Gujarat Board GSEB Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 5 Forms of Business Organisation-1 Important Questions and Answers.
GSEB Class 11 Organization of Commerce and Management Important Questions Chapter 5 Forms of Business Organisation-1
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
List out the business activities a sole proprietor does.
Answer:
The proprietor alone invests capital to start and develop it and looks after all the activities like sale and purchase, marketing, inventory management, etc. He alone reaps the profit and bears the loss.
Question 2.
How can one say it is easy to establish a sole proprietorship?
Answer:
Because one need not pass through any legal hassles for establishing. Also one can start his business from any place.
Question 3.
Why a sole proprietor has complete freedom of work and ability to take quick decisions?
Answer:
The proprietor manages everything and also takes his own decision. So, he is not answerable to anyone nor he needs to wait for someone’s inputs in his decisions. Hence ……..
Question 4.
Why a sole proprietor can maintain the business secrets in the best way?
Answer:
The sole proprietor manages every work on his own. He does not need to discuss his strategies unless he wants to. Hence ………..
Question 5.
Why can a sole proprietor understand his customers and market better?
Answer:
A sole proprietor remains in direct contact with the customer, employees, market and market trends. This direct and close and constant contact helps him to understand his customers and market better.
Question 6.
How can one say that in a sole proprietorship the ownership and management will always remain centralized?
Answer:
The sole proprietor owns the business as well as manages it too. In other words, he (i.e. a single person) is only the owner and manager and so
Question 7.
State few advantages of sole proprietorship.
Answer:
Easy establishment, requires less capital, secrets are maintained, quick decision making, lesser tax, etc.
Question 8.
With respect to sole proprietorship, what does flexibility to change means?
Answer:
The proprietor can easily bring whatever change he wishes to in his business. Authority to decide solely, quick decision making and constant personal touch makes proprietorship highly flexible to change as required.
Question 9.
Why the burden of income tax is lesser in sole proprietorship?
Answer:
The business is of small scale and so one needs to pay less income tax.
Question 10.
How does limited capital affect the sole proprietorship?
Answer:
Sole proprietorship generally works on a small scale basis. Hence, it is difficult to raise large capital out of limited business turnover.
Question 11.
Why a sole proprietorship has a short life?
Answer:
In sole proprietorship if the proprietor dies, or becomes mentally unstable, or gets involved in some crime or if there is no one who can inherit the business than the proprietorship . may end. Hence …..
Question 12.
How limited capacity to work affects sole proprietorship?
Answer:
In sole proprietorship the proprietor manages everything. He neither shares his work with anyone nor he can get benefit of skills and knowledge of other persons nor can he work beyond 24 hours per day that he has. Hence, ……
Question 13.
Why there are more chances of mistakes in decisions in a sole proprietorship in a sole proprietorship firm?
Answer:
In a sole proprietorship, the proprietor manages all the works by himself. Hence he cannot take the advantage of rich experience and skills of others. As a result he may take erroneous decisions.
Question 14.
State Louis and Henry’s definition of sole proprietorship.
Answer:
Louis and Henry have defined sole proprietorship. As per them, ‘Sole proprietorship is such a form of business in which there is only one person at the top who is responsible, who directs business activities and who bears the risk of failure himself’.
![]()
Question 15.
What is an HUF and an HUF firm?
Answer:
The meaning of Hindu Undivided Family is defined by Hindu law. As per this law a family that consists of persons lineally (unbroken straight line) descending from a common ancestor is called a Hindu Undivided Family or HUF. HUF consists of father, sons, daughters and wives. The business firm held by HUF is called HUF firm or simply HUF.
Question 16.
Who heads the HUF when Karta dies?
Answer:
The eldest male member of the HUF.
Question 17.
Who becomes Karta if the original Karta dies?
Answer:
The next eldest male member of the family.
Question 18.
What is the role of members of HUF other than the Karta.
Answer:
The other family members can help the Karta in the business activities and provide their suggestions. But they cannot interfere in Karta’s works or decisions.
Question 19.
Why the liability of Karta is unlimited whereas that of other members limited?
Answer:
Karta is the head of HUF. He controls and administers the HUF. The role other members is just to help and suggest. Since Karta can be considered the whole and soul of the HUF his liability is unlimited while that of other members is limited.
Question 20.
How did the concept of partnership firm emerge?
Answer:
As the trade and commerce grew larger and larger it became difficult for the sole proprietor to handle the large business operations. Moreover, there also arose need of specialized skills and rich experience and knowledge. These factors led to the beginning of partnership.
Question 21.
What is a partnership firm?
Answer:
A business firm run by two or more persons together with the objective of sharing the profit or loss is called a partnership firm.
Question 22.
Why partnership is called a relation by agreement?
Answer:
Partnership occurs when more than one person agrees to work together through verbal or written agreement. In this sense it is said that
Question 23.
How many partners can a partnership firm have?
Answer:
Minimum 2 and maximum 10 if it is a banking business or maximum 20 if it is any other business.
Question 24.
Why social service activities or religious activities cannot be called partnership even when they are done together?
Answer:
Because the objective of such activities is not profit. The activity can be called partnership only if the objective behind it is to earn profit.
Question 25.
How can a partnership firm live even if a partner dies?
Answer:
The partners can re-distribute the share of the dead partner among themselves or admit a new partner and keep the partnership alive.
Question 26.
State few advantages of partnership firms.
Answer:
Easy and less expensive establishment procedure, efficient management, systematic decisions, increased goodwill, division of labour, etc.
Question 27.
How can we say that a partnership firm has better management compared to proprietorship?
