Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Commerce Accounts Part 1 Chapter 4 Journal Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Accounts Part 1 Chapter 4 Journal
GSEB Class 11 Accounts Journal Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write the correct option from those given below each question :
(1) Journal is a ………………… of accounting transactions.
(a) original book
(b) main book
(c) closing book
(d) other book
Answer:
(a) original book
(2) An amount withdrawn from bank account for personal expense will be debited to ………………………. account.
(a) Bank
(b) Cash
(c) Drawings
(d) Person
Answer:
(c) Drawings
![]()
(3) Expense incurred to purchase asset is debited to …………….. account.
(a) Expense
(b) Asset
(c) Cash
(d) Sundry
Answer:
(b) Asset
(4) The total of debit and credit side of journal are …………….. .
(a) non-identical
(b) identical
(c) debit
(d) credit
Answer:
(b) identical
(5) Goods goes out for sample is debited to account.
(a) Advertisement Expense
(b) Goods Issued for Sample
(c) Purchase
(d) Sale
Answer:
(a) Advertisement Expense
Question 2.
Answer the following questions in one sentence :
(1) What is Journal ?
Answer:
Journal means a book of accounts in which all financial transactions are recorded chronologically (serially) for the first time, along with a brief explanation of the transaction.
(2) Describe types of discount.
Answer:
There are two types of discount:
- Trade discount and
- Cash discount.
(3) When combined journal entries are written ?
Answer:
When more than two accounts are associated at the same time in any accounting transaction, combined entry is written.
![]()
(4) When is purchase returns made ? To which account it will be credited ?
Answer:
When purchased goods is defective, not as per sample, of inferior quality, in these cases, goods will be returned back to the supplier from whom goods is purchased. At that time, Purchase Returns A/c will be credited.
(5) Give three illustrations of goods going out in other ways.
Answer:
Three illustrations of goods going out in other ways are :
- Goods withdrawn for personal use,
- Goods distributed as free sample for advertisement and
- Goods given in charity.
(6) Describe main types of exchange transactions of business with bank.
Answer:
Two types of financial transactions are made with bank in business :
- Cash transactions and
- Non-cash transactions.
(7) To which account bad debts return will be credited, which is received from the debtor who became insolvent in past ?
Answer:
Amount is received from the debtor who became insolvent in past, it will be credited to Bad Debts Return A/c.
Question 3.
Describe whether the following statements are true or false :
(1) Income tax of sole proprietor is an expense of business, this will be debited to income tax account.
Answer:
This statement is false.
(2) Cheque received from customer is debited to bank account.
Answer:
This statement is true.
(3) House rent and shop rent both are business expenses.
Answer:
This statement is false.
![]()
Question 4.
Answer the following questions in brief :
(1) Describe the characteristics of Journal.
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of Journal :
1. Basic books of accounts: The first step for the business transaction is the entry of the transaction. Transactions are first recorded chronologically (serially) in Journal. So it is the fundamental, first and basic books of accounts.
2. Dual effect: According to the rules of debit and credit, the dual effect of an accounting transaction is recorded in it.
3. Amount column: As per dual effect, two columns are kept for writing the amount. In debit amount column, the amount of the account to be debited is written and in credit amount column, the amount of the account to be credited is written.
4. Transactions in chronologically order of date: The transactions are recorded daily in the journal and chronologically in the order of the date.
5. Brief explanation : Just after completion of the journal entry, a brief explanation of the transaction is given in the brackets as narration. So that the detailed information about the journal entry is also available.
(2) Distinguish between Cash discount and Trade discount.
Answer:
| Cash discount | Trade discount |
| 1. Meaning | |
| • The deduction which is made in the amount of cash to be received or paid, is called Cash discount. | • The deduction which is made in the printed price of the goods bought or sold, is called Trade discount. |
| 2. Given by | |
| • Cash discount is given by the trader to their customers. | • Trade discount is given by the manufacturer to their traders. |
| 3. Purpose | |
| • Cash discount is allowed to provide incentive for immediate payment of goods sold or to encourage timely payment for outstanding amount so that there may be some less deficit of interest. | • When manufacturer wants to sell their goods at quoted price, and also wants to allow sufficient margin to a retailer, they allowed the trade discount. |
| 4. When received ? | |
| • Cash discount is received when the cash amount is paid immediately or within a stipulated time. | • Trade discount is received immediately as soon as transaction takes place. |
| 5. Calculation | |
| • Cash discount is calculated on the remaining amount arrived at after deducting the trade discount amount. | • Trade discount is calculated on the original price or on the retail price. |
| 6. Recording | |
| • Cash discount is recorded in the books of accounts. | • Trade discount is not recorded in the books of accounts. (But in the narration it is mentioned.) |
| 7. Discount rate | |
| • Generally, rate of cash discount is more for the transaction having big amount. | • Generally, according to custom, trade discount rate remains same for every transaction. |
| Cash discount | Trade discount |
| 8. Accounting effect | |
| • At the time of preparing final accounts, discount allowed is recorded on the debit side and discount received is recorded on the credit side of Proft and Loss Account. | • At the time of preparing final accounts, there is no question of recording the trade discount amount because the original entry is not recorded and therefore positing is not possible and balance will not be there. |
| 9. Time | |
| • Cash discount is given at the time of payment of cash. | • Trade discount is given at the time of sale of goods / services. |
| 10. Condition | |
| • Cash discount is given only on the condition of payment or settlement of an account. | • Trade discount is given without any condition. |
Cash discountTrade discount8. Accounting effect• At the time of preparing final accounts, discount allowed is recorded on the debit side and discount received is recorded on the credit side of Proft and Loss Account.• At the time of preparing final accounts, there is no question of recording the trade discount amount because the original entry is not recorded and therefore positing is not possible and balance will not be there.9. Time• Cash discount is given at the time of payment of cash.• Trade discount is given at the time of sale of goods / services.10. Condition• Cash discount is given only on the condition of payment or settlement of an account.• Trade discount is given without any condition.
