of Shri Marmik as on 31-3-’15 does not tally and therefore a difference of ₹ 1,440 is credited to Suspense account. The following errors are detected after final accounts are prepared :
(1) ₹ 6,490 received from Paresh is posted as ₹ 450 on the debit side of his account.
(2) ₹ 3,560 paid for repairing expenses were posted on the debit side of machinery account as ₹ 1,560.
(3) Discount of ₹ 250 given by Palak is credited to his account as well as discount received account.
(4) ₹ 4,570 paid to Sureshbhai is debited to Maheshbhai’s account as ₹ 2,570.
(5) Total of purchase book is undercast by ₹ 1,000.
(6) Purchase of furniture of ₹ 3,670 debited to purchase account.
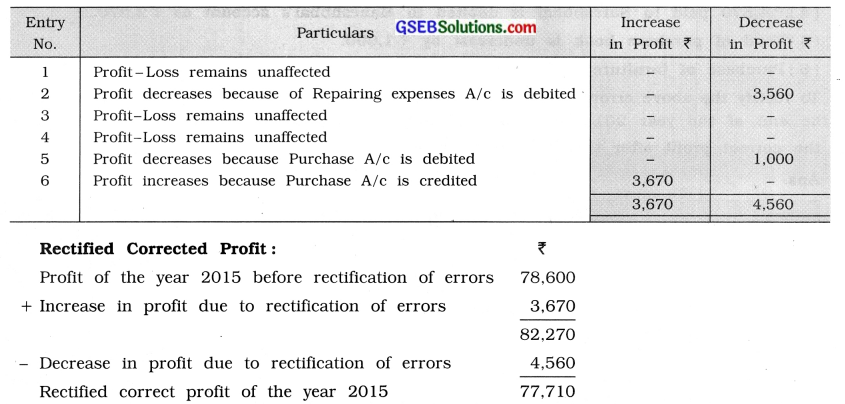
To rectify the above errors, pass necessary rectification entries and prepare Suspense account. At the end of the year 2015, if profit and loss account discloses a profit of ₹ 78,600. Find out the correct profit after the rectification of errors.
Answer:
Rectification Entries of Shri Marmik
![]()
Question 8.
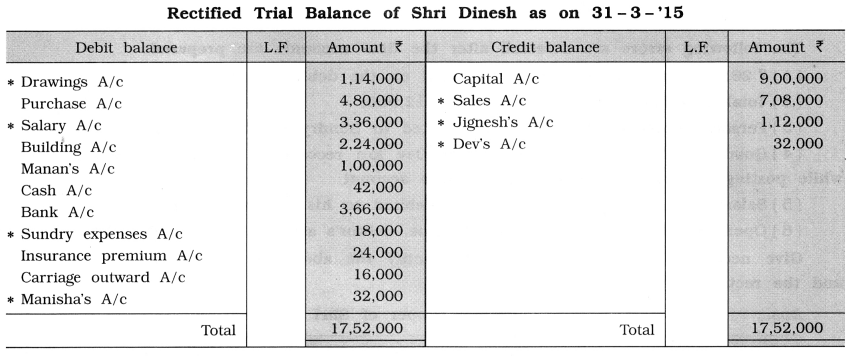
Trial balance of Shri Dinesh as on 31-3-’15 does not tally. The difference is transferred to Suspense account in order to get it tallied, which is as under:
| Debit Balance | Amount (₹) | Credit Balance | Amount (₹) |
| Drawings A/c | 1,00,000 | Capital A/c | 9,00,000 |
| Purchase A/c | 4,80,000 | Sales A/c | 7,20,000 |
| Salary A/c | 3,08,000 | Jignesh’s A/c | 84,000 |
| Building A/c | 2,24,000 | Suspense A/c | 36,000 |
| Devs A/c | 48,000 | ||
| Manan’s A/c | 1,00,000 | ||
| Cash A/c | 42,000 | ||
| Bank A/c | 3,66,000 | ||
| Sundry expense A/c | 32,000 | ||
| Insurance premium A/c | 24,000 | ||
| Carriage outward A/c | 16,000 | ||
| Total | 17,40,000 | Total | 17,40,000 |
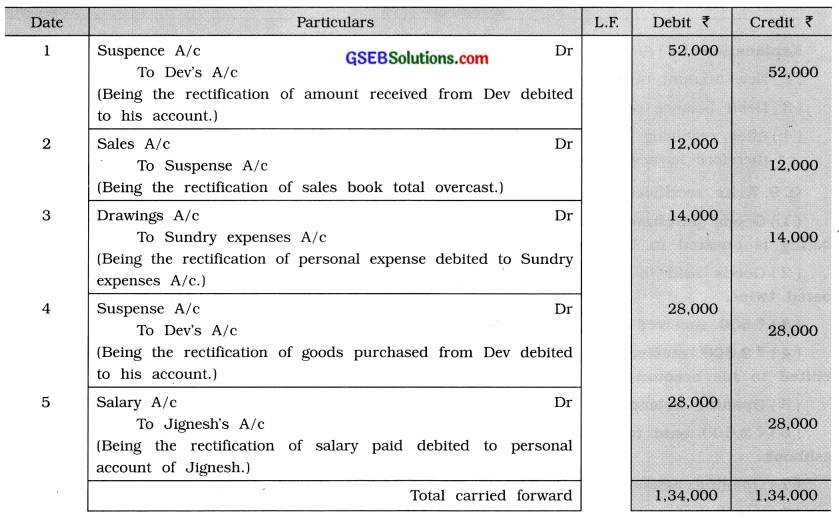
The following errors are detected after the final accounts are prepared:
(1) ₹ 26,000 received from Dev is posted on the debit side of his account.