Answer:
Unlike proprietorship, there are more than one owners of the partnership firm. Due to this there exists sharing of intelligence, knowledge, skills and experience among partners. The partners take personal interest and care in managing and controlling the business and so . the efficiency of partnership firm is higher.
Question 28.
How does having a partnership increase the goodwill of the firm?
Answer:
In partnership firm, all the partners have unlimited liability to pay-off business debts. This creates a positive impact on creditors or vendor’s mind. They do not hesitate to sell goods on credit or lend money knowing that if one of the partners fails to pay back the other will have to pay anyhow.
Question 29.
How is division of labour achieved in partnership firm?
Answer:
Partners can divide the works among themselves based on their skills and experience and obtain the benefit of division of labour.
![]()
Question 30.
How is decentralization of power partnership firm? OR How can decentralized power of funds help a partnership firm from financial crisis?
Answer:
In a partnership firm the power to control the achieved in funds of the company lies with all the partners, This helps to mobilize the funds better and to stop a partner from making wrong monetary decision. This safeguards the firm against financial crises.
Question 31.
How can disagreement among partners affect the partnership firm?
Answer:
Disagreement among partners may result in delayed decisions, poor marketing plans, poor morale, etc. and hence affect the firm badly.
Question 32.
Name the various types of partners a partnership firm can have.
Answer:
- Active partner
- Sleeping partner
- Nominal partner,
- Partner in profit only
- Partner by estopple or holding out
- Minor partner
Question 33.
Who is an active partner?
Answer:
According to Partnership Act a person who becomes a partner in the firm through partnership deed invests capital in the firm, shares profit and loss, and works actively in managing the business is called an active partner.
Question 34.
Who is a sleeping partner?
Answer:
A person who becomes the partner in the firm through partnership deed invests capital, bears loss of profit but does not play an active role in managing the business is called a sleeping or dormant partner.
Question 35.
What benefit does a nominal partner get out of partnership?
Answer:
The partnership pays fees to the nominal partner for his name.
Question 36.
Who is called a partner in profit only? Why is he made a partner?
Answer:
A partner who shares only the profits without being liable for the losses is known as partner in profit only. Such a person is made a partner only to take advantage of his special skills, knowledge and rich experience. Such partner may or may not invest his capital in the firm.
Question 37.
Question 46.
State the major types of partnerships.
Answer:
(A) Partnership according to time limit
(B) According to time limit
(C) According to business and
(D) According to registration.
Question 38.
State the types of partnership according to time limit.
Answer:
- Voluntary partnership firm
- Partnership for a fixed time
- Partnership for a specific work.
Question 39.
State the types of partnership according to liability.
Answer:
- Partnership firm with limited liability and
- Partnership firm with unlimited liability.
Question 40.
Name the types of partnership according to the business type.
Answer:
- Banking firm and
- General firm.
Question 41.
Name the types of partnership firm according to the registration.
Answer:
- Registered partnership firm and
- Unregistered partnership firm.
Question 42.
What is a voluntary partnership firm (partnership at will)?
Answer:
A partnership where in no duration is mentioned in the partnership deed is called partnership at will. This means that the life or existence of the partnership depends on the will of the partners. They can continue the partnership as long as they remain united.
![]()
Question 43.
Define partnership for a fixed time.
Answer:
When the duration of the partnership is mentioned in the agreement it is called partnership for a fixed time. Once the duration is completed, the partnership dissolves automatically. However, if the partners wish to extend the duration they can.
Question 44.
Define partnership for a specific work.
Answer:
A partnership done to accomplish a specific work such as building a bridge, completing a project, etc. is called a partnership for specific work. As soon as the work gets over, the partnership dissolves automatically.
Question 45.
What is partnership with limited liability?
Answer:
A partnership firm where in one partner is allowed to have limited liability and all remaining partners have unlimited liability is called a partnership with limited liability
Question 46.
What do you mean by banking partnership firm? How many partners it can have?
Answer:
A partnership firm that accepts deposits from public and as per specific conditions lend money to the customers is called a banking firm. A banking firm has minimum 2 partners and maximum lo partners.
Question 47.
What is a general partnership firm? How many partners it can have?
Answer:
A partnership firm created for any legal activity other than banking is called a general partnership firm. This firm can have minimum 2 partners and maximum 20.
Question 48.
What is a registered partnership firm?
Answer:
A partnership which is registered with the Registrar of Firms is called a registered partnership firm.
Question 49.
What is an unregistered partnership firm?
Answer:
A partnership firm which is not registered with the Registrar of Firms is called an unregistered partnership firm.
Question 50.
How can a partnership firm get registered?
Answer:
As per the Partnership Act, 1932, the partners need to fill a registration form, sign it and submit it along with the registration fees at the office of the Registrar of Firms. The registrar than studies the documents and form submitted by the partners and registers it.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How did the need of various (forms) types of business organization arise?
Answer:
- Man first learned to produce food grains and vegetables to satisfy his daily needs. When he produced more than be needed he started exchanging his produce with others who produced different things. This was called barter system. Barter system can be considered as the first form of trade. This is how man became trader.
- Man used to trade several things against each other like cloth against gold, grains against spices, etc. Finally, when currency was invented he started exchanging products against currency. This gave rise to a systematic form of trading business.
- An entire class of people called traders emerged in society who used to trade to satisfy needs of people for various products. These traders can also be called sole proprietors because they handled the trading activity all alone. As time passed people started establishing various types of business firms based on their needs. This gave rise to sole proprietorship, partnership, Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), co-operative society joint stock companies, etc.
Question 2.
What is a sole proprietorship? Explain.