![]()
(3) Why journal is known as the first book of accounts?
Answer:
The first step for the business transaction is the entry of the transaction. The first book in which such entries are made is known as Journal. In short, all the financial transactions are recorded chronologically of the date and their happenings, for the first time. From the rough book (Tanchan or Tippan) on the basis of the vouchers, entries are written in the journal in the serial order of the date. But a few traders do not keep a rough book. Moreover, transactions are not recorded systematically in the rough book. So rough book is not considered to be a part of the books of accounts. Hence, the journal is considered to be the fundamental or basis or first book of accounts.
Jounal is the first or basic book of accounts. As the tree is dependent of base, the same way description in detailed of accountancy is based on Journal.
(4) Write a note on the significance of journal.
Answer:
Journal is the basic book of accounts. As the tree is dependent of base, the same way description in detailed of accountancy is based on Journal and significance of it is cleared by following points :
- Journal is such a book in which transaction is recorded according to the datewise in the serial of their happening, no transaction is left out from recording.
- Financial transaction can be explained with the help of journal entry.
- Necessary information can be shown regarding the transaction with the help of journal entry.
- As the dual effects of the transactions are given in the journal as per the principles of the accountancy, the probability of accounting errors is reduced.
- There are two separate columns for writing debit amount and credit amount. Hence, while posting there is no difficulty about which account should be debited and which account should be credited.
- As both the effects of every transaction are given/shown in journal, so the ledger can be prepared easily.
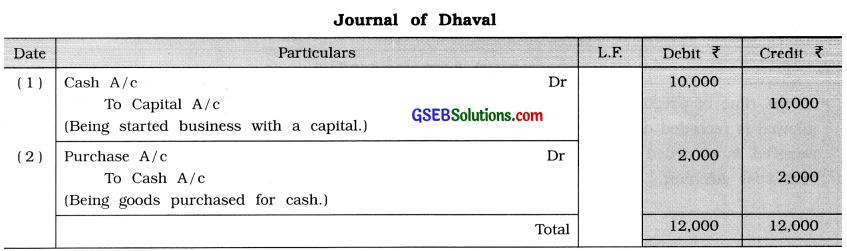
(5) Write journal for any two imaginary transactions.
Write journal entries in the books of Dhaval :
(1) Started business with a capital of ₹ 10,000.
(2) Purchased goods of ₹ 2,000 from Ashwin for cash.
Answer:
Points to be Remembered When Write the Journal
★ If ‘Personal account’ involves in given transaction, then if person has taken the benefit of business, debit his account and if person has given benefit to business, credit his account.
★ If goods or an asset comes in business, debit respective goods or asset account and if goods or an asset goes out from business, credit respective goods or asset account.
★ All expenses and losses accounts are debited and incomes and gains accounts are credited.
Explanation of it is given as per CPT study material of ICAI (March, 2015) page no. 2-23 as under:
Apart from sales and purchase return other outward of goods is recorded at cost price. These kind of goods outward are disclose as purchase reduction of business. Thus, this amount is credited to Purchase A/c.
| Nature of transaction | Account to be debited | Account to be credited |
| 1. When owner of business withdraw goods for personal use | Drawings A/c | Purchase A/c |
| 2. When goods are destroyed in fire | Loss by Fire A/c | Purchase A/c |
| 3. When goods are stolen | Loss by Theft A/c | Purchase A/c |
| 4. When goods are given in Charity / Donation | Charity/Donation A/c
|
Purchase A/c |
| 5. When goods are distributed as free samples for advertisement | Advertisement Expense A/c | Purchase A/c |
| 6. When goods are destroyed in accident | Loss by Accident A/c | Purchase A/c |
| 7. When goods received as free samples are sold | Cash A/c | Sales A/c |
![]()
Question 5.
From the following transactions write journal in the books of Pranjal :
(1) Introduced ₹ 10,000 cash and commenced business.
(2) Goods of ₹ 5,000 purchased on cash.
(3) Goods of ