Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Chapter 4 Communication, E-Commerce and Outsourcing Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Chapter 4 Communication, E-Commerce and Outsourcing
GSEB Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Communication, E-Commerce and Outsourcing Text Book Questions and Answers
1. Select the correct alternative and write answers to the following questions :
Question 1.
By which process the customer is provided the facility of purchase and sell by the bid of the cost of the product?
(A) Business by customer
(B) Business by business
(C) Customer to customer
(D) Business by customer
Answer:
(A) Business by customer
Question 2.
The railway tickets are available from any place that is known as which type of Network?
(A) Enterprise Wan
(B) LAN
(C) MAN
(D) CAN
Answer:
(A) Enterprise Wan
Question 3.
The business units allot their works to the outside institution that is known as?
(A) E-commerce
(B) Outsourcing
(C) E-mail
(D) Net-banking
Answer:
(B) Outsourcing
Question 4.
The process by which of the whole process of knowledge is created in the mind of a person is known as?
(A) Message
(B) Information broadcasting
(C) E-mail
(D) Network
Answer:
(A) Message
Question 5.
To type the message on computer screen and do communication with the help of computer by the medium of internet – that activity is known as?
(A) E-commerce
(B) Fax
(C) Internet
(D) E-mail
Answer:
(D) E-mail
![]()
Question 6.
The commercial transaction and distribution which is done by the help of electronic machine and medium is known as?
(A) Intranet
(B) E-commerce
(C) E-mail
(D) Internet
Answer:
(B) E-commerce
Question 7.
What is known as the ‘super highway’ of the information?
(A) Internet
(B) Banking service
(C) E-commerce
(D) Outsourcing
Answer:
(A) Internet
2. Answer the following questions in one sentence each :
Question 1.
What is communication?
Answer:
The process of imparting or exchanging of information either in verbal or non-verbal form is called communication
Question 2.
What is Enterprise WAN?
Answer:
An enterprise WAN is a wide area network of computers developed for very huge companies or corporate companies that connects users that could be anywhere in the world. Such a system is called ‘internet’. For example, Indian Railways connects all its computers across entire India through enterprise WAN or say intranet.
Question 3.
What is computer network?
Answer:
When a group of computers are connected with a purpose of sharing information and resources it is called a computer network.
Question 4.
Give full-form of www
Answer:
World Wide Web
Question 5.
How the payment of money in E-Commerce is made?
Answer:
One can pay by cash on delivery (COD), cheque, credit and debit cards, net-banking and digital cash.
Question 6.
What is Hacking?
Answer:
Stealing personal data of individuals or organizations on internet for fun or some objective is called hacking.
3. Answer the following questions in short :
Question 1.
Give meaning of Internet.
Answer:
A global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities consisting of interconnected network is called internet
Or
Internet:
Technically, the word ‘Internet’ can be defined as a global computer network providing a variety of information and communication facilities, consisting of interconnected networks.
Internet in the context of computer network:
- The word ‘internet’ is derived from two words ‘interconnection’ and network’.
- The word ‘inter’ refers to ‘internal’, the word ‘interconnection’ refers to connected together’. The word network’ refers to a group of computers connected with a purpose of sharing information and resources.
- When a group of computer is connected with a purpose of sharing information and resources it is called a network or say, a computer network. To build such a network one needs to have several computer hardware and software. The computers that are to be connected to form a group may be present in the same room, in different rooms, different offices or even at different offices or even at different places. In this sense the area of network covers all the computers whether near, far or even across the worlds. In the context of network internet can be defined as network of all networks. No one owns internet.
- Everyone shares it. However several organizations do the work of managing various networks and their parts so that people can access and use the internet.
- Thus, internet is a global network that connects millions of computers. More than 190 countries are linked into exchange of data.
- In older days internet was accessed using telephone lines. However, now a days various private companies have come up who have established their own separate communication systems using fiber optics and satellite links to provide services of internet to people. These companies are called Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- We can share text, pictures, audio, video, numerical data, etc. through internet.
![]()
Question 2.
Give meaning of E-Commerce.
Answer:
Electronic commerce or e-commerce is buying and selling of goods and services, or transmitting funds electronically over the internet.
Or
E-Commerce:
Electronic commerce or e-commerce is buying and selling of goods and services or transmitting funds electronically over the internet.
- Through e-commerce one can conduct all the processes such as purchase and sales of goods and services, advertising, comparison of products, transferring money, etc. that are necessary for a trade or a business.
- To conduct e-commerce transactions or say trading through e-commerce one needs to make use of medias such as computer network, internet, e-mail, internet banking, credit and debit card, etc.
Question 3.
Give meaning of Outsourcing.
Answer:
When a company or individual hands over some of its processes or works to another company or a professional group it is called outsourcing or business process outsourcing.
Question 4.
Explain the requirement of Business Process Outsourcing (BPO).
Answer:
Business Process Outsourcing (BPO):
- When a company hands over its business activities (or processes) on a contractual basis to another company it is called Business Process Outsourcing (BPO). For example, a company would outsource the work of call centre or data entry to reduce its expenditure.
- Outsourcing has become quite popular in recent years because human resource is available at very low rates in populated countries like India and China. Several foreign companies set-up their call centers in these countries to provide sales, after sales, online technical assistance to their customers.
Need of BPO:
- Cost-cutting: To save infrastructure set-up and other costs companies outsource their activities like billing, data entry, marketing survey, etc.
- Focus on principal activities of company: By outsourcing some activities the senior level employees and managers can focus properly on the core activities of the business.
- Benefit of efficiency: By outsourcing to a professional company a business can take benefit of the rich experience and efficiency a professional unit possess. If might be quite difficult or even impossible for the business firm to carry out such outsourced work on its own with such efficiency and expertise.
- To cater the dynamic demand: As a nation develops, expectations and demands of customers keep on increasing and changing. It may not be possible to meet the expectations and demands and so it becomes important to outsource some tasks to BPO who can handle such tasks. For example, in olden days companies did not have a large customer-care ‘ centre which now has become quite important with increased sales through online shopping and expanded market.
- Increased benefits: Business units can outsource few works to their subordinates in order to focus more on important activities like increasing sales, developing new products, expanding business and to serve and satisfy their customers better and thus increase the profits.
Scope of BPO:
The extent to which a company can outsource its work can be classified into two categories. They are:
- Back-office outsourcing: A company can outsource its back-office works like billing, purchase, data entry, etc.
- Front-office outsourcing: This includes customer services like sales and marketing, technical assistance, etc.
Question 5.
Write the meaning of Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO).
Answer:
Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO):
A form of outsourcing in which knowledge and information related work is given to another company or to some subsidiary department within the company is called outsourcing of knowledge related process or Knowledge
Process Outsourcing (KPO).
- KPO includes processes and services that require advance and high level skills that a company may need for its development.
- For example, a company may outsource activities like Research and Development (R&D), Legal services, analytical works, etc.
4. Answer the following questions in brief :
Question 1.
Explain the steps of Communication Process.
Answer:
Communication deals with information and processing information.
- Let us see an example as how information can be exchange between two persons for the purpose of communication.
- The example shows how communication takes place between two persons. The example discussed is for a person who wishes to know about availability of a bus from Rajkot to Vadodara.
| Steps | Explanation of steps | Example |
| 1. Formation of a message | To exchange information a message is created. The message can be in oral, written, verbal or non-verbal form. | The sender of information i.e. one who seeks information may create a message in his mind like when is the next bus from Rajkot to Vadodara available after 8 pm? |
| 2. Selection of medium | Once the sender creates the message he selects the means of communication. | The sender decides to make a telephone call. Here he has chosen telephone as a mode of communication. |
| 3. Sending message | The person now sends the message. | He uses the telephone and asks the receiver of message when will the next bus after 8 : 00 p.m. be available for Vadodara from Rajkot. |
| 4. Receiving message | The receiver receives the message sent by the sender. | The receiver receives the message on telephone that when will the next bus after 8:00 pm be available for Vadodara from Rajkot. |
| 5. Interpretation of the message
|
The sender sends information (message) using a language that the receiver can understand and interpret.
|
The receiver understands and interprets that the sender of message wants to know if there is any bus available from Rajkot to Vadodara after 8:00 pm. |
Question 2.
Explain the four main types of Computer net.
Answer:
When a group of computers are connected with a purpose of sharing information and resources it is called a network or say a computer network.
Four main categories of computer network:
1. Local Area Network (LAN):
LAN is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited ares such as within a room, within an office, a school, etc.
