Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Diseases Textbook Questions and Answers, Additional Important Questions, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Human Health and Diseases
GSEB Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are the various public health measures, which you would suggest as a safeguard against infectious diseases?
Answer:
Public Health Measures:
- Garbage – regularly disposed of at proper locations. Containers to be properly cleaned should be reused or recycled when applicable.
- Drainage – To be covered to prevent flies and mosquitoes. Stag nation of water near household to be removed. Slums to be cleaned.
- Water reservoirs- To be covered and periodically cleaned and disinfected.
- Sewage disposal – Properly treated before find disposal.
- Public places – To be kept clean and fogging to be done periodically.
- Pollution – Antipollution laws to be enforced strictly.
- Vaccination and medical care Periodic medical examination and vaccination to be taken properly.
- Drinking water- To be free from contamination.
- Facilities- Public toilets and bathrooms to be provided.
![]()
Question 2.
In which way has the study of biology helped us to control infectious diseases?
Answer:
The use of vaccines and immunisation programmes has enabled us to eradicate smallpox. Diseases like polio, diphtheria, tetanus, etc. have been controlled to an extent by the use of vaccines. Nowadays biotechnology is focussing on the preparation of newer and safer vaccines, A large number of antibiotics are available to treat many infectious diseases.
Question 3.
How does the transmission of each of the following diseases take place?
a. Amoebiasis
b. Malaria
c. Ascariasis
d. Pneumonia
Answer:
(a) Amoebiases – Family disposal of fecal matter causing contamination of drinking water and food. Houseflies and air current transport cysts Pet animals.
(b) Malaria – Female Anopheles inject sporozoites along with saliva
(c) Ascariasis – Food particles, dirty hands, taps, soaps etc., by faecal
(d) Pneumonia – Droplets and aerosols of an infected person.
![]()
Question 4.
What measure would you take to prevent water-borne diseases?
Answer:
- Practise personal and public hygienic measures.
- Drink clean water.
Question 5.
Discuss with your teacher what does ‘a suitable gene’ means, in the context of DNA vaccines.
Answer:
In DNA vaccines suitable gene means genes controlling the formation of immunogenic protein. Gene integrated with vectors immunize a person.
Question 6.
Name the primary and secondary lymphoid organs.
Answer:
The thymus and bone marrow are primary lymphoid organs Lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils etc. are secondary lymphoid organs.
Question 7.
The following are some well-known abbreviations, which have been used in this chapter. Expand each one to its full form.
- MALT
- CMI
- AIDS
- NACO
- HIV
Answer:
- MALT – Mucosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue
- CMI – Cell-Mediated Immunity
- AIDS – Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
- NACO – National AIDS Control Organisation
- HIV – Human Immunodeficiency Virus
![]()
Question 8.
Differentiate the following and give examples of each.
a. Innate and acquired immunity
b. Active and passive immunity
Answer:
a. The non-specific type of defense, that is present at the time of birth is called innate immunity. The resistance that an individual acquires during his life is known as acquired immunity.
b. The antibodies produced in an animal’s own body following its exposure to an antigen are called active immunity. When ready-made antibodies are directly given to protect the body against foreign agents, it is called passive immunity.
Question 9.
Draw a well-labelled diagram of an antibody molecule.
Answer:
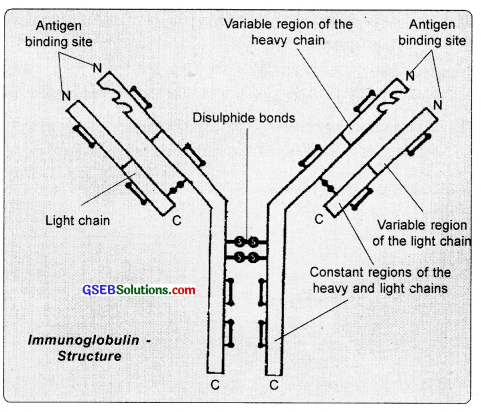
![]()
Question 10.
What are the various routes by which transmission of the human immunodeficiency virus takes place?
