Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules Textbook Questions and Answers, Additional Important Questions, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules
GSEB Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules InText Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
Glucose or sucrose are soluble in water but cyclohexane or benzene (simple six-membered ring compounds) are insoluble in water. Explain.
Answer:
Benzene and cyclohexane are neither polar nor possess – OH groups. Therefore, they are not able to form H- bonding with water molecule hence, insoluble in water. Glucose and sucrose are polar molecules. Further, they contain large number of – OH groups (five in case of glucose and eight in case of sucrose). They form extensive H-bonding with a water molecules and are thus soluble in water.
Question 2.
What are the expected products of hydrolysis of lactose?
Answer:
Lactose on hydrolysis forms an equimolar mixture of D – glucose and D – galactose.
Question 3.
How do you explain the absence of aldehyde group in the pentaacetate of D-glucose?
Answer:
When glucose (α) or (β) is treated with acetic anhydride it forms a penta acetyl derivative which does not contain a free – OH group at C – l, it cannot be hydrolysed in aqueous solution to give open-chain aldehyde form and hence glucose penta-acetate does not react with NHC2OH to form glucose oxime.
![]()
Question 4.
The melting points and solubility in water of amino acids are generally higher than that of the corresponding halo acids. Explain.
Answer:
– NH2 group present in amino acids has the ability to form intermolecular H-bonds. Thus melting points and solubility in water of amino acids are generally higher than that of the corresponding halo acids.
Question 5.
Where does the water present in the egg go after boiling the egg?
Answer:
When egg is boiled, the denaturation of protein and then coagulation takes place probably through H-bonding. Water present in the egg gets absorbed or adsorbed during denaturation and disappears. In this process, the globular protein in egg changes to insoluble fibrous protein.
Question 6.
Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body?
Answer:
Vitamin C is water-soluble and is thus readily excreted in urine and cannot be stored in our body. It is due to this reason that it must be supplied regularly in diet.
![]()
Question 7.
What products would be formed when a nucleotide from DNA containing thymine is hydrolysed?
Answer:
Hydrolysis products:
2 – deoxy – D – ribose (Sugar) + Thiamine (Base) + Phosphoric acid.
Question 8.
When RNA is hydrolysed, there is no relationship among the quantities of different bases obtained. What does this fact suggest about the structure of RNA?
Answer:
It suggests the absence of existence of complementary base pairs and that RNA has a single-strand structure.
GSEB Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are monosaccharides?
Answer:
Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones which cannot be hydrolysed to give simpler carbohydrates, example Glucose, fructose etc.
Question 2.
What are reducing sugars?
Answer:
Carbohydrates which can reduce Fehling’s solution to red precipitate of Cu2O are called reducing sugars. All monosaccharides and most of the disaccharides (except sucrose) are reducing sugars.
Question 3.
Write two main functions of carbohydrates in plants.
Answer:
- Cellulose acts as the structural material for plant cell walls.
- Starch acts as the major reserved food material in the plants.
![]()
Question 4.
Classify the following into monosaccharides and disaccharides. Ribose, 2 – deoxyribose, maltose, galactose, fructose and lactose.
Answer:
Monosaccharides : Ribose, 2 – deoxyribose, galactose, fructose Disaccharides: Maltose, lactose
Question 5.
What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage?
Answer:
The C – O – C (ether) linkage through which two monosaccharides joined to form a disaccharide is called the glycosidic linkage.
Question 6.
What is glycogen? How is it different from starch?
Answer:
Carbohydrates stored in animal body is called glycogen. It is also known as animal starch. The structure of glycogen is similar to that of amylopectin, but is highly branched and on hydrolysis with dilute acids give D-glucose.
Starch is a mixture of amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a linear polymer of α – D – glucose while amylopectin is branched. Amylopectin chains consist of 20 – 25 glucose units while glycogen consists of 10 – 14 units. Hydrolysis of starch gives dextrins of varying complexity, maltose and finally D – glucose.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the hydrolysis products of i. sucrose and ii. lactose?