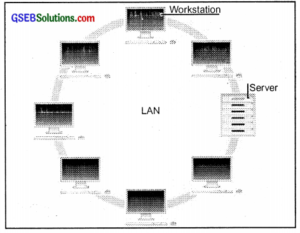
LAN (Large Area Network) (For information only)
2. Campus Area Network (CAN):
- CAN is a computer network that interconnects the computers within a geographical area such as a college campus, industrial complex, etc.
- CAN consist of two or more LANS.
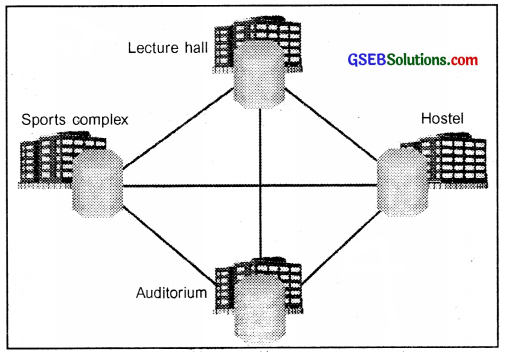
Campus Area Network (CAN) (For information only)
3. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) :
Metropolitan Area Network or MAN is a computer network that interconnects computers of entire city.
4. Wide Area Network (WAN):
- Wide Area Network (WAN) is a computer network that extends over a very large geographical distance compared to l_AN, CAN or MAN. In this sense the computers under WAN are connected globally through telephone line, fiber optic cables, or satellite links.
- The internet can be considered as the biggest WAN in the world.

Wide Area Network (WAN) (For information only)
WAN is further divided into two types:
(A) Enterprise WAN:
An enterprise WAN is a wide area network of computers developed for very huge companies or corporate companies. It connects users that could be anywhere in the world. Such a system is called ‘internet’. For example, Indian Railways connects all its computers across entire India through enterprise WAN or say internet.
(B) Global WAN (or GAN):
Global WAN is a network that has no geographical boundaries. It is spread in various countries and even continents. It is a collective network of networks of various organizations and is also called World Wide Web (WWW).
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the function of the three major types of Internet.
Answer:
Major types of works that one can do on internet:
1. Contact other persons:
- Internet helps to communicate with any person in the world using facility of e-mail, social networking sites like Facebook, Twitter, etc.
- We can also talk with people across the world using internet chats, internet calls, etc.
2. Receiving information:
Using internet we can easily and quickly search and obtain information about any subject or topic. We can go to websites like Google, Yahoo, etc. and search for any information we wish for.
3. Connecting other computer systems:
Through internet we can get in touch with other computer networks and system. For example:
- We can access banking networks through banking websites,
- We can obtain railway ticket on the internet,
- The Gujarat State Education Board monitors the students through CCTV cameras connected via. internet to prevent mishaps.
Question 4.
Give the name of tools required for successful implementation of E-commerce.
Answer:
Website, computer with internet connectivity, and credit and debit cards.
Question 5.
Write Short Note :
1. Digital Cash
Answer:
Digital cash:
- Digital cash is a system of purchasing cash credit is from the banks, storing the credit in your computer in a banking software and spend while purchasing electronically over the internet. In this sense digital cash is called e-currency and it exists only in the cyber space i.e. the digital world.
- Digital cash is not physical money as we see.
- The customer pays real physical money to the bank to buy digital cash. The bank then provides the buyer e-cash or say, digital cash in the form of credit. Banks provides the software which the buyer needs to install in his computer and use it for making online payment.
2. Safety and security of transactions
Answer:
Unlike traditional trade online trade is quite risky. These risks can be divided in three parts. They are:
- Risks of wrong transaction
- Risk of data getting stolen
- Risk of intellectual wealth and privacy
We can safeguard ourselves from these risks in the following manner:
1. Security against risks of wrong transaction:
- At times it may happen the seller says that the customer did not place order and so the item was not sent to him. Sometimes the customer himself says that he has not placed the order but had actually placed it.
- Online sales also face complaints like the customer received a bad quality product or a defective product, etc.
Safety measure:
- The seller should verify customer’s identity and address when he fills the registration form.
- The customers should purchase from reliable websites only.
- Order history of buyer must be checked.
2. Security against risk of data collection (dates getting stolen):
- While shopping online we share our personal details like name, address, bank name, etc. There lies a risk of such data getting stolen. Hackers may steal our data for fun or for some advantage.
- Hackers and data thieves create computer programs called virus and float them on internet. These viruses may enter our computer and steal our data or damage our computer processes. Virus may interrupt the screen, prevent the computer from working properly, damage data files and even whole computer system.
Safety measures:
- One should have proper anti-virus software installed on the computer.
- One should not surf unreliable websites.
3. Security against intellectual wealth and privacy:
- Internet is a public platform i.e. everyone in the world is allowed to access it.
- Once information is placed on internet it means it is publicly published.
- In this regard one needs to take care while providing the information on the internet.
Safety measures:
- One should be careful while placing information such as e-mail, address, phone number, bank details, password, etc. during online transactions.
- One should provide information only when necessary that too only to reliable websites.
5. Answer the following questions in detail :
Question 1.
Explain the steps of the process of searching information on internet
Answer:
It is quite easy to search any information on the internet. Given below are few steps to search on information.
Step 1: Selecting a web browser:
- A web browser or browser is a software application through which we can search any information on the internet. Few popular web browsers are Google Chrome, Internet Explorer, Mozilla Firefox, etc.
- These browsers are also called search engines because they search whatever we type in their search-bar.
- Once your computer is connected to internet, open a browser installed on your computer. For example, Firefox. It will look as shown below.
Mozilla Firefox home page (For information only)
Step 2: Selecting a search engine
Type www.google.co.in either in the address-bar or in search-bar and press enter or click ‘search’. The homepage of Google India will open.

Google home page (For information only)
Step 3: Enter required information in search bar.
- Type the information you seek in search-bar. For example if you wish to obtain information about lion then type the word ‘lion’ and press enter.
- The browser will then search all those websites that contain information on lions and display the list of websites. Refer image.
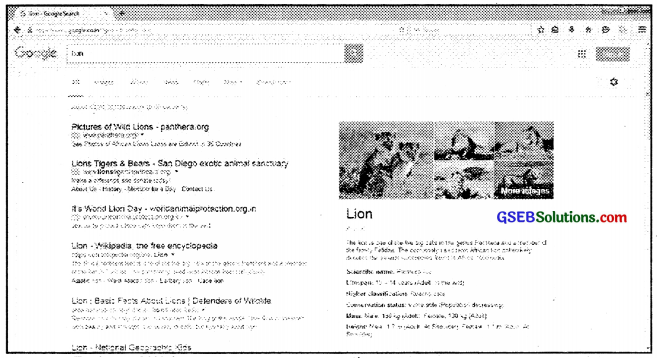
List of Websites containing information on lions (For information only)
Step 4: Selecting a website
Click on the website you wish to and it will show information on lions.
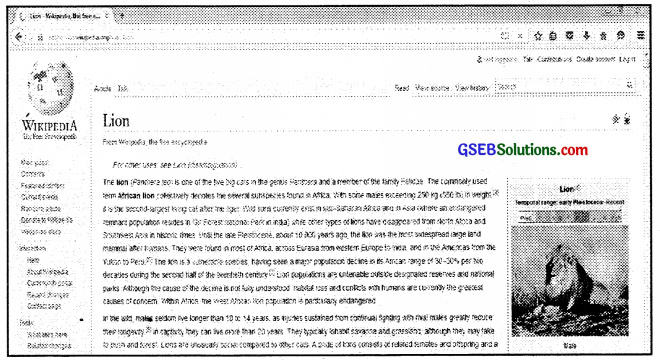
Wikipedia website displaying information on lions (For information only)
Step 5: Obtain required information:
- You can now study about lions on this website.
- If you wish to see various images of lions you need to click on ‘images’. The search engine will search all the available images of lions and display them.
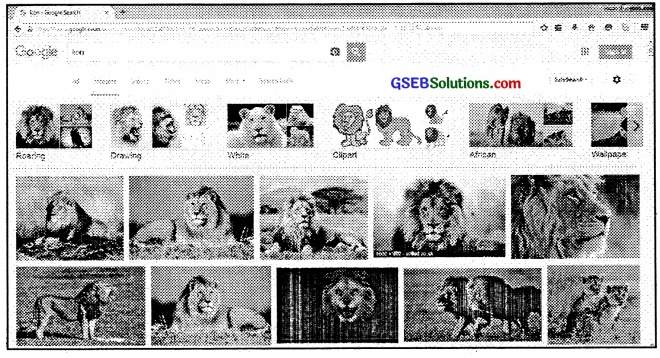
Images of lions as searched by the search engine
Conclusion:
Following these steps one can find any information on the internet. One can search text, various types of images audio, video, etc.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the scope of E-commerce services.
