Gujarat Board GSEB Class 12 Commerce Economics Important Questions Chapter 10 Industrial Sector Important Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 12 Economics Important Questions Chapter 10 Industrial Sector
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the major sectors of production world over.
Answer:
Agriculture sector, industry sector and service sector.
![]()
Question 2.
List down few developed nation having industrial economies.
Answer:
America, Britain and Japan.
Question 3.
List down developed nations having agriculture as their main occupation.
Answer:
Australia and New Zealand
Question 4.
Why is industrialization necessary?
Answer:
Industrialization helps to attain fastest economic development by developing agriculture sector, increasing employment opportunities, assisting in optimum utilization of internal resources, increasing overall income and Improving living standards of people.
Question 5.
What is the contribution of industrial sector in India’s national income since 1951?
Answer:
In the year 1951, industrial sector had contributed of 16.6% in national income, which rose to 27% (at constant prices) in the year 2013-14.
Question 6.
Why is it important to export industrial products made in India?
Answer:
The industrial sector builds excess products which can be exported to other countries. This helps India to earn foreign, exchange which in turn is very useful to import scarce products of the economy.
Question 7.
How does industrialization help to attain balanced economic development?
Answer:
Industrialization helps equal development of all the sectors of economy, Industrialization also creates employment opportunities and high standard of living of people in urban as well as rural areas. Hence…
Question 8.
How does industrialization lead to modernization of agriculture?
Answer:
Industries provide latest technology that help in increasing productivity of land and labour. This leads to development of agriculture sector. For example, tractor, thresher, chemical based fertilizer, etc. are the industrial products of modern technology that have modernized agriculture. Hence, …
Question 9.
Give three names of industrial products used as instruments of safety by Indian government?
Answer:
Rifles, bullets and tanks.
Question 10.
List the types of industries on basis of investment.
Answer:
- Cottage industry,
- Tiny industry,
- Small scale industry,
- Medium scale industry, and
- Large scale industry.
![]()
Question 11.
List the types of industries on basis of ownership.
Answer:
- Public sector units,
- Private sector industries
- Joint sector industries
- Cooperative sector industries
Question 12.
List the types of industries on basis of products.
Answer:
- Consumer goods industries and
- Intermediate goods industries
Question 13.
What is cottage industry?
Answer:
An industry run only by the family members using simple tools and with negligible use of electricity and investment is called cottage industry. E.g. Industries producing khadi cloth, papad, khakhra, incense sticks, etc.
Question 14.
What are tiny industries?
Answer:
Industries which run on labour intensive production technique along with the investment limit up to Rs. 25 lakhs are known as tiny industries. E.g. Industries producing artistic products made from metal, leather and clay.
Question 15.
What are small scale industries?
Answer:
Industries that run on labour intensive production technique and with an investment of Rs. 25 lakhs to Rs. 5 crore are called small scale industries (SSI). E.g. Industries producing tools and simple consumer goods like bread and biscuits, furniture, garments, etc.
Question 16.
What are large scale industries?
Answer:
Industries that run on capital intensive production technique and with an investment of more than Rs. 10 crores are known as large scale industries. E.g. Industries producing railway coaches and engines, big vehicles, iron and steel, petroleum, etc.
Question 17.
What are public sector units?
Answer:
Industries which are owned and managed by the government or say the industries that have ownership and administration of government are known as Public Sector Units (PSUs). E.g. Railways, Telecommunication, Post, Insurance, etc
Question 18.
What are departmental industries?
Answer:
Departmental industries are a type of public sector units. These industries are run, financed and managed by government departments i.e. the expenditure and income budget is decided by the government. E.g. Railways, post and telegraph, radio and television broadcasting, etc
![]()
Question 19.
What are government companies?
Answer:
A company owned by central and/or state government is called a government company. It operates as per the Company Law, 2013. Either whole of the capital or majority of the shares are owned by the government. E.g. Hindustan Machine Tools, Oil and Natural Gas Limited, Indian Oil Corporation, etc
Question 20.
Explain private sector industries.
Answer:
Industrial units owned and run by private sector or say private owners are known as private sector industries. E.g. Units manufacturing car, TV, shoes, etc.
Question 21.
What are joint sector industries?
Answer:
Industries owned jointly by the government and the private individuals who have contributed in the capital and managed by private individuals are called joint sector industries. E.g. Gujarat State Petroleum Corporation (GSPC).
Question 22.
What are cooperative sector industries?
Answer:
Industries that run on co-operative basis with an aim to stop exploitation of small (marginal) owners, to stop exploitation of labourers or to stop exploitation of consumers and to provide benefit to all are known as industries of co-operative sector. E.g. Amul, IFFCO, KRIBHCO, etc.
Question 23.
Define consumer goods industries.
Answer:
Industries that produce goods used directly by the consumers are called consumer goods industries. E.g. Industries producing ghee, oil, cosmetics such as soaps and shampoo, etc
Question 24.
What are intermediate goods industries?
Answer:
Industries producing semi-finished goods that are not consumed directly by the consumers but are sent to other industries for further processes are called intermediate goods industries. E.g. Industries producing yarn, steel sheets, machines, etc
Question 25.
State the two measures taken by government for industrial development
Answer:
(a) Government has introduced import tariff i.e. high tax on the imports of foreign products to safeguard local products,
(b) Government provides various types of technical and professional training to domestic industries
Question 26.
Why are state owned enterprises?
Answer:
For the economic development to take place, certain industries like iron and steel plants, insurance etc. play very important role. But the investment is very high in these industries which forces the government to set up such industries. These industries are known as state owned enterprise and help the growth of the economy.
Question 27.
Mention the ways the government promotes private sector industries.
Answer:
Government promotes private sector industries by providing land at concessional rate, providing electricity, water, tax benefits and finance at lower rates.
Question 28.
Define import tariff.
Answer:
The rate of import duty (tax) charged for importing the goods is called the import tariff.
![]()
Question 29.
Why does the government charge import tariff on foreign goods imported to India?
Answer:
The government charges high import duty on foreign goods to save the local companies from foreign companies. Doing so makes imported items costlier than the local made. As a result, the local industries can survive properly.
Question 30.
Why is it important for the government to provide technical skills and trainings to domestic companies?
Answer:
Technical skills and trainings are important for survival of the domestic companies in India especially after liberalization and globalization. These skills and trainings help to improve the local products so that they can compete with foreign products in the market which in turn benefits our economic growth.
Question 31.
Why does government provide economic help to domestic companies?
Answer:
Economic help provided by the government helps the domestic companies to reduce their production cost and sell their products in international market at competitive prices. This benefits domestic products to increase the demand/market share in the international market.
Question 32.
What are some of the basic facilities provided by the government, to industries?
Answer:
Basic facilities provided by the government are roads, water, electricity, banks, insurance, sewage, etc.
Question 33.
Why does the government provide basic facilities to the industries?
Answer:
Government provides basic facilities like road, water, electricity, banks, insurance, sewage and many more to develop industries. By availing these basic facilities industries can save their money, time and efforts and produce and sell products faster and more efficiently.
Question 34.
List the institutes created by the government to provide financial help to the industries.
Answer:
IDBI, SIDBI, ICICI, IFCI, LIC, GIC, etc.
Question 35.
What does the government do so that industries does not have to face unfair competition?
Answer:
Government drafts laws like Industries Act, Company Act, Competition Act, etc. to prevent unfair competition.
Question 36.
List some of the policies set by the government to help industries develop at a faster rate.
Answer:
Import policy, export policy, monetary policy, fiscal policy, tax policy, etc.
Question 37.
What are special economic zones?
Answer:
A Special Economic Zone (SEZ) is an area in which business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. It is created to increase trade, increase investment, job creation, provide tax benefits and for effective administration.
Question 38.
What is the main objective of special economic zone?
Answer:
The main objective of setting up SEZ in India was to attract foreign investment and to develop free environment for exports.
Question 39.
List five countries who utilize special economic zones for better growth of the economy?
Answer:
China, India, Jordan, Poland, Philippines, Russia and North Korea.
Question 40.
Who can start special economic zones and who controls them?
Answer:
Any individual, government, private and public sector jointly, state government or their representative body may start special economic zone. Even foreign institution can start special economic zone. All special economic zones are ultimately controlled by government.
![]()
Question 41.
List the importance of small scale industries.
Answer:
Small scale industries are very useful for generating employment, giving platform for manufacturing with small capital, industrialization in rural areas, developing backward areas, reducing regional imbalance and to maintain the adequate distribution of national income and wealth.
Question 42.
Small scale industries are blessing to the nation’. Explain.
Answer:
Small scale industries are primarily labour intensive industries and have huge potential for generating employment. This continuous employment generation helps reduce poverty, improve standard of living,
and increase income. Hence
Question 43.
How does a small scale industry complement large scale industry?
Answer:
Small scale industries produce goods for the people. To produce these goods, these industries require machineries which are made by large scale industries. So, more the small scale industries, more utilization of machineries, more production of these machineries by large scale industries. Hence
Question 44.
How have the small scale industries grown in terms of exports?
Answer:
Small scale industries of India had exported goods and services worth Rs. 29,068 crores in 1994-95. It reached to Rs. 71,244 crores in the years 2001-02 and it rose to Rs. 1,77,600 in the year 2006-07.
Question 45.
Why is labour intensive production technique more beneficial for India?
Answer:
Labour intensive production technique is used by small scale industries where more labour is utilized instead of capital for production. In India, availability of labour is in excess. Thus, this technique helps to generate more employability in the nation.
Question 46.
How does small scale industries help to improve balance of payment?
Answer:
Small scale industries on one hand generate export incomes and on the other hand reduce India’s import expenditure by producing many necessary goods locally. This helps to improve balance of payment and save spending foreign exchange unnecessarily.
Question 47.
How does small scale industry result in balance regional development?
Answer:
Small scale industries can be started with less capital, less material and less resources at any part of nation. This means that small scale industries can develop in any region of the nation and does not remains concentrated to large cities. This results in balanced regional development.
Question 48.
Why is it said that the large scale industry help the economy to grow at an irregular rate?
Answer:
Large scale industries require huge investment and they cannot change their products and production methods as per the changes of market. In other words, with the change in market, large scale industry takes time to make the required changes and Hence
Question 49.
Define foreign direct investment.
Answer:
Foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment made by a company or individual in one country in business interests in another country, in the form of either establishing business operations or acquiring business assets in the other country, such as ownership or controlling interest in a foreign company.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the contribution of industries in national income.
Answer:
Contribution in national income:
- At the time of independence, agriculture sector dominated in India because India was an agriculture oriented country from the very beginning.
- After the development of industries, the agriculture economy was reduced and the contribution of industries increased in comparison with agriculture.
- Government has put various systematically planned efforts to boost the economy which in turn has increased share of industries in national income.
- In the year 1951, industrial sector had contributed 16.6% in national income. This rose to 27% (at constant prices) in the year 2013-14.
![]()
Question 2.
MOW do industries help in raising employment?
Answer:
Employment:
- India is a highly populated nation. The country is not able to provide employment to its entire labour force. However, India has increased employment opportunities with the planned efforts in the development of industrial sectors.
- Through the planned effort in industrial sector, India has increased employment opportunities.
- In the year 1951, 10.6% labourers were employed in industries. It rose to 24.3% in 2011-12.
- There was a rapid increase in small scale industries which mainly work on labour intensive methods. With increase in small scale industries employment problem has been solved to a great extent. This can be further increased by proper planning.
Question 3.
Briefly explain the role of industries in earning export income.
Answer:
Export income:
- As agriculture sector increased it also led to the development of industrial sector. When the volume of industrial production increased, the surplus started getting exported. This earned us export income. Foreign exchange also helps to import products that are scarce.
- In 2013-2014, about 2/3rd of export income was earned through industries.
Question 4.
Industries lead to balanced economic development. Explain.
Answer:
Balanced economic development:
- Industries pay a very important role to attain speedy and balanced economic growth.
- Government establishes several public sector enterprises in less developed or backward areas to increase employment opportunities and to raise life standard of living of that area.
- When the basic needs of people are satisfied, they move towards savings and buying luxurious products. This gives rise to industries involved in such services and products.
- Thus, along with the industries for primary commodities the demand of industries related to luxury and entertainment increases.
Question 5.
How do industries strengthen the economic structure?
Answer:
Strengthens the structure of economy:
- Industries produce products like iron and steel, cement, etc. which are useful to build infrastructure such as dams, roads, bridges, etc.
- These industries also produce vehicles such as buses, trucks, railway, plane, car, two wheelers, etc. used for transportation.
- Instruments of safety-protection i.e. arms and ammunition such as rifles, bullets, tanks, etc. are also produced by industries. This reduces dependency on other nations and makes our nation much stronger.
- So, industries form a base for strengthening the structure of our economy.