Answer:
Sucrose on hydrolysis gives one molecule each of glucose and fructose while lactose on hydrolysis gives one molecule each of glucose and galactose.
Question 8.
What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose?
Answer:
Starch is a polysaccharide of α – D – glucose formed by 1 – 4 glycosidic linkage. It consists of water soluble amylose and water insoluble amylopectin. Amylose is a linear polymer of α – D – glucose and amylopectin is a branched chain polymer of α – D – glucose.
Cellulose is a polysaccharide of β – D – glucose. It is a linear polymer of β – D – glucose formed by 1 – 4 glycosidic linkage.
Question 9.
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents?
i. HI
ii. Bromine water
iii. HNO3
Answer:
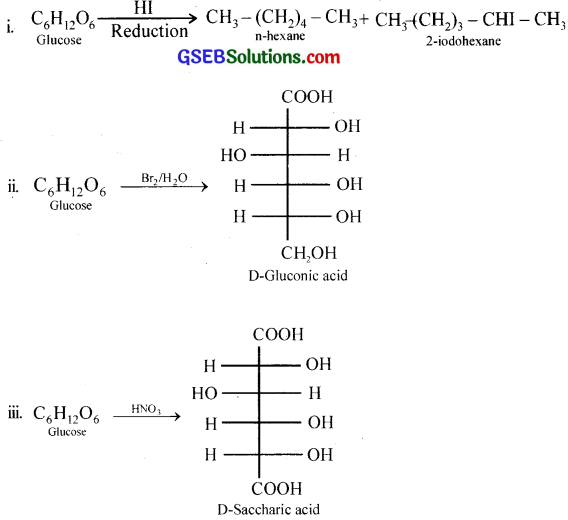
Question 10.
Enumerate the reactions of D – glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
Answer:
(i) The aldehydic group in glucose does not answer Schiff’s test and also it does not form the bisulphite addition product with NaHCO3
(ii) The penta – acetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine indicating the absence of free – CHO group.
Question 11.
What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each type.
Answer:
(i) Amino acids which cannot be synthesised by die body and must be supplied in the diet are called essential amino acids, example Valine, leucine.
(ii) The amino acids that can be synthesised from other compounds by the tissues of the body are called non-essential amino acids, example Glycine, alanine.
![]()
Question 12.
Define the following as related to proteins.
(i) Peptide linkage
(ii) Primary structure
(iii) Denaturation.
Answer:
(i) Peptide linkage: Proteins are condensation polymers of a -amino acids in which the same or different α – amino acids are connected by peptide bonds. Chemically, a peptide bond is an amide linkage formed between – COOH group of one α – amino acid and NH2 group of the other a amino acid by loss of a molecule of water.
(ii) Primary structure: Proteins may contain one or more polypeptide chains. Each polypeptide chain has a large number of α – amino acids which are linked to one another in a specific manner. The specific sequence in which the various α – amino acids present in a protein are linked to one another is called its primary structure.
(iii) Denaturation: The complex three-dimensional structure of proteins gets destroyed by changing the pH, temperature or by adding some salt. This disruption of the native structure of protein is called denaturation of protein.
Question 13.
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins?
Answer:
α – helix and β – pleated.
Question 14.
What type of bonding helps in stabilising the α – helix structure of proteins?
Answer:
The α – helix structure of proteins is stabilised by intramolecular H-bonding between C = O of one amino acid residue and the N – H of the fourth amino acid residue in the chain.
![]()
Question 15.
Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins.
Answer:
Depending on their shape and function, proteins are broadly classified into two: fibrous proteins and globular proteins.
(i) Fibrous proteins: These are thread-like molecules, lying side by side to form fibres. In fibrous proteins, the polypeptide chains are extended. They are so arranged that they intertwine with (like the strands of a rope) or lie parallel to neighbouring chains (like threads in a piece of fabric).
Fibrous proteins serve as chief structural material of animal tissue. They are insoluble in water and are chemically inactive, example Keratin in skin, hair, nails etc., myosin in muscles, fibroin in silk etc.
(ii) Globular proteins: In globular proteins, the polypeptide chain is folded, looped and twisted so that the molecules are more or less spherical. They are soluble in water and are chemically reactive. Examples are egg albumin, haemoglobin, enzymes and some hormones (e.g. insulin).
Question 16.
How do you explain the amphoteric behaviour of amino acids?
Answer:
In aqueous solution, the carboxyl group can lose a proton and amino group can accept a proton, giving rise to a dipolar ion known as zwitter ion. This is neutral but contains both positive and negative charges. In zwitter ionic form, amino acids show amphoteric behaviour as they react both with acids and bases.
Question 17.
What are enzymes?
Answer:
Enzymes are biological catalysts produced by living cells which catalyse the biochemical reactions in living organisms.
Question 18.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Answer:
During denaturation, 2° and 3° structures of proteins are destroyed but 1° structure remains intact.
Question 19.
How are vitamins classified? Name the vitamin responsible the coagulation of blood.
Answer:
Vitamins are classified into water soluble vitamins (example vitamin B – complex, vitamin C) and fat soluble vitamins (vitamin A, D, E and K). Fat soluble vitamins are stored in liver and adipose (fat storing tissue). Vitamin K is responsible for the coagulation of blood.
![]()
Question 20.
Why are vitamin A and vitamin C essential to us? Give their important sources.
Answer:
In childhood, lack of vitamin A retards growth and hence like other vitamins, it is also said to be a growth promoting factor. In mild deficiency it leads to night blindness or nyctalopia. Its prolonged deficiency leads to xerophthalmia.
Deficiency of vitamin C causes scurvy (i.e., tendency to haemorrhage). The main features of scurvy are swollen bleeding gums and bleeding into the skin and deeper tissues.
- Sources of vitamin A: Fish liver oil, carrots, butter and milk.
- Sources of vitamin C: Citrus fruits, amla and green leafy vegetables.
Question 21.
What are nucleic acids? Mention their two important functions.
Answer:
Nucleic acids are biomolecules found in the nuclei of all living cells in the form of nucleoproteins. They are of two types – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
- DNA is responsible for transmission of hereditary effects from one generation to another.
- DNA and RNA are responsible for synthesis of all proteins needed for the growth and maintenance of our body.
Question 22.
What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide?
Answer:
Each nulceotide is made up of three parts namely a sugar molecule, a heterocyclic nitrogenous base and phosphoric acid. example adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP) etc. Combination of a base with a sugar is called a nucleoside. example adenosine, deoxyadenosine etc.
![]()
Question 23.
The two strands in DNA are not identical but are complementary. Explain.
Answer:
Structure of DNA:
The three dimensional structure of DNA was elucidated by James Watson and Francis Crick in Cambridge in 1953. They proposed that a DNA chain consists of two strands of polynucleotides coiled around each other in the form of a doublehelix. The nucleotides of each strand of DNA are connected by phosphate ester bonds.
This forms the backbone of each DNA strand from which the bases extend. The bases (purines and pyrimidines) project towards each other within this structure, while the sugar and phosphate components form a structural framework on the outside of the duplex.
The bases are held by hydrogen bonding between them. The hydrogen bonding is very specific as the structures of bases are such that they permit only one mode of pairing with other bascs. For example, adenine pairs with only thymine via two hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs with cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. The other combinations are energetically less favoured and do not occur in normal DNA.
Two strands of DNA molecules are said to be complementary to each other in the sense that the sequence of bases in one strand automatically decides that of the other. This specific base pairing is the most important principle of the structure of DNA molecule. In 1962. Watson, Crick and Wilkins were awarded the Nobel Prize for this achievement.
DNA is the constituent of genetic material of the cell nucleus. It controls the synthesis of RNA and through this it guides the synthesis of proteins. It has the unique property of self replication (i.e., power to build another identical molecule) and is, therefore, responsible for maintaining heredity from one generation to another.
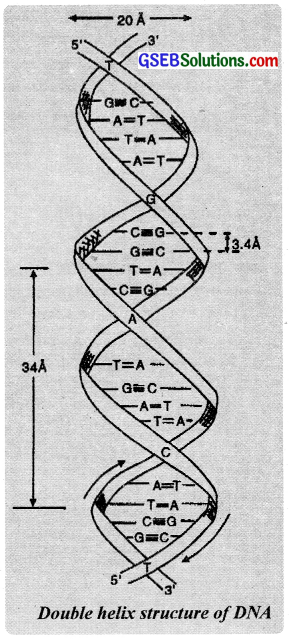
Question 24.
Write the important structural and functional differences between DNA and RNA.
Answer:
DNA:
- DNA has deoxy ribose as sugar unit.
- The bases in DNA are adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine.
- DNA nucleotide chain is a double helix.
RNA:
- RNA has ribose as sugar unit.
- Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil are the bases in RNA.
- RNA nucleotide chain is a single helix.
![]()
Question 25.
What are the different types of RNA found in the cell?
Answer:
There are three types of RNA:
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
- Messenger RNA (mRNA)
- Transfer RNA (tRNA)
GSEB Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the chemical name formula source and disease caused by Vitamin ‘C
Answer:
- The chemical name of Vitamin ‘C’: Ascorbic acid Source of Vitamin ‘C’: Green vegetables, salad, citrus fruits.
- Disease caused by Vitamin ‘C’: Scurvy, spongy and bleeding gums. The formula of Vitamin ‘C’: C6H8O6.
Question 2.
The Haworth structure of a monosaccharide sugar is drawn on a chart as follows.
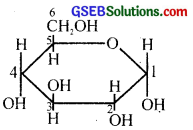
(i) Identify the compound and draw the Haworth structure of its anomer.
(ii) Explain the phenomenon of mutarotation.
Answer:
(i) α – D – (+) – glucopyranose or
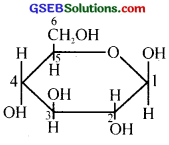
α – D – glucose
(ii) The specific rotation of aqueous solution of α – D glucose and β – D glucose gradually changes and attains a constant value when they are allowed to stand for some time. Mutarotation is due to the interconversion of α and β forms of glucose through its open-chain form and attains an equilibrium among the three forms.
Question 3.
What is Zwitter ion? Give the Zwitter ion structure of α – amino acid.
Answer:
Zwitter ions are dipolar ions formed by the transfer of H+ ions from acidic to the basic group on the same molecule. In the case of amino acids containing basic – NH2 and acidic – COOH group; H+ ion moves from – COOH group to – NH2 group to form a dipolar ion. These are called zwitterions.

Question 4.
Give the names and functions of any four proteins.
Answer:
Proteins and their functions:
- Hemoglobin: Transport of oxygen from lungs to different tissues of the body.
- Myosin: For the motion of muscles
- Pepsin: As a catalyst in biochemical reactions
- Keratin: Present in hairs, nails, and teeth.
![]()
Question 5.
What are vitamins? Name the vitamin whose deficiency causes scurvy.
Answer:
Vitamins are organic compounds which are essential for the normal growth of the body.
Vitamins are of two types
- Water-soluble vitamins example vitamin B complex
- Fat-soluble vitamins example vitamin A, vitamin E Deficiency of vitamin C causes scurvy.
Question 6.
Some vitamins and their deficiency diseases are given in the wrong order. Match them in the correct order.
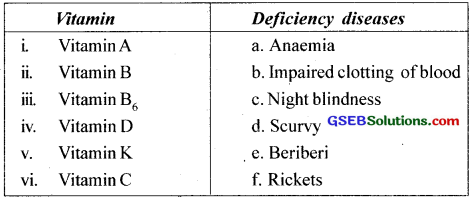
Answer:
i. c
ii. e
iii. a
iv. f
v. b
vi. d
![]()
Question 7.
What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each type.
Answer:
Essential Amino Acid: Amino acids which are not synthesized in our body but have to be taken in our food are known as an essential amino acid.
Example: Valine, Neucline, Alinine etc.
Non-essential Amino Acid: Amino acids which can be synthesized in our body are known as a non-essential amino acid.
Example: Glycine, Glutamic acid.