Answer:
Scope (categories) of e-commerce services:
Based on the parties included and activities done e-commerce can be divided (or done) in four ways. They are:
- Business to Customer (B2C)
- Business to Business (B2B)
- Customer to Customer (C2C)
- Customer to Business (C2B)
1. Business to Customer (B2C):
- in business to customer (B2C) there exists a seller (businessman) at one end and customers on the other.
- The seller creates its website, puts it on internet and displays the products it sells on that website.
- Thebuyer (customer) sees these products on the seller’s website and if he likes them he places an order on the website itself.
- Once the seller receives the order be sends the product to the customer without the need of any mediator such as wholesaler, retailer, etc.
- Companies like Amazon, Flipkart, etc. provide online shopping facility which is an excellent example of B2C.
- B2C model is quite prevalent due to quick and easy sales and purchase transactions it offers.
Online banking, railway ticket booking, etc. are other examples.
2. Business to Business (B2B):
- In B2B model both the parties are businessman i.e. one businessman sells its product to another.
- For example, a businessman would like to create its website for its customers or would like to design brochures for advertising his products. On the other hand – there is a businessman whose company does the activity of designing websites brochures, etc. for clients.
- When these two businessmen come in contact online we call it Business to Business (B2B) transaction achieved through e-commerce.
- In today’s fast changing world business units are interdependent. They need B2B trading for faster and effective results.
- Through B2B, suppliers, distributors, and other mediators come in contact. Since several businesses provide their services online to other businesses they compete among themselves which results in better products and services. It increases efficiency of routine business activities like that of supply management, inventory management, managing payments, etc.
3. Customer to Customer (C2C):
- In C2C, a customer directly comes in contact with another customer, without any mediator.
- Any internet user becomes a seller as well as buyer.
- The best example for C2C would be e-bay.com. It is an e-auction website where in a customer (seller) who wishes to sell logs into e-bay website and provide detail about the item and asks interested customers (buyers) to bid. The highest bidder buys that item.
- Other examples are Olx.com, quicker.com where a customer (seller) posts details of the items he wish to sell and interested customer (buyer buys it).
4. Customer to Business (C2B):
- In C2B model a consumer let’s say an individual who has something to offer either a service or a good sells it to companies (businesses) and in turn companies pay such customers, for the work they provide. For example, a designer (i.e. a customer) may sell his designs to a garment manufacturing company.
- Since the customer is selling his product or service he decides its price.
Other models in e-commerce:
If we consider government as an autonomous body then we may have following different categories too:
(A) Government to Business
(B) Government to Citizen
(C) Government to Government
Question 3.
Explain the steps of process of online transaction.
Answer:
The process of online shopping from a customer’s point of view is discussed below:
Here, we assume that customer has studied the product on the seller’s website and is willing to buy.
1. Registration:

Register online (For information only)
In order to make a purchase first of all the buyer needs to register himself with the seller’s shopping portal or say website.
- To do so the buyer needs to fill up the registration form online provided on the website. This is known as opening an account with the seller or sign-in or seller’s website.
- The form will ask the customer to fill his personal details like customer name, address, phone number, etc.
- While filling the form the customer also needs to set a password. By doing so only the customer will be able to sign-in from his account. This saves the customer from misuse of his account.
2. Place an order:

Add items ¡n your cart (For information only)
- Once the customer sign-in he can select the product he wish to buy and place an order.
- The customer selects the product and put it in the shopping cart. Shopping cart is a pool of products that the customer has selected and wishes to buy.
- Once he has selected all the products he then proceeds to payment section.
3. Payment system:

Make payment (For in formation only)
- Depending upon seller’s conditions he may allow the customer to pay for his products using facilities like cheque, credit/debit card, internet banking, Cash on Delivery (COD), digital cash, etc.
- When the seller receives the order and the payment confirmation he dispatches the product at the customer’s address.