Gujarat Board GSEB Solutions Class 7 Social Science Chapter 7 India: Location, Border, Area and Physiography Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 7 Social Science Chapter 7 India: Location, Border, Area and Physiography
GSEB Class 7 Social Science India: Location, Border, Area and Physiography Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Answer the following questions
Question 1.
How did islands come into existence?
Answer:
Through earthquakes, volcanic eruptions or water currents.
![]()
Question 2.
Why are deserts thinly populated?
Answer:
I. Features of the desert:
- The land is sandy in desert region.
- The climate is dry, hot and barren.
- The temperature is unbearable.
- There is scanty rainfall, even lesser than 20 cm.
- Hence, there is scarcity of water.
- Even the basic goods necessary for sustaining life are not available in this region.
- The only trees that can be grown here are dates or cactus.
- Camels are used for transportation. .
- Due to all these issues, maximum part of the desert is sparsely (thinly) populated.
Question 3.
The plains of the North are densely populated. Why?
Answer:
The plains of North India are very densely populated and prosperous due to the following reasons:
- The plains of North India have been formed by the rivers flowing from Himalayas. Hence, these plains have rich alluvium deposits. This makes them fertile. Thus, agriculture has developed on a large scale in North India.
- Moreover, these rivers are perennial. They flow round the year. So there is no scarcity of water in these rivers. Thus, irrigation facility has helped in yielding good crops.
- Due to the development in agriculture sector, there are many agro-based industries and other agriculture related industries in North India.
- Therefore, North India is prosperous and densely populated.
Question 4.
Why do cities near the sea shore develop?
Answer:
Cities near sea shores develop due to the following reasons:
- Development of fishing industry
- Internal and international waterways
- Rich alluvium deposits in the soil
- Black fertile soil
- Import-export facilities
- Development of ports and other trading activities
Question 5.
What if there would be no variation in the physiography of India?
Answer:
If there were no variations in the physiography of India, there would be no:
- Himalayas to block the cold winds blowing from the north. ,
- Plains of North India to yield rich agricultural production for us.
- Coastal plains to develop ports, fisheries and transportation industries.
- Hill stations, sea-shores, beaches, rivers, falls, lakes, etc. for recreation of tourists.
- Thus, physiographic variations are important for an overall development of the nation.
![]()
2. State whether the following sentences are true or false
1. India is the seventh largest country in the world.
Answer:
True
2. Mt. Everest of India is the highest peak.
Answer:
False
3. Central and Deccan Plateau regions of India are known as treasury of minerals.
Answer:
True
4. Tropic of Capricorn passes through India.
Answer:
False
5. Rann of Kachchh is very sandy.
Answer:
False
GSEB Class 7 Social Science India: Location, Border, Area and Physiography Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Give a brief idea of the location and border of India.
Answer:
A. Location of India:
- India has a very strategic location.
- It lies in the Northern Hemisphere.
- It lies in the southern part of the continent of Asia.
- It lies between 8.4° N to 37.6° N latitudes and 68.7° E to 97.25° E longitudes.
B. Borders of India:
- The Himalayas are in the north of India.
- India shares its northern border with China and Tajikistan.
- In the north-east, India shares its border with Nepal.
- In the east of India, lie Bangladesh and the Bay of Bengal.
- While the north-western border of India is shared by Pakistan.
- The Arabian Sea is the west of India.
- In the south of India is the huge Indian Ocean and a small island country Sri Lanka.
![]()
Question 2.
Give an idea of the area of India.
Answer:
Area of India:
- India extends from Kashmir in the north to Kanyakumari in the south.
- The north-south length of India is 3214 km.
- Also India extends from Arunachal Pradesh in the east to Dwarka in the west.
- The east-west length of India is 2933 km.
- Thus, the total land area of India is approximately 32,87,263 (3214 km × 2933 km) sq. km.
- This makes India the 7th largest country in the world in terms of land area.
- There are 28 states and 7 union territories in India.
- The shape of India is narrow in the north, broad in the middle and again narrow in the south.
