Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Chapter 1 Nature and Significance of Management Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Chapter 1 Nature and Significance of Management
GSEB Class 12 Organization of Commerce and Management Nature and Significance of Management Text Book Questions and Answers
1. Select the correct alternative and write answer to the following questions :
Question 1.
Art of getting work done from others is known as
(A) Planning
(B) Organizing
(C) Directing
(D) Co-ordinating
Answer:
(C) Directing
Question 2.
What type of activity is management?
(A) Universal
(B) Inefficient
(C) Defining objectives
(D) Transparent
Answer:
(A) Universal
Question 3.
What is the method that puts knowledge easily into practice called?
(A) Profession
(B) Science
(C) Art
(D) Direction
Answer:
(C) Art
Question 4.
What does management association frame for its own profession?
(A) Inconsistency
(B) Improper
(C) Code of conduct
(D) Decisions
Answer:
(C) Code of conduct
Question 5.
How many levels of management are there?
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) Three
(D) Four
Answer:
(C) Three
Question 6.
Who are included in top level management?
(A) Experts
(B) Workers
(C) Departmental heads
(D) Board of Directors
Answer:
(D) Board of Directors
Question 7.
What is the other name for bottom level management?
(A) Functional level
(B) Worker’s level
(C) Policy making level
(D) Officer’s level
Answer:
(A) Functional level
![]()
Question 8.
Who among the following is not included in any of the level of management?
(A) Supervisor
(B) Jobber
(C) Worker
(D) Accountant
Answer:
(D) Accountant
Question 9.
If planning is the brain of business then what is organization?
(A) Heart
(B) Limbs
(C) Structure
(D) Blood
Answer:
(C) Structure
Question 10.
Which of the following is the function of marketing management?
(A) Distribution of income
(B) Production
(C) Product-mix
(D) Use of finance
Answer:
(C) Product-mix
Question 11.
Which of the following is not included in Human Resource Management?
(A) Repairing and maintenance
(B) Training and development
(C) Promotion and transfer
(D) Recruitment and selection
Answer:
(A) Repairing and maintenance
2. Answer the following questions in one sentence each :
Question 1.
What is management?
Answer:
Management is the art of getting things done through others.
![]()
Question 2.
In which activities management is necessarry?
Answer:
- Industries,
- religion,
- defense, management
- society,
- politics,
- education, and
- sports.
Question 3.
Which level of management has the supreme authority to manage the business?
Answer:
Top level management.
Question 4.
What is other name of middle level of management?
Answer:
Officer’s level
Question 5.
Which level of management follows the order and instruction given by chief executive officer?
Answer:
Middle level management.
Question 6.
Which level of management does the function of machinery layout and repairing?
Answer:
Question 7.
What are the elements included in product-mix?
Answer:
Appearance of the product, colour of the product, size of the product, shape of the product, weight of the product, print on the product, packing of the product, guarantee of work, after-sales service, variety of product, etc
Question 8.
Give the full form of IIM.
Answer:
Indian Institute of Management
Question 9.
Give the full form of MBA.
Answer:
Management of business administration
![]()
Question 10.
Give the full form of CEO.
Answer:
Chief Executive Officer
3. Answer the following questions in short :
Question 1.
State any two functions performed at the top level management.
Answer:
- The top level (or higher level) management is the supreme authority for managing the enterprise.
It consists of Board of Directors, Managing Directors (MD), General Manager (GM) and Chief Executive Officers (CEO). - The top management takes important policy decisions for the business unit.
Functions of the top management:
- To lay down primary and subsidiary objectives of business.
- The directors act as the trustees of the business enterprise.
- To select Chief Executive Officer and higher officers and to assign them authority and responsibility.
- To sanction the budget for different departments of the business unit.
- To abide by law and to take care of interest of different stakeholders of the business.
- To take strategic decisions by making long term plans.
- To analyse and resolve complex problems of management as per legal provisions.
- To draft plans for the enterprise, implement them and to supervise them.
- To conduct functions like distribution of profit, dividend, reserve fund, re-investment of profit, etc.
- To analyse reports of different activities and to instruct further activities accordingly.
Question 2.
How does management benefit the society?
Answer:
Social benefit:
- A business is done while remaining in the society and for the interest of the society.
- Management makes uses of resources such as manpower, knowledge gained from the society, etc. available in the society and then works in the favour of the society.
