Gujarat Board GSEB Solutions Class 7 Social Science Chapter 1 Two Big States Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 7 Social Science Chapter 1 Two Big States
GSEB Class 7 Social Science Two Big States Textbook Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions in brief
Question 1.
Which regions of India were ruled by Harshvardhana and Pulkeshi II? OR Study the maps of the states of Harsha and Pulkeshi II and note down the major cities and rivers.
Answer:
Regions under Harshvardhana:
- States: Vallabhi, Kanauj, Patliputra, Thaneshwar, Bangladesh, Malwa, Saurashtra, Kamrup, Gauda, etc.
- Rivers: Ganga, Yamuna, Narmada, Son, Kama, Suvarna, Brahmaputra, etc.
Regions under Pulkeshi II:
-
- States: Badami-Karnataka, Laat, Gurjar, Vengi states, Andhra Pradesh, Vatapi, Maharashtra, etc.
- Rivers: Krishna, Godavari, Narmada, Mahanadi, etc.
![]()
Question 2.
What was the difference between Pulkeshi II and Harshvardhana’s personality?
Answer:
- Harshvardhana and Pulkeshi II were contemporary kings.
- After fighting a few battles, Harshvardhana had a feeling of satisfaction. So he stopped indulging into wars.
- On the other hand, Pulkeshi II was over ambitious. He kept on expanding his kingdom by conquering regions through more and more wars.
- Thus, Pulkeshi II kept on fighting all his life.
- Resultantly, he died while fighting with the Pallava king of Kanchivaram in 642 A.D.
- King Harshvardhana died after 5 years of the death of Pulkeshi II, i.e. in 647 A.D.
Question 3.
Why did Huen Tsang take Buddhist books, remnants and statues to China?
Answer:
So that he could study Buddhist religion in depth when he reached China.
Question 4.
What was the first task that Harshvardhana carried out after becoming the king? OR ‘Whom did Harsha think of liberating after coming to the throne?
Answer:
Free his imprisoned sister Rajyashree from the clutches of Devgupta, the King of Malwa.
Question 5.
Which plays have been written by Harshvardhana?
Answer:
Nagananda, Ratnavali and Priyadarshika.
Question 6.
Which caves were constructed during Pulkeshi M’s reign?
Answer:
Vatapi and Dharapurai.
Discuss
Question 1.
Why was Harsha not able to defeat Pulkeshi?
Answer:
Because Pulkeshi’s army was more powerful than that of Harsha.
![]()
Question 2.
Who was better as a king – Harsha or Pulkeshi II?
Answer:
- As a king, Harshvardhana can be considered better than Pulkeshi II.
- Harshvardhana was ambitious, valiant, religious and lover of art as well as education.
- He was equally fond of literature.
- Also, he was a great donor.
- He made various constructions for the welfare of his public.
- His subjects were very happy, satisfied and prosperous.
- Harshvardhana had a deep knowledge about the rule, administration and welfare of his kingdom.
- He had appointed various ministers to look after his kingdom.
- Thus, he was an efficient king.
- On the other hand, Pulkeshi II was an over ambitious king.
- He spent most of his time in expanding his kingdom by conquering new territories.
- Hence, he did not find enough time for administration and public welfare.
- He had a huge kingdom but he did not know how to manage it efficiently like Harshvardhana.
- Hence Harshvardhana was a better king.
Question 3.
Harsha and Pulkeshi II were brave, then why did they fight? Why did they not fight again?
Answer:
- Harshvardhana was the king of most of the regions of north India.
- Hence, he wanted to expand his kingdom till south India.
- On the other hand, Pulkeshi II was the king of the regions of south India.
- Hence he wanted to expand his kingdom till north India.
- When Harshvardhana left with his army to attack Pulkeshi II, at the same time the latter also left with his army to attack Harshvardhana.
- Both the armies met at Narmada.
- This led into a great war.
- Pulkeshi II defeated Harshvardhana in the war.
- Hence, Harshvardhana could not expand his kingdom.
- However, Harshvardhana was a contented king. He was not greedy.
- So he never thought of fighting with Pulkeshi II again.
- He preferred to return to his kingdom and administer his regions well.
Question 4.
What are the differences between present day universities and Nalanda University?
Answer:
Modern universities in India do not have such infrastructures and academic courses like Nalanda University. Apart from that, Nalanda University has a rich historical background, and present day universities do not have such historical importance.
GSEB Class 7 Social Science Two Big States Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write a note on how Harshvardhana became a king.
Answer:
- Harshvardhana was born in 606 A.D.
- His father Prabhakarvardhana was the king of Thaneshwar (presently Punjab and Haryana).
- When Prabhakarvardhana died, the elder brother of Harshvardhana, Rajyavardhana, came to the throne.
- The two brothers had a sister called Rajyashree.
- Devgupta, the King of Malwa killed Rajyashree’s husband and imprisoned her.
- To take revenge, Rajyavardhana attacked Malwa. But, meanwhile, Shashank, the King of Gauda region, murdered Rajyavardhana using dishonest means.
- Hence, there was no one to beseat the throne of Thaneshwar.
- So, on the advice of the leaders of the state, Harshvardhana became the King of Thaneshwar.
Question 2.
How did King Harshvardhana expand his kingdom? OR Write a note on King Harshvardhana’s conquer of the major regions of India.
Answer:
- Harshvardhana was the King of Thaneshwar.
- When he became the king, his sister Rajyashree was in the imprisonment of the King of Malwa.
- He took help of his friend-like Buddhist saint Diwakarmitra and freed Rajyashree.
- At this point, he realized that his sister’s kingdom Kanauj (presently Uttar Pradesh) did not have any king.
- So he brought Kanauj under his rule.
- This was the beginning of the expansion of the empire of Harshvardhana.
- Later, he defeated Devgupta, the King of Malwa, and brought Malwa also under his rule.
- Then he planned to attack the Gauda King, Shashank, who had killed his brother.
- Shashank was a powerful King.
- Harshvardhana would require a huge army to defeat him.
- Hence, he joined hands with Bhaskarvarman, the King of Kamrup (presently Assam).
- With his help, he defeated King Shashank and won a major part of his state.
- Later, he also won Saurashtra.
- Finally, Harshvardhana proceeded towards south India.
- But he could not defeat Pulkeshi II, the King of Chalukya dynasty in South India.
- Thus, Harshvardhana could not rule over the southern regions.
- However, within a short span of seven years, this great king conquered the major regions of north India and made the small state of Thaneshwar a big empire.
![]()
Question 3.
Which states did King Harshvardhana rule over?
Answer:
- Harshvardhana was the King of Thaneshwar (presently Punjab and Haryana).
- But later he also established his rule over Kanauj, Malwa, Kamrup, Gauda, Saurashtra, etc.
- Thus the major regions of North India were under the rule of King Harshvardhana.
Question 4.
Write a note on the way Harshvardhana ruled over his states.
- Harshvardhana was a great king.
- He would take care of his kingdom personally.
- He had divided his daily routine into three parts:
A. State administration
B. Public welfare
C. Religious duties.
A. State administration:
Harshvardhana used to keep personal watch on the administration of his state.
- He was very just and regular in conducting his administrative duties.
- He used to travel extensively in different parts of his empire to supervise the administration of his kingdom.
- He had sub-divided his administration work among different posts like the state commander of the army, Pratihara (Dwarpal), Sandhivigrahika (Foreign Minister), Rajdoot (Messenger), Parrajya Mantri (Minister of External Affairs), Maha Dandanayka (Chief Justice), Aksharpatalika (Registrar), etc.
- All these people helped in speedy and efficient administration of the state.
B. Public welfare:
- Harshvardhana’s prime focus was the welfare of his subjects.
- Infact, Harshvardhana would get so much engrossed in public welfare that he would forget to take his meals.
- He built many rest houses, inns, step wells, well, lakes, mathas, chaityas and viharas for the welfare of his people.
C. Religious duties:
- King Harshvardhana was a very religious person.
- He held a Buddhist religious meeting in his kingdom every year.
- Every five years, he organized a religious congregation at Prayag.
- He donated lavishly in this congregation.
- In fact, he used to donate his entire treasury in the congregation.
- He would even donate the ornaments on his body and give them away as charity during the congregation.
- He even prohibited killing of animals.
Question 5.
Write a note on the literature in the reign of King Harshvardhana.
Answer:
- King Harshvardhana was a great lover of arts and literature.
- Banabhatta was a gem in the court of this King. He was a great poet and writer.
- Banabhatta composed two famous works in Sanskrit language. They are :
A. Harshcharita – The biography of King Harshvardhana, B. Kadambari - Harshcharita covers a lot about the life of the great King, Harshvardhana.
- King Harshvardhana was also a great writer himself.
- He wrote three plays namely Nagananda, Ratnavali and Priyadarshika.
![]() Z
Z
Question 6.
What did King Harshvardhana do for public welfare?
Answer:
Public welfare:
- Harshvardhana’s prime focus was the welfare of his subjects.
- Infact, Harshvardhana would get so much engrossed in public welfare that he would forget to take his meals.
- He built many rest houses, inns, step wells, well, lakes, mathas, chaityas and viharas for the welfare of his people.
Question 7.
Explain the statement: King Harshvardhana was a very religious man.
Answer:
Religious duties:
- King Harshvardhana was a very religious person.
- He held a Buddhist religious meeting in his kingdom every year.
- Every five years, he organized a religious congregation at Prayag.
- He donated lavishly in this congregation.
- In fact, he used to donate his entire treasury in the congregation.
- He would even donate the ornaments on his body and give them away as charity during the congregation.
- He even prohibited killing of animals.
Question 8.
How did Harshvardhana administer his kingdom?
A. State administration:
Harshvardhana used to keep personal watch on the administration of his state.
- He was very just and regular in conducting his administrative duties.
- He used to travel extensively in different parts of his empire to supervise the administration of his kingdom.
- He had sub-divided his administration work among different posts like the state commander of the army, Pratihara (Dwarpal), Sandhivigrahika (Foreign Minister), Rajdoot (Messenger), Parrajya Mantri (Minister of External Affairs), Maha Dandanayka (Chief Justice), Aksharpatalika (Registrar), etc.
- All these people helped in speedy and efficient administration of the state.
Question 9.
Write a short note on Nalanda Vidhyapith.
Answer:
- Nalanda Vidhyapith was a renowned university in the kingdom of Harshvardhana.
- Harshvardhana provided all the amenities and aid to Acharaya Shilbhadra, the in-charge of
- Vidhyapith, so that Nalanda could be made a world famous university.
- He gave 100 villages for the maintenance and financial aid of Nalanda Vidhyapith.
- The famous alchemist, Acharaya Nagarjuna, who proved that iron, arsenic and mercury could be used as medicine belonged to the Nalanda Vidhyapith.
- King Harshvardhana provided education, lodging and boarding free of cost to all the students of the Vidhyapith.
- There was a grand and royal library of the Vidhyapith which was called ‘Dharmaganj’,
- With the efforts of King Harshvardhana, Nalanda Vidhyapith became world famous.
- Students from across the globe flocked to study here.
- However, only those who could clear the entrance test were granted admission in this renowned university.
Question 10.
How was the life of the people in the reign of King Harshvardhana?
The following points give detailed explanation of the life of the people of King Harshvardhana:
1. Social life:
The society was divided into four varnas (castes). There was no existence of veil (purdaah) system or inter-caste marriages. People mainly followed Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. However, they were not rigid in terms of religion. Many evils like sati system, child marriage and polygamy started in the society during the reign of King Harshvardhana.
2. Architecture:
The villages and towns of the kingdom of Harshvardhana were protected from external threats and enemies through surrounding fortified walls. There were huge doors at the entrance of the town or village.
3. Food:
People ate wheat, rice, fruits, vegetables, milk and milk products.
4. Clothing:
The male subjects of King Harshvardhana wore dhoti while the females wore sari. ‘People generally wore white colour. They dressed simply and neatly. As far as ornaments are concerned, people wore garlands, rings, bangles, bracelets, necklaces, etc.
5. Entertainment:
People entertained themselves by playing games like chess and sogathabaji. Acrobats and conjurers who moved from village to village also entertained people.
6. Occupation:
The main occupation of the subjects of King Harshvardhana was farming and animal husbandry. The revenue collected from farmers was almost 1/6th of the total crop production. Thus, there was no heavy taxing on people.
7. Trade and commerce:
Internal and external trade was carried on by the Vaishyas. Gold and silver coins were used as currency. People exported various things like ornaments, statues, ivory pieces, carved wooden pieces, etc. Thus, India was a prosperous country. Also, during Harshvardhana’s reign, people had good business relations with Rome due to which lots of gold came to India. Harshvardhana built a highway for the transportation of goods, right from Patliputra to Brugu Kachchh Port (presently Bharuch).
Thus, overally people lived a very simple yet prosperous life in the reign of King Harshvardhana.
![]()
Question 11.
How was the trade and commerce in the reign of King Harshvardhana?
Answer:
Trade and commerce:
Internal and external trade was carried on by the Vaishyas. Gold and silver coins were used as currency. People exported various things like ornaments, statues, ivory pieces, carved wooden pieces, etc. Thus, India was a prosperous country. Also, during Harshvardhana’s reign, people had good business relations with Rome due to which lots of gold came to India. Harshvardhana built a highway for the transportation of goods, right from Patliputra to Brugu Kachchh Port (presently Bharuch).
Thus, overally people lived a very simple yet prosperous life in the reign of King Harshvardhana.
Question 12.
Write a note on the food, clothing and occupation of the subjects of Harshvardhana.
Answer:
Architecture:
The villages and towns of the kingdom of Harshvardhana were protected from external threats and enemies through surrounding fortified walls. There were huge doors at the entrance of the town or village.
Food:
People ate wheat, rice, fruits, vegetables, milk and milk products.
Occupation:
The main occupation of the subjects of King Harshvardhana was farming and
animal husbandry. The revenue collected from farmers was almost 1/6th of the total crop
production. Thus, there was no heavy taxing on people.
Question 13.
Write a short note on Huen Tsang.
Answer:
- Huen Tsang was a Chinese traveler who stayed in India for 15 years and visited different places of India.
- He was born in 629 A.D.
- Of the 15 years of his stay in India, he spent 5 years at Nalanda Vidhyapith studying Buddhism.
- During his stay, he described the social, political and religious conditions of India elaborately in his dairy.
- He was a part of the 6th Buddha religious congregation held by King Harshvardhana at Prayag.
- Since Huen Tsang visited India during the reign of King Harshvardhana, he made lots of notes about the King and his subjects.
- Today, we know a lot of King Harsha only because of the diaries maintained by Huen Tsang.
- In 645 A.D., Tsang went back to China.
- He carried many books, remnants and statues with him.
- However, he died in the same year.
Two important notes from the diary of Huen Tsang are:
I. There were 100 Buddhist mathas in the state of King Harshvardhana.
II. The people in the reign of King Harshvardhana lived a simple and pious life. They had high moral standards. They believed in truth and justice. The people considered cheating and breaching as a sin.
Question 14.
Give a detailed explanation of how Pulkeshi II became the King of Vatapi.
Answer:
- Vatapi was the capital of Karnataka state in south India.
- It was ruled by the Solanki kings of the Chalukya dynasty.
- Vatapi was a huge state whose borders extended to far-off regions.
- Pulkeshi I was the King of this huge capital.
- After him, his son Kirtivarma sat on the throne.
- Later on, Pulkeshi I’s brother, Manglesh, became the king.
- And lastly, after Manglesh, Pulkeshi II, the virtuous king came to the throne.
- He ruled for almost 30 years.
![]()
Question 15.
Over which regions did Pulkeshi II rule? OR What was the contribution of Pulkeshi II in expanding his territories?
- Pulkeshi II, the virtuous king, ruled over south India for almost 30 years.
- He was a majestically valiant and brave soldier.
- He had won many battles.
- First he won Laat in south Gujarat and then he gained victory over Gurjar in North Gujarat.
- He also conquered Vengi states located between the rivers Krishna and Godavari.
- He also won Andhra Pradesh.
- Thus, Pulkeshi II expanded the territories of his kingdom to a great extent.
Question 16.
What happened when Harshvardhana and Pulkeshi II fought a battle? OR Which battle was fought on the banks of Narmada? What was its result?
- Harshvardhana, the King of Kanauj, was very ambitious.
- He had a powerful army with the help of which he fought wars and conquered territories.
- After gaining victory over most of the regions of north India, Harshvardhana marched victoriously towards south to conquer it.
- At the same time, Pulkeshi II, the King of south India, also led his army towards north.
- Hence, both the armies met at Narmada.
- This led into a great war.
- The powerful army of the vaiiant King Pulkeshi II defeated the great king, Emperor Harshvardhana.
- This brought an end to the victorious march of Harshvardhana.
- Due to this war, Harshvardhana could not extend his empire beyond Narmada.
Question 17.
Write a note on Pulkeshi M’s love for art and religious.
Answer:
Art:
Pulkeshi II, the brave ruler, was very fond of art.
- The caves of Vatapi and Dharapurai were built during his time.
- The world famous paintings on the walls of Ajanta caves were also done during his time.
- Huen-Tsang once visited the royal court of Pulkeshi II. He could not stop praising the king’s love for art after seeing his court.
Religion:
- Pulkeshi II was a follower of Hindu religion.
- Hardly, a few people followed Buddhism in his time.
- The impact of one of the sects of Jainism called ‘Digambar’ increased in the reign of Pulkeshi II.
Question 18.
Harshvardhana can be considered a great donor. Explain how.
- King Harshvardhana organized a religious congregation at Prayag every five years.
- He donated lavishly in this congregation.
- In fact, he used to donate his entire treasury in this congregation.
- He would even donate the ornaments on his body and give them away as charity during the congregation.
- Thus, Harshvardhana can be considered a great donor.
![]()
Question 19.
How can you say that King Pulkeshi II was a great lover of arts?
Answer:
Art:
Pulkeshi II, the brave ruler, was very fond of art.
- The caves of Vatapi and Dharapurai were built during his time.
- The world famous paintings on the walls of Ajanta caves were also done during his time.
- Huen-Tsang once visited the royal court of Pulkeshi II. He could not stop praising the king’s love for art after seeing his court.
Religion:
- Pulkeshi II was a follower of Hindu religion.
- Hardly, a few people followed Buddhism in his time.
- The impact of one of the sects of Jainism called ‘Digambar’ increased in the reign of Pulkeshi II.
Question 20.
Which important details did Huen Tsang note in his diary?
Answer:
- Huen Tsang was a Chinese traveler who stayed in India for 15 years and visited different places of India.
- He was born in 629 A.D.
- Of the 15 years of his stay in India, he spent 5 years at Nalanda Vidhyapith studying Buddhism.
- During his stay, he described the social, political and religious conditions of India elaborately in his dairy.
- He was a part of the 6th Buddha religious congregation held by King Harshvardhana at Prayag.
- Since Huen Tsang visited India during the reign of King Harshvardhana, he made lots of notes about the King and his subjects.
- Today, we know a lot of King Harsha only because of the diaries maintained by Huen Tsang.
- In 645 A.D., Tsang went back to China.
- He carried many books, remnants and statues with him.
- However, he died in the same year.
Two important notes from the diary of Huen Tsang are:
I. There were 100 Buddhist mathas in the state of King Harshvardhana.
II. The people in the reign of King Harshvardhana lived a simple and pious life. They had high moral standards. They believed in truth and justice. The people considered cheating and breaching as a sin.
Answer in One or Two Sentences
(Note : Here, answers are given in short for memorizing easily. Students must write full sentences.
Question 1.
When did Rajyavardhana come to the throne?
Answer:
When his father Prabhakarvardhana died.
Question 2.
Who killed Rajyavardhana? How?
Answer:
King Shashank of Gauda state; By using fraudulent means.
Question 3.
Why did Harshvardhana acquire the throne of Thaneshwar?
Answer:
Because the leaders of the state advised him to do so.
Question 4.
Who helped Harshvardhana in liberating Rajyashree?
Answer:
His friend who was also a Buddhist saint, namely Diwakarmitra
Question 5.
Who was the King of Malwa? Who defeated him?
Answer:
Devgupta; Harshvardhana.
Question 6.
Who helped Harshvardhana in defeating King Shashank?
Answer:
The King of Kamrup (present Assam), namely Bhaskarvarman.
![]()
Question 7.
How did Harshvardhana divide his routine?
Answer:
Into three parts; administration, public welfare and religious duties.
Question 8.
What did Harshvardhana build for his people?
Answer:
Rest houses, inns, step wells, wells, lakes, mathas, chaityas and viharas.
Question 9.
What is Harshcharita?
Answer:
Biography of King Harshvardhana written by a great poet and writer Banabhatta.
Question 10.
What did Acharaya Nagarjuna prove?
Answer:
That iron, arsenic and mercury could be used as medicine.
Question 11.
Which amenities were provided free of cost in Nalanda Vidhyapith?
Answer:
Education, lodging and boarding.
Question 12.
Which evils entered the society in the reign of King Harshvardhana?
Answer:
Sati system, child marriage and polygamy.
![]()
Question 13.
What types of clothes did the subjects of Harshvardhana wear?
Answer:
Males wore dhoti, females wore sari.
Question 14.
Which systems did not exist in the society in the reign of Harshvardhana?
Answer:
Veil (Purdaah) system and inter-caste marriage system.
Question 15.
What type of ornaments did people wear during the rule of Harshvardhana?
Answer:
Garlands, rings, bangles, bracelets, necklaces, etc.
Question 16.
Who entertained people in the reign of King Harsha?
Answer:
Acrobats and conjurers.
Question 17.
What was the main occupation of the people during the reign of Harshvardhana?
Farming and animal husbandry.
Question 18.
What did people export in the time of Harsha?
Answer:
Ornaments, states, carved wooden pieces, ivory, etc.
![]()
Question 19.
Which religion did people follow in the reign of Harshvardhana?
Answer:
Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism.
Question 20.
What has Huen Tsang described in his diary?
Answer:
About the social, political and religious conditions of India at that time.
Question 21.
What opinion did Huen Tsang have about the people of India?
Answer:
The people lived a simple and pious life. They had high moral standards. They beleived in truth and justice. They considered cheating and breaching as a sin.
Question 22.
Who was Pulkeshi II?
Answer:
The King of Chalukya dynasty who ruled over south India.
Question 23.
Who was Pulkeshi I?
Answer:
A strong King of Badami-Karnataka who performed Ashwamegha yagna.
Question 24.
When did Pulkeshi II die? How?
Answer:
In 642 A.D.; while fighting with the Pallava king of Kanchivaram.
![]()
Question 25.
The impact of which religion increased in the reign of Pulkeshi II?
Answer:
One of the sects of Jainism called Digambar.
Question 26.
What makes Ajanta Caves world famous?
Answer:
The beautiful pictures drawn on the walls of the caves in the reign of Pulkeshi II
Question 27.
What did Manglesh build?
Answer:
The ideal Vishnu temple.
Question 28.
List out four qualities you can attribute to Pulkeshi II.
Answer:
Majestic, valiant, ambitious, religious and lover of arts.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Who was the father of Rajyashree?
(A) Prabhakarvardhana
(B) Rajyavardhana
(C) Harshvardhana
(D) Udayrajvardhana
Answer:
(A) Prabhakarvardhana
Question 2.
Who was the King of Gauda?
(A) Shashank
(B) Devgupta
(C) Diwakarmitra
(D) Bhaskarvarman
Answer:
(A) Shashank
![]()
Question 3.
Rajyavardhana was the …………….. of Harshvardhana.
(A) Younger brother
(B) Elder brother
(C) Brother-in-law
(D) Father
Answer:
(B) Elder brother
Question 4.
King Shashank killed ………………. .
(A) Prabhakarvardhana
(B) Rajyavardhana
(C) Harshvardhana
(D) Bhaskarvarman
Answer:
(B) Rajyavardhana
Question 5.
Rajyashree was the sister of ……………….. .
(A) Prabhakarvardhana
(B) Rajyavardhana
(C) Harshvardhana
(D) Both B and C
Answer:
(D) Both B and C
Question 6.
Rajyashree was imprisoned by ……………… .
(A) Devgupta
(B) Diwakarmitra
(C) Shashank
(D) Bhaskarvarman
Answer:
(A) Devgupta
Question 7.
Devgupta was the King of …………….. .
(A) Thaneshwar
(B) Kamrup
(C) Saurashtra
(D) Malwa
Answer:
(D) Malwa
Question 8.
Thaneshwar is present ……………. .
(A) Punjab
(B) Assam
(C) Uttar Pradesh
(D) Saurashtra
Answer:
(A) Punjab
Question 9.
Who was Diwakarmitra?
(A) Maha Dandanayka
(B) King of Chalukya dynasty
(C) Buddhist hermit
(D) King of Gauda
Answer:
(C) Buddhist hermit
![]()
Question 10.
Which state was without any king?
(A) Kanauj
(B) Malwa
(C)Kamrup
(D) Saurashtra
Answer:
(A) Kanauj
Question 11.
Harshvardhana took help of …………………. to defea
(A) Diwakarmitra
(B) Bhaskarvarman
(C) Shilbhadra
(D) Pulkeshi II
Answer:
(B) Bhaskarvarman
Question 12.
Bhaskarvarman was the King of ………………. .
(A) Thaneshwar
(B) Kanauj
(C) Kamrup
(D) Badami
Answer:
(C) Kamrup
Question 13.
Pulkeshi II belonged to the ……………….. dynasty.
(A) Chalukya
(B) Chola
(C) Pallava
(D) Kalinga
Answer:
(A) Chalukya
Question 14.
Pulkeshi II ruled over …………….. India.
(A) East
(B) West
(C) North
(D) South
Answer:
(D) South
Question 15.
It took about ……………… years for Harshvardhana to conquer north India.
(A) 5
(B) 7
(C) 9
(D) 12
Answer:
(B) 7
Question 16.
Formerly, Harshvardhana was the King of ………………… .
(A) Thaneshwar
(B) Kanauj
(C) Kamrup
(D) Maiwa
Answer:
(A) Thaneshwar
![]()
Question 17.
Who helped Harshvardhana in liberating Rajyashree?
(A) Devgupta
(B) Diwakarmitra
(C) Shashank
(D) Bhaskarvarman
Answer:
(B) Diwakarmitra
Question 18
Harshvardhana had divided his routine into ……………… parts.
(A) Two
(B) Three
(C) Four
(D) Several
Answer:
(B) Three
Question 19.
While carrying out works of …………………. Harshvardhana would forget to take his meals.
(A) Administration
(B) Public welfare
(C) Religious duties
(D) All of these
Answer:
(B) Public welfare
Question 20.
Who was Sandhivigrahika?
(A) Commander-in-Chief
(B) Foreign Minister Affairs
(C) Minister of External Affairs
(D) Chief Justice
Answer:
(B) Foreign Minister Affairs
Question 21.
Pratihara refers to the ……………. .
(A) Senapati
(B) Rajdoot
(C) Sipahi
(D) Dwarpal
Answer:
(D) Dwarpal
Question 22.
Harshvardhana held the Buddha Religious Meet every ……………… year(s).
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 5
(D) 10
Answer:
(A) 1
![]()
Question 23.
Harshvardhana held a religious congregation every……………….. year(s).
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 5
(D) 10
Answer:
(C) 5
Question 24.
Which writer was a gem in the courts of Harshvardhana?
(A) Kalidas
(B) Meghdoot
(C) Banabhatt
(D) Bharavi
Answer:
(C) Banabhatt
Question 25
Which of these works was not written by King Harshvardhana?
(A) Nagananda
(B) Ratnavali
(C) Kadambari
(D) Priyadarshika
Answer:
(C) Kadambari
Question 26.
A lot about the life of King Harshvardhana can be known from …………………. .
(A) Harshcharita
(B) Kadambari
(C) Ratnavali
(D) Nagananda
Answer:
(A) Harshcharita
Question 27.
King Harshvardhana had written ……………… plays.
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Answer:
(B) 3
Question 28.
King Harshvardhana wrote …………………… .
(A) Novels
(B) Poetry
(C) Plays
(D) All of these
Answer:
(C) Plays
![]()
Question 29.
Harshvardhana gave …………….. villages for the maintenance of the Nalanda Vidhyapith.
(A) 50
(B) 100
(C) 500
(D) 1000
Answer:
(B) 100
Question 30.
Who was the in-charge of Nalanda Vidhyapith?
(A) King Harshvardhana
(B) King Pulkeshi II
(C) Acharaya Shilbhadra
(D) Acharaya Nagarjuna
Answer:
(C) Acharaya Shilbhadra
Question 31.
Acharaya Nagarjuna proved that ………………. could be used as medicine.
(A) Iron
(B) Arsenic
(C) Mercury
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 32.
The society in the reign of Harshvardhana was divided into ……………….. varnas.
(A) Four
(B) Six
(C) Eight
(D) Ten
Answer:
(A) Four
Question 33.
Internal and external trade was carried on by …………….. .
(A) Brahmins
(B) Kshatriyas
(C) Vaishyas
(D) Shudras
Answer:
(C) Vaishyas
Question 34.
During the reign of Harshvardhana, India had good business relations with ……………… .
(A) Rome
(B) Italy
(C) Sweden
(D) Portugal
Answer:
(A) Rome
Question 35.
Huen Tsang was a ……………….. traveler.
(A) Japanese
(B) Nepalese
(C) Korean
(D) Chinese
Answer:
![]()
Question 36.
Huen Tsang stayed at Nalanda University for ……………… years.
(A) 2
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 7
Answer:
(C) 5
Question 37.
Huen Tsang had remained present in the …………………… Buddha religious congregation held at Prayag.
(A) 4th
(B) 5th
(C) 6th
(D) 9th
Answer:
(C) 6th
Question 38.
AccordIng to Huen Tsang, there were ………………. mathas in Harshas state.
(A) 50
(B) 100
(C) 500
(D) 1000
Answer:
(B) 100
Question 39.
……………… was the capital of Solanki kings.