Answer:
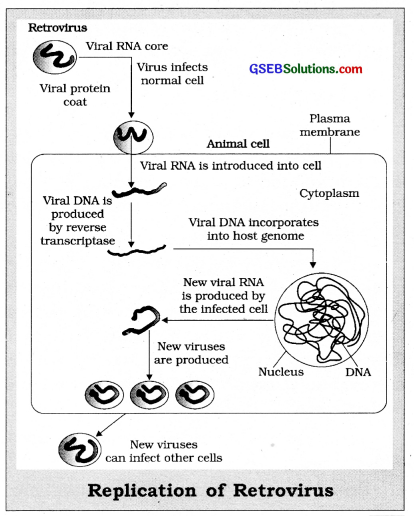
After getting into the body, the virus enters into the macrophages and converts its RNA genome into DNA with the help of a reverse transcriptase enzyme. The viral DNA takes and directs the infected cells to produce more virus particles i.e., the infected macrophages act like an HIV factory. Simultaneously, the HIV attack the T- lymphocytes and replicate and produce more viruses. Then they are released into the blood and attack other T-lymphocytes.
This will lead to a decrease in the number of T-lymphocytes and the patient begins to show the symptoms such as fever, diarrhea, weight loss etc. Subsequently, his immune system weakens and becomes more prone to infections of bacteria (like Mycobacterium), viruses, fungi, and even parasites like Toxoplasma. Finally, he is unable to protect himself.
Question 11.
What is the mechanism by which the AIDS virus causes a deficiency of the immune system of the infected person?
Answer:
Macrophages helper T-cells and some nerve cells possess T-4, OV CD-4 antigen receptor sites over their surface. HIV gets attached to this site and passes into cells. It multiplies in cells. Virus particles bud out of the cells which die afterward.
The newly released – virus particles attack new cells especially the helper T-cells. Soon the number of helper T- cells decreases. Since helper T-cells are essential for the functioning of the immune system their reduced number results in deficient functioning of the immune system of the infected person.
![]()
Question 12.
How is a cancerous cell different from a normal cell?
Answer:
Cancer cell is different from a normal cell in having
- it does not differentiate.
- It grows and disorganizes the tissue in which it occurs.
- It has a large nucleus, nucleolus, and more ribosomes.
- It loses adhesive junction with other cells.
- It has an abnormal amount of DNA and hence is genetically abnormal.
- lt shows metastasis.
Question 13.
Explain what is meant by metastasis.
Answer:
The spread of cancerous cells to distant sites is called metastasis.
Question 14.
List the harmful effects caused by alcohol/drug abuse.
Answer:
Alcoholism refers to the extreme condition in which a man is completely addicted to the evil power of alcohol. The victims are known as alcoholics. A person becomes intoxicated when the alcoholic content is about 0. 1% of his blood. Beyond this level affects thinking ability, speech, movements, reflexes etc. Further consumption leads to blurred vision, incoherent speech, loss of body balance, etc. When the level reaches 80mg/ 100 ml of blood, leads to nausea, vomiting, headache, etc. The immediate effects of alcohol abuse are manifested in the form of reckless behaviour, vandalism, and violence.
In addition to these, alcoholism may lead to
- Low to moderate doses can cause reckless behaviour, vandalism and violence depression, fatigue, weight fluctuations, etc.
- Excessive doses of drugs may lead to coma and death due to respiratory failure, heart failure, or cerebral hemorrhage.
- A combination of different drugs or alcohol mixed with drugs results in overdosing and even death.
Another misuse of drugs is the use of drugs by certain sportsperson to enhance their performance. They misuse narcotic analgesics, anabolic steroids, diuretics and certain hormones. They promote the male sexual characteristics such as growth of bones, muscles, thickening voice, hair pattern etc. They also found to increase the size and efficiency of skeletal muscles. This has led to the use of steroids by bodybuilders, weight lifters and athletes.
Now it is widespread among the athletes that affect the outcome of sports contests. The side effects of the use of anabolic steriods in females include masculinization (male-like characters), depression, abnormal menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth on the face and body, enlargement of the clitoris, thickening of voice etc. In male, the effects are mood swings, increased aggressiveness, depression, reduction in the size of testicles, decreased sperm production, kidney and liver dysfunctions, enlargement of prostate gland, breast enlargement, premature baldness etc. In adolescent male or female the prolonged use may lead to the premature closure of the growth centers of the long bones, which may result in stunted growth.
![]()
Question 15.
Do you think that friends can influence one to take alcohol/drugs? If yes, how may one protect himself/herself from such an influence?
Answer:
Education about the harmful effect of alcohol, counselling and seeking immediate professional and medical help would totally relieve the individual from the evil of taking alcohol.
Question 16.
Why is it that once a person starts taking alcohol or drugs, it is difficult to get rid of this habit? Discuss it with your teacher.
Answer:
It is difficult to get rid of this habit because these substances are addictive and one starts having unpleasant feelings or withdrawal symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shivering, muscle twitching, excessive perspiration, muscular and abdominal cramps. The mind loses control and all one can think of is taking the addictive substance. That is why resisting the temptation/pressure for the first time is the only way to avoid getting into the addictive habit and committing slow suicide.
![]()
Question 17.
In your view what motivates youngsters to take to alcohol or drugs’and how can this be avoided?
Answer:
Usually the first use of drug or alcohol may be out of curiosity or experimentation. Gradually they start this habit to escape facing problems. Generally the teenagers and youngsters fall into the habits of smoking, drinking or taking drug. One of the most effective measures to save them is to identify the situations that may push an adolescent towards the use of alcohol or drug.
GSEB Class 12 Biology Human Health and Diseases Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What do you mean by “Health’?
Answer:
Health is the state of complete physical, mental and social well-being.
![]()
Question 2.
Who is a healthy person according to you? What affects health generally?
Answer:
According to my, health is not just the absence of disease. It is the state of physical, mental, psychological and social well-being. Health is affected by many things like genetic disorders, infections, lifestyle etc. Health can be maintained by a balanced diet, personal hygiene, regular exercise and yoga.
Question 3.
Complete the following.

Answer:
a. Typhoid fever
b. Pneumonia
c. Rhinovirus
d. Wuchereria bancrofti
Question 4.
Typhoid is caused by the attack of salmonella Typhi.
a. Is this a virus or bacteria?
b. Which part of the body is affected by this disease?
c. Name the test used for the diagnosis.
d. Who is Typhoid Mary?
Answer:
a. Bacteria
b. Alimentary canal
c. Widal test
d. Mary Mallon is nicknamed as Typhoid Mary. She was a cook and was a typhoid carrier. She continued to spread typhoid for several years through the food she prepared.
![]()
Question 5.
“All pathogens are parasites” Why?
Answer:
Because they cause damage to the host body by living inside the body of the host.
Question 6.
“AIDS and cancer are caused by ignorance”. Anil said to his classmates. Do you agree with the statement?
Answer:
I can’t fully agree with the statement. This is because AIDS is caused by ignorance and cancer is caused due to mutation and the action of carcinogens.
Question 7.
Name the vectors of malaria and dengue fever?
Answer:
- Malaria fever – Female Anopheles mosquito
- Dengue fever – Female aedes mosquito
![]()
Question 8.
Taking the little amount of alcohol is good for health. Do you agree with this statement?
Answer:
Yes. The statement is true according to medical practitioners. But the danger in it is that first of all they start it as a medicine, after some days it will become a habit and the amount would increase. Then he would become addict to it. According to a proverb, “prevention is better than cure”. So don’t use alcohol even if it is good for your health.
Question 9.
Patients suffering from filariasis suffer, swelling in the lower limbs. Why?
Answer:
The filarial worm lives in the lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs, where they cause inflammation, that causes swelling of the lower, limbs.
Question 10.
What is the importance of MALT in human health and disease?
Answer:
MALT: Mucosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue is a lymphoid tissue found in the lining of the major tract such as respiratory, digestive and urinogenital tracts. The lymphoid tissues participate in the immunological action against the foreign particles entering the body.
Question 11.
Nowadays more than 40% of young people use drugs, pan masala, cigarettes etc. There is also an alarming increase in the use of psychedelic drugs by adolescents. In view of this prepare an article showing the after-effects of drug use and its social implications in the community.
