This GSEB Class 12 Commerce Accounts Notes Part 2 Chapter 6 Cash Flow Statement covers all the important topics and concepts as mentioned in the chapter.
Cash Flow Statement Class 12 GSEB Notes
In financial accounts, besides profit and loss statement and balance Sheet, cash flow statement is also included. Amongst all assets of business, cash is the most liquid asset. The investment of cash is very essential creation of reward and earnings. It is necessary to keep cash on hand to pay easily the debt of the business unit in time. What are the sources of cash ? Where cash is invested ? This information is available from cash flow statement. In this chapter we will study about cash flow activities and cash flow arising from it and preparation of cash flow statement.
Cash Flow:
Cash Flow means receipt-payment of cash and cash equivalent. There are two types of cash flows :
- Cash inflow
- Cash outflow.
Cash Flow Statement:
The statement showing balance of cash and cash equivalent and cash inflow and cash outflow of different activities of a business unit during the year.
![]()
Classification of Cash Flow Activities:
In cash flow statement, activities of specific period are classified into three categories.
Operating Activities and Cash Flow from Operating Activities:
Operating activities means main activities of business to earn income, which are neither investing activities nor financing activities. These are those activities on the basis of which main income of the business is created. Cash flow emerging from operating activities means cash flow from day to day transactions of business unit. Calculation of cash flow arising from operation activities is depends upon (i) Profit allocation and (ii) Changes in Current Assets and Current Liabilities (working capital).
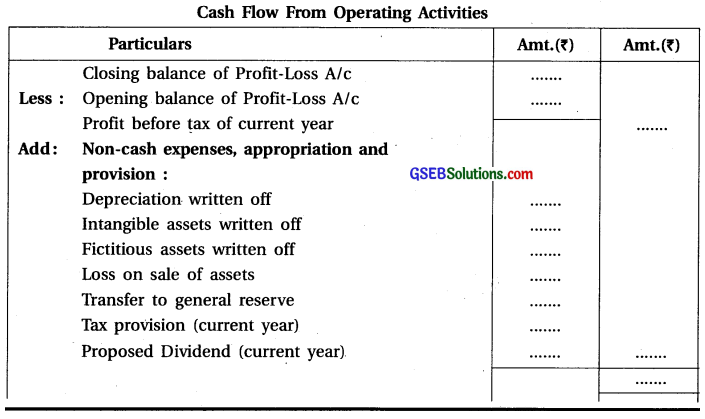
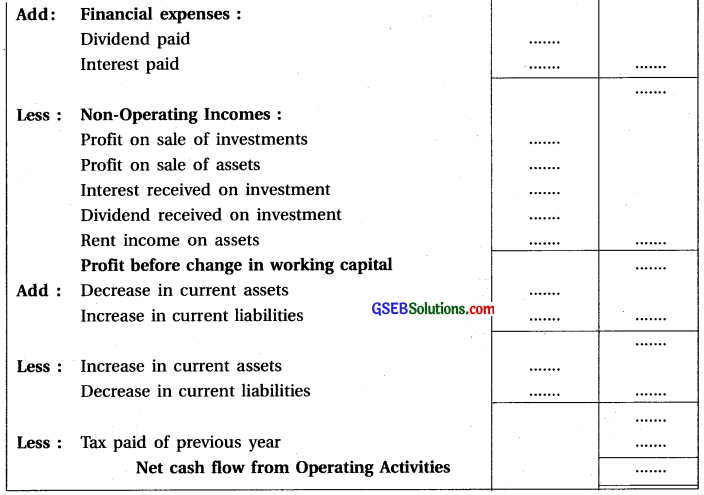
Investing Activites and Cash Flow from Investing Activities:
Investing activities means purchase sale of long-term investments and other investments. Cash flow arising from investing activities means cash flow from purchase sale of long-term investment and other investments of business unit. Calculation of cash flow from investing activities is depends upon (i) Activities of assets side of balance sheet and (ii) Non-operating income of profit and loss statement.
Cash Flow From Investing Activities
| Particulars | Amt (₹) |
| Sale of Fixed Tangible & Intangible Assets | ……….. |
| Sale of Non-current Investments | ……….. |
| Return of long-term lending | ……….. |
| Interest received on Investment | ……….. |
| Dividend received on Investment | ……….. |
| Rent received on rented assets | ……….. |
| Purchase of Fixed Tangible & Intangible Assets | (………..) |
| Purchase of Non-current Investment | (………..) |
| Capitalised expenses | (………..) |
| Self constructed assets | (………..) |
| Long-term lending | (………..) |
| Net cash flow from Investing Activities | (………..) |
Financing Activities and Cash Flow from Financing Activities:
Financing activities means changes in owner’s capital and borrowed capital of business. Financing activities have relation with increase or decrease of equity share capital, preference share capital, debenture, loan ect. It means that the increase in long-term owner’s capital and borrowed capital shows cash inflow and their reduction shows cash outflow of financing activities. Calculation of cash flow of financing activities is depends upon
- Capital and Liability side of balance sheet and
- Appropriation of profit of profit of loss statement.
Cash Flow From Financing Activities
| Particulars | Amt (₹) |
| Issue of Equity/Preference share | ………. |
| Issue of Debentures | ………. |
| Procurement of loan and creation of long term liabilities | ………. |
| Increase in bank overdraft | ………. |
| Buy back of equity shares | (………..) |
| Redemption of preference shares | (………..) |
| Redemption of debentures | (………..) |
| Reduction in bank overdraft | (………..) |
| Redemption of loan or any other long-term liabilities | (………..) |
| Dividend paid on equity/preference share capital | (………..) |
| Interest paid on debt or bank loan | (………..) |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities | ……….. |
![]()
Closing Cash and Cash Equivalent:
Mainly their types of activities :
- Operating activities
- Investing activities and
- Financing activities are shown in cash flow statement. Adding opening cash or cash equivalent in total of cash flow arising from these three activities we get closing cash or cash equivalent.
Following points to be remember while preparing cash flow statement.
1. Under section-2(40) of Companies Act, 2013, the cash flow statement is included in the definition of financial statements.
2. As per accounting standard-3 discloure of cash flow statement is mandatory from 1-4-2004 and onwards for certain business enterprises.
3. The indentification of operating activities of each business is based on the nature of business.
4. Salary, wages, bonus to employees, employees welfare expenses are always included in operating activities.
5. Purchase of non-current assets like purchase of machine, purchase of furniture etc. are always included in investing activities.
6. Dividend paid on share capital is a transaction linked with capital, so it is considered as financing activity.
7. In the payment of hire purchase instalment method, payment of principle is known as investing activity and payment of interest is known as financing activity.
8. In any cash deposit or withdraw from bank is known as cash transaction. It is not considered as cash flow.
9. There is inverse relation between current asset and cash and cash equivalent. If current assets increases then cash and cash equivalent decreases and if current assets decreases then cash and cash equivalent increases. There is direct relation between current liabilities and cash and cash equivalent. If current liabilities increases then cash and cash equivalent increases and if current liabilities decreases then cash and cash equivalent decreases.
10. At the time of calculation of cash flow from investing activities if the amount of depreciation, profit on sale of assets, loss on sale of assets, selling price of assets, purchase price of assets is not given in question then find out that amount by preparing respective assets account.
11. The following transactions show changes in size/composition of owners capital and borrowed capital of business entity. Still these are not considered as cash flow from financing activities.
- Increase in equity share capital due to issue of bonus share
- There is conversion of debenture into share.
12. When issue of equity share/debenture is done of premium, the amount of premium is considered as cash inflow of financing activities.
13. Underwriting commission paid at the time of issue of share or debentures is financing activity and is shown as cash outflow of financing activity.
| Type of → Activity | Operating Activity | Investing Activity | Financing Activity |
| ↓ Cash Flow | |||
| Cash Inflow | (1) Commission received (2) Brokerage received (3) Bills receivable, Collection from debtors (4) Refund of income tax |
(1) Sale of tangible and intangible noncurrent assets (2) Sale of non-current investment (3) Return of long term lending (4) Interest-dividend received on investment (5) Rent income of assets |
(1) Issue of equity/ preference share (2) Issue of debentures (3) Long-term loan from bank (4) Increase in bank overdraft and cash credit (5) Increase in long term liabilities |
| Cash
Outflow |
(1) Purchase of raw-material (2) Factory exepenses (3) Selling-distributions expenses (4) Office or administrative expenses (5) Wages, salary, rent, bonus (6) Employees welfare expenses (7) Payment of creditors and bills payable (8) Income tax paid (9) Royalty paid (10) Purchase expenses |
(1) Purchase of tangible and intangible non-current assets (2) Purchase of noncurrent investment (3) Self-constructed assets (4) Long-term lending (5) capitalised expenses |
(1) Redemption of debentures and preference shares (2) Buy back of equity shares (3) Redemption of loan or any other long-term liabilities (4) Dividend paid on equity/preference share capital (5) Reduction in long-term liabilities and bank over-drraft (6) Interest paid on debt (7) Interest paid on debenture (8) Interim dividend |