Question 6.
Classify industries with the help of a chart.
Answer:
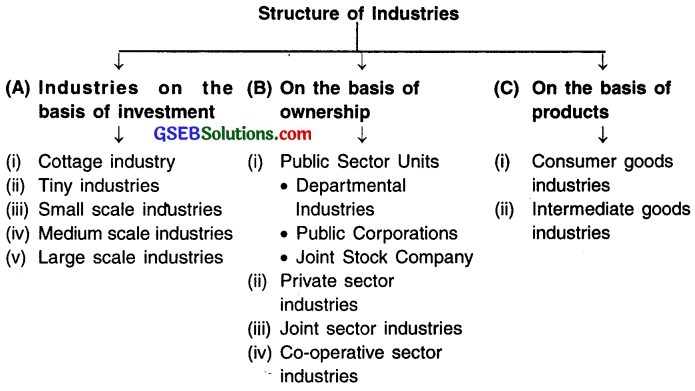
Question 7.
Explain the types of industries on the basis of products.
Answer:
Types of industries on the basis of products:
1. Consumers goods industries:
Industries that produce goods used directly by the consumers are called consumer goods industries.
Example:
Industries producing ghee, oil, cosmetics such as soaps and shampoo, etc.
2. Intermediate goods industries:
Industries producing semi-finished goods that are not consumed directly by the consumers but are sent to other industries for further processing are called intermediate goods industries.
Example:
Industries producing yarn, steel sheets, machines, etc.
![]()
Question 8.
What are departmental industries?
Answer:
Departmental industries:
- The industries run, financed, and managed by government departments are called departmental industries.
- The minister of the specific department is the ultimate in-charge of such an enterprise. Civil servants look after the operations.
- Government decides the management of expenditure and income of such industries through its budget.
Example:
Railways, post and telegraph, radio and television broadcasting, etc.
Question 9.
Explain public corporations.
Answer:
Public corporations:
- An industrial unit owned by either central or state government but established for administering certain public programs or for a specific purpose is called a public corporation.
- Government plays the supreme role in the administration and decision of such industries.
Example:
Life Insurance Corporation (LIC), state transport corporation, Air India and fertilizer producing and selling units are examples of public corporations.
Question 10.
State and explain government companies.
Answer:
Government company:
- A company owned by central and/or state government is called a government company. It operates as per the Company Law, 2013.
- Either whole of the capital or majority of the shares are owned by the government. In some cases, private investment is also encouraged but at least 51% shares are held by the government.
- These units do not work under direct control of government.
Example:
Hindustan Machine Tools, Oil and Natural Gas Limited, Indian Oil Corporation, etc
Question 11.
Differentiate between small scale industries and large scale industries.
Answer:
| Small scale industries | Large scale industries |
| 1. Industries that run on labour intensive production technique and with an investment of ₹ 25 lakhs to ₹ 5 crores are called small scale industries (SSI). | 1. Industries that run on capital intensive production technique and with an investment of more than ₹ 10 crores are known as large scale industries. |
| 2. Generally these industries are labour intensive industries. | 2. These industries are capital intensive industries. |
| 3. Production takes place on a small scale. | 3. Production takes place on a large scale. |
| 4. These industries work as ancillary industries for bigger industries. | 4. Bigger industries give rise to several small scale industries. |
| 5. Example: Industries prpducing tools and simple consumer goods like bread and biscuits, furniture, garments, etc. | 5. Example: Industries producing railway coaches and engines, big vehicles, iron and steel, petroleum, etc. |
![]()
Question 12.
Small scale industries are very important for the economy. Explain.
Answer:
- Small scale industries use labour intensive techniques and need less capital as compared to large scale industries. Hence, people having low capital can be self-employed. Also, they then give employment to others.
- Small scale industries contribute significantly in India’s total production that too using very less capital.
- These industries also export a very large quantity of goods thus increasing foreign exchange for the country.
- These industries can be set-up at any part of the nation. The advantage is they do not remain concentrated to large cities. This results in balanced regional development.
- Owing to several advantages, small scale industries play a very important role for the economy.
Measures Taken by Government for Industrial Development
Question 13.
How government ownership helps in boosting economy?
Answer:
State-owned enterprise:
- Certain industries such as infrastructural industries, iron and steel plants, insurance, etc. are called key industries of an economy. These industries form the platform for economic development.
- These industries require very huge amount of investment and skills and also are very risky. Hence, private sector fears entering such industries.
- Hence, government itself set-up such industries to boost and maintain the economy.
Question 14.
Sate government’s role in encouraging private sector industries.
Answer:
Encouragement to private sector industries:
- To encourage private sectors, government provide various type of assistance to private individuals like purchasing land at concessional rate, electricity, water, tax benefits and finance at lower rates.
- This way government encourages competition and creates a favourable market environment.
- Government has also given entry to private sector in several areas which initially were restricted to public sector only.
Question 15.
Charging high import duty is actually a way of saving industries. Explain.
Answer:
Import tariff:
- The rate of import duty (tax) charged for importing the goods is called the import tariff.
- To save the local companies from foreign companies, the government charges high import duty on foreign goods. This makes imported items costlier than the local made. As a result, the local industries can survive properly.
![]()
Question 16.
Why does government provide technical skills and training to domestic industries?
Answer:
Technical skills and training:
- Government provides various types of technical and professional training to domestic industries. This helps them to upgrade their products and services at par with international products which in turn helps the local industries to compete against the foreign products.
- These trainings were given largely during the period of liberalization and globalization.
- By such trainings the government makes the local industries aware about new global technologies, goods, selling techniques, management, etc.
- Technical skills also help to create values in the domestic industries.
Question 17.
How does government help industries economically?
Answer:
Economic help:
- Government provides various types of economic helps to industries to reduce their production cost.
- This helps the domestic industries to reduce their production costs and sell their products in international market at competitive prices with products of other countries.
- The various forms in which the government provides economic help could be providing concession on land rates, water, electricity, telephone, transport charges, etc. It may also provide finance at a subsidized rate and various other subsidies.
Question 18.
Write a brief note on role of government in establishing various industries and policies.
Answer:
Establishing various institutions and policies:
- Government makes industrial policies and also makes necessary changes time to time to help industries grow properly.
- Government frames several favourable policies like import policy, export policy, monetary policy, fiscal policy, tax policy, etc.
- Government drafts laws like Industries Act, Company Act, Competition Act, etc. to prevent unfair competition.
- Government has also created institutions such as IDBI, SIDBI, ICICI, IFCI, GIC, etc. to provide financial help to various industries.
- It also makes efforts and policies to attract roreign investment in India.
Question 19.
State the various SEZs of India.
Answer:
India has set up 8 Special Economic Zones (SEZs). They are:
- Santa Cruz (Maharashtra)
- Kochin (Kerala),
- Kandla (Gujarat)
- Surat (Gujarat)
- Chennai (Tamil Nadu)
- Visakhapattanam (Andhra Pradesh)
- Falta (West Bengal)
- (Noida (Uttar Pradesh)
Question 20.
State the meaning and importance of small scale industries in brief.
Answer:
Small Scale Industries:
- Industries that run on labour intensive production technique and with an investment of ₹ 25 lakhs to ₹ 5 crores are called small scale industries (SSI).
- These industries use labour intensive techniques and need less capital compared to large scale industries.
Importance:
- Over and above producing products that can be used directly by consumers these industries also produce products that can be or ancillary used further by large scale industries. Thus, they work as complementary to large industries.
- Small scale industries have played a very important role and are quite progressive during last five decades.
- Small scale industries are very useful for generating employment, giving platform for manufacturing with small capital, industrialization in rural areas, developing backward areas, reducing regional imbalance and to maintain the adequate distribution of national income and wealth.
- Small scale industries are extremely important for social and economic development of India economy.
Question 21.
State the contribution of small scale industries in generating employment.
Answer:
Employment generation:
- Since small scale industries are primarily labour intensive industries they have huge potential for generating employment.
- In the year 1994-95 small scale industries generated 191.40 lakhs employment opportunities. It rose to 249.33 lakhs in 2001-02 and it sharply increased to 1,012.59 lakhs in the year 2011-12.
- So, small scale industries have continuously increased their employment generation capacity which is serving like a blessing for the nation
Question 22.
State the contribution of small scale industries in increase in production.
Answer:
Increase In production:
- Generally, large scale industries produce machinery and small scale industries produce essential goods for the nation using these machineries. Owing to a very large number of small scale industries in India, their production capacity is very huge.