Answer:
Sole proprietorship:
- A form of business in which the business firm is owned, managed and controlled by only one person is called a sole proprietorship and the person is called proprietorship or sole proprietor.
- According to Louis and Henry, sole proprietorship is such a form of business in which there is only one person at the top who is responsible, who directs business activities and who bears the risk of failure himself.
- From the above definition one can conclude that a lone trader or a sole proprietor is only and wholly responsible for the entire business and that the entire business is carried out under his direction. He alone enjoys the profit and is responsible for loss in business or insolvency.
- The proprietor alone invests capital to start and develop it and looks after all the activities like sale and purchase, marketing, inventory management, etc. He alone reaps the profit and bears the loss.
Example:
Generally, grocery stores, sweet shops, food joints, small trading firm, etc. run as sole proprietorship firms.
Question 3.
Explain the advantages of sole proprietorship.
Answer:
Advantages of soie proprietorship:
1. Easy establishment process:
- One can easily start a sole proprietorship without any documents or passing from any complex laws and procedures.
- Any person, educated or illiterate but having general capabilities can start a proprietorship with minimal capital.
2. Less capital:
Since the proprietorship can be set up even with very less capital it is a very important characteristic and special advantage. Moreover, in case the business needs more capital, the proprietor can even borrow it.
3. Maintenance of secrets:
It is extremely important for a business to maintain its trade secrets. Since the proprietorship is entirely owned and managed by a single person the business secrets can be very well maintained. This again is a special advantage which is difficult to obtain in other forms of business.
4. Quick decisions:
Since the entire business is owned by a single person quick decisions can be made as per the changes in market, demands consumer preference, etc. Such quick decisions helps to save business and even grow faster.
5. Personal contact:
- The reach of a sole proprietorship is generally not very far. Hence, the proprietor is able to maintain personal contact with customers, vendors, etc. This helps him
to understand the customers, employees, creditors, etc. better, serve them as per their taste, fashion and demand, etc. and keep them satisfied. - Based on the opinions of customers and employees he gathers through personal contact he can even change the product or production method or distribution system, etc. and keep the business safe and sound.
6. Flexibility:
The proprietor can easily bring whatever change he wishes to in his business. Authority to decide solely, quick decision making and constant personal contact makes proprietorship highly flexible to change as required,
7. Less burden of tax:
- The income of sole proprietorship can be considered as the income of the owner. Hence, the proprietor falls into the bracket of personal rate of income tax which is lower than other business forms.
- Moreover, generally the sole proprietorship is not very large and so the burden of income tax is also less.
8. Less legal restrictions:
Compared to other business forms there are lesser regulatory and legal controls on the proprietorship firm. The proprietor does not need to take approval from anyone for making changes in his business methods increase or decrease capital etc. Moreover, since the business is small, regulatory controls are also less.
![]()
Question 4.
List and explain the limitations of sole proprietorship.
Answer:
Limitations of sole proprietorship:
1. Limited capital:
- Generally, it is difficult for a sole proprietorship to raise large capital.
- After industrial revolution and with advent of e-commerce the size of businesses have grown and is growing. In such cases it becomes almost impossible for the owners to raise large capital, large space or purchase machinery, raw materials, etc. in larger quantity. As a result, business may not grow much.
2. Unlimited liability:
Sole proprietors cannot free themselves from business liabilities. If their borrowings exceeds their business profits and the proprietors are unable to pay, they will even have to sell their personal assets to repay business debts. In this sense the proprietors have unlimited liability.
3. Short duration:
If the proprietor becomes insolvent or dies or faces some unforeseen event like loss of mental balance or gets involved in some crime, the existence of business comes in danger. In such situations if there are no inheritors of the proprietors or if they do not possess the knowledge to run the business, the business may become weak or even shut down.
4. Limited capacity to work:
- In proprietorship the owner does everything. He formulates policies, he manages funds, he sells and he markets.
- It is a known fact that an individual has got only 24 hours per day to work and a limited set of skills and preferences towards works. Even if the proprietor is highly efficient he will have limited time and knowledge.
- The sole proprietor may lose out the benefit of skills possessed by other persons, opinions and suggestions, etc. and so the growth of business may be limited.
5. Possibility of wrong decisions:
All the decisions are taken by the proprietor himself. Hence, he does not have the advantage to take help of rich experience and specialized knowledge possessed by others in their own fields.
This may result in mistakes in business decisions.
6. Lack of advantages of large scale business:
The proprietorship firm generally works on a smaller scale with limited capital and skills. Under such circumstances the businessman cannot get the advantage of large volume or large scale business to earn large profits.
Question 5.
How do owner and management remain centralized in sole proprietorship?
Answer:
Less legal restrictions:
Compared to other business forms there are lesser regulatory and legal controls on the proprietorship firm. The proprietor does not need to take approval from anyone for making changes in his business methods increase or decrease capital etc. Moreover, since the business is small, regulatory controls are also less.
Question 6.
Why is the burden of income tax lesser in sole proprietorship?
Answer:
Less burden of tax:
- The income of sole proprietorship can be considered as the income of the owner. Hence, the proprietor falls into the bracket of personal rate of income tax which is lower than other business forms.
- Moreover, generally the sole proprietorship is not very large and so the burden of income tax is also less.
Question 7.
‘Limited capital hinders growth’. Explain the statement with reference to sole proprietorship.
Answer:
Limited capacity to work:
- In proprietorship the owner does everything. He formulates policies, he manages funds, he sells and he markets.
- It is a known fact that an individual has got only 24 hours per day to work and a limited set of skills and preferences towards works. Even if the proprietor is highly efficient he will have limited time and knowledge.