Question 3.
What is physiography? Which are the physiographic divisions of India?
Answer:
- The study of physical features of earth’s surface is called physiography.
- In India also, the earth’s surface is not same everywhere.
- There are different forms of land in our nation.
- On the basis of these variations in the landforms, India can be divided into the following five
physiographic divisions:
- Northern Mountain Ranges
- Plains of North India
- Peninsular Plateaus of Central and South India
- Coastal Plains
- Archipelagos (Islands)
Question 4.
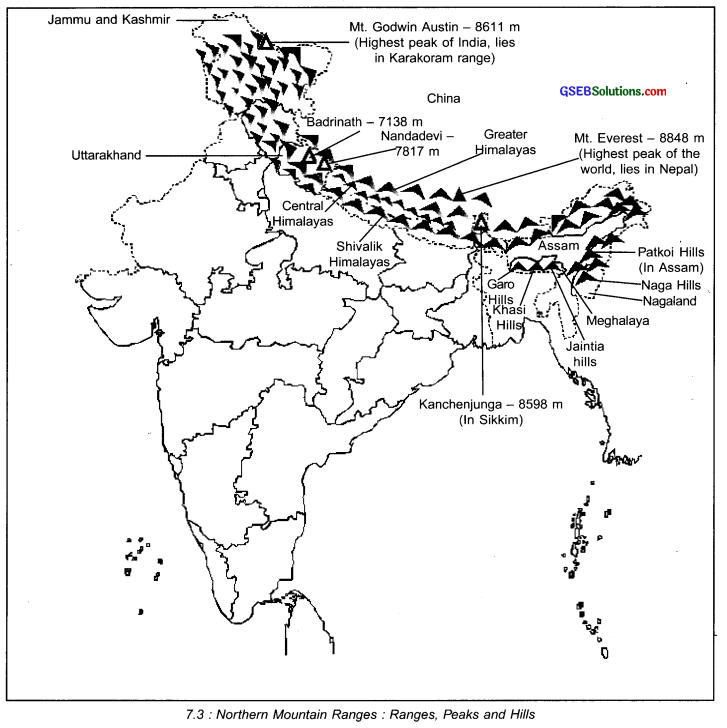
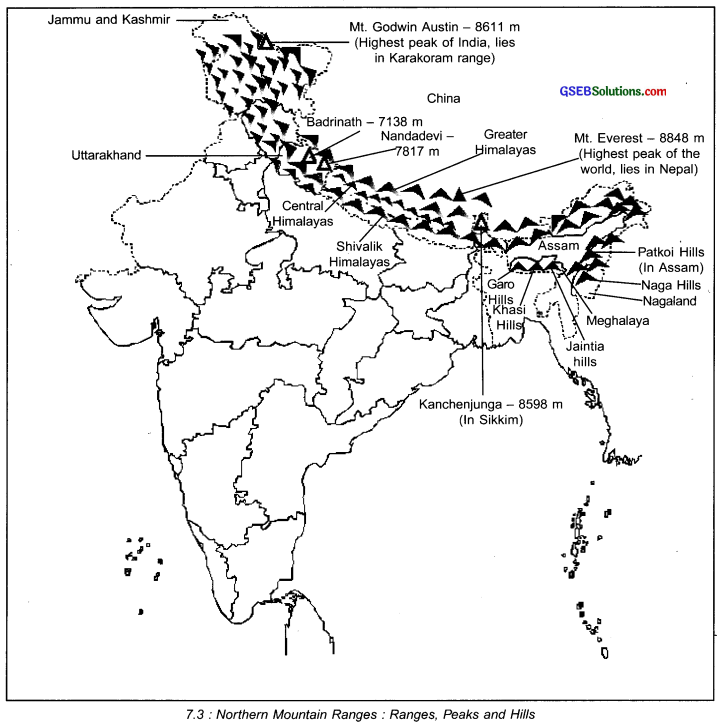
Write a short note on Northern Mountain Ranges.
Answer:
- The northern region of India is covered by Himalayas.
- Himalayas is not a single mountain.
- It is a long chain of mountains.
- Hence it is called the Himalayan chain of mountains.
- It is the highest mountain range of the world.
- The Himalayan chain of mountains consists of three distinct and parallel ranges.
- The northern most range which extends towards China is known as the Greater Himalayas.
- The chain of mountains right in the middle is called Central Himalayas.
- The southern most range of mountains that extend towards the eastern part of India is called Shivalik Himalayas.
Division of Northern Mountain Ranges:
The northern mountain ranges can be divided into the following two categories:
A. Mountain ranges of Himalayas:
- The highest mountain of the world, Mt. Everest which is 8848 m, lies in the Himalayan range in Nepal.
- The highest peak of the Himalayas in India is the Mt. Godwin Austin which is 8611 m high.
- Other important mountains of the world which are located in Himalayas are Kanchenjunga (8598 m), Nandadevi (7817 m) and Badrinath (7138 m). All these mountains are located in India.
B. Mountainous region of Eastern Himalayas:
- The Himalayas in the eastern part of India are hilly. Hence, the mountains here are not very high.
- The main ranges in this region are Patkoi and Lushai.
- The important mountains located in the southern part of this region, ranging in east-west
direction are Garo, Khasi, Jaintia and Naga.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a short note on the Plains of North India.
Answer:
- The plains located in the south of the northern mountain ranges (Himalayas) of India are known as the Plains of North India.
- These plains cover a vast part of north India.
- These plains have been formed by the alluvium brought by the Himalayan Rivers.
- These plains are so huge and vast that they are one of the biggest plains of the world formed by the rivers.
- The Plains of North India are one of the most prosperous and thickly populated areas of India.
Question 6.
Write a note on the plateaus of India.
Answer:
- Just below the Plains of north India, in the southern direction, is the Central and Deccan Plateau „ of India.
- This plateau is in the shape of an inverted triangle.
- Since this plateau is surrounded by water on three sides, it is called a peninsula.
- This plateau is the oldest landmass of India. It is made up of hard rocks.
- The valleys of Narmada and Son rivers are located right in the middle of this plateau.
- These valleys divide the plateau into two parts.
- The northern part is called Malwa Plateau and the southern part is called Deccan Plateau.
- The soil of the Central and Deccan Plateau is black but it is not very fertile.
- However, many areas of this plateau yield good crops.
- This plateau is so rich in minerals that it is called the Treasury of Minerals’.
Question 7.
Write a note on the coastal plains of India.
Answer:
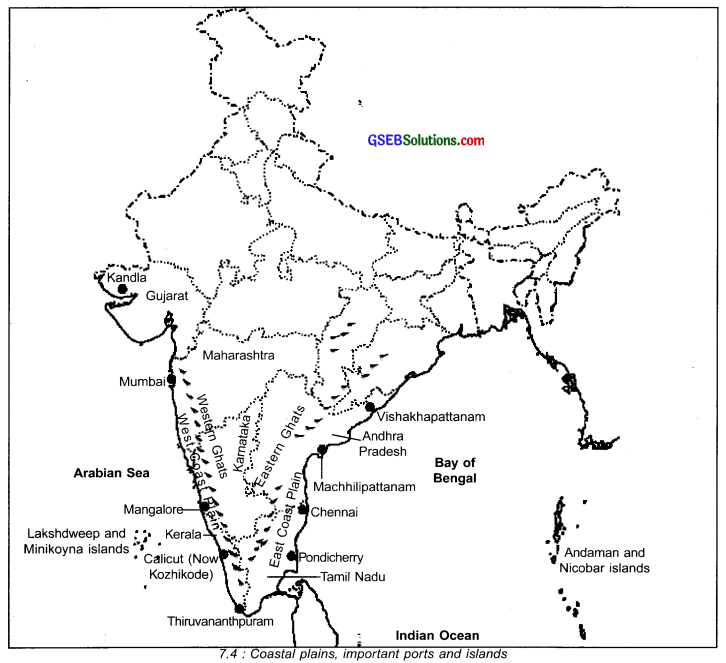
- The southern part of India is covered by sea from three sides.
