Gujarat Board GSEB Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Ex 6.2 Textbook Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Ex 6.2
Question 1.
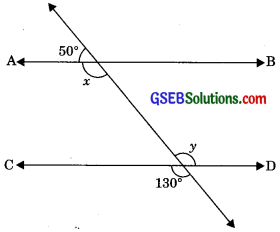
In figure, find the values of x and y and then show that AB || CD.
Solution:
x + 50° = 180° (Linear pair)
⇒ x = 180° – 50°
⇒ x = 130°
y = 130° (Vertically opposite angles)
∴ x = y (Alternate interior angles)
If alternate interior angles are equal then lines are parallel.
∴ AB || CD
![]()
Question 2.
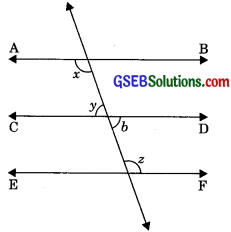
In figure, if AB || CD, CD || EF and y : z = 3 : 7, find x.
Solution:
Let y = 3a
and z = 7a
b = y (Vertically opposite angles)
CD || EF
∴ b+z = 180°
(Interior angles of same side of transversal)
⇒ y + z = 180°
⇒ 3a + 7a = 180°
⇒ 10a = 180°
a = \(\frac {180°}{10}\)
a = 18°
∴ y = 3a = 3 x 18°
⇒ y = 54°
z = 7a = 7 x 18°
2 = 126°
Now AB || CD and CD || EF
∴ AB || EF
(Lines parallel to same line are parallel to one another.)
⇒ x = z
(Alternate interior angles) x = 126°
![]()
Question 3.
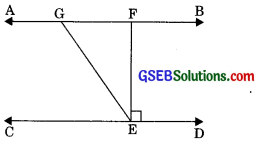
In figure, if AB || CD, EF ⊥ CD and ∠GED = 126°, find ∠AGE, ∠GEF and ∠FGE.
Solution:
We have AB || CD, EF ⊥ CD
and ∠GED = 126°
∠AGE = ∠GED (Alternate interior angles)
⇒∠AGE = 126°
Again, ∠GED = ∠GEF + ∠FED
⇒ 126° = ∠GEF + 90°
⇒ ∠GEF = 126° – 90°
⇒ ∠GEF = 36°
∠FGE + ∠GED = 180° (co-interior angles)
⇒ ∠FGE + 126° = 180°
⇒ ∠FGE = 180° – 126°
∠FGE = 54°
Question 4.
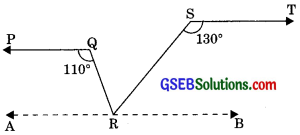
In figure, if PQ || ST, ∠PQR = 110° and ∠RST = 130°, find ∠QRS.
(Hint: Draw a line parallel to ST through point P).
 img
img
Solution:
We draw a line AB || ST through R
∠TSR + ∠SRB = 180° (Interior angles of same side of transversal)
⇒ 130° + ∠SRB = 180°
⇒ ∠SRB = 180° – 130°
⇒ ∠SRB = 50° ……….(1)
PQ || AB (Lines parallel to same line are parallel to each other)
∠PQR + ∠ARQ = 180° (Interior angles of same side of transversal)
⇒ 110° + ∠APQ = 180°
⇒ ∠ARQ = 180° – 110°
⇒ ∠ARQ = 70° ……….(2)
Now, ∠ARQ + ∠QRB = 180°
(Linear pair)
⇒ ∠ARQ + ∠QRS + ∠SRB = 180°
⇒ 70° + ∠QRS + 50° = 180°
[Putting values from eqn. (1) and (2)]
⇒ ∠QRS + 120° = 180°
∠QRS = 180° – 120° = 60°
![]()
Question 5.
In figure, if AB || CD, ∠APQ = 50° and ∠PRD 127°, find x and y.
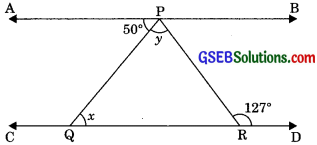
Solution:
AB || CD
then ∠APQ = ∠PQR (Alternate interior angles)
⇒ 50° = x
⇒ x = 50°
and ∠APR – ∠PRD
⇒ ∠APQ + ∠QPR = 127°
⇒ 50° + y = 127°
⇒ y= 127° – 50°
⇒ y = 77°
Question 6.
In figure, PQ and RS are two mirrors placed parallel to each other. An incident ray AB strikes the mirror PQ at B, the reflected ray moves along the path BC and strikes the mirror RS at C and again reflects back along CD. Prove that AB || CD.
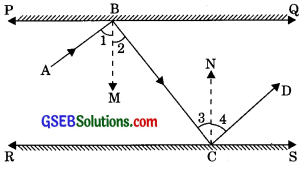
Solution:
Given: PQ || RS, incident ray AB which strikes the mirror PQ at B, and reflected ray BC which strikes the mirror RS at C and again reflects back along CD.
To Prove: AB || CD
Construction: Draw BM ⊥ PQ and CN ⊥ RS
Proof: We have BM ⊥ PQ and CN ⊥ RS
∠2 = ∠3 ………..(1)
(Alternate interior angles)
∠1 = ∠2 ……….(2)
(Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection)
∠3 = ∠4 ……….(3)
(By law of reflection, angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection)
From eqn. (1), (2) and (3)
∠1 = ∠4 ……….(4)
Adding eqn. (1) and (4)
∠1 + ∠2 = ∠3 + ∠4
∠ABC = ∠BCD (Alternate interior angles)
∴ AB || CD
(If. alternate interior angles are equal then lines are parallel).
![]()