- When the business earns success it in turn increases the wealth and welfare of society. For example, with time, development and competition business units produce goods and services at low cost for the people. This results into welfare of the entire society.
Question 3.
What is planning?
Answer:
- The process of selecting facts for obtaining the desired results and establishing inter -relationship between them, as well as observing necessary activities for forecasting and anticipating the future of business is called planning.
- Planning is the first step of management.
- Planning consists of deciding well in advance as what work has to be done, who will do what, when, how, to what extent and when will the work be finished for achieving predetermined objectives.
Question 4.
What is organisation?
Answer:
- Organizing or organization is a structure for assigning authority and responsibility among individuals for achieving business objectives.
- Business objectives, policy, programmes, etc. are decided through planning whereas organizing is done for executing the plans.
- Under organizing, various sections and groups of people are allotted various business activities so that the objectives can be fulfilled.
- The structure of organization decides on matters like who will supervise, who will have authority and responsibility of work, inter-relationship among individuals, etc.
![]()
Question 5.
What is co-ordination?
Answer:
Co-ordination:
- To task of maintaining co-ordination and harmony among the different functions carried out by different departments in the business unit is called co-ordination.
- Although co-ordination is not a function of management but it is required at each and every stage of management.
- It is necessary right from the planning stage to controlling.
Question 6.
Who are included in the top level management?
Answer:
Board of Directors, Managing Directors, General Manager, Chief Executive Officer, etc.
Question 7.
Which are the main elements of marketing management?
Answer:
The main function of marketing management is to get information about the market demand.
Question 8.
Discuss various elements of price-mix.
Answer:
Question 9.
Discuss about staffing.
Answer:
Staffing:
- It is said that “Employees are arms and legs (limbs) of unit.”
- According to Dr. George Terry, “Staffing is concerned with availing and maintaining satisfactory manpower.”
- Every business organization requires staff. Hence, staffing is a very important function of management. An organization without staff is like a mere skeleton. Activities of all businesses depend on their staff.
- The function of staffing is to recruit employees for the right position, at the right time, in the right number, with the right qualification. It also includes selection, training, transfer, promotion, dismissal, retirement and welfare activities of employees.
- This function is carried out by the Human Resource Department of the business organization.
- Staffing also monitors the output of work of each employee. It also listens to the problems of the employees. This helps in maintaining the enthusiasm and zeal of employees. Enthusiasm for work and comfortable and encouraging work environment leads to increase in productivity and efficiency of the organization.
- Today staffing also includes man-power planning, human resource development, evaluation of work, job analysis, etc. It is a highly known fact that a satisfied staff is an invaluable asset of the business.
4. Answer the following questions in brief :
Question 1.
Discuss the importance of management.
Answer:
- Management has always held a central and am extremely important position in any activity.
- The success or failure of any business activity heavily depends on how it is managed.
- If a business unit has best of the resources that too in all the required quantities and qualities but are not managed properly then they cannot be utilized with their full efficiency. This will lead to under-performance of the unit.
The importance of management can be understood in detail through the following points:
1. Necessary in every field:
- Use of management is not limited to business activities but also in each and every type of activities including religion, defence, society, politics, education, sports, etc.
- While managing an activity, the functions of management namely Planning, Organization, Direction and Control are put into use.
2. Optimum utilization of resources:
- Through management optimum utilization of business resources such as land, capital, raw materials, humans and machinery can be done.
- Proper management reduces wastage of resources and improves their efficiency.
3. Accomplishment of objectives:
- Management is necessary for accomplishing objectives.
- Management makes optimum utilization of resources which in turn helps to achieve business objectives.
4. Useful for the success of business:
- The contribution of management in the success of a business unit is more compared to other elements.
- Success or failure of a business largely depends on management.
- The entire credit of a small scale industry rising into a large scale industry goes to management.
- Efficient management can also convert a loss making unit into a profit making unit.
5. Increase in job opportunities:
Efficient management can grow a small firm into company whereas on the other hand, inefficient management can lead to closure of full-fledged developed companies.
6. Increase in profit:
- The main aim of business is to earn profit.
- Competent and proficient managers have in depth knowledge about management and hold business skills.
- They make maximum and the most economic utilization of available resources and earn maximum profit out the business.
- Thus, management playa a key role in earning and increasing profit.
7. Social benefit:
- A business is done while remaining in the society and for the interest of the society.