- Small scale industries produced goods worth ₹ 4,22,154 crores in 1994-95. It rose to ₹ 2,82,270 crores in the year 2001-02 and to ₹ 18,34,332 crores in the year 2011-12.
- Thus, small scale industries contribute significantly in India’s total production that too using very less capital.
Question 23.
How can one say there is a rise in small scale production units?
Answer:
Increase in production units (industries):
- Rise in production is only possible with rise in production units i.e. rise in number of industries.
- India had 79.60 lakh small industrial units in 1994-95. It increased to 105.21 lakhs in 2001-02. It then rose to 447.73 lakhs units in 2011-12.
- The number clearly shows that development of small scale industries has led India towards industrialization.
![]()
Question 24.
Explain role of SSI in earning foreign exchange.
Answer:
Exports:
- Small scale industries have noticeable role in exports of India.
- Small scale industries of India had exported goods and services worth Rs. 29,068 crores in 1994-95. It reached to ₹ 71,244 crores in the years 2001-02 and it rose to ₹ 1,77,600 in the year 2006-07.
- The numbers tell that small scale industries helps India earn a huge foreign exchange. This is extremely beneficial for India to manage import-export balance.
Question 25.
How do SSIs save foreign exchange?
Answer:
Saves foreign exchange:
- Small scale industries, on one hand, generate export incomes and on the other hand reduce India’s import expenditure by producing many necessary goods locally.
- This helps to improve balance of payment and save spending foreign exchange unnecessarily.
Question 26.
Explain – Short set-up.period as a key to high national production.
Answer:
Short period of time:
- Small scale industries can be started within very short time.
- A very big advantage is that these industries can start producing goods within a very short time of investment. This helps to quickly overcome scarcity of goods.
- Shorter set-up and production time are the key factors to achieve production targets of the nation.
Question 27.
How do small scale industries help in balanced regional development?
Answer:
Balanced regional development:
In contrast to large scale industries, small scale industries can be started with less capital, less material and less resources at any part of nation. This is a unique advantage since the development does not remains concentrated to large cities and can be spread to any region the nation wishes. This results in balanced regional development.
This unique advantage also helps to reduce imbalance between rich and poor and developed and developing regions.
Question 28.
Explain – decentralization as a sure benefit of SSIs.
Answer:
Decentralization:
- Large scale industries need very large amount of capital. So, they can be started only by very few people who are extremely rich. This results in centralization of capital and wealth.
- In case of small scale industries very less amount of capital is needed and so it can be started by small producers.
- Moreover, small scale industries can also make use of such resources and equipment which are otherwise dormant, unutilized and scattered. As a result, resources of every nook and corner are put into use and hence overall production volume increases.
- When such resources are used for production, they generate employment and income for people who were otherwise deprived.
- In all these senses we can say that small scale truly does the task of decentralization.
Question 29.
How do small scale industries result in high rate of development?
Answer:
High rate of development:
- Large scale industries are few. Also they invest very huge capital and so they need high profits to run their expenses.
- These industries develop the economy at an irregular rate because they cannot change their products and production methods as per the changes of market.
- Contrast to this, small scale industries are set up with small amount of capital. So, several producers are producing a given product. This increases the volume of production and income in the economy.
- Additionally, small scale industries are more capable to bring change in products and production techniques as per market changes because they do not need very huge capital or long term investment.
- Owing to these benefits small scale industries give very high rate of development highly needed to develop nation.
Question 30.
Small scale industries are very important for the economy. Explain.
Answer:
- Small scale industries use labour intensive techniques and need less capital as compared to large scale industries. Hence, people having low capital can be self-employed. Also, they then give employment to others.
- Small scale industries contribute significantly in India’s total production that too using very less capital.
- These industries also export a very large quantity of goods thus increasing foreign exchange for the country.
- These industries can be set-up at any part of the nation. The advantage is they do not remain concentrated to large cities. This results in balanced regional development.
- Owing to several advantages, small scale industries play a very important role for the economy.
Question 31.
Differentiate between labour intensive and capital intensive production techniques.
Answer:
| Capital intensive | Labour intensive |
| 1. Capital intensive production technique makes more use of machinery and automation. | 1. Labour intensive production technique makes more use of physical strength of people. |
| 2. It involves a large amount of capital. | 2. It requires less amount of capital |
| 3. Capital intensive production requires more equipment and machinery to produce goods. | 3. Labor intensive production requires a higher labor input to carry out production activities. |
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following country is a developed nation but does not have an industrial economy?