- The coastline of India is approximately 7517 km. long.
- There are narrow plains located at the border of the southern coast.
- Thus, on one side of these coastal plains is the ocean and on the other side is the peninsular plateau.
Mainly, there are two coastal plains in the southern part of India:
A. East Coast Plain:
- The plains on the eastern coast of India are known as East Coast Plain.
- The important ports and cities in the East Coast Plain are Chennai, Pondicherry, Machhalipatnam and Vishakhapattanam.
- The East Coast Plain is known for its fishing industry.
B. West Coast Plain:
- The plains on the western coast of India are known as West Coast Plain.
- The important ports and cities in the West Coast Plain are Kandla, Mumbai, Mangalore, Calicut and Thiruvananthpuram.
- The West Coast Plain is also known for its rich black fertile soil. Also some regions of this coast have rich alluvium deposits. Hence, overally the West Coast Plain is fertile and yields good crop.
- The West Coast Plain is narrower than the East Coast Plain.
![]()
Question 8.
Write a note on the archipelagos of India.
Answer:
- A piece of land covered by water from all the sides is called archipelagos or island.
- The islands of India can be divided into two main parts, one located in the east and the other in the west.
- The Andaman and Nicobar islands are located in the east of India in the Bay of Bengal.
- The Lakshadweep and Minikoyna islands are located in the west of India in the Arabian Sea.
Question 9.
Write a note on the deserts of India.
Answer:
The two main deserts of India are as follows:
A. Desert of Rajasthan:
The desert of Rajasthan lies in the west of the Aravalli Mountains.
It is also called the Great Indian Desert or the Thar Desert.
I. Features of the desert:
- The land is sandy in desert region.
- The climate is dry, hot and barren.
- The temperature is unbearable.
- There is scanty rainfall, even lesser than 20 cm.
- Hence, there is scarcity of water.
- Even the basic goods necessary for sustaining life are not available in this region.
- The only trees that can be grown here are dates or cactus.
- Camels are used for transportation. .
- Due to all these issues, maximum part of the desert is sparsely (thinly) populated.
II. Bringing revolution in desert:
- The northern part of Rajasthan is provided irrigation facility from river Satluj through the Indira canal.
- This has changed the face of the desert region of Rajasthan. .
- This change has made the desert region greener by developing agriculture in Rajasthan.
B. Desert of Gujarat:
- The desert of Gujarat lies in the northern part of Gujarat.
- It is also called the Rann of Kachchh.
- The Rann of Kachchh is different from the desert of Rajasthan.
I. Features of the desert:
- The Rann of Kachchh is vast saline land.
- It is sandy. The sand here is white in colour.
- In the Rann of Kachchh, it seems as if the earth has been covered with a white sheet.
- This is the only white desert of the world.
The Rann of Kachchh can be divided into two parts: The Little Rann of Kachchh and the Great Rann of Kachchh.
Question 10.
Write a note on the Thar Desert. OR Give an idea of the desert of Rajasthan.
Answer:
A. Desert of Rajasthan:
The desert of Rajasthan lies in the west of the Aravalli Mountains.
It is also called the Great Indian Desert or the Thar Desert.
Question 11.
Write a note on the Rann of Kachchh.
Answer:
B. Desert of Gujarat:
- The desert of Gujarat lies in the northern part of Gujarat.
- It is also called the Rann of Kachchh.
- The Rann of Kachchh is different from the desert of Rajasthan.
Question 12.
Give an idea of the mountain ranges of Himalayas.
Answer:
Mountain ranges of Himalayas:
- The highest mountain of the world, Mt. Everest which is 8848 m, lies in the Himalayan range in Nepal.
- The highest peak of the Himalayas in India is the Mt. Godwin Austin which is 8611 m high.