- The sole proprietor may lose out the benefit of skills possessed by other persons, opinions and suggestions, etc. and so the growth of business may be limited.
Question 8.
Why a sole proprietorship firm may be short lived?
Answer:
Short duration:
If the proprietor becomes insolvent or dies or faces some unforeseen event like loss of mental balance or gets involved in some crime, the existence of business comes in danger. In such situations if there are no inheritors of the proprietors or if they do not possess the knowledge to run the business, the business may become weak or even shut down.
Question 9.
What do you mean by a Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)?
Answer:
The meaning of Hindu Undivided Family is defined by Hindu law. As per this law a family that consists of persons lineally (unbroken straight line) descending from a common ancestor is called a Hindu Undivided Family or HUF. HUF consists of father, sons, daughters and wives. The business that the HUF does is called HUF firm. Only male members are considered part of HUF firm.
![]()
Question 10.
Why is it difficult to raise funds in HUF firm?
Answer:
Difficulty in raising funds:
The success of an HUF firm depends on the efficiency of the Karta. The firm depends on the Karta and family members for raising the funds needed to run the business. In such cases since the fund is to be raised by family members only it might be difficult to raise a good amount of capital.
Question 11.
How did the concept of partnership form of business come into existence?
Answer:
- Sole proprietorship firm has limitations of unlimited responsibility on the proprietor, difficult to raise more capital, invest in buying large space and doing business at a larger scale. These limitations limit the span of the business.
- On the other hand, with time trade and commerce got bigger and bigger.
- To divide the responsibilities, avail more capital, skills, administrative powers and risk bearing capacity, establish business at a large scale and overcome the limitations of sole proprietorship, came the concept of partnership where in more than one person owns and manages the firm.
Question 12.
State the purpose of a partnership firm.
Answer:
Purpose of partnership firm:
- The main objective of a partnership firm is to earn profit by doing activities that are legally permitted.
- Activities such as social service managing religious programmes or tasks though done together cannot be called partnership because the objective of profit does not exist in such cases.
Question 13.
Explain the advantages of a partnership firm.
Answer:
Advantages of a partnership firm:
1. Easy and less expensive process of establishment:
- The process of establishing a partnership firm is quite easy and cheap. One also need not pass through lengthy and complex legal procedures.
- In fact as per the Partnership Act, one can even run a partnership without registering it however it is always advisable to register.
2. Efficient management:
Unlike proprietorship, there are more than one owners of the partnership firm. Due to this there exists sharing of intelligence, knowledge, skills and experience among partners.
The partners take personal interest and care in managing and controlling the business and so the efficiency of partnership firm is higher.
3. Increase in goodwill/credit worthiness:
In partnership firm, all the partners have unlimited liability to pay-off business debts. This creates a positive impact on creditors or vendor’s mind. They do not ‘ hesitate to sell goods on credit or lend money knowing that if one of the partner fails to pay back the other will have to pay anyhow. This increases the goodwill or credit of the firm compared to sole proprietorship.
4. More capital:
A partnership consists of more than one owner and so more capital can be raised collectively.
Moreover, when the business expands and one needs more capital than it can be done by adding a new partner.
5. Advantage of division of labour:
Partners can divide the works among themselves based on their skills and experience and obtain the benefit of division of labour.
6. Systematic decisions:
At the time of taking an important decision the partners gather and discuss it thoroughly. They share their experience, knowledge and opinions with respect to the decision. When everyone agrees and come to a common conclusion a decision is made.
Thus, in partnership firms there are quite less chances of wrong decisions.
7. Flexibility:
A partnership firm is formed by the voluntary agreement of each partner. So, it is easy to make changes in the business as per the situation. For example, as per the changing market environment the partners can change their products or processes after thoughtful discussions among themselves.
8. Protection to the interests of minority:
Generally in a partnership firm all the works are done with mutual consent of all the partners. So, even if one partner disagrees the firm may not be able to execute a desired work or a decision. Moreover, a partner who does not wish to continue with the firm can ask for dissolving the partnership.
In these senses we can say that in a partnership firm the interests of minority also get protection and are taken care of.
9. Direct relations with customers:
Just like sole proprietorship, the partners of the partnership firm remains in contact with their customers, employees, vendors, etc. Hence, they can take good care of their needs and expectations.
10. Decentralization of economic power:
In a partnership firm the power to control the funds of the company lies with all the partners. This helps to mobilize the funds better and to stop a partner from making wrong monetary decision. This safeguards the firm against financial crises.
11. Less burden of income tax:
The profit of the firm gets divided among the partners as decided in the deed. So, the income tax liability also gets divided among partners and they are less burdened.
Question 14.
How does a partnership firm helps to increase goodwill?
Answer:
Increase in goodwill/credit worthiness:
In partnership firm, all the partners have unlimited liability to pay-off business debts. This creates a positive impact on creditors or vendor’s mind. They do not ‘ hesitate to sell goods on credit or lend money knowing that if one of the partner fails to pay back the other will have to pay anyhow. This increases the goodwill or credit of the firm compared to sole proprietorship.
Question 15.
A partnership firm takes better decision. Give reason.
Answer:
Systematic decisions:
- At the time of taking an important decision the partners gather and discuss it thoroughly. They share their experience, knowledge and opinions with respect to the decision. When everyone agrees and come to a common conclusion a decision is made.
- Thus, in partnership firms there are quite less chances of wrong decisions
Question 16.
Decentralized power of funds saves a partnership firm. Explain.
