This GSEB Class 8 Maths Notes Chapter 11 Mensuration covers all the important topics and concepts as mentioned in the chapter.
Mensuration Class 8 GSEB Notes
→ Perimeter: It is the distance around the boundary of any figure. Perimeter becomes the sum of all sides of the given figure. It is measured using units.
→ Perimeter of different figures:
- Square = 4 × length Rectangle = 2 (length + breadth)
- Triangle = sum of lengths of all 3 sides Perimeter of any regular polygon
= Number of sides × Length of each side The perimeter of a circle is called its circumference. - Circumference = 2 πr [r = radius]
- Perimeter of semicircle = \(\frac{2 \pi r}{2}\) = πr
→ Area: Area is the part of the plane occupied by a closed figure. A closed figure can be of different regular and irregular shapes. It is measured using square units.
→ Area of different figures :
- Square = (side)2
- Rectangle = length × breadth
- Triangle = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × base × height
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × b × h - Parallelogram = base × height = b × h
- Trapezium = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × (sum of parallel sides) × height
- Rhombus = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × product of diagonals
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × d1 × d2 - Circle = πr2 (r = radius)
→ Cuboid: It is a solid bounded by six rectangular plane regions.
- Lateral surface area of a cubold
= 2 × height × (length + breadth)
= 2 × h × (l + b) - Total surface area of cubold
= 2 (lb + bh + hl)
![]()
→ Cube: It is a special type of a cubold whose length, breadth and height are all equal.
- Lateral surface area of a cube
= 4 × (side)2 = 4l2 - Total surface area of a cube
= 6 × (side)2 = 6l2
→ Cylinder:
- A pipe of water, a cistern to store grains. a tin of talcum powder. a 1-rupee coin, etc. are some objects having cylindrical shape.
- A cylinder has two flat a top and a base. The the cylinder Is not flat as curved surface of the Cylinder circular surfaces. other surface of and It Is known cylinder.
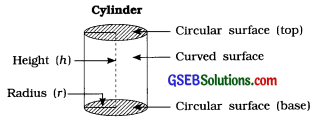
- The top and the base of a cylinder are circles of same size and hence their areas are equal.
- Area of the base of a cylinder = r2. where r = radius of the base of the cylinder (also called radius of the cylinder)
- Circumference of the base of a cylinder = 2r
= πd. where d = diameter of the cylinder
→ Curved surface area of a cylinder
= circumference × height
= 2πr × h = 2πrh
OR
Curved surface area of a cylinder
= circumference × height
= πd × h = πdh
→ Volume: The measure of space occupied by a three dimensional object is called Its volume.
→ Volume of a cubold
= Area of the base × Height
= l × b × h
→ Volume of a cube: l × l × l = l3
→ Volume of a cylinder

= Area of the base × Height
= Area of the circle × Height
= πr2 × h = πr2h
Where r Is the radius of the base of the cylinder and h Is the height of the cylinder.
→ All the coins like 1-rupee coin. 2-rupee coin. 5-rupee coin and 10-rupee coin are cylindrical In shape.

Of course, taken only one coin, the height is quite less as compared to the radius. But, when more coins of the same type are stacked, they form a cylinder with considerable height.
![]()
→ The volume of liquids and gases that do not have fixed shape are usually measured In units like litres and millilitres (ml).
→ Remember:
- 1 m3 = 10,00,000 cm3
- 1 litre = 1000 millilitres
- 1 m3 = 1000 litres
- I litre = 1000 cm3
- 1 m3 = 1000 litres
- 1 cm3 = 1 millilitre