- Other important mountains of the world which are located in Himalayas are Kanchenjunga (8598 m), Nandadevi (7817 m) and Badrinath (7138 m). All these mountains are located in India.
![]()
Question 13.
Write a note on the Himalayas of east India.
Answer:
Mountainous region of Eastern Himalayas:
- The Himalayas in the eastern part of India are hilly. Hence, the mountains here are not very high.
- The main ranges in this region are Patkoi and Lushai.
- The important mountains located in the southern part of this region, ranging in east-west
direction are Garo, Khasi, Jaintia and Naga.
Question 14.
Write a note on East Coast Plain.
Answer:
A. East Coast Plain:
- The plains on the eastern coast of India are known as East Coast Plain.
- The important ports and cities in the East Coast Plain are Chennai, Pondicherry, Machhalipatnam and Vishakhapattanam.
- The East Coast Plain is known for its fishing industry.
Question 15.
Write a note on West Coast Plain.
Answer:
B. West Coast Plain:
- The plains on the western coast of India are known as West Coast Plain.
- The important ports and cities in the West Coast Plain are Kandla, Mumbai, Mangalore, Calicut and Thiruvananthpuram.
- The West Coast Plain is also known for its rich black fertile soil. Also some regions of this coast have rich alluvium deposits. Hence, overally the West Coast Plain is fertile and yields good crop.
- The West Coast Plain is narrower than the East Coast Plain.
Question 16.
Which are the main islands of India?
Answer:
- A piece of land covered by water from all the sides is called archipelagos or island.
- The islands of India can be divided into two main parts, one located in the east and the other in the west.
- The Andaman and Nicobar islands are located in the east of India in the Bay of Bengal.
- The Lakshadweep and Minikoyna islands are located in the west of India in the Arabian Sea.
Question 17.
Write a note on Mt. Godwin Austin.
Answer:
- The highest peak of Himalayas in India is the Mt. Godwin Austin.
- It is the second highest mountain in the world.
- It lies in the Karakoram Range of the Himalayas.
- It is 8611 m high.
![]()
Answer in One or Two Sentence
Note : Here, answers are given in short for memorizing easily. Students must write full sentences.
Question 1.
What is the exact geographical location of India?
Answer:
Between 8.4°N to 37.6°N latitudes and 68.7°E to 97.25°E longitudes.
Question 2.
Which are the extreme corners of India in each direction?
Answer:
Kashmir state in north, Kanyakumari in south, Arunachal Pradesh state in east, Dwarka in west.
Question 3.
What is the shape of India?
Answer:
Narrow in north and south, broad in the middle.
Question 4.
What is physiography?
Answer:
The study of physical features of earth’s surface is called ……..
Question 5.
What kind of variations do we see in India?
Answer:
Mountain ranges, large plains, deserts, huge coastal areas, plateaus and highlands, archipelagos, etc.
Question 6.
Why are the Himalayas called chain of mountains?
Answer:
Because the Himalayas is not a single mountain but a chain of three distinct and parallel ranges.
![]()
Question 7.
Which are the three ranges of the Himalayas?
Answer:
A. Greater Himalayas – The northern most range of Himalayas towards China, B. Central Himalayas – The range that lies in the middle of Greater Himalayas and Shivalik range C. Shivalik Range – The north eastern most range of Himalayas towards east India.
Question 8.
List out the important Himalayan peaks of India with their height.
Answer:
A. Mt. Godwin Austin – 8611 m, B. Kanchenjunga – 8598 m, C. Badrinath – 7138 m, D. Nandadevi – 7817 m
Question 9.
Which are the important ranges and peaks in the Eastern Himalayas?
Answer:
Patkoi and Lushai ranges; Garo, Khasi, Jaintia and Naga peaks.
Question 10.
Which is the most distinct feature of the Eastern Himalayas?
Answer:
The mountains are hilly; So they are not very high.
Question 11.
Why are the plains of North India very prosperous?
Answer:
Due to the fertile lands which have developed agriculture and agro-based industries on large scale.
Question 12.
Which rivers flow from Himalayas?
Answer:
Sindhu, Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, Satluj, Indus, Ganga, Yamuna, Gomti, Ghaghra, Gandak, Kosi, Brahmaputra, Tista, etc.
![]()
Question 13.
Which are the main lakes of India?
Answer:
Sambhar, Wular, Nainital, Bhimtaal, Chilka, Koleru, Pulicat, Dal, etc.
Question 14.
Which are the two parts of the Central and Deccan Plateau?
Answer:
The northern part called Malwa Plateau and the southern part called Deccan Plateau.
Question 15.
What divides the Central and Deccan Plateau into two?
Answer:
The valley of Narmada and Son rivers.
Question 16.
Where are the coastal plains located?
Answer:
On the coastal borders of southern part of India.
Question 17.
Which are the famous ports of East Coast Plain?
Answer:
Chennai, Pondicherry, Machhalipattanam and Vishakhapattanam.
Question 18.
Which coastal plain is narrow?
Answer:
The West Coast Plain is narrower than the East Coast Plain.
![]()
Question 19.
Why is West Coast Plain fertile?
Answer:
Because it has rich alluvium deposits and fertile black soil.
Question 20.
Which are the famous ports of West Coast Plain?
Answer:
Kandla, Mumbai, Mangalore, Calicut and Thiruvananthapuram.
Question 21.
Which islands are in west India?
Answer:
Lakshadweep and Minikoyna
Question 22.
Where are the Andaman and Nicobar islands located?
Answer:
In the east of India in Bay of Bengal.
Question 23.
What are usually seen in deserts?
Answer:
Date trees and camel caravans.
Question 24.
Why has north Rajasthan turned green?
Answer:
Due to the irrigation facility from Satluj River through Indira Canal.
![]()
Question 25.
What is the most unique feature of the Rann of Kachchh?
Answer:
The desert is covered with white sand.
Question 26.
How is the land of the Rann of Kachchh?
Answer:
Saline and white in colour.
Question 27.
Which are the two parts of the Rann of Kachchh?
Answer:
A. Little Rann of Kachchh, B. Great Rann of Kachchh.
Question 28.
How is the weather in desert?
Answer:
Dry and extremely hot.
Question 29.
Why are deserts sparsely populated?
Answer:
A. Scarcity of water, B. Unavailability of basic goods.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
India lies between ………………. °N to ………………… °N latitudes.
(A) 8.4, 37.6
(B) 9.8, 36.7
(C) 8.4, 36.7
(D) 9.8, 37.6
Answer:
(A) 8.4, 37.6
Question 2.
India lies in the continent of ………………….
(A) Africa
(B) Australia
(C) Asia
(D) Europe
Answer:
(C) Asia
![]()
Question 3.
………………. is in the east of India.
(A) Indian Ocean
(B) Bay of Bengal
(C) Arabian Sea
(D) Gulf of Kachchh
Answer:
(B) Bay of Bengal
Question 4.
The Indian Ocean is in the ………………… of India.
(A) East
(B) West
(C) North
(D) South
Answer:
(D) South
Question 5.
……………… is in the north-west of India.
(A) Sri Lanka
(B) China
(C) Bangladesh
(D) Pakistan
Answer:
(D) Pakistan
Question 6.
Which state Is in the most northern part of India?
(A) Jammu and Kashmir
(B) Himachal Pradesh
(C) Uttarakhand
(D) Haryana
Answer:
(A) Jammu and Kashmir
Question 7.
The southernmost point of India is ……………….. .
(A) Thirucherrapalli
(B) Thiruvananthpuram
(C) Munnar
(D) Kanyakumari
Answer:
(D) Kanyakumari
Question 8.
What is the north-south distance of India?
(A) 3214 km
(B) 2933 km
(C) 3120 km
(D) 2812 km
Answer:
(A) 3214 km
Question 9.
Which state ¡s the eastern most corner of India?
(A) Assam
(B) Meghalaya
(C) Arunchal Pradesh
(D) Sikkim
Answer:
(C) Arunchal Pradesh
![]()
Question 10.
…………………… is in the extreme western corner of India.
(A) Wanakbori
(B) Khedbrahma
(C) Dwarka
(D) Mundra
Answer:
(C) Dwarka
Question 11.
The east-west distance of India is ………………. km.
(A) 3214
(B) 2933
(C) 3120
(D) 2812
Answer:
(B) 2933
Question 12.
India is the ………………….. th largest country of the world in terms of area.
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 7
Answer:
(D) 7
Question 13.
India is broad in the ……………….. .
(A) North
(B) Middle
(C) South
(D) None of these
Answer:
(B) Middle
Question 14.
There are ………………. states in India.
(A) 27
(B) 28
(C) 29
(D) 30
Answer:
(B) 28
Question 15.
There are ……………….. union territories in India.
(A) 5
(B) 6
(C) 7
(D) 8
Answer:
(C) 7
Question 16.
The highest mountain range of the world is ……………….. .
(A) Aravalli
(B) Western Ghats
(C) Eastern Ghats
(D) Himalayas
Answer:
(D) Himalayas
![]()
Question 17.
There are ………………. ranges in the Himalayas.
(A) 2
(B) 3
(C) 4
(D) 5
Answer:
(B) 3
Question 18.
The northern most range of mountains towards China is cafled ………………… Himalayas.
(A) Higher
(B) Central
(C) Lower
(D) Greater
Answer:
(D) Greater
Question 19.
Which is the highest peak in world?
(A) Kanchenjunga
(B) Nandadevi
(C) Mt. Everest
(D) Mt. Godwin Austin
Answer:
(C) Mt. Everest
Question 20.
Which is the highest peak in India?
(A) Kanchenjunga
(B) Nandadevi
(C) Mt. Godwin Austin
(D) Mt. Everest
Answer:
(C) Mt. Godwin Austin
Question 21.
Mt. Everest is located in ……………….. .
(A) Himachal Pradesh
(B) Kashmir
(C) Sikkim
(D) Nepal
Answer:
(D) Nepal
Question 22.
What is the height of Mt. Everest?
(A) 8488 m
(B) 8884 m
(C) 8848 m
(D) 8484 m
Answer:
(C) 8848 m
![]()
Question 23.
What are Garo, Khansi and Jaintia?
(A) Important peaks of Eastern Himalayas
(B) Important lakes in the Himalayas
(C) Some of the highest peaks of India
(D) Important peaks of the Karakoram Range
Answer:
(A) Important peaks of Eastern Himalayas
Question 24.
What Is the height of the highest mountain of India?
(A) 8611 m
(B) 8616m
(C) 8166m
(D) 8116m
Answer:
(A) 8611 m
Question 25.
The Central and Deccan Plateau is in the …………………. direction of the plains of North India.
(A) East
(B) West
(C) North
(D) South
Answer:
(D) South
Question 26.
What is the shape of the Central and Deccan Plateau?
(A) Triangular
(B) Oblongular
(C) Inverted triangle
(D) Both B and C
Answer:
(C) Inverted triangle
Question 27.
The northern part of the Central and Deccan Plateau is called ………………. Plateau.
(A) Malabar
(B) Malwa
(C) Coromandal
(D) Deccan
Answer:
(B) Malwa
Question 28.
The Central and Deccan Plateau is a treasure house of ……………… .
(A) Minerals
(B) Sea food creatures
(C) Timber
(D) Ayurvedic herbs
Answer:
(A) Minerals
![]()
Question 29.
What is the colour of the soil of Central and Deccan Plateau?
(A) Brown
(B) Red
(C) Black
(D) Yellowish
Answer:
(C) Black
Question 30.
The coastline of India is approximately ………………. km long.
(A) 5717
(B) 7517
(C) 5177
(D) 7715
Answer:
(B) 7517
Question 31.
The West Coast Plain is famous for its …………… .
(A) Ports
(B) Fishing industry
(C) Transportation industry
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 32.