Answer:
Decentralization of economic power:
In a partnership firm the power to control the funds of the company lies with all the partners. This helps to mobilize the funds better and to stop a partner from making wrong monetary decision. This safeguards the firm against financial crises.
Question 17.
How many types of partners can a partnership firm have? Name them.
Answer:
A partnership firm can consist of six types of partner. They are:
- Active partner
- Sleeping partner
- Nominal partner
- Partner in profit only
- Partner by estopple or holding out
- Minor partner
Question 18.
Name the types of partners a partnership firm can have and explain their roles and duties in the firm.
Answer:
Types of partners a firm can have and their duties and roles are explained below.
1. Active partner:
- According to Partnership Act, a person who becomes a partner in the firm through partnership deed, invests capital in the firm, shares profit and loss, and works actively in managing the business is called an active partner.
- The active partner is considered as the agent of the firm for the purpose of business activities of the firm.
2. Sleeping/Dormant partner:
- A person who becomes the partner in the firm through partnership deed invests capital, bears loss of profit but does not play an active role in managing the business is called a sleeping or dormant partner. Just like the active partners, the liability of the sleeping partner is also unlimited.
- People who wish to have capital and cannot raise on their own often invites people to join the firm as sleeping partner.
3. Nominal partner:
- Sometimes a business firm aspires to grow quickly in the fast growing competitive market. The firm members then approach such a person who holds a strong influence and reputation in the market to become a partner in their firm. Such a partner neither invests capital nor plays an active role in the management but allows the partnership firm to use his name and influence for credibility, growth and expansion. Such a partner is called a nominal partner.
- The nominal partner gets a fees for this service and like other partners has unlimited liability.
4. Partner in profit only:
A partner who shares only the profits without being liable for the losses is known as partner in profit only.
Such a person is made a partner only to take advantage of his special skills, knowledge and rich experience. Such partner may or may not invest his capital in the firm.
5. Partner by estopple or holding out:
- A person who does not signs the partnership deed, does not bring capital and does not share the profit or loss in the firm but permits himself to be represented as a partner and behaves as a partner is called a partner by holding out or estopple partner.
- When a third party due to goodwill of such person (estopple partner) believes that the person sitting in the firm is a partner and transacts with the firm then the – liability of that partner becomes unlimited too.
6. Minor partner:
- According to the Partnership Act only an adult can sign a partnership deed and become a partner. However, at times the partnership firm for its own benefit can make a minor a temporary partner of the firm. For example , if a partner dies his child can be made a minor partner.
- Such minor partner has the right to share the profit of the firm but does not have liability to pay for the business loss. Creditors cannot claim to recover loss from the assets of minor partner.
- When the minor partner becomes adult he can become the partner of the firm if he desires to.
![]()
Question 19.
What do you mean by an active partner? Explain.
Answer:
Active partner:
- According to Partnership Act, a person who becomes a partner in the firm through partnership deed, invests capital in the firm, shares profit and loss, and works actively in managing the business is called an active partner.
- The active partner is considered as the agent of the firm for the purpose of business activities of the firm.
Question 20.
Who is a sleeping (dormant) partner? Explain.
Answer:
Sleeping/Dormant partner:
- A person who becomes the partner in the firm through partnership deed invests capital, bears loss of profit but does not play an active role in managing the business is called a sleeping or dormant partner. Just like the active partners, the liability of the sleeping partner is also unlimited.
- People who wish to have capital and cannot raise on their own often invites people to join the firm as sleeping partner.
Question 21.
Explain – Nominal partner.
Answer:
Nominal partner:
- Sometimes a business firm aspires to grow quickly in the fast growing competitive market. The firm members then approach such a person who holds a strong influence and reputation in the market to become a partner in their firm. Such a partner neither invests capital nor plays an active role in the management but allows the partnership firm to use his name and influence for credibility, growth and expansion. Such a partner is called a nominal partner.
- The nominal partner gets a fees for this service and like other partners has unlimited liability.
Question 22.
Explain partner in profit only.
Answer:
Partner in profit only:
A partner who shares only the profits without being liable for the losses is known as partner in profit only.
Such a person is made a partner only to take advantage of his special skills, knowledge and rich experience. Such partner may or may not invest his capital in the firm.
Question 23.
What do you mean by partner by estopple or holding out?
Answer:
Partner by estopple or holding out:
- A person who does not signs the partnership deed, does not bring capital and does not share the profit or loss in the firm but permits himself to be represented as a partner and behaves as a partner is called a partner by holding out or estopple partner.
- When a third party due to goodwill of such person (estopple partner) believes that the person sitting in the firm is a partner and transacts with the firm then the – liability of that partner becomes unlimited too.
Question 24.
Who is a minor partner? Explain.
Answer:
Minor partner:
- According to the Partnership Act only an adult can sign a partnership deed and become a partner. However, at times the partnership firm for its own benefit can make a minor a temporary partner of the firm. For example , if a partner dies his child can be made a minor partner.
- Such minor partner has the right to share the profit of the firm but does not have liability to pay for the business loss. Creditors cannot claim to recover loss from the assets of minor partner.
When the minor partner becomes adult he can become the partner of the firm if he desires to.
Question 25.
Classify the various types of partnership firm.
Answer:
Types of partnership firm
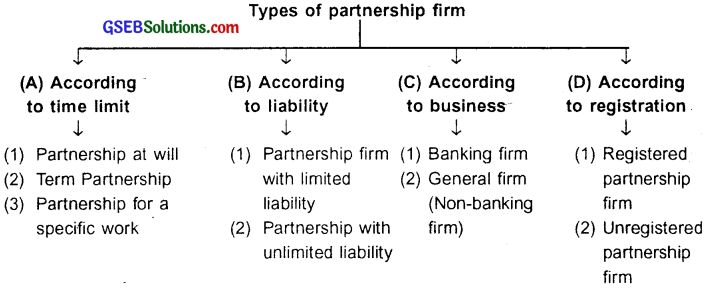
Question 26.
State and explain the various types of partnership firm.
Answer:
The types of partnership firm and their explanation is given below,
(A) Partnership according to time limit.
1. Partnership at will:
- A partnership where in no duration is mentioned in the partnership deed is called partnership at will. This means that the life or existence of the partnership depends on the will of the partners. They can continue as long as they remain united.
- If any of the partner wishes to dissolve the firm then he can do so by giving a legal notice to dissolve the firm.
2. Term partnership:
When the duration of the partnership is mentioned in the agreement it is called partnership for a fixed time.
Once the rturation is completed, the partnership dissolves automatically. However, if the partners wish to extend the duration they can.
3. Partnership for a specific work:
- A partnership done to accomplish a specific work such as building a bridge, compl eting a project, etc. is called a partnership for specific work.
- As soon as the work gets over, the partnership dissolves automatically.
(B) Partnership according to liability:
- Partnership with limited liability: It partnership firm where in one partner is allowed to have limited liability and all remaining partners have unlimited liability is called a partnership with limited liability. This is a special type of partnership.
- Partnership firm with unlimited liability: The partnership firm in which the liability of each member is unlimited is called a partnership firm with unlimited liability.
(C) Partnership according to business:
1. Banking firm:
- A partnership firm that accepts deposits from public and as per specific conditions lend money to the customers is called a banking firm.
- A banking firm has minimum 2 partners and maximum 10 partners.
2. General (Non-banking) firm:
- A partnership firm created for any legal activity other than banking is called a general partnership firm.
- This firm can.have minimum 2 partners and maximum 20.
(D) Partnership according to registration:
1. Registered partnership firm:
- A partnership which is registered with the Registrar of Firms is called a registered partnership firm. It is not compulsory to register a partnership firm but it is advisable to do so.
- A registered firm can go to court of law to solve disputes and to recover debts from a third party/person.
2. Unregistered partnership firm:
- A partnership firm which is not registered with the Registrar of Firms is called an unregistered partnership firm.
- It is difficult for an unregistered firm to recover its debts from third party by going to court of law.
Question 27.
Explain partnership at will.
Answer:
Partnership at will:
- A partnership where in no duration is mentioned in the partnership deed is called partnership at will. This means that the life or existence of the partnership depends on the will of the partners. They can continue as long as they remain united.
- If any of the partner wishes to dissolve the firm then he can do so by giving a legal notice to dissolve the firm.
Question 28.
Explain term partnership.
Answer:
Term partnership:
When the duration of the partnership is mentioned in the agreement it is called partnership for a fixed time.
Once the rturation is completed, the partnership dissolves automatically. However, if the partners wish to extend the duration they can.
Question 29.
Explain partnership for a specific work.
Answer:
Partnership for a specific work:
- A partnership done to accomplish a specific work such as building a bridge, compl eting a project, etc. is called a partnership for specific work.
- As soon as the work gets over, the partnership dissolves automatically
Question 30.
Write a short note on partnership according to time limit.
Answer:
Partnership according to time limit.
1. Partnership at will:
- A partnership where in no duration is mentioned in the partnership deed is called partnership at will. This means that the life or existence of the partnership depends on the will of the partners. They can continue as long as they remain united.
- If any of the partner wishes to dissolve the firm then he can do so by giving a legal notice to dissolve the firm.
2. Term partnership:
When the duration of the partnership is mentioned in the agreement it is called partnership for a fixed time.
Once the rturation is completed, the partnership dissolves automatically. However, if the partners wish to extend the duration they can.
3. Partnership for a specific work:
- A partnership done to accomplish a specific work such as building a bridge, compl eting a project, etc. is called a partnership for specific work.
- As s oon as the work gets over, the partnership dissolves automatically.
![]()
Question 31.
Write a short note on partnership according to liability.
Answer:
Partnership according to liability:
- Partnership with limited liability: partnership firm where in one partner is allowed to have limited liability and all remaining partners have unlimited liability is called a partnership with limited liability. This is a special type of partnership.
- Partnership firm with unlimited liability: The partnership firm in which the liability of each member is unlimited is called a partnership firm with unlimited liability.
Question 32.
Explain partnership with limited liability.
Answer:
Partnership with limited liability:
It partnership firm where in one partner is allowed to have limited liability and all remaining partners have unlimited liability is called a partnership with limited liability. This is a special type of partnership.
Question 33.
Explain partnership firm with unlimited liability.
Answer:
Partnership firm with unlimited liability:
The partnership firm in which the liability of each member is unlimited is called a partnership firm with unlimited liability.
Question 34.
Explain banking as a partnership firm.
Answer:
Banking firm:
- A partnership firm that accepts deposits from public and as per specific conditions lend money to the customers is called a banking firm.
- A banking firm has minimum 2 partners and maximum 10 partners.
Question 35.
Write a short note on partnership firm according to the type of business.
Answer:
Partnership according to business:
1. Banking firm:
- A partnership firm that accepts deposits from public and as per specific conditions lend money to the customers is called a banking firm.
- A banking firm has minimum 2 partners and maximum 10 partners.
2. General (Non-banking) firm:
- A partnership firm created for any legal activity other than banking is called a general partnership firm.
- This firm can.have minimum 2 partners and maximum 20.
Question 36.
State the types of partnership according to the registration.
Answer:
Partnership according to registration:
1. Registered partnership firm:
- A partnership which is registered with the Registrar of Firms is called a registered partnership firm. It is not compulsory to register a partnership firm but it is advisable to do so.
- A registered firm can go to court of law to solve disputes and to recover debts from a third party/person.
2. Unregistered partnership firm:
- A partnership firm which is not registered with the Registrar of Firms is called an unregistered partnership firm.
- It is difficult for an unregistered firm to recover its debts from third party by going to court of law.
Question 37.
What is a registered partnership firm? Explain.
Answer:
Registered partnership firm:
- A partnership which is registered with the Registrar of Firms is called a registered partnership firm. It is not compulsory to register a partnership firm but it is advisable to do so.
- A registered firm can go to court of law to solve disputes and to recover debts from a third party/person.
Question 38.
How can a partnership firm get registered? List out the details to be furnished while registering a partnership firm.
Answer:
- A partnership firm can be registered as per the Partnership Act, 1932.
- It is not compulsory to register a firm but always advisable to do so.
- The state government appoints a Registrar of Firms in the state under whom a partnership firm can get registered.
- The partners need to fill a registration form and then all of them need to sign it and submit it to the registrar along with the registration fees.
Details to fill in the registration form:
- Name and address of the firm
- Branches of the firm
- Name, addresses and telephone numbers of all the partners
- Date of admission of each partner in the firm
- The ratio of profit and loss of each partner
- Details regarding the capital invested by each partner
- Duration of the partnership firm
Once the form is submitted, the registrar studies all the details and issues a certificate of registration.
Question 39.
List out the details one need to fill in the registration form for registering a partnership firm.
Answer:
- A partnership firm can be registered as per the Partnership Act, 1932.
- It is not compulsory to register a firm but always advisable to do so.
- The state government appoints a Registrar of Firms in the state under whom a partnership firm can get registered.
- The partners need to fill a registration form and then all of them need to sign it and submit it to the registrar along with the registration fees.
Details to fill in the registration form:
- Name and address of the firm
- Branches of the firm
- Name, addresses and telephone numbers of all the partners
- Date of admission of each partner in the firm
- The ratio of profit and loss of each partner
- Details regarding the capital invested by each partner
- Duration of the partnership firm
Once the form is submitted, the registrar studies all the details and issues a certificate of registration.
Question 40.
Differentiate between partnership firm and HUF firm.
Answer:
| No. Point of difference | Partnership firm | HUF firm |
| 1. Establishment | A partnership firm is established by oral or written aqreement. | An HUF is established as per the Hindu law. |
| 2. Membership | One can become a member or say a partner through a partnership agreement | A male born in the family automatically becomes the member of HUF firm |
| 3. Decisions | All the partners together take the decision. | Only the Karta has the power to take the decision. |
| 4. Number of members | Minimum 2 and maximum 10 for a banking business and maximum 20 for other businesses. | There is no limit to the number of members. All males born in the family are the members. |
| 5. Gender | A person of any gender can be a partner. | Only male members can be the part of HUF firm. |
| 6. Liability | All the members have unlimited liability. | The Karta’s liability is unlimited whereas that of other members is limited. |
| 7. Management | All the partners have the right to manage. | Only the Karta has the right to manage. |
Question 41.
Though not mandatory it is recommended to have a registered partnership. Give reason.
Answer:
- A registered partnership agreement becomes a legal document. On getting registered the partners try to maintain the terms and conditions mentioned in the registered deed.
- if a partner breaches the agreement then the other partners can file a case against that partner and can demand justice for their rights and share.
- Moreover, if a third party does some fraud than the partners can go the court to fight against him.
- Owing to the several benefits of a registered partnership it is advisable to register a partnership firm.
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Who gave the definition of sole proprietorship?
(A) George Thomas
(B) Peter Woods
(C) Lewis Charlie
(D) Louis Henry
Answer:
(D) Louis Henry
Question 2.
Who is liable to pay off business debts^ of a sole proprietorship firm?
(A) Proprietor and his family
(B) Proprietor and his parents
(C) Proprietor
(D) Proprietor and his brothers involved in proprietorship firm
Answer:
(C) Proprietor
![]()
Question 3.
In which of the following forms of business does one get complete freedom of work and decision making?
(A) Proprietor
(B) HUF firm
(C) Partnership
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Question 4.
Which of the following is not a feature of sole proprietor?
(A) Maintenance of secret
(B) Limited capital
(C) Systematic decisions
(D) Freedom of work and quick decisions
Answer:
(C) Systematic decisions
Question 5.
What is the unique characteristic of a sole proprietorship?
(A) Centralization of ownership and management
(B) Increased goodwill
(C) More capital
(D) Quick decision
Answer:
(A) Centralization of ownership and management
Question 6.
Even an illiterate person can start a
(A) Partnership firm
(B) Sole proprietorship firm
(C) HUF firm
(D) All of these
Answer:
(D) All of these
Question 7.
The most important advantage of a sole proprietorship firm is that
(A) One can maintain utmost secrecy
(B) One can always be in contact with its customers
(C) It can be started with very less capital
(D) All of these
Answer:
(C) It can be started with very less capital
Question 8.
Maintenance of secrets can be best achieved in
(A) Proprietorship
(B) Partnership
(C) HUF
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(A) Proprietorship
Question 9.
Which form of business generally has the shortest life?
(A) HUF
(B) Partnership
(C) Proprietorship
(D) None of these
Answer:
(C) Proprietorship
Question 10.