- Management makes uses of resources such as manpower, knowledge gained from the society, etc. available in the society and then works in the favour of the society.
- When the business earns success it in turn increases the wealth and welfare of society. For example, with time, development and competition business units produce goods and services at low cost for the people. This results into welfare of the entire society.
8. National motive:
Role of management is extremely important in utilizing untapped human resources and factors of production for the economic, social and national development of an economy.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain: Management as a profession
Answer:
Management as a profession:
- Profession is an activity where specialized knowledge in specific field is acquired and it is used for the welfare of the entire society. In return, a fee is charged. Doctors, lawyers, chartered accountants, engineers, etc. are professionals.
- Today’s business management is also handled by people who are trained and expert in the field. In other words they are thorough professionals. In this sense, management is also considered as a profession.
The profession of such people has following characteristics:
1. Requires specialized knowledge:
- Specialized knowledge is required for a profession. For example, a degree of L.L.B is needed for becoming a lawyer and degree of MBBS, MD or MS is necessary for the profession of doctor.
- Similarly, degree of BBA (Bachelor of Business Administration), MBA (Master of Business- Administration) degrees is necessary for the specialized knowledge of management.
2. Increase in knowledge and research:
- The management professionals undergo several training, enrich their experience through work.
- This increases their knowledge and research capabilities as well as activities.
3. Professional association:
All professionals form their associations. For example, there is association of doctors, association of lawyers, chartered accountants, etc.
In the same way there is also association of management professionals.
- These associations provide education and training and update professionals with latest practices of management.
- IIM (Indian Institutes of Management) is one of the finest management education Institutes of India. It is working at national and international level. This institute works for developing management professionals.
- There are also other hundreds of universities and institutions that provide management training and education.
4. Framing and implementation of code of conduct:
Each professional association frames code of conduct for its members. It is mandatory for all members to follow the code of conduct.
5. Moral responsibility:
- Moral responsibility is an important factor for all the professions.
- All the professionals must be loyal to their professions and they need to fulfill their moral responsibilities. For example, it is the moral responsibility of the chartered accountant to remain loyal to his clients and not disclose their financial information.
Conclusion:
From these characteristics we can conclude that management has evolved and is also yet evolving as an independent profession for the benefit of individual, society and the mankind.
Question 3.
Explain functions performed by top level management.
Answer:
- The top level (or higher level) management is the supreme authority for managing the enterprise.
It consists of Board of Directors, Managing Directors (MD), General Manager (GM) and Chief Executive Officers (CEO). - The top management takes important policy decisions for the business unit.
Functions of the top management:
- To lay down primary and subsidiary objectives of business.
- The directors act as the trustees of the business enterprise.
- To select Chief Executive Officer and higher officers and to assign them authority and responsibility.
- To sanction the budget for different departments of the business unit.
- To abide by law and to take care of interest of different stakeholders of the business.
- To take strategic decisions by making long term plans.
- To analyse and resolve complex problems of management as per legal provisions.
- To draft plans for the enterprise, implement them and to supervise them.
- To conduct functions like distribution of profit, dividend, reserve fund, re-investment of profit, etc.
- To analyse reports of different activities and to instruct further activities accordingly.
Question 4.