(A) Laat
(B) Vatapi
(C) Vengi
(D) Badami
Answer:
(B) Vatapi
Question 40.
Who performed Ashwamegha Yagna?
(A) Pulkeshi I
(B) Pulkeshi II
(C) Kirtivarma
(D) Manglesh
Answer:
(A) Pulkeshi I
Question 41.
Pulkeshi II acquired the throne after ………………. .
(A) Pulkeshi I
(B) Kirtivarma
(C) Manglesh
(D) Harshvardhana
Answer:
(C) Manglesh
![]()
Question 42.
Laat is located in ………………. Gujarat.
(A) East
(B) West
(C) North
(D) South
Answer:
(D) South
Question 43.
Harshvardhana and Pulkeshi il fought on the banks of ………………. .
(A) Narmada
(B) Krishna
(C) Godavari
(D) Mahanadi
Answer:
(A) Narmada
Question 44.
Which religion slackened in the reign of Pulkeshi II?
(A) Hinduism
(B) Buddhism
(C) Jainism
(D) All of these
Answer:
(B) Buddhism
Question 45.
King Harsha held a religious congregation at ……………….. every 5 years.
(A) Mathura
(B) Prayag
(C) Haridwar
(D) Kashi
Answer:
(B) Prayag
Fill in the blanks
1. …………………. had imprisoned Rajyashree.
Answer:
Devgupta
2. Harshvardhana ruled mostly over ……………… India.
Answer:
North
3. …………… and ……………… are the famous works of Banabhatta.
Answer:
Harshcharita, Kadambari
![]()
4. Banabhatta was a master at literature in ………………. language.
Answer:
Sanskrit
5. Acharaya Nagarjuna was a/an ………………. by profession.
Answer:
Alchemist
6. Students got admission in the Nalanda Vidhyapith through …………….. .
Answer:
Entrance test
7. The name of the library of the Nalanda Vidhyapith was ……………… .
Answer:
Dharamganj
8. People in the reign of Harshvardhana ate …………… and ………………. grains.
Answer:
Wheat, rice
9. In the reign of Harshvardhana, people mostly played ……………… and …………… games.
Answer:
Chess, Sogathabaji
![]()
10. Harshvardhana collected the ………………… part of the total crop production as land revenue.
Answer:
1/6th
11. Lots of ………………… flowed in India due to her good relations with Rome.
Answer:
Gold
12. Huen Tsang had visited India during the reign of ……………… .
Answer:
Harshvardhana
13. Huen Tsang studied …………….. at Nalanda Vidhyapith.
Answer:
Buddhism
14. Huen Tsang was born in ………………. A.D.
Answer:
629
15. Huen Tsang returned to China in …………….. A.D.
Answer:
645
16. Huen Tsang was present in the religious congregation held at ……………….. by Harshvardhana.
Answer:
Prayag
![]()
17. Harshvardhana was born in ………………. A.D.
Answer:
606
18. ……………… kings belong to Chalukya dynasty.
Answer:
Solanki
19. The flag of Vatapi kingdom had the symbol of ……………… on it.
Answer:
Varahavtar
20. After Pulkeshi I. ……………….. became the king.
Answer:
Kirtivarma
21. After Kirtivarma, ……………… became the king.
Answer:
Manglesh
22. Pulkeshi I had performed the ……………….. yagna.
Answer:
Ashwamegha
23. Kirtivarma was the …………….. of Pulkeshi I.
Answer:
Son
![]()
24. Manglesh was the brother of ………………. .
Answer:
Pulkeshi I
25. Pulkeshi II ruled for over ………………. years.
Answer:
30
26. ……………….. decorated Vatapi very beautifully.
Answer:
Pulkeshi II
27. The empire of Kanauj could not extend beyond the river ……………… .
Answer:
Narmada
28. Pulkeshi II built the caves of ………………. and …………………
Answer:
Vatapi, Dharapurai
29. Huen Tsang had visited the royal court of King ………………….
Answer:
Pulkeshi II
30. Solanki Kings were the worshippers of ……………… religion.
Answer:
Hindu
![]()
31. Pulkeshi II died while fighting with the king of ……………… state.
Answer:
Kanchivaram
32. Pulkeshi II died in …………… A.D.
Answer:
642
33. Harshvardhana died after ……………… years of the death of Pulkeshi II.
Answer:
5
True or False
1. ‘Si-yu-Ki’ means The revenge of the western world’.