(2) Total of sales book is overcast by ₹ 12,000.
(3) Personal expense of ₹ 14,000 is debited to Sundry expenses account.
(4) Goods of ₹ 14,000 purchased from Dev are recorded correctly in purchase book but while posting the same were debited to Dev’s account.
(5) Salary paid to Jignesh ₹ 28,000 is debited to his personal account.
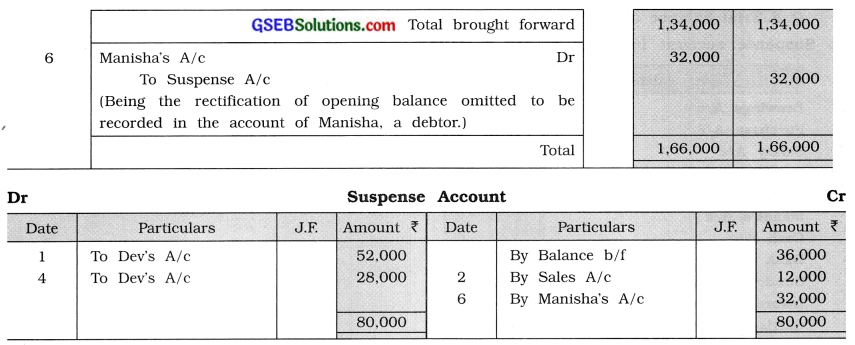
(6) Opening balance of ₹ 32,000 of Manisha, debtor’s account, is omitted to be carried down. Give necessary rectification entries to rectify the above errors. Prepare Suspence account and the rectified trial balance.
Answer:
Journal Proper of Shri Dinesh

Explanation:
(1) Amount of accounts having asterisk mark, is changed after rectification of errors.
(2) New account of Manisha is added.
(3) Debit balance of Dev’s A/c is now converted into a credit balance.
(4) After rectifying all errors, when the effect is given in Suspense Account it is closed and therefore in the new rectified trial balance its balance is not shown.
Question 9.
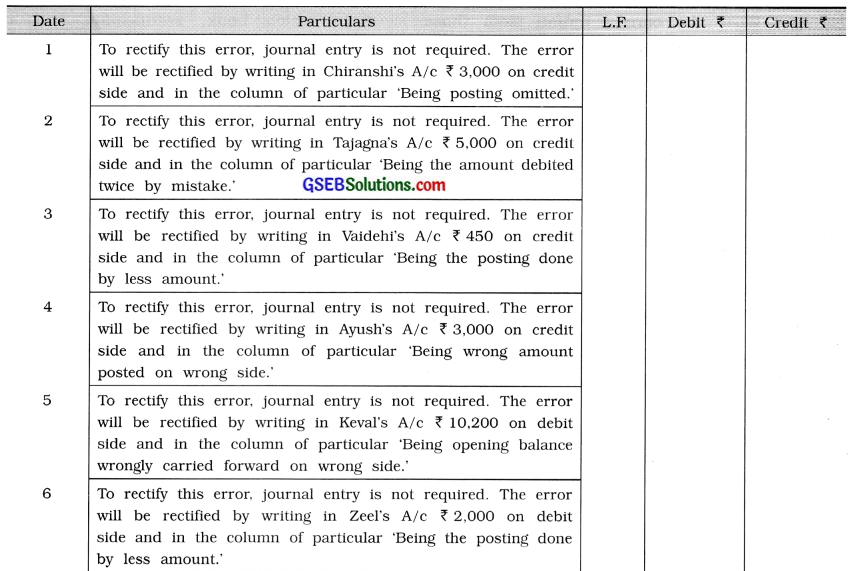
Write rectification entries for the errors found in the books of Priyansh:
(1) Goods purchased of ₹ 3,000 from Chiranshi is recorded correctly in the purchase book. But posting is omitted in her account.
(2) Goods sold to Tajagna ₹ 5,000 is correctly recorded in the sales book, but her account is posted twice.
(3) ₹ 500 received from Vaidehi is posted to her account by ₹ 50.
(4) ₹ 2,500 received from Ayush is correctly recorded in the cashbook, but ₹ 500 has been debited to his account.
(5) Opening balance of a debtor, Keval, ₹ 5,100 is carried forward on the credit side.
(6) ₹ 2,500 paid to a creditor, Zeel is debited to her account by ₹ 500 while posting from cashbook.
(7) Opening balance of machine account ₹ 54,000 is recorded as ₹ 45,000.
(8) Credit balance of bank loan account ₹ 7,500 is omitted to be recorded in trial balance.
(9) Balance of rent paid ₹ 860 is recorded as credit balance by ₹ 680 in trial balance.
Question 10.
Total of sales return book undercast by ₹ 500.
Answer:
Journal Proper of Shri Priyansh