Give difference between levels of management. (Any five points)
Answer:
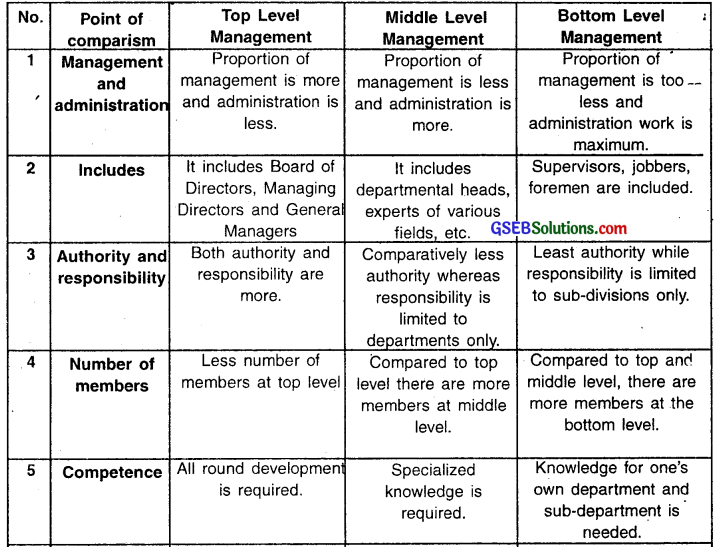
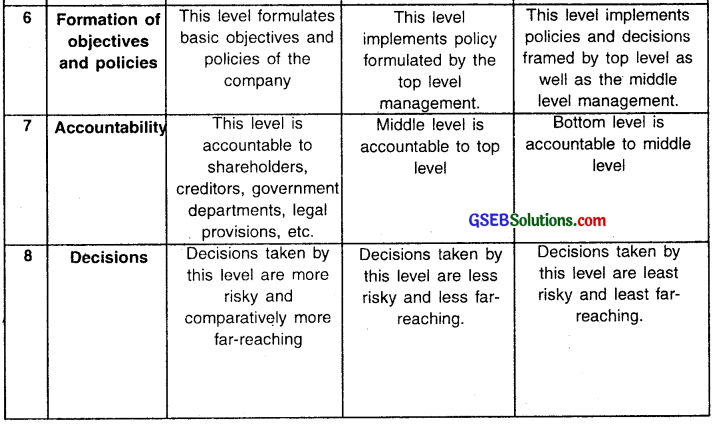
Question 5.
Discuss the importance of co-ordination.
Answer:
Importance of co-ordination:
- Co-ordination makes management functions like planning, organizing, directing, controlling, etc. effective.
- Co-ordination makes possible smooth functioning of all the business activities.
- When there is proper co-ordination then neither any work remains incomplete nor any work gets duplicated.
- Co-ordination maintains harmony among various departments of management.
- Co-ordination enables to maintain a balance between order and time of business activities performed by various departments.
- Co-ordination enables accomplishment of pre-decided objectives.
Question 6.
Discuss the importance of human resource management.
Answer:
Importance of Human Resource Management:
- Efficiency of employees increases
- Profitability of the business increases
- Business prestige is maintained
- Higher standards are maintained for the quality of goods or services
- Feeling of oneness among employees is developed
- Maximum utilization of factors of production is possible –
- Reduction in labour turnover rate occurs
- Job satisfaction among the employees enhances
- Employees get job satisfaction which finally creates an environment of industrial peace.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the functions of financial management?
Answer:
Financial Management:
Financial management is the process of dealing with all the finance related functions of the business.
- The function of acquisition, utilization and allocation of capital is called financial function or financial management.
- Finance is the lifeblood of business. No activity is possible without finance.
- Finance is required for the establishment, development, expansion and modernization of a business.
Following functions are included in financial management:
- To estimate the financial needs of the business activities
- To make financial plans keeping in mind the time duration
- To prepare budget
- To allocate funds to various departments
- To decide capital structure and to select sources of acquiring capital
- To carry out the procedure for acquiring the finance
- To see that the acquired funds are properly utilized and to keep control over financial activities
- To form financial policy
- To plan for taxes
- To make arrangement of assets
5. Answer the following questions in detail :
Question 1.
Define management and explain its characteristics.
Answer:
Management:
Management is the process of reaching organizational goals by working with and through people and other organizational resources.
Following characteristics of management are to be kept in mind in order to understand the concept and nature of management:
1. Universal process:
Management is a universal process i.e. it is required everywhere and anywhere.
- Whenever people work in group to accomplish a desired objective it needs proper management.
- Although management is a commercial term its use is not limited to industries or companies. It is also used in various social and religious fields and activities like agriculture, army, education, etc.
- Each field and unit or department of that field makes use of management in its own ways.
2. Goal-oriented activity:
Management is a tool to attain a goal and not a goal itself.
Every business unit is formed to achieve certain business and profit objectives. Proper management is extremely important to achieve these objectives in a competent and economical way.
3. Group activity:
- Management is required when two or more people are working together to accomplish pre-determined objectives.
- In this sense, management is a group or say collective activity.
4. Continuous process:
- Management is a continuous process which keeps on going till the organization lasts.
- It is quite difficult or even impossible to stop management of things, processes and people as long as the organization exists.
- Although management aims at attaining certain pre-defined goals, it cannot be stopped on attainment of goals unlike other goal based activities.
- Once the previously set goals are attained, new objectives and targets are set by the business unit. This keeps the management process on and on. Thus, the cycle of defining objectives, achieving them and re-defining them goes on continuously.