_________ can be called as the biggest disadvantage of a sole proprietorship firm.
(A) Possibility of mistakes
(B) Unlimited liability
(C) Lack of advantages of large scale business
(D) Limited work capacity
Answer:
(D) Limited work capacity
Question 11.
Why there is less burden in proprietorship?
(A) Because the proprietor cheats tax authorities
(B) Because proprietor’s income is less
(C) Because proprietor is under lots of regulatory control
(D) Because proprietor can maintain the secrets
Answer:
(B) Because proprietor’s income is less
Question 12.
An HUF firm is defined by _________
(A) Partnership Act, 1932
(B) Hindu law
(C) Hindustan law
(D) Humanities law
Answer:
(B) Hindu law
Question 13.
According to Hindu law, business
(A) Is sellable
(B) Can be insolvent
(C) Is expandable
(D) Is inheritable
Answer:
(D) Is inheritable
Question 14.
Who cannot be a member of HUF firm?
(A) Son
(B) Daughter
(C) Wife
(D) Son-in-law
Answer:
(D) Son-in-law
Question 15.
If the ‘Karta’ dies becomes the Karta.
(A) Eldest male
(B) Eldest brother
(C) Eldest son
(D) None
Answer:
(D) None
![]()
Question 16.
Apart from India where can one see the concept of HUF?
(A) Sri Lanka
(B) Nepal
(C) Myanmar
(D) Bhutan
Answer:
(B) Nepal
Question 17.
In an HUF, the members
(A) Can suggest the Karta
(B) Can object the Karta
(C) Can interfere in decisions of Karta
(D) Can lawfully take part in decision making
Answer:
(A) Can suggest the Karta
Question 18.
Only can become members of an HUF firm.
(A) Sons of family
(B) Males of family
(C) Brothers of family
(D) Adult males
Answer:
(B) Males of family
Question 19.
Who is the financial controller of an HUF firm?
(A) Karta
(B) All sons and the Karta
(C) All male members
(D) Karta and his brothers
Answer:
(A) Karta
Question 20.
The success of an HUF firm depends on
(A) Efficiency of members
(B) Efficiency of Karta and members
(C) Efficiency of Karta
(D) Everyone’s efficiency
Answer:
(C) Efficiency of Karta
Question 21.
When an HUF firm becomes insolvent is/are declared insolvent.
(A) Karta
(B) All members
(C) All adult members
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Answer:
(C) All adult members
Question 22.
In an HUF firm has/have unlimited liability.
(A) Karta
(B) All members
(C) All adult members
(D) The entire family
Answer:
(A) Karta
Question 23.
When was the Partnership Act framed?
(A) 1927
(B) 1943
(C) 1950
(D) 1932
Answer:
(D) 1932
Question 24.
Who does the registration of partnership firm?
(A) Nodal Officer
(B) National Registrar
(C) Document Registrar
(D) Registrar of Firms
Answer:
(D) Registrar of Firms
![]()
Question 25.
Any general partnership firm can have maximum _________ partners.
(A) 2
(B) 10
(C) 20
(D) Unlimited
Answer:
(C) 20
Question 26.
Which is not an example of a partnership firm?
(A) Together organizing a religious procession
(B) Mutually agreeing to take care of cooking and catering at brother’s wedding
(C) Raising capital in the ratio of 10:90 for opening a restaurant
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Answer:
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Question 27.
Who cannot be called a partner?
(A) One who invested less than 50% capital
(B) One who did not invest any capital
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
Answer:
(D) None of these
Question 28.
Transfer of ownership is not easy in
(A) Proprietorship
(B) Partnership
(C) HUF
(D) All of these
Answer:
(B) Partnership
Question 29.
In a partnership firm, approval of minimum partners is necessary to transfer ownership.
(A) One
(B) Two
(C) All
(D) No
Answer:
(C) All
Question 30.
If any partner transfers his share without the approval of other partners then
(A) Any partner holds the power to dissolve the partnership
(B) That person can be taken to the court
(C) Th person automatically gets removed from the firm
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(A) Any partner holds the power to dissolve the partnership
Question 31.
Protecting interests of minority is a special feature of
(A) Proprietorship
(B) HUF
(C) Partnership
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(C) Partnership
Question 32.
Possibility of disagreement may occur in
(A) Proprietorship
(B) HUF
(C) Partnership
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(C) Partnership
Question 33.
How many types of partners are there?
(A) 3
(B) 4
(C) 5
(D) 6
Answer:
(D) 6
Question 34.
A partner who works full time in the firm is called a partner.
(A) Nominal
(B) Partner in profit only
(C) Partner by Estopple
(D) Active partner
Answer:
(D) Active partner
Question 35.
A partner added to the firm for increasing the influence and goodwill of the firm is called _________
(A) Nominal partner
(B) Partner by holding out
(C) Partner by estopple
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(A) Nominal partner
Question 36.
A partnership can be majorly classified into types.
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 9
Answer:
(A) 4
Question 37.
In total, there are types of partnership firms.
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 9
Answer:
(D) 9
Question 38.
In which partnership the life of a firm depends on the wish of the partners?
(A) Partnership for a specific work
(B) Voluntary partnership
(C) General partnership
(D) Registered partnership
Answer:
(B) Voluntary partnership
Question 39.
Which partnership gets dissolved automatically?
(A) General partnership
(B) Partnership of a specific work
(C) Fixed time limit partnership
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer:
(D) Both (B) and (C)
![]()
Question 40.
Which detail of a partner is not necessary to mention in the registration form?
(A) Date of admission
(B) Marital status
(C) Address
(D) None of these
Answer:
(B) Marital status