Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Algebraic Expressions InText Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Algebraic Expressions InText Questions
![]()
Try These (Page 230)
Question 1.
Describe expressions are obtained:
(i) 7xy + 5
(ii) x²y
(iii) 4x² – 5x
Solution:
(i) 7xy + 5
To obtain this expression, we first multiply two variables x and y, i.e. x × y = xy.
Then we multiply their product by 7 to get 7xy.
Next, we add 5 to 7xy to obtain 7xy + 5.
(ii) x²y
First, x is multiplied by itself i.e., x × x = x²
Then multiply x² by y to get the required expression, i.e. x² × y = x²y
(iii) 4x² – 5x
Here, the variable x is multiplied by itself, i.e. x × x = x²
Then x² is multiplied by 4, i.e. x² x 4 = 4x²
Next, we multiply the variable x by 5, i.e. x × 5 = 5x
Now, we subtract 5x from 4x² to get 4x² – 5x
![]()
Try These (Page 231)
Question 1.
What are the terms in the following expressions? Show how the terms are formed. Draw a tree diagram for each expression:
(i) 8y + 3x²
(ii) 7mn – 4
(iii) 2x²y
Solution:
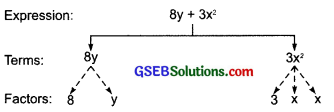
(i) 8y + 3x²
Terms of 8y + 3x² are 8y and 3x²
The term 8y is formed by multiplying the variable y by 8.
The term 3x² is formed by first multiplying the variable x with itself to get x × x = x² and then multiplying x² by 3.
Tree diagram:
(ii) 7mn
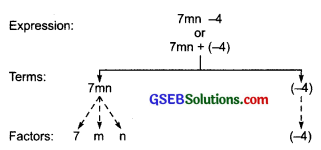
Terms of 7mn – 4 are 7mn and – 4.
The term 7mn formed by first multiplying variables m and n to get m x n = mn
Then multiplying mn by constant 7 to get 7 x mn = 7mn. The term – 4 is a constant.
Tree diagram:
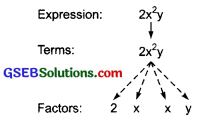
(iii) 2x²y
This expression has only one term, i.e. 2x²y. To form this term first we multiply the variable x by itself to get x × x = x².
Then the variable y is multiplied by x² to get y × x² = x²y
Next, the product x1y is multiplied by 2 to get 2 × x²y = 2x²y
Tree diagram:
Question 2.
Write tree expressions each having 4 terms.
Solution:
(i) 2x3 – 4x² + 9xy + 8
(ii) 6x3 + 9y² – 3xy² – 12
(iii) 9x² – 3x + 12xy – 1
![]()
Try These (Page 231)
Question 1.
Identify the coefficients of the terms of following expressions:
(i) 4x – 3y
(ii) a + b + 5
(iii) 2y + 5
(iv) 2xy
Solution:
(i) 4x – 3y
The coefficient of x in 4x is 4.
The coefficient of y in – 3y is (- 3).
(ii) a + b + 5
The coefficient of a is 1.
The coefficient of b is 1.
The coefficient of 5 is 1.
(iii) 2y + 5
The coefficient of y in 2y is 2.
The coefficient of 5 is 1.
(iv) 2xy
The coefficient of xy in 2xy is 2.
The coefficient of y in 2xy is 2x.
The coefficient of y in 2xy is 2y.
Try These (Page 233)
Question 1.
Group the like terms together from the following:
12x, 12, -25x, -25, -25y, 1, x, 12y, y
Solution:
We have:
(i) 12x, -25x and x are like terms.
(ii) – 25y, 12y and y are like terms.
(iii) 12, – 25 and 1 are like terms.
![]()
Try These (Page 233)
Question 1.
Classify the following expressions as a monomial, a binomial or a trinomial: a, a + b, ab + a + b, ab + a + b – 5, xy, xy + 5, 5x² – x + 2, 4pq – 3q + 5p, 7, 4m – 7n + 10, 4mn + 7.
Solution:
(i) a is containing 1 term. It is a monomial.
(ii) a + b is containing 2 terms. It is a binomial.
(iii) ab + a + b is containing 3 terms. It is a trinomial.
(iv) ab + a + b – 5 is containing 4 terms. It is a polynomial.
(v) xy is containing only 1 term. It is a monomial.
(vi) xy + 5 is containing 2 terms. It is a binomial.
(vii) 5x² – x + 2 is containing 3 terms. It is a trinomial.
(viii) 4pq – 3q + 5p is containing 3 terms. It is a trinomial.
(ix) 7 is containing only 1 term. It is a monomial.
(x) 4m – In + 10 is containing 3 terms. It is a trinomial.
(xi) 4mn + 7 is containing 2 terms. It is a binomial.
Try These (Page 236)
Question 1.
Think of at least two situations in which you need to form two algebraic expressions and add or subtract them.
Solution:
Situation – I
Rohan’s per month earning is twice the per month earnings of Vibha. Kavita’s per month earnings is ₹ 400 more than the sum of Rohan’s and Vibha’s per month earnings. What is the monthly earning of Kavita?
Situation – II
Mahesh has twice the number of toys Kanta has: Lata has 5 toys more than twice the number of toys Mahesh and Kanta together have. What is the number of toys that Kanta has?
![]()
Try These (Page 238)
Question 1.
Add and subtract:
(i) m – n, m + n
(ii) mn + 5 – 2, mn + 3
Solution:
(i) Adding (m – n) and (m + n), we have:
(m – n) + (m + n) = m – n + m + n
Collecting like terms, we have:
(m + m) + (-n + n) = (1 + 1)m + (-1 + 1)n
= 2 m + (0)n
= 2m
Now subtracting (m – n) from (m + n), we have:
= (m + n) – (m – n)
= m + n – m + n
= (m – m) + (n + n)
= (1 – 1 )m + (1 + 1)n
= 0m + 2n
= 2 n
(ii) Adding mn + 5 – 2 and mn + 3, we have:
(mn + 5 – 2) + (mn + 3)
= mn + 5 – 2 + mn + 3
= (mn + mn) + (5 – 2 + 3)
= (1 + 1 )mn + (6)
= 2mn + 6
Now, subtracting (mn + 3) from (mn + 5 – 2), we have:
(mn + 5 – 2) – (mn + 3)
= mn + 5 – 2 – mn – 3
= (mn – mn) + (5 – 2 – 3)
= (0)mn + 0 = 0 + 0 = 0
![]()
Try These (Page 245)
Question 1.

(The number of segments required to make the figure is given to the right. Also, the expression for the number of segments required to make n shapes is also given).
Solution:
Do these yourself.