5. Human process:
Although management is a universal activity, it cannot be done without humans.
The human element is the most significant and central element of management. ‘Without man’ there is no ‘management’. All other means of production are useless without man. Management is done by the human being and for the human being.
6. Decision process:
- Management has to continuously take decisions while managing business. Each and every work needs decision making.
- The organization cannot proceed without taking any decision. Moreover, after taking the decision, the organization has to put it into implementation. Thus, the process of decision is a function of management.
7. Science, Art and Profession:
The way science works on its own set of rules and principles, so does management. Hence many experts consider management as a science. On the other hand, management focuses heavily on managing man i.e. people. Managing people is an art and so management is also considered as an art. Getting work done from man requires proficiency, intelligence, cleverness and insight. So, management is the art of getting the work done.
Today’s business management is also handled by people who are trained and are expert in the field. In other words they are thorough professionals. For example, professionals like lawyers, doctors, chartered accountants, etc. manage their works quite professionally. Similarly, people who have
acquired knowledge in fields of BBA and MBA are considered management professionals.
![]()
Question 2.
Draw a diagram of different levels of management. Also explain its functions.
Answer:
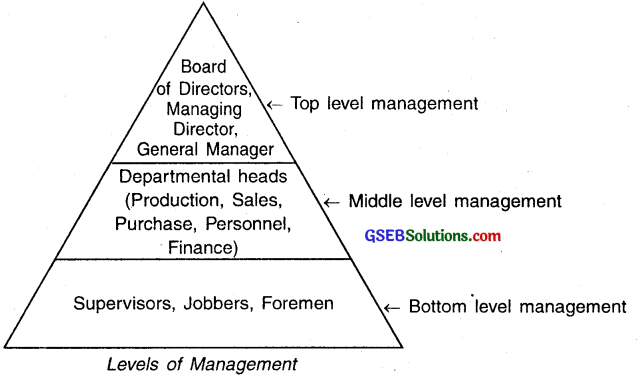
Middle level management:
- The middle level of management is an important link between top level and bottom level of management.
- It consists of departmental officers, divisional officers and experts of various fields. For example, production manager, sales head, purchase officer finance manager, human resource manager, accounts head, etc.
- The middle level is also known as Officer’s Level.
Functions:
- To implement the orders and instructions given by Chief Executive Officers.
- Each departmental head prepares the budget for its department and presents it before the top level management for approval.
- To formulate policies, rules and structures for the accomplishing objectives of the enterprise. To decide suitable methods for achieving these objectives, to analyse the methods and also to decide appropriate measures.
- To take necessary steps to increase efficiency and effectiveness of departmental activities.
- To make attempts to motivate the employees of department.
- To keep in constant touch with the officers of the other departments and establish co-ordination.
- To focus on functioning of sub-divisions.
- To supervise the working of the departments, get information, provide directions and provide information about progress and working of the department to the top level management.
- To help the top level management in taking policy decisions.
The bottom level of management:
- The lowest level of management in an organization is called the Bottom Level or Supervisors’ Level Management.
- The decisions and policies taken by top level management are actually implemented by this level. Hence, this level is also known as Functional/ Operational Level of Management.
- This level of management includes supervisors, jobbers, foremen, etc.
- Supervisors working at this level are actually representatives of management. At this level, management there is more of administrative work rather than managerial functions.
- Although bottom level of management is the lowest level of management, it plays a very important role in the business.
- Efficient and successful performance of this level leads to achievement of business objectives. This then provides support to the entire business.
Functions:
- To supervise function of employees.
- To maintain the discipline and morale of employees.
- To plan routine work of the respective department.
- To perform functions related to employees like transfer, promotion, training, etc.
- To get instructions, orders and programme from the departmental officers to carry out the departmental functions.
- To perform the functions like the layout, repairing and maintenance of machinery.
- To make arrangement for necessary equipment, raw-materials, etc. for the workers. ‘
- To solve the genuine problems of workers.
- To implement decisions and policies decided by top level of management.
- To forward reports of various activities taking place at the bottom level, suggestions and complaints of employees to the middle level of management.
Question 3.
Define co-ordination and explain characteristics of it.
Answer:
Co-ordination:
- To task of maintaining co-ordination and harmony among the different functions carried out by different departments in the business unit is called co-ordination.