Answer:
False
2. Huen Tsang, a Chinese trader came to India in the 7th century for starting trade with King Harshavardhana.
Answer:
False
3. Devgupta, the king of Malwa killed Rajyashree’s husband and imprisoned her.
Answer:
True
4. Maha Dandanayka refers to Chief Justice.
Answer:
True
5. Harshvardhana wanted to make Takshashila a world famous university.
Answer:
False
![]()
6. In the reign of Harshvardhana, people mostly preferred to wear red coloured clothes.
Answer:
False
7. As per Pulkeshi II, there were 100 Buddhist maths in the state of King Harshvardhana.
Answer:
False
8. The sequence of kings of Vatapi is Pulkeshi-I, Pulkeshi-ll, Kirtivarma.
Answer:
False
9. Regions under Pulkeshi-ll – Badami, Vengi, Laat, Vatapi, Vallabhi, etc.
Answer:
False
10. Rivers in the region of Harshvardhana – Narmada, Son, Kama, Suvarna.
Answer:
True
11. Harshvardhana built a highway from Patliputra to Brugu Kachchh Port for easy transportation of goods.
Answer:
True
![]()
12. Huen Tsang stayed in India for 15 years.
Answer:
True
13. Huen Tsang died in 647 A.D.
Answer:
False
14. Harshvardhana was defeated by King Pulkeshi-I.
Answer:
False
15. Vengi states lie between Krishna and Kaveri rivers.
Answer:
False
16. Pulkeshi I got paintings drawn on the Ajanta caves.
Answer:
False
17. The impact of one of the sects of Jainism called shwetambar increased during the reign of Pulkeshi II.
Answer:
False
18. The King of Kanchivaram belonged to Pallava Dynasty.
Answer:
True
![]()
19. Harshvardhana died in 645 A.D.
Answer:
False
Match the Following
| A | B |
| 1. Devgupta | (a) Gauda |
| 2. Prabhakarvardhana | (b) Kanauj |
| 3. Bhaskarvarman | (c) Karnataka |
| 4. Pulkeshi II | (d) Thaneshwar |
| 5. Shashank | (e) Kanchivaram |
| 6. Rajyashree | (f) Malwa |
| (g) Kamrup |
Answer:
1 – f, 2 – d, 3 – g, 4 – c, 5 – a, 6 – b
(ii)
| A | B |
| 1. Diwakarmitra | (a) Gem of Harsha’s court |
| 2. Banabhatta | (b) Renowned alchemist |
| 3. Acharaya Shilbhadra | (c) Chinese traveler |
| 4. Acharaya Nagarjuna | (d) Decorated Vatapi |
| 5. Huen Tsang | (e) Buddhist saint |
| 6. Pulkeshi I | (f) Ashwamegha Yagna |
| 7. Manglesh | (g) Nalanda Vidhyapith in- charge |
| 8. Pulkeshi II | (h) Ideal Vishnu Temple |
Answer:
1 – e, 2 – a, 3 – g, 4 – b, 5 – c, 6 – f, 7 – h, 8 – d
![]()
Two Big States Class 7 GSEB Notes
- India was ruied by Gupta Dynasty from approximately 320 A.D. to 550 A.D. The Gupta Empire was spread in most of the Indian subcontinent. This period is called the Golden Age of India.
- However, at the end of 6th century when the Gupta Empire collapsed, India was again ruled by numerous regional kingdoms. In this chapter, we will talk about two such regional kingdoms, one belonging to North India and other to South India.
The two regional kingdoms: - By the end of 6th century A.D., Gupta Empire almost faded away from the map of India. The last Gupta ruler Devgupta was ruling over a relatively smaller state of Malwa. (Note: Ujjain shown in the map was a part of Malwa region.)
A. Vardhana dynasty in North India : - In the North, Thaneshwar was ruled by Pushyabhuti family belonging to Vardhana dynasty. Prabhakarvardhana was the ruler of Thaneshwar (presently Punjab and Haryana) at that time.
- After Prabhakarvardhana, Harshvardhana established a larger kingdom in North India. Harshvardhana brought Kanauj (in Uttar Pradesh) under his rule and united the two kingdoms of Thaneshwar and Kanauj. He then transferred his capital from Thaneshwar to Kanauj.
There are mainly two chief sources that provide the history of King
Harshvardhana. They are:

i. Harshacharita which is a biography of King Harshvardhana written by Banabhatta.
ii. A book called Si-yu-ki i.e. The Records of the Western World’, written by Huen Tsang. Huen Tsang was a Chinese pilgrim who came to India in the first half of the 7th century A.D. in order to visit the places of pilgrimage associated with Buddha. He stayed here for 15 years during which he travelled widely and closely observed the country and its people. On returning to China, he wrote all the details of his visit into his book Si-yu-ki. This book is an invaluable source of information to historians about Harsha and the political, social, economic and religious conditions in India during his reign.
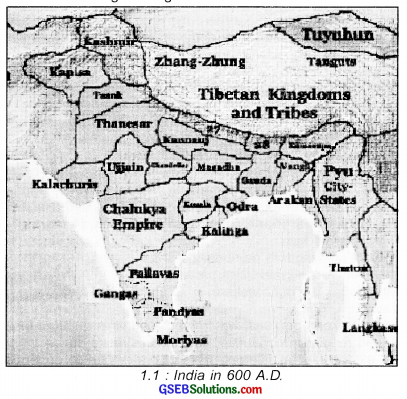
B. Chalukya (Solanki) dynasty in South India:
- From the middle of 6th century, Chalukya dynasty of South India ruled from Vatapi (now known as Badami in Karnataka state).
- The rule of the Chalukyas marks an important milestone in the history of South India and a Golden Age in the history of Karnataka.
- It is interesting to know that when the Chalukya Kings migrated to Gujarat, the name Chalukya
was pronounced in local language as Salukya or Saluki, and later got changed to Solanki.