Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Gujarat Board Class 9 Science Tissues InText Questions and Answers
Page – 69
Question 1.
What is a tissue?
Answer:
A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms?
Answer:
Multicellular organisms show division of labour. In multicellular organisms the different types of cells are specialised to form tissues which perform a specific function. This helps to carry out the various functions more efficiently as each tissue is specialised to perform a specific function.
Page – 74
Question 3.
Name types of simple tissues.
Answer:
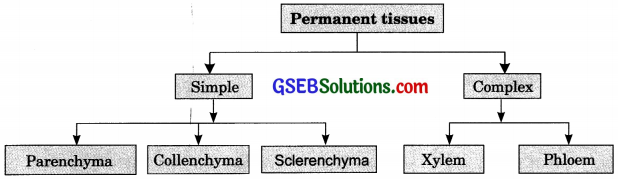
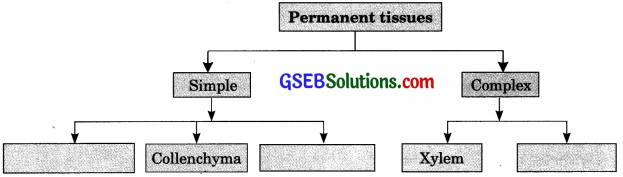
The three types of simple tissues in plants are: Parenchyma, Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma.
Question 4.
Where is apical meristem found?
Answer:
Apical meristem is found at the root tip and the shoot tip.
Question 5.
Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer:
The husk of the coconut is made up of sclerenchymatous tissue.
Question 6.
What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer:
Phloem is composed of four types of elements: sieve tubes, companion cell, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
![]()
Page – 78
Question 7.
Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer:
Muscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
Question 8.
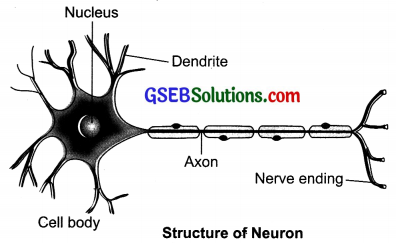
What does a neuron look like?
Answer:
The fundamental unit of our nervous system is a neuron. Neuron has three parts : dendrites, cell body and axon.
Question 9.
Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer:
The three features of cardiac muscles are:
- They are striped, cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
- They are involuntary in nature as they do not act as per our will.
- They show rhythmic contraction and relaxation.
Question 10.
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer:
Areolar connective tissue is found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow. Its functions are to:
- Fill the space inside the organs
- Support internal organs
- Help in repair of tissues.
![]()
In-Text Activities Solved
(Textbook Page 69)
Activity 6.1
Answer:
- The onion place on Jar 1 has longer roots as its roots have root tips which enable them to keep growing.
- No, the roots do not continue growing after the removal of their root tips (i.eonion kept on jar 2).
- The apical meristem which helps in the growth of the roots is present on the root tips. So, the roots are unable to grow on removal of their root tips.
(Textbook Page 70)
Activity 6.2
Answer:
- No, all the cells are not similar in structure.
- About eight types of cells can be seen.
- The various types of cells are present as they perform different roles in the plants
Meristematic cells actively divide to form new cells, some of which differentiate to perform specific function and become part of permanent tissue. The cells thus formed, perform specific function like: parenchymatous cells help in storage of food and photosynthesis; collenchymatous and sclerenchymatous cells provide mechanical support to various parts of the plant; xylem and phloem help to respectively transport water and food to various parts of the plant. Thus, various types of cells are needed to carry out the different functions of the plants in an efficient way.
(Textbook Page 72)
Activity 6.3
Answer:
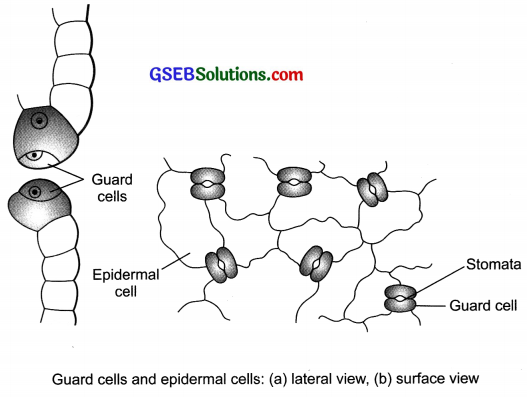
We will be able to observe that: The outermost covering is made up of a single layer of almost rectangular, compactly arranged cells. This layer is called as the epidermis. Small minute pores called stomata are visible on the epidermis of the leaf. The structure seen will be as given below:
Gujarat Board Class 9 Science Tissues Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Define the term “tissue”.
Answer:
A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue.
Question 2.
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer:
Xylem consists of four elements which are:
(a) tracheids
(b) vessels
(c) xylem parenchyma
(d) xylem fibres.
Question 3.
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer:
Simple tissues are made up of only one type of cells. There are three types – parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
Complex tissue is made up of more than one type of cells. The conducting tissues called xylem and phloem are complex tissues.
![]()
Question 4.
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer:

Question 5.
What are the functions of the stomata?
Answer:
Stomata perform the following functions in the plants:
- Exchange of gases like carbon dioxide and oxygen with the atmosphere.
- Loss of water in form of water vapour by the process called transpiration.
Question 6.
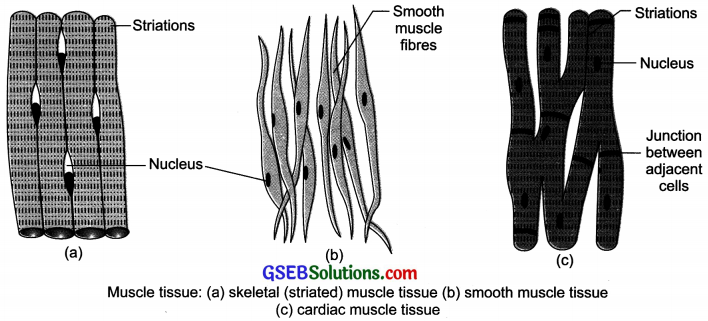
Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Answer:
Question 7.
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Answer:
Cardiac muscles are the muscles of heart which show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life.
Question 8.
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Answer:

Question 9.
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron. Answer: Nucleus
Answer:
Question 10.
Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humAnswer:
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer:
(a) Squamous epithelium
(b) Tendon
(c) Phloem
(d) Adipose tissue
(e) Blood
(f) Nervous tissue
Question 11.
Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer:
- Skin: Epithelial tissue (Stratified squamous epithelium)
- Bark of tree: Cork
- Bone: Connective tissue (skeletal tissue)
- Lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelium
- Vascular bundle: Complex permanent tissue
Question 12.
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer:
Parenchyma is present in the mesophyll of the leaves as well as the cortex and pith of stem and the roots.
Question 13.
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer:
The outermost layer of cells covering an organism is called epidermis. It is usually made up of a single layer of cells and gives protection.
The epidermis may be thicker in some plants living in dry habitats or often secrete a waxy, water- resistant layer on their outer surface called cutin (chemical substance with waterproof quality) to prevent water loss.
The stomata present on the epidermis of leaves helps in gaseous exchange and the loss of water vapour by transpiration.
The epidermal cells of roots bear root hairs that greatly increase the total absorptive surface area of the roots for absorption of water.
Question 14.
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer:
Cells of cork are dead, compactly arranged without intercellular spaces and have a chemical called suberin in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water. These features help it to act as a protective tissue.
Question 15.
Complete the table:
Answer: