Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare Textbook Questions and Answers, Additional Important Questions, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare
GSEB Class 12 Biology Microbes in Human Welfare Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Bacteria cannot be seen with the naked eyes, but these can be seen with the help of a microscope. If you have to carry a sample from your home to your biology laboratory to demonstrate the presence of microbes under a microscope, which sample would you carry and why?
Answer:
Curd – contains Lactic Acid Bacteria Lactobacillus acidophilus).
![]()
Question 2.
Give examples to prove that microbes release gases during metabolism.
Answer:
Dough and Swiss cheese.
Question 3.
In which food would you find lactic acid bacteria? Mention some of their useful applications.
Answer:
Curd Uses:-
- Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) convert milk into curd by producing lactose. Converts sugar lactose into acid which converts casein in milk to curd.
- Removes lactose, produces Vitamin B12 and checks growth of putrefying bacteria as well as harmful microbes.
Question 4.
Name some traditional Indian foods made of wheat, rice and Bengal gram (or their products) which involve use of microbes.
Answer:
Bread, dosa, idli, beverages etc.
Question 5.
In which way have microbes played a major role in controlling diseases caused by harmful bacteria?
Answer:
Microbes have been a source of antibiotics. Antibiotics have been used successfully against pathogenic bacteria. E.g.: streptomycin (str. griseus), erythromycin
(str. erythreus), Bacitracin (Bacillus licheni – formis)
![]()
Question 6.
Name any two species of fungus, which are used in the production of antibiotics.
Answer:
Penicillium notatum, Cephalosporium
Question 7.
What is sewage? In which way can sewage be harmful to us?
Answer:
Sewage/municipal wastewater is human excreta and other organic wastes containing a large number of pathogenic microbes and harmful chemicals. It is harmful to us because
- Source of various water
- Causes eutrophication of water
- Produces scum and sludge, bad taste, foul smell, and turbidity to water to which they are dumped.
Question 8.
What is the key difference between primary and secondary sewage treatment?
Answer:
Primary treatment: It involves the physical removal of large and small particles from the sewage through sedimentation and filtration. First of all floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Soil and small pebbles (grit) are then removed by sedimentation. All the solids that settle from the primary sludge and the supernatant forms are called effluents. The effluent is subjected to secondary treatment.
Secondary treatment: In this, the effluent is passed on to large aeration tanks where it is constantly agitated. The agitation allows vigorous growth of aerobic microbes into floes. The mass of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures constitutes floes. The microbes use the major part of the organic matter from the effluent. The growth of the microbes by consuming organic matter will probably reduce the biological oxygen demand (BOD). It is the amount of oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidized by the microbes. BOD is a measure of the organic matter present in the water, because BOD test measures the rate of uptake of oxygen by microbes in a sample of water. The greater the BOD in sewage, more is its polluting potential. So the effluent is treated till the BOD is reduced.
![]()
Question 9.
Do you think microbes can also be used as source of energy? If yes, how?
Answer:
No, But their fermentation products Biogas, Alcohol, etc, are used as source of energy.
Question 10.
Microbes can be used to decrease the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides. Explain how this can be accomplished.
Answer:
The use of biological methods for controlling plant diseases and pests is called biocontrol. This method has been replaced by the indiscriminate use of chemicals used in the chemical control of pests. The chemicals used for killing pests are toxic and extremely harmful to man and domestic animals. They also pollute the environment and our crop plants.
Question 11.
Three water samples namely river water, untreated sewage water and secondary effluent discharged from a sewage treatment plant were subjected to BOD test. The samples were labelled A, B and C; but the laboratory attendant did not note which was which. The BOD values of the three samples A, B and C were recorded as 20mg/L, 8mg/L and 400mg/L, respectively. Which sample of the water is most polluted? Can you assign the correct label to each assuming the river water is relatively clean?
Answer:
B least BOD, so its river water A discharged from sewage treatment plant C highest BOD, untreated sewage water.
![]()
Question 12.
Find out the name of the microbes from which Cyclosporin A (an immunosuppressive drug) and Statins (blood cholesterol-lowering agents) are obtained.
Answer:
Cyclosporin is produced by Trichoderma polysporum. Statin is produced by Monascus purpureus.
Question 13.
Find out the role of microbes in the following and discuss it with your teacher.
a. Single-cell protein (SCP)
b. Soil
Answer:
(i) Single Cell protein – Used as food and feed with all essential Amino Acids, low fat. E.g.: Spirulina, yeast, Mushroom.
(ii) Soil
- Humification
- Mineralization – release minerals during degradation
- Biofertilizers
- Denitrification – Discuss all with the teacher.
![]()
Question 14.
Arrange the following in the decreasing order (most important first) of their importance, for the welfare of human society. Give reasons for your answer.
Biogas, Citric acid, Penicillin and Curd
Answer:
Penicillin, biogas, curd and citric acid.
Penicillin is the first antibiotic discovered by Alexander Flemming. It is a potent antibiotic used to kill pathogenic bacteria. Nowadays antibiotics have played a major role in controlling infectious diseases like diphtheria, whooping cough and pneumonia.
Today, we cannot imagine a world without antibiotics.
Biogas produced by microbes is used as a source of energy in rural areas.
Curd is a nutritive food. In the stomach, it plays a vital role in checking disease-causing microbes.
Citric acid is a good source of vitamin C.
Question 15.
How do biofertilizers enrich the fertility of the soil?
Answer:
Biofertilizers are micro-organisms which increases soil fertility and enhances nutrients to crop plants.
- Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and Cyanobacteria – Converts free N2 from the atmosphere to salts of N2.
- Phosphate bacteria – Secrete phosphatase that dissolves insoluble phosphate from the soil for absorption by plants.
- Mycorrhiza – occurs in forest plants solubilizes and absorbs nutrients from organic matter.
GSEB Class 12 Biology Microbes in Human Welfare Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Do you agree with the statement that microbes are omnipresent?
Answer:
Yes. They live in all parts of biosphere like water, soil, hot springs, ocean floor, high in atmosphere, deep inside the rocks in earth’s crust. Methanopyrus kandleri is a species that can live in 122°C temperature.
Trichosporonoid.es nigerescens is a microbe which can survive for almost a decade without exposure to water.
![]()
Question 2.
A person complained to the doctor about the myocardial infraction he suffered and about a doctor he consulted earlier. The earlier doctor told about curing of the diseases using microbes. Will the doctor support the earlier doctor or not? Substantiate your answer.
Answer:
Yes. The doctor will support the earlier doctor because streptokinase produced by streptococcus is modified by genetic engineering and is used as a clot-buster for removing clots from blood vessels of patients who have undergone heart attack.
Question 3.
“Antibiotics are chemical substances produced from microbes”.
a. What is the meaning of the term antibiotics?
b. Name the first antibiotic.
c. Who discovered antibiotics?
Answer:
a. Anti – against, bio – life (Against the life of pathogens)
b. Penicillin
c. Alexander Fleming
Question 4.
Some discoveries are made unexpectedly.
a. What is it known as?
b. Give one example.
Answer:
a. Serendipity
b. Discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming. He was working on staphylococci bacteria. He once observed that in a contaminated culture plate this bacteria did not grow. He came to the conclusion that it was due to a chemical produced by the blue-green mould. Hence named penicillin because it was found from blue-green mould penicillium notatum.
![]()
Question 5.
(a) What is the source of statins and how they reduce the level of cholesterol in our body.
(b) Write the technical terms for VAM. Pickup examples of endomycorrhiza and ectomycorrhiza from sclerosis, Laccaria, Gigaspora, glomas, Hebeloma, Psilocybes. (CBSE – 2006)
Answer:
(a) Stain which reduces the cholesterol level in our body is synthesized by the activity of yeast Monascus purpureus egs of statins are Lovastatin, simvastatin pravastatin, fluvastatin.
(b) VAM – It is vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza where the hyphae send vesicular and branched haustoria into root cortical cells for obtaining nourishment in endomycorrhizal
eg:
Ectomychorrhiza – Laccaria, Hebeloma, Psilocybes
Endomuchorrhiza – Sclerocystis, Gigaspora, Glomos.
Question 6.
Complete the following.
| Microbes | Products |
| I. …………(a)……………… | (a) Penicillin |
| ii. Trichoderma polysporum | ………………(b)……………… |
| iii. Propionibacterium Sharmanii | ………………(c)……………… |
| iv. ………………(d)……………… | Statin |
Answer:
| Microbes | Acids |
| i. Aspergillus niger | a. Citric acid |
| ii. Acetobacter aceti | b.Acetic acid |
| iii. Lactobacillus | c. Lactic acid |
![]()
Question 7.
The puffed-up appearance of dough is due to the production of C02 gas. Can you tell which metabolic pathway is taking place resulting in the formation of C02?
Answer:
Alcoholic fermentation
Question 8.
Name the organism that causes large holes in “Swiss cheese”. How are these cause? (CBSE, Delhi 2009)
Answer:
Propioni bacterium sharmani. The large holes are due to the large quantity of carbon dioxide produced.
Question 9.
Which among the following is used for making Roquefort cheese?
a. Propionibacterium sharmanii
b. LAB
c. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
d. None of these
Answer:
None of these
Question 10.
Curd is more nutritious than milk. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Curd contains more vitamin B12
Question 11.
What is alcoholic fermentation?
Answer:
The conversion of glucose to ethyl alcohol is known as alcoholic fermentation. C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + energy
![]()
Question 12.
Penicillin was a chance discovery. Is it true or not? If the answer is true, give reason.
Answer:
Serendipity is a phenomenon associated with scientific method. It is the faculty of making interesting discoveries unexpectedly. One of the best examples is the discovery of Penicillin by Alexander Fleming.
The chance observation of an infected petri dish by Alexander Fleming in 1928 led to the discovery of antibiotics, their manufacture and use to cure the disease caused by staphylococcus which causes throat infection. Alexander Fleming while working on Staphylococci bacteria, once observed contamination of one of the culture plates around which Staphylococci could not grow. He found out that it was due to a chemical produced by blue-green mould. Fleming called the chemical substance as Penicillin after the blue green mould, Penicillium notatum.
Question 13.
Today, we cannot imagine a world without antibiotics. Justify the statement.
Answer:
Antibiotics save man from deadly diseases such as plague, diphtheria, whooping cough, leprosy etc. Without antibiotics we can’t survive because we are living amidst the bacteria, which cause fatal diseases in man. Antibiotics have greatly improved our capacity to treat deadly diseases.
![]()
Question 14.
Observe the table and fill in the blanks.
| Microbes | Acids |
| i. Aspergillus niger | a. ………… |
| ii. Acetobacter aceti | b. …………….. |
| iii. ……………………………… | c. Lactic acid |
Answer:
| Microbes | Acids |
| i. Aspergillus niger | a.Citric acid |
| ii. Acetobacter aceti | b. Acetic acid |
| iii. Lactobacillus | c. Lactic acid |
Question 15.
Name a bioactive molecule produced by TrichocLerma polysporum. Mention the significance also.
Answer:
Cyclosporin. It is an immunosuppressive agent used in organ-transplant patients.
Question 16.
Expand the following.
a. Bt cotton
b. BOD
c. LAB
Answer:
a. Bacillus thuringiensis cotton
b. Biological Oxygen Demand
c. Lactic Acid Bacteria
![]()
Question 17.
What are methanogens?
Answer:
The bacteria which are responsible for the production of biogas are called methanogens.
Question 18.
What are baculoviruses?
Answer:
Baculoviruses are pathogens that attack insects and other arthropods.
Question 19.
Identify the figure and write a short note on it.
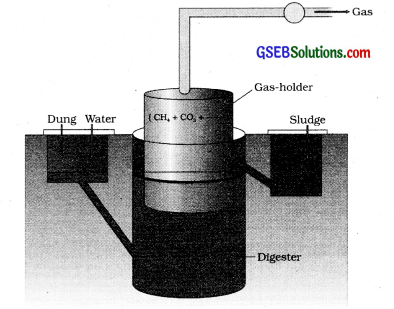
Answer:
Biogas plant
Question 20.
Name a microbial biocontrol agent.
Answer:
Bacillus thuringiensis
![]()
Question 21.
Rhizobium, Azospirillum and Azotobacter act as biofertilisers. How?
Answer:
These bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen and enrich the nitrogen content of the soil.
Question 22.
Do you think that fungi can help the plant to grow and develop resistance? If yes, how?
Answer:
Yes. Fungiform symbiotic association with plants. This association absorbs phosphorus from the soil and passes it to the plant.
Question 23.
Name a microbe which serves as a biofertilizer in the paddy field.
Answer:
Anabaena
Question 24.
Write about “Organic farming”.
Answer:
Organic farming is a holistic approach that seeks to develop an understanding of the webs of interaction among the myriads of organisms that form the flora and fauna of the field.
- The organic matter works to create a system where the insects are not eradicated but kept at manageable levels by a complex system of checks and balance within a leaving and vibrant ecosystem.
- According to the former the eradication of the creatures, called pests, is not only possible but also undesirable because many beneficial predatory and parasitic insects cannot survive without them. Such a method reduces the use the chemical pesticides and thereby pollution.
![]()
Question 25.
Match the following.
| Microbe | Uses |
| i. Anabaena | a. Biogas |
| ii. Penicillium notation | b. Cheese |
| iii. Methanobacterium | c. Penicillin |
| iv. Monascus purpureus | d. Biofertiliser |
Answer:
| Microbe | Uses |
| i. Anabaena | d. Biofertiliser |
| ii. Penicillium notation | c. Penicillin |
| iii. Methanobacterium | a. Biogas |
| iv. Monascus purpureus | b. Cheese |
Question 26.
Name a fungus used for the control of pests.
Answer:
Trichoderma species
Question 27.
You have been deputed by your school Principal to a bain local village in the use of biogas plant. With the help of a labelled sketch explain the various parts of the biogas plant.
Answer:
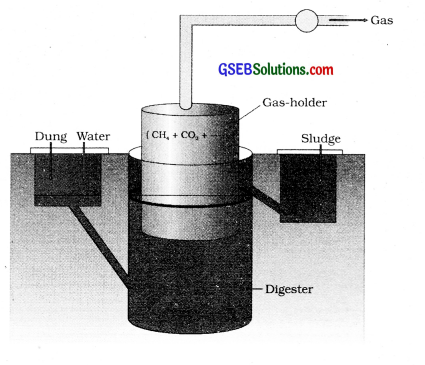
The technology of biogas production was developed in India mainly due to the effort of the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) and Khadi and Village Industries Commission. The biogas plant consists of a concrete tank (10-15 feet deep) in which biowastes are collected and a slurry of dung is fed. A floating cover is placed over the slurry. The biogas plant has outlet which is connected to a pipe to supply biogas to nearby houses. Biogas plants are built more in rural areas. The biogas thus produced is used for cooking and lighting.
![]()
Question 28.
How are biofertilizers different from fertilizers such as NPK that we buy from the market? Justify the role of rhizobium as a biofertilizer.
Answer:
Today environmental pollution is a major threat due to the thoughtless use of chemicals to meet the ever-increasing demands of agricultural production. Due to the overuse of chemical fertilizers, there is a large pressure to switch to organic farming using biofertilizers. Biofertilizers are organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil.
The main sources of biofertilizers are bacteria, fungi, and cyanobacteria. The root nodules of leguminous plants are formed by the symbiotic association of Rhizobium. These bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms, which is used by the plant as a nutrient.
Question 29.
Bacteria that convert milk into curd play two other beneficial roles. What are they?
Answer:
i. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) improve nutritional quality by increasing vitamin B12
ii. LAB play a very beneficial role in checking disease-causing microbes.
![]()
Question 30.
What are ‘floes’? State their role in effluent treatment and their ultimate fate in the sewage treatment tanks.
Answer:
Floes: It is the masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form a mesh-like structure.
Effluent treatment: The treated sewage effluent is subjected to chemical treatment for disinfection before releasing it into natural water bodies like rivers and streams. Sewage treatment: The BOD of sewage or wastewater is reduced significantly. The effluent is then passed into a settling tank where the bacterial ‘floes’ are allowed to sediment. It is called activated sludge.