- Although co-ordination is not a function of management but it is required at each and every stage of management.
- It is necessary right from the planning stage to controlling.
Characteristics of co-ordination:
- Co-ordination is required for all the activities, right from planning to controlling. As a result, none of the management process is possible without co-ordination.
- Co-ordination is required at every level of management.
- Success of co-ordination depends upon effective communication.
- Co-ordination is not possible without co-operation. Co-operation of employees engaged in different activities is necessary to maintain co-ordination among various activities of the organization.
- Co-ordination makes possible optimum utilization of business resources.
- Co-ordination is a part of every activity of management. Therefore co-ordination is considered soul of management.
Importance of co-ordination:
- Co-ordination makes management functions like planning, organizing, directing, controlling, etc. effective.
- Co-ordination makes possible smooth functioning of all the business activities.
- When there is proper co-ordination then neither any work remains incomplete nor any work gets duplicated.
- Co-ordination maintains harmony among various departments of management.
- Co-ordination enables to maintain a balance between order and time of business activities performed by various departments.
- Co-ordination enables accomplishment of pre-decided objectives.
Question 4.
Define marketing management and explain its functions.
Answer:
Marketing management:
1. In a broader sense we can say that marketing management is the activity of providing goods or services from producers to customers. Over and above exchange of goods with money it also includes market research, distributive method, sales promotion, storage, insurance, etc.
The main elements of marketing management are goods or services, forming physical distribution policy, price policy, increase in sale, packaging, etc.
2. Marketing management studies the needs of customers and passes the information to the production department. The production department then produces goods or services that are needed by the customers which are then finally made available to the customers.
3. Thus, marketing management helps in satisfying the needs of a particular customer or group of such customers. It focuses on optimum utilization of resources and increasing the profitability of the organization.
4. Marketing management also aims at creating demand for goods or services in the market.
Functions of marketing management:
1. Product or Product-mix:
The marketing management gives inputs for taking decision regarding development of new product or upgrading existing product. The input could be for appearance, colour, size, shape, weight, print, packing, guarantee of work, after sales services, variety of product, etc.
2. Price:
- In modern times, a customer expects availability of better quality of goods at reasonable rate. Therefore utmost care should be taken while deciding the price of the product.
- The price decision includes sales policy, credit policy, policy regarding discount, wholesale or retail sale and also commission to mediators, etc.
3. Distribution:
- Distribution-mix include decisions regarding various ways of selling like direct selling, through the whole seller, retailers agents, as well as problems related to transportation, etc.
- Distribution-mix is related to the size and scope of a business unit.
4. Promotion:
- The main aim of promotion is to increase the sale.
- It includes advertisement, publicity, selling through salesmen, ways and means to attract customers and traders, etc.
- Though promotion mix is expensive, it leads to increase in sale, which results into higher profitability.
![]()
Question 5.
Define human resource management and explain its functions.
Answer:
Human Resource Management (HRM):
- The process which takes into consideration matters like proficiency, knowledge, intelligence, likes and dislikes, personal development, necessity, etc. of employees, integrates them with business objectives and channelizes the business towards the path of success and profitability is called Human Resource Management (HRM).
- Land, building, machinery, furniture and vehicles are all material assets of a business unit. The business takes care that these assets are fully utilized and do not get eroded unnecessarily.
- Similarly, employees working in the business unit are its live asset. Without them no business can ever work. Hence, it is necessary to take care of them. .
- Business objectives can be easily and successfully achieved if the needs of employees are taken care and conducive work environment is provided.
- Due to such care, enthusiasm, loyalty and feeling of oneness among employees develop. This increases their work efficiency.
Question 6.
Define production management and explain its functions.
Answer:
Production management:
- The process which includes planning for production, deciding programmes, maintaining co-ordination, direction and keeping control is called production c management.
- The process of converting naturally available raw material into consumable finished goods with the help of human efforts is known as production:
- Production management takes care that the goods and services produced are capable of satisfying the needs of the customers.
Following functions are included in production management:
- To decide production plan
- To undertake production researdh
- To select product development as well as product-mix
- To select technology and machinery for production
- To take decisions regarding selection of location for production as well as its layout
- To estimate material and other needs for production
- To control production activity
- To control product quality
- To undertake activities for controlling expenditure maintaining and increasing productivity _
- To introduce variety of products and simplify production process