Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Commerce Accounts Part 1 Chapter 7 Cash Book and Its Types Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Accounts Part 1 Chapter 7 Cash Book and Its Types
GSEB Class 11 Accounts Cash Book and Its Types Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the correct option from those given below each question :
1. A book prepared to keep a record of cash transactions is ……………. .
(a) Purchase book
(b) Sales book
(c) Cash book
(d) Bills payable book
Answer:
(c) Cash book
2. How many types of two columnar cash book can be prepared ?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
![]()
3. …………………. serves the purpose of journal and cash account.
(a) Cash book
(b) Sales book
(c) Sales return book
(d) Bills receivable book
Answer:
(a) Cash book
4. Which type of discount is not recorded in the cash book ?
(a) Kasar
(b) Discount received
(c) Discount allowed
(d) Trade discount
Answer:
(d) Trade discount
5. When bank credits interest in our account then …………….. .
(a) bank balance decreases
(b) bank balance increases
(c) cash balance decreases
(d) cash balance increases
Answer:
(b) bank balance increases
6. Which transactions are not recorded in the cash book ?
(a) Cash purchase
(b) Cash sales
(c) Cash discount
(d) Non-cash transactions
Answer:
(d) Non-cash transactions
Question 2.
Answer the following questions in two or three sentences:
(1) Explain the meaning of cash book.
Answer:
Cash book is a type of subsidiary book in which all cash transactions are recorded. Transactions relating to cash, bank and cash discount are recorded in the cash book.
Cash book is a separate book of the subsidiary books. It works as a ledger and as a journal both. Cash receipts and payment are recorded in the cash book and at the end of the given period cash balance as well as bank balance can also be known from cash book.
![]()
(2) What is Bank overdraft ?
Answer:
With the prior arrangement with bank, when a trader is able to withdraw more amount than the deposited amount, the difference of amount is known as Bank overdraft. In other word, if the total of bank column of payment side of cash book is more than the total of bank column of receipt side, then it is known as Bank overdraft.
- Bank overdraft is liability for business.
- Interest on bank overdraft is an expense for business.
- Bank overdraft account always shows credit balance.
- Current account holder gets the facilities of bank overdraft.
(3) What does balance of bank account indicate ?
Answer:
Since bank account is a personal account, it can have debit balance or credit balance, when the total of receipts side of bank column is greater than the total of payment side, the difference (i.e., balance) is called ‘Debit balance’ (i.e., Bank balance). This balance is shown on the payment side as ‘By balance carried forward’.
When the total of payments side of bank column is greater than the total of receipts side, the difference (i.e., balance) is called ‘Credit balance’ (i.e., Bank overdraft). This balance is shown on the debit side of Cash book (receipts side) under bank column as ‘To balance carried forward’.
(4 ) Explain the meaning of petty cash book.
Answer:
Petty cash book is a part of cash book. The book (cash book) kept by the petty cashier for keeping a record for payment of petty or small expenses is known as Petty cash book.
Petty cashier prepares the petty cash book, in which separate columns are maintained for various petty or small expenses to be paid by the petty cashier. So that the information of various types of expenses (and total amount) paid by the petty cashier is available.
Petty cash book can be prepared in two types :(1) Simple petty cash book and (2) Petty cash book on Imprest system.
(5) Explain the full form of NEFT and RTGS.
Answer:
- The full name of NEFT Is National Electronic Fund Transfer.
- The full name of RTGS is Real Time Gross Settlement.
Above both services are provided to the customer by participating banks in this scheme. Banks charge nominal amount for this service.
![]()
(6) Explain the importance of cash book in short.
Answer:
Importance of a cash book are as follows :
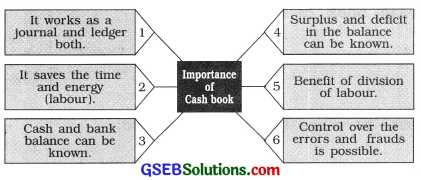
1. It works as a journal and ledger both : By maintaining cash book, it is not necessary to pass the journal entry for the transactions recorded in it. Moreover, it is not necessary to open a separate cash account in the ledger. Thus, cash book works as a ledger and as a journal both.
2. It saves the time and energy (labour) : If in the cash book, the transactions related to bank and discount are entered then cash book works as an account, therefore the time and energy (labour) are saved.
3. Cash and bank balance can be known: Bank balance and cash balance of the business can be known as the transactions of cash and with bank are properly recorded in the cash book.
4. Surplus and deficit in the balance can be known: Balance of cash from cash book is found at the end of the everyday and it can be compared with actual cash of the cash-box. So that difference in the balance can be known.
5. Benefit of division of labour : Cash book is a separate book of the subsidiary books, and an independent person can maintain it so business can get the benefit of division of labour.
6. Control over the errors and frauds is possible: Balance as per cash book and as in cash-box is compared daily, so if any fraud or error is there in entering the incomes and expenses can be known from the deficit or surplus of the balance. Against this types of the errors or frauds action can be taken.
(7) Explain : Contra transaction
Answer:
‘Contra transaction’ means such financial transaction, in which cash and bank, both the accounts get affected.
- Contra transaction is recorded on both the side of cash book.
- Generally, contra transactions are of two types : (1) Cash deposited in the bank and (2) Cash withdrawn from the bank.
- Contra transaction affects only ‘cash’ and ‘bank’ account and no other accounts. Hence, the positing of ‘Contra transaction’ is not required. Further, ‘C’ will be written in the L. F. No. column of cash book on both the sides.
(8) Explain Bank Book with illustrations.
Answer:
Bank Book : Majority of cash transactions are done through bank in the present age. When business has account in more than one bank or in a one bank they have more than one accounts, in that case to record the transactions with the bank, a book is prepared which is known as Bank book. Business has an account in more than one bank or in a bank more than one account is there, in that circumstances to get the necessary information quickly and to tally the balances, a bank book having different columns is kept by the businessman.
Illustrations : If the accounts are in the different banks then in the different columns name of bank is to be written, e.g., Dena Bank, Canara Bank, SBI. But if in a one bank more than one accounts are there, then in the different columns A/c no. 1,2,… are to be written. The structure and style of bank book is like the cash book only.
Utilities (Importance) : Utilities of the bank book are as under :
- Easily recorded : The transactions with the banks can be easily recorded, especially, when the volume of transactions through the bank is more.
- Reconciliation : With the help of bank book transactions can be easily reconciled with pass book or bank statement.
- Bank balance : At any given point of time, the bank balance of various bank accounts can be known.
- Liquidity : A constant watch on the different financial transactions entered into through different bank current accounts by the business organisation is possible. With the help of which liquidity of the business can be maintained.