Answer:
Addiction and Dependence
Drugs are habit-forming substances. They react with the nervous system affecting the individual physically and mentally. Dependence of the body on drugs due to prolonged use is known as drug addiction. Physicians prescribe drugs to cure certain diseases. Some help to fight infection. Others assist in altering mood. Drugs may be inhaled or taken orally. They may also be taken through injection.
With repeated use of drugs, the tolerance level of the receptors in our body increases. Gradually the receptors respond to the drugs only at higher doses. This will lead to high intake and addiction. If proper counselling is not provided, the victim gets addicted and becomes dependent on their use.
If a habitual user terminates taking drug, his body ceases to function normally (physical dependence). The drug addicted person finds it difficult to discontinue the use of drug since it produces adverse physiological effects, which constitute withdrawal symptoms. The withdrawal symptoms may range from mild tremors to convulsions, severe agitation and fits, depending upon the type of drug abused. Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and even life-threatening and the person needs medical help. Dependence also leads the person to ignore social commitments and adjustments.
![]()
Question 12.
Some drugs when taken for a long time cause addiction.
a. What is withdrawal symptom?
b. How can you prevent the addiction?
Answer:
a. The drug or alcohol-addicted persons find it difficult to discontinue the use of the drug since it produces adverse physiological effects. This causes restlessness and anxiety, nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, anorexia, twitches etc. This is known as withdrawal symptom.
b. Drug or alcoholic addiction can be prevented by treating them in deaddiction centres and giving them proper guidance.
Question 13.
Drugs are habit forming substances. They react with the nervous system affecting individual physically and mentally.
a. Distinguish between psychotropic drugs and psychedelic drugs.
b. Name the source of opium.
c. What do you mean by withdrawal symptoms?
Answer:
a. Psychotropic drugs act on the brain and alter the mood and powers of perception.
Psychedelic drugs give a state of relaxation and pleasure.
b. Papaver somniferun
c. The drug addicted person finds it difficult to discontinue the use of the drug since it produces adverse physiological effects and show some symptoms such as restlessness, anxiety etc. Such symptoms are known as withdrawal symptoms.
![]()
Question 14.
How can you prevent your best friend from becoming a drug addict who has started taking drug?
Answer:
Try to understand the ill effects such as deterioration of moral and cultural standards, violence, antisocial activities etc. caused by drugs. Proper advice and awareness about the drugs can save a person from becoming a drug addict.
Question 15.
What is vaccination? How does it help in producing immunity?
Answer:
The process of introducing a preparation of antigenic proteins of the pathogens or weakened or killed pathogen into the body.
- The vaccines induce quick multiplication of B and T lymphocytes, some of them are stored as memory cells.
- The B-lymphocytes quickly produce antibodies which neutralize the antigen during infection.
Question 16.
Mention a single word for the following.
a. Spread of cancer cells to a distant site.
b. Abnormal sensitivity to any substance.
c. Cancer-inducing substances.
d. Non-specific proteins preventing virus multiplication.
Answer:
a. Metastasis
b. Allergy
c. Carcinogens
d. Interferon
![]()
Question 17.
Correct the table.
| Drugs | Source |
| i. Opium | Cannabis sativa |
| ii. LSD | Papaver sominiferum |
| iii. Cocaine | Claviceps purpurea |
| iv. Charas | Erythroxylum coca |
Answer:
| Drugs | Source |
| i. Opium | Papaver sominiferum |
| ii. LSD | Claviceps purpurea |
| iii. Cocaine | Erythroxylum coca |
| iv. Charas | Cannabis sativa |
Question 18.
Identify the structure.
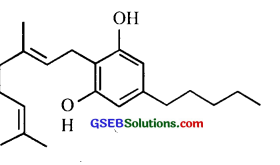
Answer:
Structure of Cannabinoid molecule
![]()
Question 19.
Why do sportspersons always caught by authorities for cocaine addiction? (CBSE2008)
Answer:
Sportspersons become addicted to cocaine because.
- Cocaine has a potent stimulating action on central nervous system.
- It produces a sense of euphoria and increased energy for performance.
Question 20.
Hints given in the following table on cancer and the tissues are wrongly arranged. Copy the table and arrange it in correct order.
| Name | Tissues |
| Carcinoma | Lymph node |
| Sarcoma | WBC |
| Melanoma | Connective tissue |
| Leukaemia | Epithelial cells |
| Lymphoma | Central nervous system |
| Glioma | Melanocytes |
Answer:
| Name | Tissues |
| Carcinoma | Epithelial cells |
| Sarcoma | Connective tissue |
| Melanoma | Melanocytes |
| Leukaemia | WBC |
| Lymphoma | Lymph node |
| Glioma | Central nervous system |
Question 21.
Cancer can be cured completely by using chemotherapy.
a. Is this statement true?
b. What is chemotherapy?
c. Name any other five types of treatment against cancer.
Answer:
a. Yes
b. Treatment of a disease by medicine
c. i. Surgery
ii. Radiation therapy
iii. Chemotherapy
iv. Hormone therapy
v. Immuno therapy
![]()
Question 22.
The diagram shows an important event taking place in an animal body.
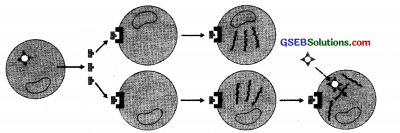
a. Identify the process.
b. What are interferons?
c. How do the interferons prevent virus multiplication?
Answer:
a. Virus multiplication prevented by interferon.
b. Interferons are non-specific proteins preventing virus multiplication.
c. The binding of interferons to the plasma membrane triggers the synthesis of several enzymes by the cell. If the cell is infected, these enzymes block the reproduction of virus and thus prevent its multiplication.
Question 23.
It is said that “Chikunguinea” once affected will not affect a person in the next half of his life. As a student of biology, can you justify this statement.
Answer:
Our body produces the T-lymphocytes against the antigen i.e., Chickun- guinea causing agent and they attack and destroy the antigen. Some of the T-cells get differentiated into memory T-cells. These cells are stored in the lymph nodes and spleen. They recognise and produce antibodies when the same attack the body a second time. This is a very rapid process. Memory T-cells have a long life. These cells are responsible for the life long immunity to certain diseases like Chikunguinea.
Question 24.
In 1974, WHO officially launched a global immunisation programme for children to protect them against six preventable diseases. The following diagram shows the vaccination of the disease.
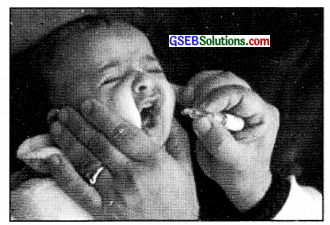
a. Name the disease.
b. Name the vaccine.
c. Mention the times for vaccination scheduled by WHO.
Answer:
a. Polio
b. OPV (Oral Polio Vaccine)
c. Yearly 2 times from birth to 2 years. But now the Government of India is giving this vaccination at free of cost yearly twice upto 5 years of age.
![]()
Question 25.
In the case of certain diseases like mumps, measles and chickenpox, the secondary immune response gives a life long immunity. Give the scientific reason behind this.
Answer:
Our body produces the T-lymphocytes against the antigen i.e., chicken pox causing agent and they attack and destroy the antigen. Some of the T-cells get differentiated into memory T-cells. These cells are stored in the lymph nodes and spleen. They recognise and produce antibodies when the same attack the body a second time. This is a very rapid process. Memory T-cells have a long life. These cells are responsible for the life long immunity to certain diseases like chicken pox, measles and mumps.
Question 26.
Copy and complete the flow chart on immunity.
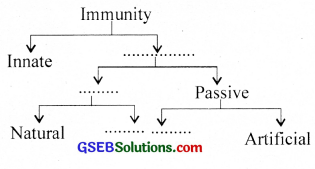
Answer:
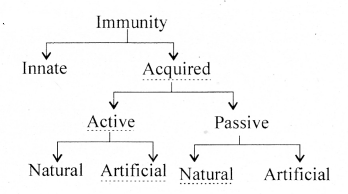
![]()
Question 27.
Copy the diagram and label the following parts.
heavy chain, light chain and specific antigen binding site.
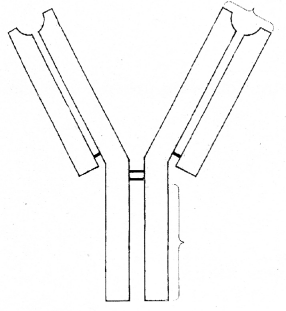
Answer:
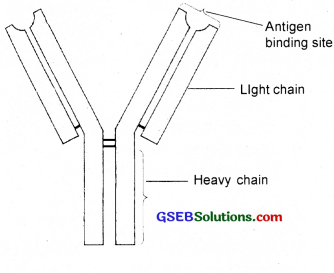
Question 28.

a. Identify the personality.
b. What are his contributions to science?
Answer:
a. Edward Jenner
b. He is considered as the father of immunology. The process of vaccination was first developed by Edward Jenner.
Question 29.
Match the following.
| Diseases | Pathogens |
| i. Ascariasis | Entamoeba histolytica |
| ii. Malaria | Wuchereria bancrofti |
| iii. Elephantiasis | Ascaris lumbricoides |
| iv. Amoebiasis | Plasmodium vivax |
Answer:
| Diseases | Pathogens |
| i. Ascariasis | Entamoeba histolytica |
| ii. Malaria | Wuchereria bancrofti |
| iii. Elephantiasis | Ascaris lumbricoides |
| iv. Amoebiasis | Plasmodium vivax |
Question 30.
Mention the types of malaria caused by the following species of plasmodium.
i. Plasmodium vivax
ii. Plasmodium malariae
iii. Plasmodium ovale
iv. Plasmodium falciparum
Answer:
| Name | Types of fever |
| Plasmodium vivax | Benign tertian, every 48 hrs |
| Plasmodium malariae | Quartan, every 72 hrs. |
| Plasmodium ovale | Mild tertian, every 48 hrs. |
| Plasmodium falciparum | Malignant, every 48 hrs. or every 24 hrs. It is often fatal |
![]()
Question 31.
Name the fungi causing ringworms in man.
Answer:
Epidermophyton, Trichophyton and Microsporum.
Question 32.
Name the causative organisms of typhoid fever. Mention the symptoms and the test which is used for detecting typhoid fever.
Answer:
Salmonella typhi.
High fever, weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache, loss of appetite. Widal test
Question 33.
For the detection of filariasis, blood is taken only between 10 pm and 5 am. Give reason.
Answer:
Microfilaria (larva of filarial parasite) comes in the peripheral circulation only during night i.e., between 10 pm and 5 am.
![]()
Question 34.
Plasmodium vivax is a digenetic parasite. Justify your answer.
Answer:
Plasmodium requires two hosts (man and mosquito) for the completion of its life cycle.
Question 35.
‘Smoking is injurious to health’. This is the slogan seen in all cigarette packets.
a. As said above “is smoking injurious to health?
b. Name the toxic alkaloid seen in it.
c. Give some consequences a smoker has to face in the future.
Answer:
a. Yes, smoking is injurious to health.
b. Nicotine
c. Refer Section 6.5 [Harmful effects of nicotine]
Question 36.
What is AIDS? Write down its causes, transmission, and symptoms.
Or
Write the name, two symptoms, and important preventive measures of today’s deadening disease spread through blood transfusion.
Or
Where is AIDS reported for the first time? Describe the causes, method of transmission, and control measures of this disease.
Answer :
AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) disease is discovered for the first time in America in the year 1981.
Causes of Disease: This disease is caused by the infection of a virus known as HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
Transmission: It is transmitted through sexual contact, homosexuality, contaminated needles, blood transfusion, drugs, artificial insemination and organ transplantation etc.
Symptoms of Disease: It is characterized by showing swollen lymph nodes, fever, loss of weight. The person loses immunity against the infection. In this disease, the number of helper T-cells are reduced.
Treatment: No suitable drug is available so far against this disease. Only anti-viral cells may increase in the number by immune stimulation method.
Control: The following measures are advised to prevent the spreading of disease :
- Providing health education and explain the hazardous effects of AIDS.
- Do not reutilize the used syringe. Throw it away or destroy it.
- The blood of donor person and organs of transplantation like kidney, liver, cornea of eyes, growth hormones would be carefully examined before use.
- Sexual contact with many people must be avoided.
![]()
Question 37.
Observe the following structure and answer the questions.
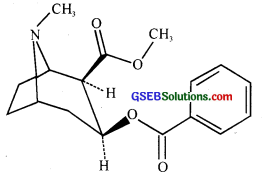
a. Identify the chemical structure.
b. Name the source.
c. Name the organ which it affects.
Answer:
a. Structure of morphine
b. Popy plant Papaver somniferum
c. Central nervous system
Question 38.
Expand ELISA.
Answer:
Enzyme Linked Immno Sorbant Assay
Question 39.
‘Human life is a battlefield.’ Justify the statement.
Answer:
Human life is a battlefield in which we, the human beings are like soldiers, attacked from all sides by dreadful organisms such as viruses, bacteria, fungi etc.
Question 40.
“It is dangerous to take drugs without prescription of a doctor at early months of pregnancy”.Comment on this statement.
Answer:
Drugs may cause a teratogenic effect
Mention about Teratogens
Rudimentary development of organs
Malformed embryo
![]()
Question 41.
A doctor noticed a small internal growth in the abdomen of a patient.
He suspected it as a cancer.
a. Which biomedical technique enabled the doctor to diagnose the disease?
b. Suggest the methods to treat this disease.
Answer:
a. Biopsy / Scanning / MRI / Sonography or any other relevant technique
b. Chemotherapy
- Surgery
- Hormone treatment
- Immune treatment
- Radiation therapy
Question 42.
A doctor detected a tumour in the body of a person. The patient feels that he would die soon due to tumour. How can you help him to overcome his fear?. Write your response.
Answer:
It was tumour, not cancer. All tumours are not so dangerous. It will not spread. It can be removed by surgery. It is the permanent treatment for tumour.
Question 43.
“The soldiers of a country kill their own king”. Similar situation takes place in our body. Find out that process.
Answer:
Auto-Immune disease
![]()
Question 44.
Mention any two measures for prevention and control of alcohol and drug abuse among adolescents.
Answer:
- Avoid undue peer pressure.
- Seek professional and medical help.
Question 45.
Given below are pairs of disease and causative organisms. Which one out of these is not a matching pair and why?
Filariasis – Wuchereria
Ringworm – Ascaris
AIDS – Human Immuno Virus
Malaria – Piasmodium
Answer:
AIDS – Human Immuno Virus. Because all the others are vector borne diseases and AIDS is spread through a virus.
![]()
Question 46.
i. In which disease is there an uncontrolled division of cells resulting in formation of tumours? How is this disease detected?
ii. How do interferons help in controlling the disease?
Answer:
i. In cancer disease there is an uncontrolled division of cells resulting in formation of tumours. Detection of cancer is done by biopsy and histopathological tests.
ii. Interferons are antiviral protein by virus infected cells. They are released from the infected cells and make the nearby uninfected cells more resistant to the viral infection.
Question 47.
What is meant by metastasis?
Answer:
Shifting of a fraction (cells) of cancerous tumour from one organ to other through blood or lymph and its translocation to other organs is called metastasis.
![]()
Question 48.
What is rehabilitation?
Answer:
Rehabilitation; The long-term treatment of addicts requires behavioral training which enables the patient to make different and useful responses to die stimuli that led him/her to drug-taking. This is called rehabilitation of a drug dependent.
Rehabilitation requires psychological and social therapy in the form of counseling by relatives, friends, and physicians They educate the patients about the ill-effects of taking drug and motivate them total drug abstinence in a sympathetic manner. The counselors should not criticize the patient for the past actions and should be affectionate and sympathetic to him/her. The measure taken to realize a drug-dependent are referred to as psychological therapy.
Vitamin administration, proper nutrition, restoration of electrolyte balance and proper hydration are necessary during the rehabilitation. These measures are aimed at process of restoring the health damaged by drug abuse. It has been noticed that the level of cyclic AMP suddenly rises in the brain of an addict who has denied the drug. It increases withdrawal symptoms. Vitamin C checks the rise in cAMP level and helps in preventing the withdrawal symptoms.