(A) Saudi Arabia
(B) Japan
(C) British
(D) United States of America
Answer:
(A) Saudi Arabia
Question 2.
Which of the following country has economy based on agriculture as its main occupation and is a developed nation too?
(A) British
(B) Saudi Arabia
(C) India
(D) Australia
Answer:
(D) Australia
Question 3.
Which sector helps a country to grow economy at the fastest rate?
(A) Agriculture sector
(B) Industrial sector
(C) Service sector
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(B) Industrial sector
![]()
Question 4.
Why is industrialization necessary?
(A) It improves standard of living of people
(B) It helps overcome unemployment
(C) It helps to increase the income of the country
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 5.
Which sector dominated. Indian economy during independence?
(A)’ Industrial sector
(B) Service sector
(C) Agriculture sector
(D) Fishing and forestry
Answer:
(C) Agriculture sector
Question 6.
How much did the industrial sector contribute in the national income in the year 1951?
(A) 27%
(B) 16.6%
(C) 10.6%
(D) 24.3%
Answer:
(B) 16.6%
Question 7.
Which of the following industries uses majorly labour intensive production technique?
(A) Small scale industries
(B) Medium scale industries
(C) Large scale industries
(D) All of these
Answer:
(A) Small scale industries
Question 8.
Increase in small scale industries in India has mainly led to
(A) Increase in production
(B) Increase in economic growth
(C) Increase in employment
(D) Increase in standard of living of people
Answer:
(C) Increase in employment
Question 9.
How much share of export income was earned by the industries in the year 2013-14?
(A) 1/3rd
(B) 2/3rd
(C) 4/5th
(D) 1/10th
Answer:
(B) 2/3rd
Question 10.
What can the government do to increase the employment in backward areas in India?
(A) Establish public sector enterprises in backward areas
(B) Give benefits to private sector enterprises to promote developing urban areas whose income will then be used to develop backward areas
(C) Build good roads so that people from backward areas can come and work in developed areas
(D) Give aids and monetary help to people in backward areas so that they can promote self-employment
Answer:
(A) Establish public sector enterprises in backward areas
Question 11.
Which of the following equipment can help to increase agricultural land and labour productivity?
(A) Tractor
(B) Submersible pumps
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Solar panel
Answer:
(C) Both (A) and (B)
![]()
Question 12.
Which of the following are used as instruments of safety?
(A) Rifles
(B) Artillery
(C) Warfare
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Question 13.
Which of the following is not a type of industry based on investment?
(A) Cottage industry
(B) Tiny industry
(C) Consumer goods industry
(D) Large scale industry
Answer:
(C) Consumer goods industry
Question 14.
Industries producing items like khadi, papad, khakhra, incense sticks are examples of which type of industry?
(A) Tiny industry
(B) Small scale industry
(C) Cottage industry
(D) Medium scale industry
Answer:
(C) Cottage industry
Question 15.
What is the investment bracket of medium scale industry?
(A) 5 crores-10 crores
(B) 10 crores-20 crores
(C) Above 20 crores
(D) Upto 25 lakhs
Answer:
(A) 5 crores-10 crores
Question 16.
Artistic products made from metal is an example of
(A) Tiny industries
(B) Cottage industry
(C) Small scale industries
(D) Medium scale industries
Answer:
(A) Tiny industries
Question 17.
Which of the following industries does not use labour intensive production technique?
(A) Small scale industries
(B) Tiny industries
(C) Medium scale industries
(D) Large scale industries
Answer:
(D) Large scale industries
Question 18.
What is the investment limit of tiny industry?
(A) Upto 10 lakhs
(B) 10 lakhs – 25 lakhs
(C) Upto 25 lakhs
(D) 25 lakhs – 5 crores
Answer:
(C) Upto 25 lakhs
Question 19.
What is the investment limit of small scale industry?
(A) Upto 10 lakhs
(B) 10 lakhs – 25 lakhs
(C) Upto 25 lakhs
(D) 25 lakhs – 5 crores
Answer:
(D) 25 lakhs – 5 crores
Question 20.
Which of the following characteristics hinders industrialization?
(A) Institutional capability
(B) Fatalism
(C) Secularism
(D) Cut throat competition
Answer:
(B) Fatalism
Question 21.
Which of the following are industries whose ownership as well as administration does not lie with government?
(A) Private sector units
(B) Public sector units
(C) Cooperative sector industries
(D) Joint sector industries
Answer:
(A) Private sector units
Question 22.
Which of the following is an example of public corporation?
(A) Air India
(B) Railways
(C) Oil and Natural Gas Limited
(D) Post
Answer:
(A) Air India
![]()
Question 23.
Which of the following is an example of joint sector industry?
(A) Indian Oil Corporation
(B) Oil and Natural Gas Limited
(C) GSPC
(D) Hindustan Machine Tools
Answer:
(C) GSPC
Question 24.
What is the main reason for establishing cooperative sector industries?
(A) To stop exploitation of marginal owners
(B) To stop exploitation of consumers
(C) To stop exploitation of labourers
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 25.
‘Dairies of villages’ is an example of which of the following industries?
(A) Public corporations
(B) Joint stock companies
(C) Cooperative sector industries
(D) Joint sector industries
Answer:
(C) Cooperative sector industries
Question 26.
‘Steel sheets’ are example of which of the following industry?
(A) Consumer goods industry
(B) Intermediate goods industry
(C) Departmental industry
(D) Cooperative sector industry
Answer:
(B) Intermediate goods industry
Question 27.
Which of the following is not a provision of government for encouragement/ development of private sector units?
(A) Provision of land at concessional rate
(B) Provision of electricity and water
(C) Provision of tax breaks
(D) Provision of latest technology
Answer:
(D) Provision of latest technology
Question 28.
Why do foreign products become expensive?
(A) Due to import tariff
(B) Due to high cost of production in foreign country
(C) Because of high technical skill and training used by the foreign companies
(D) Due to inflation in our country
Answer:
(A) Due to import tariff
Question 29.
Government provide various economic help to industries to
(A) Sell their product in the domestic market
(B) Reduce their production cost
(C) Increase the competition of selling products
(D) Sustain in competition with foreign goods
Answer:
(B) Reduce their production cost
Question 30.
Which of the following institute is set up by the government to provide financial help?
(A) SIDBI
(B) IDBI
(C) GIC
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 31.
When was special economic zone implemented in India?
(A) 1st April, 2000
(B) 1st April. 2004
(C) 3rd April, 2000
(D) 3rd April, 2004
Answer:
(A) 1st April, 2000
Question 32.
Why are tax incentives given for special economic zones in India?
(A) To promote free environment for exports
(B) To attract foreign investors
(C) To bring down the material handling costs.
(D) To increase exports
Answer:
(B) To attract foreign investors
Question 33.
Which of the following countries have not introduced special economic zones in their country?
(A) Poland
(B) Jordan
(C) Saudi Arabia
(D) Russia
Answer:
(C) Saudi Arabia
Question 34.
How many special economic zones has India set up?
(A) 7
(B) 10
(C) 8
(D) 15
Answer:
(C) 8
![]()
Question 35.
Which of the following is currently not a special economic zone?
(A) Kandala (Gujarat)
(B) Falta (West Bengal)
(C) Mulund (Mumbai)
(D) Chennai (Tamil Nadu)
Answer:
(C) Mulund (Mumbai)
Question 36.
Which of the following is the main outcome of development of small scale industries?
(A) Increase in production
(B) Increase in exports
(C) Development of backward areas
(D) Control over migration
Answer:
(C) Development of backward areas
Question 37.
Approximately how much employment was generated by small scale industries in the year 2011-12?
(A) 1013 lakhs
(B) 1054 lakhs
(C) 1000 lakhs
(D) 1562 lakhs
Answer:
(A) 1013 lakhs
Question 38.
How much was the export of small scale industries in the year 2006-07?
(A) Rs 1,56,600 crores
(B) ₹ 1,77,600 crores
(C) ₹ 71,244 crores
(D) ₹ 1,90,600 crores
Answer:
(B) ₹ 1,77,600 crores
Question 39.
Why is ‘labour intensive production technique’ known as blessing for India?
(A) Because it reduces poverty
(B) Because India has excess of labour which need to be employed anyhow
(C) Because it reduces cost of production
(D) Because less capital is invested
Answer:
(B) Because India has excess of labour which need to be employed anyhow
Question 40.
Which of the following industries can be started within short period of time?
(A) Small scale industries
(B) Medium scale industries
(C) Cottage industries
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (C)