![]()
(9) Explain the meaning of petty cash book on Imprest system.
Answer:
Imprest petty cash book: In this type of petty cash book, some fixed amount is given to the petty cashier, considering the maximum sundry expenses that would have to be paid. This amount with the petty cashier should not be more than the predecided amount, at any time. At the end of this fixed period, the petty cashier gives accounts for the amount spend to the head cashier, who examines these accounts and pays the petty cashier the total amount expended. Thus, the petty cashier has a fixed amount (imprest) at the beginning of every specified period.
Question 3.
Record the following transactions in the cash book of Prapti :
2015
June 1 Opening cash balance ₹ 10,000.
2 Cash sales ₹ 3,000.
3 Cash of ₹ 2,000 brought in the business, as more funds are required. Cash purchase ₹ 6,000.
7 Salary of ₹ 1,000 and brokerage of ₹ 1,500 paid by cash.
9 Goods of ₹ 5,000 purchased from Drona by cash.
11 Goods of ₹ 6,000 sold to Mansi for cash.
19 ₹ 3,000 paid to Nairuti for goods purchased in the previous month.
23 Kinjal paid ₹ 1,500 for goods sold to her in the previous month.
25 Old cycle of ₹ 600 is purchased for business.
28 ₹ 1,000 received towards commission.
30 Machine of ₹ 3,500 purchased for business.
Answer:
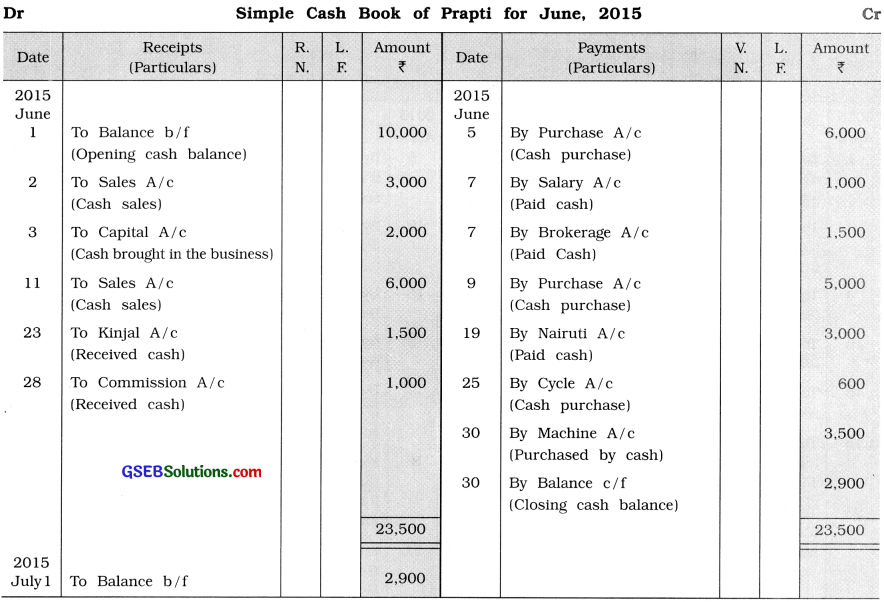
Question 4.
From the following transactions, prepare cash and discount columnar cash book of Javlit: 2015
April 1 Opening cash balance ₹ 5,500.
3 Goods of ₹ 4,000 sold at 10 % cash discount.
4 Goods of ₹ 3,000 sold at 10 % trade discount.
5 Cash of ₹ 2,000 paid to Arth in full settlement of his account of ₹ 2,030.
10 Goods of ₹ 4,000 purchased at 5 % cash discount.
13 Salary of ₹ 1,000 and wages of ₹ 600 are paid by cash.
15 Commission of ₹ 100 and brokerage of ₹ 900 are received.
17 Cash of ₹ 1,400 paid to Krishna in full settlement of account of ₹ 1,420.
18 Goods of ₹ 5,000 sold at 10% trade discount and 5% cash discount.
19 A machine of ₹ 6,000 purchased from Ramesh, for which ₹ 2,000 paid by cash and it is decided that the remaining amount will be paid after one month.
23 As more funds are required in the business, household furniture of ₹ 3,000 is sold for ₹ 3,500 and out of this ₹ 2,500 are brought in the business.
27 ₹ 225 paid to Vepari Mahamandal towards annual fees.
29 Godown rent ₹ 600 paid by cash and carriage of ₹ 300 paid to Shambhu by cash.
Answer:
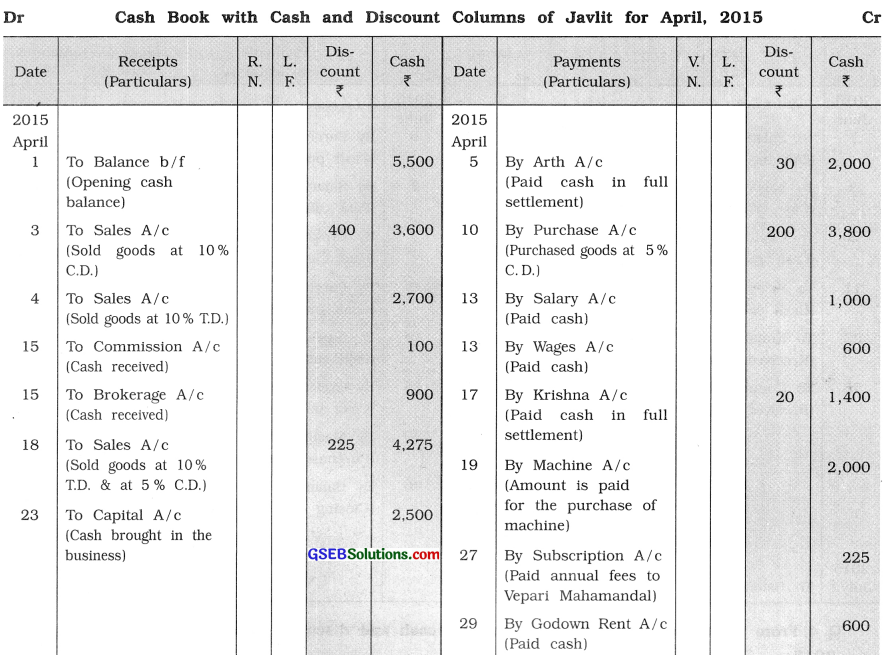
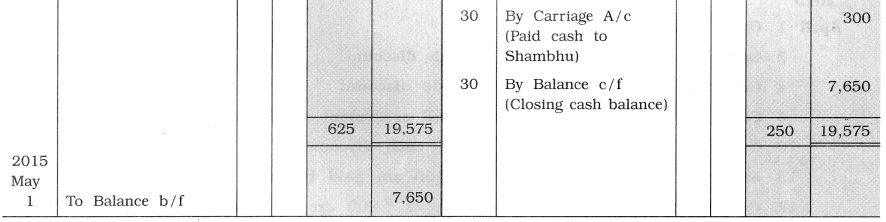
![]()
Question 5.
From the following transactions, prepare cash and bank columnar cash book of Riddhi : 2015
May 1 Opening cash balance ₹ 4,000, opening bank balance ₹ 6,000.
2 Goods of ₹ 5,000 sold to Monika at 10 % trade discount. Monika issued cheque for the necessary amount, which is immediately deposited in the bank.
4 ₹ 2,000 paid towards salary and ₹ 100 paid towards brokerage by cash.
6 ₹ 3,000 withdrawn from the bank for personal use.
10 Goods of ₹ 6,000 sold to Hiren. Hiren paid ₹ 4,000 by cash and remaining amount is paid by cheque, which is deposited in the bank.
12 Goods of ₹ 5,000 purchased and the amount is paid by cheque.
17 Shop rent of ₹ 2,000 paid by cheque.
21 Goods of ₹ 4,500 purchased in cash at 10% trade discount.
24 Karishma has paid ₹ 2,550 by cash towards her debt.
26 Atmakalyani has been paid ₹ 1,200 towards full settlement of an old account.
29 Jhanvi issued a cheque of ₹ 3,000, which is immediately deposited in the bank.
30 ₹ 1,000 cash deposited in the bank.
Answer:
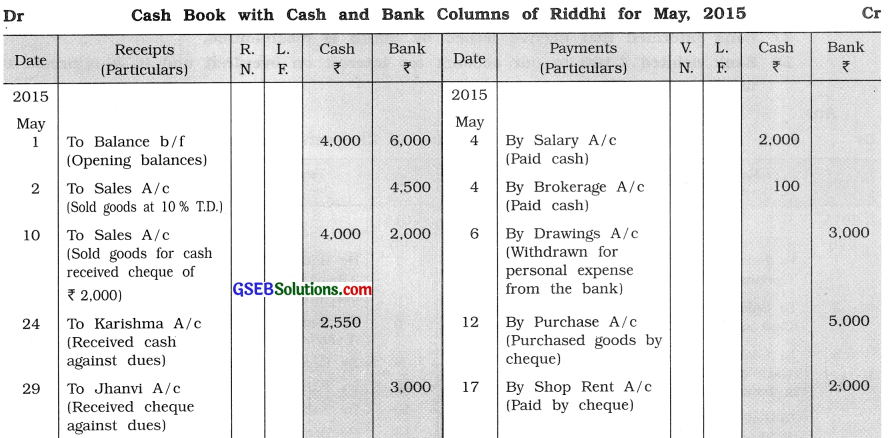
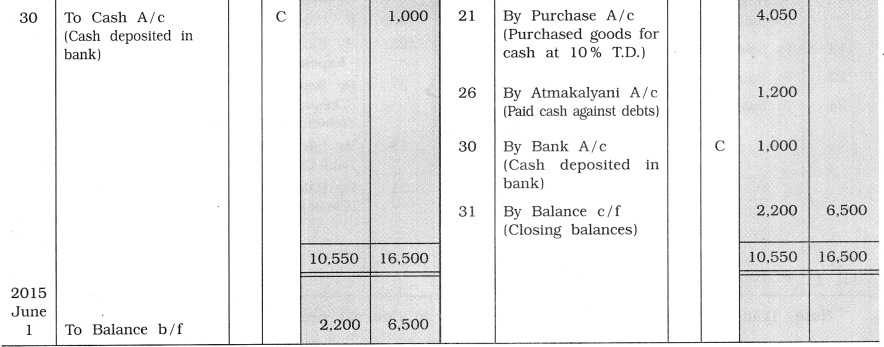
Question 6.
From the following transactions, prepare cash and bank columnar cash book in the books of Bhagwati Traders :
2015
July 1 Opening cash balance ₹ 5,000, opening bank overdraft ₹ 1,500.
3 Goods of ₹ 8,000 sold to Janki at 10 % trade discount for cash.
5 ₹ 3,000 deposited in the bank.
6 Goods of ₹ 2,000 sold to Jinal. Jinal paid the amount immediately by cheque which is deposited in the bank.
8 Furniture of ₹ 2,000 purchased and the amount is immediately paid by cheque.
9 Cheque of ₹ 3,000 received from Bhargavi, which is endorsed in favour of Parth.
13 Goods of ₹ 6,000 sold to Harshit. Harshit has paid half of the amount by cash and
remaining amount is paid by cheque, which is immediately deposited in the bank.
15 Goods of ₹ 6,000 purchased from Divyesh and amount is immediately paid by cash.
18 Salary of ₹ 1,000 and brokerage of ₹ 500 are paid by cash.
22 ₹ 1,000 withdrawn from the bank for the payment of the electricity bill.
23 Electricity bill paid.
24 Goods of ₹ 1,400 sold to Smith, for which he issued a cheque of the necessary amount, which is immediately deposited in the bank.
27 Bank informed that cheque issued by Smith is dishonoured.
28 Bank debited ? 100 to our account for interest on overdraft and it is informed to us through bank advice.
Answer:
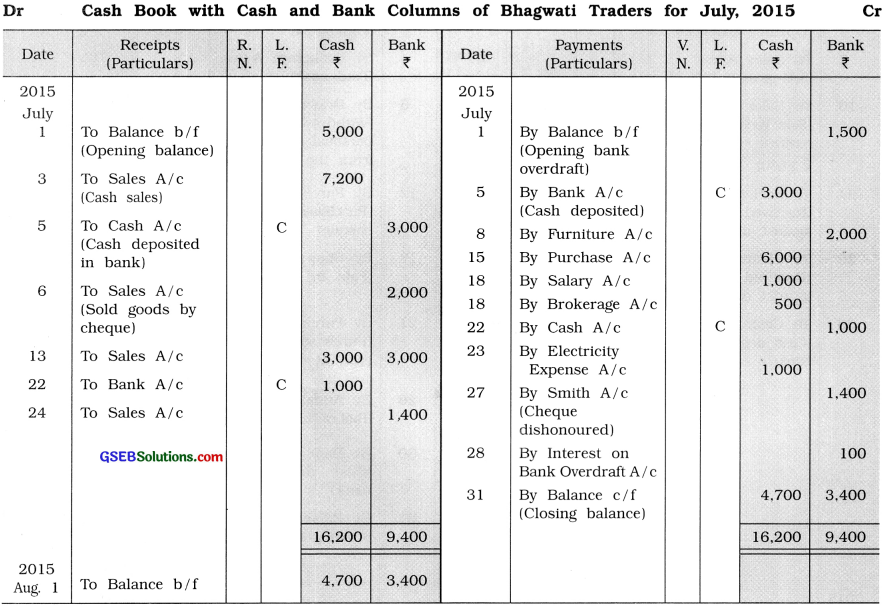
Note : Transaction of Date 9 will be recorded in Journal proper.