Which of these ports is on the East Coast Plain?
(A) Mangalore
(B) Calicut
(C) Machhalipattanam
(D) Thiruvananthapuram
Answer:
(C) Machhalipattanam
Question 33.
Lakshadweep islands are in the ………………… .
(A) Arabian Sea
(B) Bay of Bengal
(C) Indian Ocean
(D) Pacific Ocean
Answer:
(A) Arabian Sea
Question 34.
Where is the desert region of Rajasthan?
(A) In the east of the plains of North India
(B) On the west of Aravalli Mountains
(C) In the south of the East Coast Plain
(D) In the north of the Patkoi and Lushai Hills
Answer:
(B) On the west of Aravalli Mountains
![]()
Question 35.
The land in desert is …………….. .
(A) Lumpy
(B) Sandy
(C) Muddy
(D) Marshy
Answer:
(B) Sandy
Question 36.
Which trees mostly grow in deserts?
(A) Date
(B) Oak
(C) Pine
(D) All of these
Answer:
(A) Date
Question 37.
North Rajasthan is irrigated by ………………. river.
(A) Ganga
(B) Godavari
(C) Son
(D) Satluj
Answer:
(D) Satluj
Question 38.
The Rann of Kachchh is in ……………….. .
(A) Gujarat
(B) Rajasthan
(C) Madhya Pradesh
(D) Both A and B
Answer:
(A) Gujarat
Question 39.
The Rann of Kachchh is the only desert in Gujarat with ………………… coloured sand.
(A) Yellow
(B) Light brown
(C) White
(D) Black
Answer:
(C) White
Question 40.
Which island is located in the Bay of Bengal?
(A) Sri Lanka
(B) Lakshadweep
(C) Minikoyna
(D) Andaman and Nicobar
Answer:
(D) Andaman and Nicobar
![]()
Fill in the Blanks
1. The ………………. (water body) is located in the west of India.
Answer:
Arabian Sea
2. The total land area of India is ……………… sq. km.
Answer:
32,87,263
3. The shape of India is …………….. in the north.
Answer:
Narrow
4. Study of variations in land forms is called ………………. .
Answer:
Physiography
5. There are ……………….. physiographic divisions of India.
Answer:
Five
6. Himalayas are a chain of ……………….. distinct mountain ranges.
Answer:
Three
![]()
7. The range of Himalayas that lies towards east India is called ……………… range.
Answer:
Shivalik
8. Mt. Godwin Austin lies in the ……………….. range.
Answer:
Karakoram
9. Badrinath is ………………. meters high.
Answer:
7138
10. The two important ranges of the Eastern Himalayas are ……………… and …………………
Answer:
Patkoi, Lushai
11. The Plains of North India are formed by the ………………….. brought by Himalayan River.
Answer:
Alluvium
12. ………………. is the oldest landmass of India.
Answer:
Central and Deccan Plateau
![]()
13. The Central and Deccan Plateau is made up of ……………….. .
Answer:
Hard rocks
14. The valleys of ………………. and ……………… rivers divide the Central and Deccan Plateau into two parts.
Answer:
Narmada, Son
15. A piece of land covered by water from three sides is called ………………….. .
Answer:
Pennisula
16. East Coast Plain is mainly known for its ………………. industry.
Answer:
Fishing
17. A piece of land covered by water from all four sides is called ……………….. .
Answer:
Archipelagos (Island)
18. The rainfall is less than …………………. cm in desert.
Answer:
20
![]()
19. ………………. animal is used in deserts.
Answer:
Camel
20. ……………. canal provides irrigation facility to north Rajasthan.
Answer:
lndira
True or False
1. Nandadevi peak is 7871 m high.
Answer:
False
2. The plains of north India are highly populated.
Answer:
True
3. Betwa is a famous lake of India.
Answer:
False
4. Machhalipattanam and Thiruvananthapuram are located on the East Coast Plain.
Answer:
False
5. Minikoyna Islands are in Bay of Bengal.
Answer:
False