![]()
Question 7.
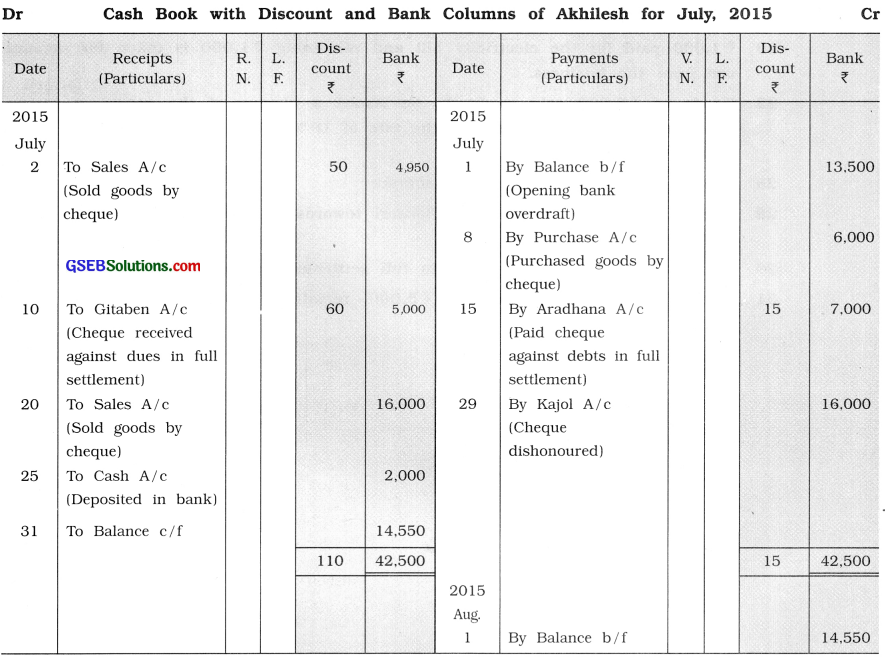
From the following transactions, prepare bank and discount columnar cash book of Akhilesh :
2015
July 1 Opening bank overdraft ₹ 13,500.
2 Goods of ₹ 5,000 sold to Premal, against which he issued a cheque of ₹ 4,950 in full settlement of account, which is immediately deposited in the bank.
8 Goods of ₹ 6,000 purchased and a cheque is issued for the necessary amount.
10 Cheque of ₹ 5,000 is received from Gitaben in full settlement of account of ₹ 5,060. 15 Cheque of ₹ 7,000 issued to Aradhana in full settlement of the debt of ₹ 7,015.
20 Goods of ₹ 16,000 sold to Kajol, for which she issued a cheque of the necessary amount, which is deposited in the bank.
25 Cash of ₹ 2,000 deposited in the bank.
29 Cheque issued by Kajol is dishonoured.
Answer:
![]()
Question 8.
From the following transactions, prepare three columnar cash book of Namrata:
2015
August
1 Opening cash balance ₹ 7,000, opening bank balance ₹ 6,000.
3 Cash purchase ₹ 6,000; cash sales ₹ 7,000.
5 ₹ 3,000 is deposited in the bank.
6 As more funds are required in the business, a loan of ₹ 5,000 is taken from Prabhu bearing
8 % interest rate.
8 Goods of ₹ 3,000 sold to Mansi at 10 % cash discount, Mansi issued a cheque of the necessary amount, which is deposited in the bank.
10 Goods of ₹ 7,000 purchased from Dvij and 50 % of the amount is immediately paid by cash.
12 Salary of ₹ 3,000, wages of ₹ 500 and stationery of ₹ 200 are paid by cheque.
14 Commission of ₹ 1,000 and brokerage of ₹ 500 received by cash.
16 Bank credited interest ₹ 100 on balance in Namrata’s bank.
17 ₹ 2,000 withdrawn from the bank for the payment of the electricity bill.
20 ₹ 1,000 paid for the electricity bill and remaining ₹ 1,000 is taken for personal use from the business.
22 Goods of ₹ 5,000 sold to Parth, he issued a cheque of the necessary amount after deducting cash discount at the rate of 10%, which is immediately deposited in the bank.
25 Cheque issued by Parth is dishonoured.
28 Cheque of ₹ 6,050 is issued to Bansari towards an old debt. Total debt was of ₹ 6,100.
29 Gopi has paid ₹ 2,000 by cash in full settlement of the debt ₹ 2,040.
31 After keeping cash on hand of ₹ 5,000, remaining amount is deposited in the bank.
Answer:
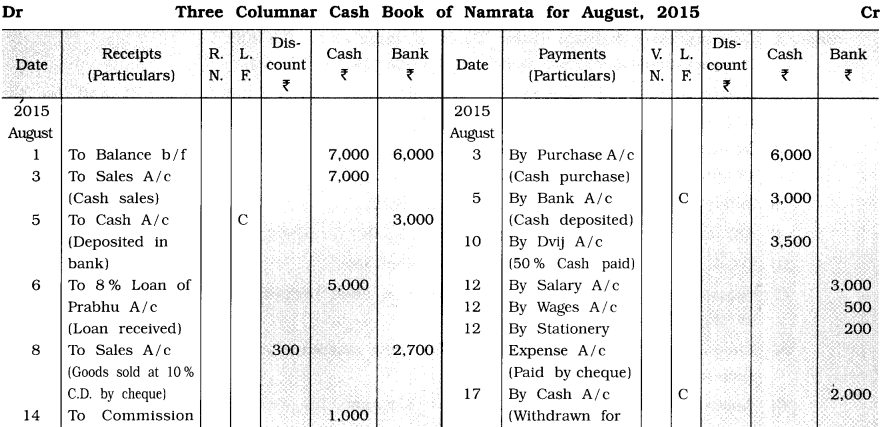
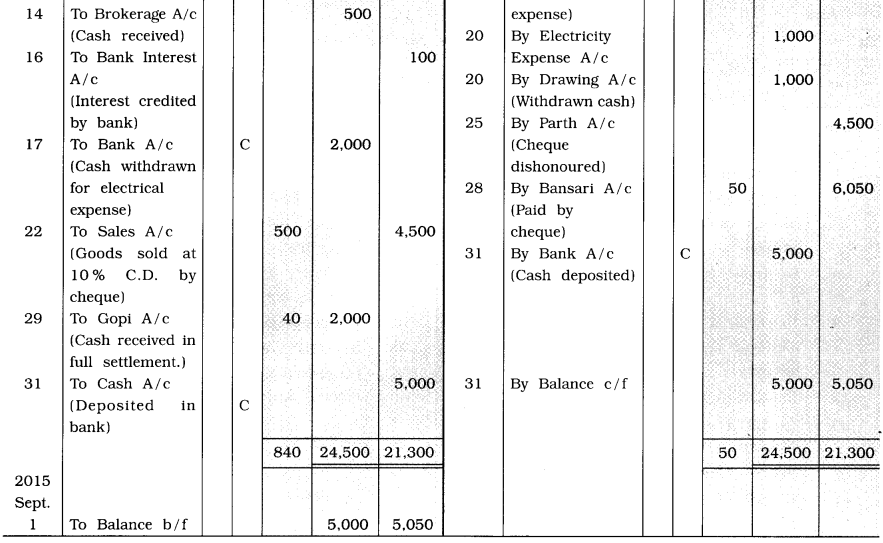
Explanation: Account entry for cancelled discount due to dishonoured of cheque dated 25th is as under in the journal. proper :
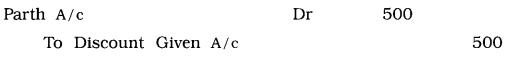
![]()
Question 9.
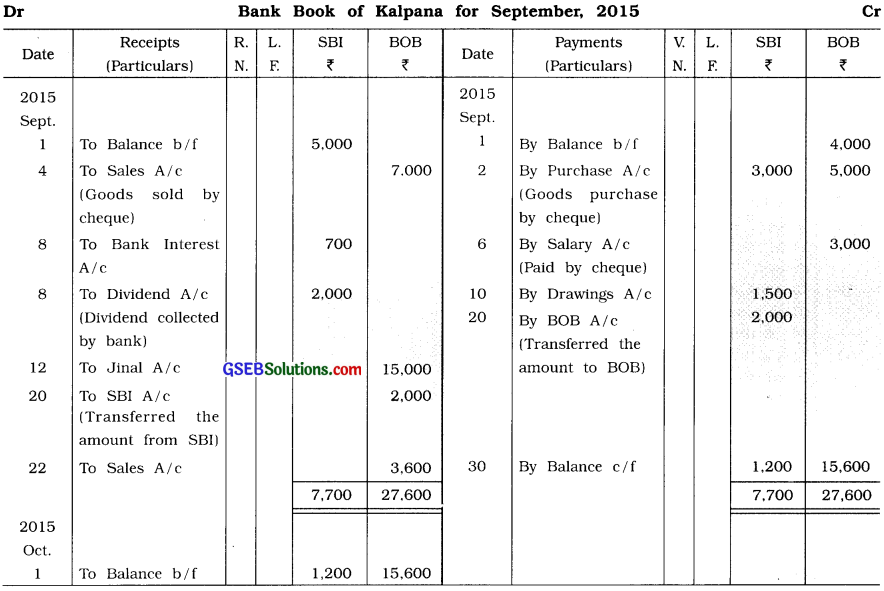
From the following transactions, prepare bank book in the books of Kalpana:
2015
Sept. 1 Opening bank balance (State Bank of India – SBI) ₹ 5,000,
Opening bank overdraft (Bank of Baroda – BOB) ₹ 4,000.
2 Goods of ₹ 8,000 purchased, for which cheque of ₹ 3,000 on SBI and for the
remaining amount, a cheque of BOB is issued.
4 Goods of ₹ 7,000 sold to Jeni, Jeni issued a cheque of the necessary amount, which is deposited in the BOB account.
6 Salary of ₹ 3,000 paid by cheque of BOB.
8 SBI credited ₹ 700 for interest and ₹ 2,000 for dividend.
10 ₹ 1,500 withdrawn from SBI for personal use.
12 Crossed cheque of ₹ 15,000 received from Jinal towards her due, which is deposited in the BOB account.
20 Cheque of ₹ 2,000 issued from SBI bank account and is deposited in the bank account of BOB.
22 Goods of ₹ 4,000 sold at 10% cash discount, for which cheque is received, which is deposited in the BOB account.
Answer:
Question 10.
From the following transactions, prepare petty cash book of Jigar:
2015
October 1 Opening petty cash balance of ₹ 4,000.
1 Amount received from the chief cashier ₹ 1,000.
3 Wages of ₹ 600 and carriage of ₹ 400 are paid.
5 ₹ 700 paid for postage and postal stamps expenses.
8 ₹ 200 paid for wages.
10 ₹ 400 paid for stationery expenses.
12 ₹ 150 paid for Tea and Refreshment expenses.
14 ₹ 500 received from the chief cashier.
15 Misc. expenses paid ₹ 500.
17 ₹ 400 given to Mishal for the payment of misc. expenses.
Petty Cash Book of Jigar for October, 2015
Answer:
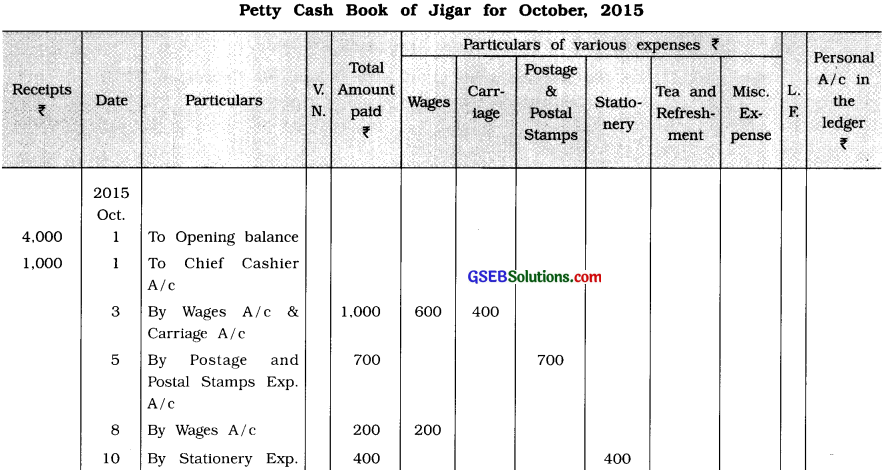
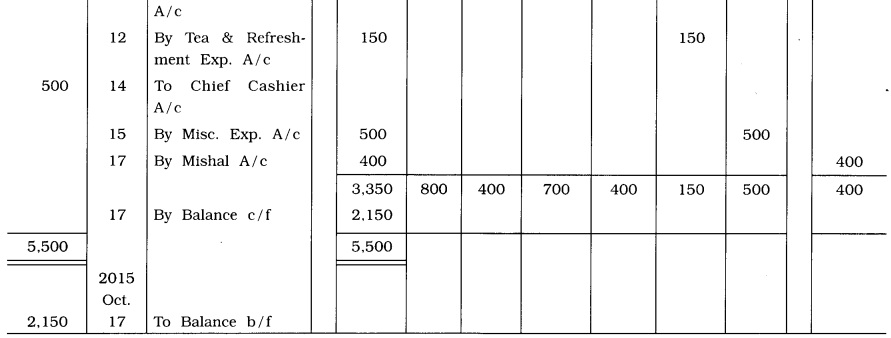
![]()
Question 11.
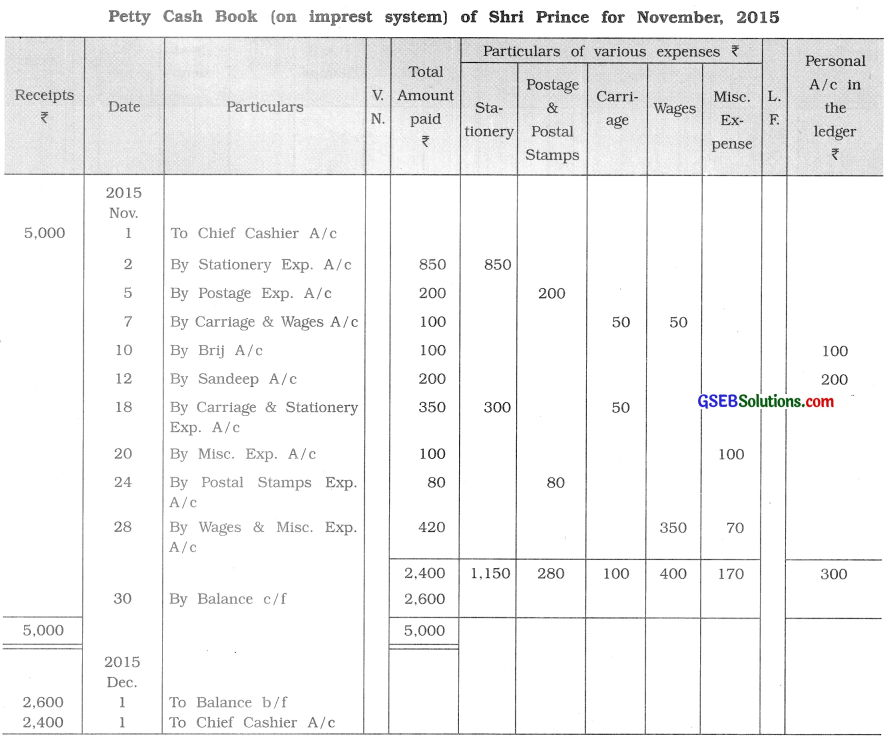
From the following transactions, prepare petty cash book of Sfari Prince as per -petty imprest system :
2015
Nov. 1 Cash received from chief cashier ₹ 5,000.
2 ₹ 500 for printing charges of bill book and ₹ 350 for other stationery items are
paid.
5 Postage expenses paid ₹ 200.
7 Carriage ₹ 50 and wages of ₹ 50 paid.
10 ₹ 100 is paid to Brij towards salary.
12 ₹ 200 is given to Sandeep for the payment of misc. expenses.
18 Carriage of ₹ 50 and stationery expenses of ₹ 300 are paid,
20 ₹ 100 paid for misc. expenses.
24 ₹ 80 paid for postal stamps.
28 ₹ 350 for wages and ₹ 70 for misc. expenses are paid.
Answer:
Question 12.
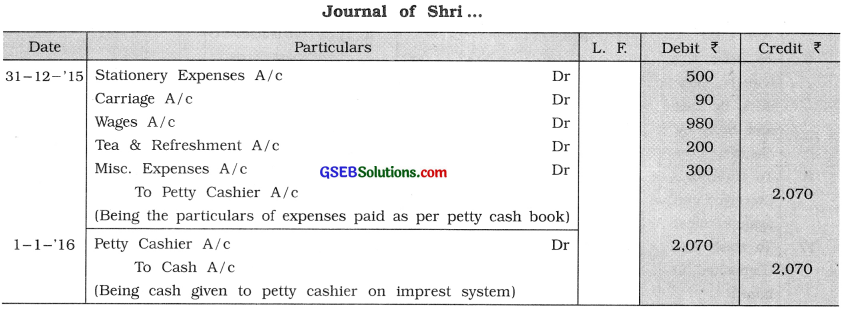
The following information has been obtained in respect of the petty cash book maintained as per petty cash book on imprest system for the month ending on dt. 31-12-’15:
Stationery expenses ₹ 500
Carriage ₹ 90
Wages ₹ 980
Tea & Refreshment ₹ 200
Misc. expenses ₹ 300
From this information pass journal entries.
Amswer:
Special exercises for practice of three columnar cash book:
![]()
Question 13.
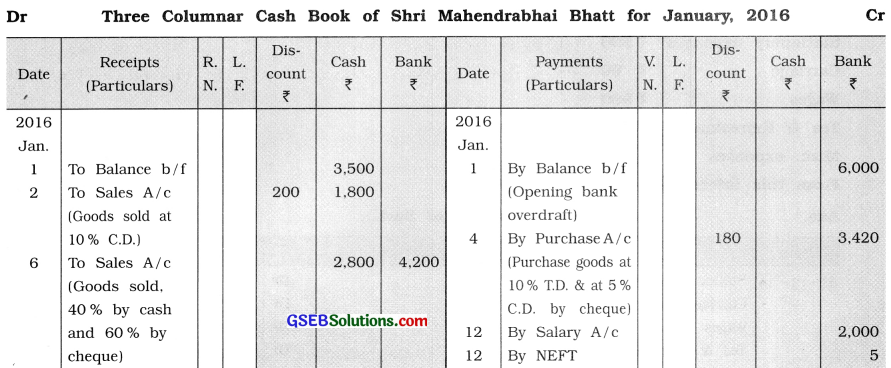
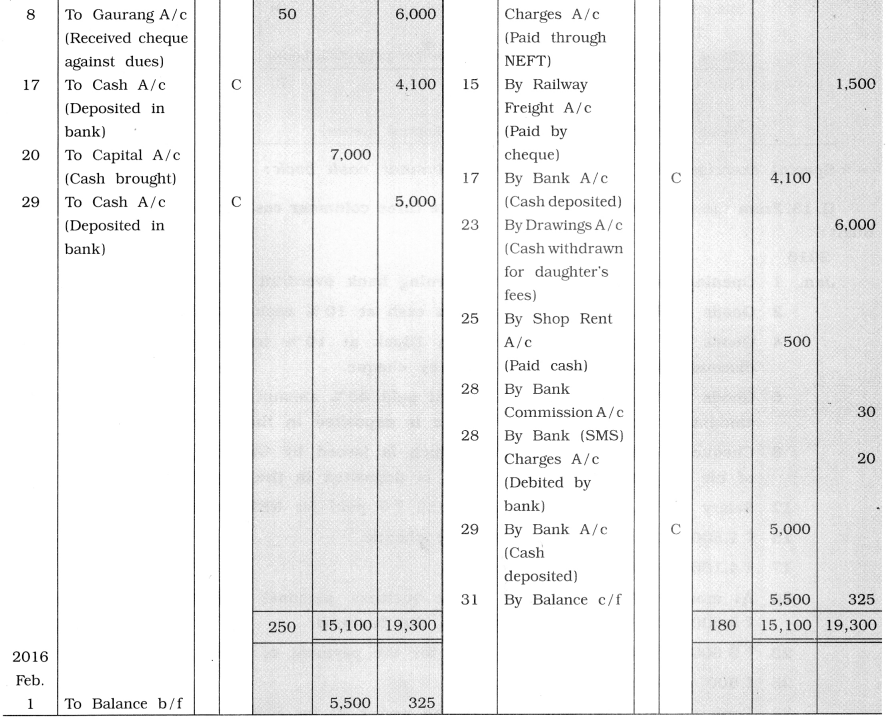
From the following transactions, prepare three columnar cash book of Shri Mahendrabhai Bhatt:
2016
Jan 1 Opening cash balance ₹ 3,500, opening bank overdraft ₹ 6,000.
2 Goods of ₹ 2,000 sold to Parag in cash at 10 % cash discount.
4 Goods of ₹ 4,000 purchased from Dipak at 10 % trade discount and 5% cash
discount and the amount is paid by cheque.
6 Goods of ₹ 7,000 sold to Ami. Ami paid 40% amount by cash and the remaining amount is paid by cheque. Cheque is deposited in the bank.
8 Cheque of ₹ 6,000 is received, which is issued by Gaurang towards the payment of his old debt of ₹ 6,050, which is deposited in the bank.
12 Salary of ₹ 2,000 paid by MEET and ₹ 5 paid for NEFT charge.
15 ₹ 1,500 paid for railway freight by cheque.
17 ₹ 4,100 deposited in the bank.
20 As more funds are required in the business, personal vehicle of ₹ 10,000 sold for ₹ 8,000 and ₹ 7,000 is brought in the business.
23 ₹ 6,000 withdrawn from the bank for the payment of school fees of his daughter.
25 ₹ 500 paid for the shop rent.
28 Bank debited ₹ 30 bank commission and ₹ 20 for SMS charges.
29 ₹ 5,000 deposited in the bank account.
Answer:
Question 14.
From the following transactions, prepare three columnar cash book of Sonamben:
2016
Feb. 1 Cash balance ₹ 16,000, bank balance ₹ 18,000.
4 Goods of ₹ 8,000 sold to Shri Ashokbhai. He has paid the amount in the bank through NEFT.
6 Goods of ₹ 10,000 sold to Hetal in cash at 10 % cash discount.
9 ₹ 3,000 deposited in the bank.
11 Life insurance premium of ₹ 2,000 is paid by NEFT and bank debited ₹ 3 for
charges.
13 Salary of ₹ 3,000 paid.
14 Wages of ₹ 2,000 paid.
17 Cash purchase ₹ 1,000; cash sales ₹ 3,000.
19 Bank credited ₹ 2,500 for dividend through NEFT.
21 Commission of ₹ 1,200 paid.
23 Fire insurance premium of ₹ 2,500 paid by NEFT and bank debited ₹ 2 for charges.
25 Bank credited Bank-interest of ₹ 200 and commission of ₹ 200 in our account
through NEFT.
28 Bank has paid the vehicle loan installment of ₹ 12,000 on behalf of us through NEFT and bank debited ₹ 3 for charges.
Answer:
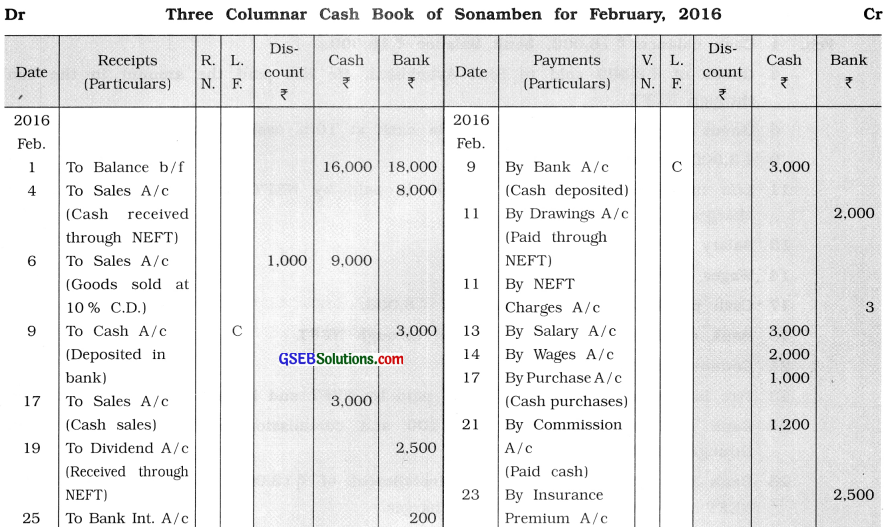
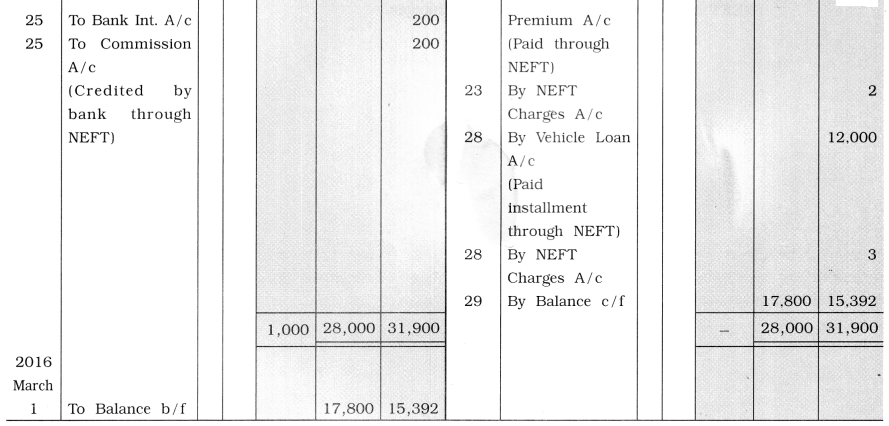
![]()
Question 15.
From the following transactions, prepare three columnar cash book of Mansi:
2015
Sept. 1 Cash balance ₹ 10,000; bank overdraft ₹ 5,000.
2 Goods of ₹ 5,000 purchased for cash from Keval at 10 % trade discount and 2 % cash discount.
6 ₹ 8,000 is received through NEFT and ₹ 1,900 cash received from Jyoti in full settlement of account of ₹ 10,000.
10 Salary of ₹ 500 paid to Vinod through NEFT and ₹ 100 paid for rent by cash and bank debited ₹ 3 for charges.
15 Goods of ₹ 3,000 sold to Kashmiraben for cash.
20 ₹ 500 withdrawn for office expenses and ₹ 350 withdrawn for personal use from the bank.
25 Machine of ₹ 3,000 purchased and machine installation wages ₹ 250 paid.
30 After keeping cash on hand of ₹ 1,000, the balance amount is deposited in the bank.
Answer:
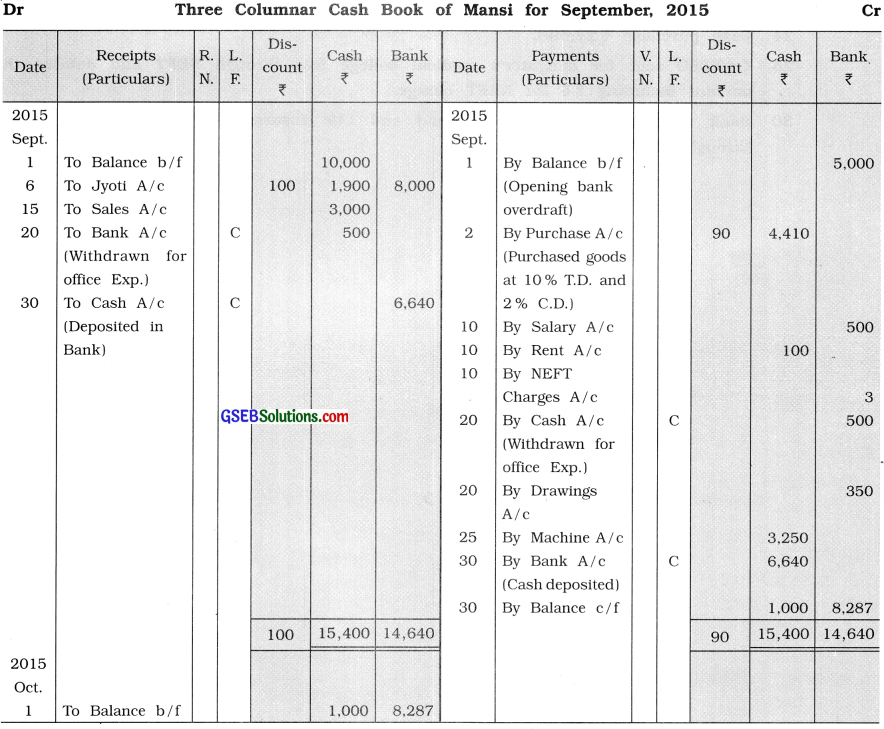
![]()
Question 16.
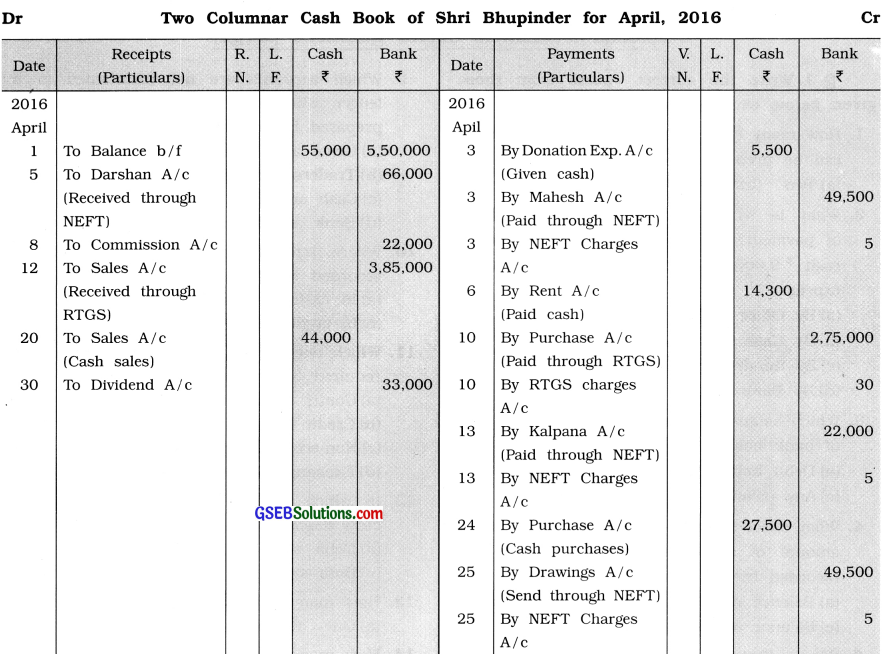
Record the following transactions in two columnar cash book of Shri Bhupinder for April, 2016 :
2016
April 1 Opening cash balance ₹ 55,000, bank balance ₹ 5,50,000.
3 ₹ 5,500 is given in donation.
3 ₹ 49,500 paid to Mahesh through NEFT for his receivables. NEFT charge is ₹ 5.
Bank debited this amount.
5 Darshan paid ₹ 66,000 through NEFT towards his debt. Bank credited the amount. Darshan paid NEFT charges ₹ 5.
6 Rent of ₹ 14,300 is paid by cash.
8 Bank credited ₹ 22,000 for commission.
10 Cash purchase ₹ 2,75,000, amount paid through RTGS. RTGS charge is ₹ 30.
12 Cash sales ₹ 3,85,000, amount is received through RTGS.
13 ₹ 22,000 paid to Kalpana towards her receivables through NEFT and NEFT charge is ₹ 5.
20 Cash sales ₹ 44,000.
24 Cash purchase ₹ 27,500.
25 ₹ 49,500 sent for daughter’s medical college fees through NEFT and debited the amount including ₹ 5 for NEFT charge.
30 Bank credited ₹ 33,000 of dividend and Life Insurance premium paid ₹ 11,000 through NEFT.
Answer: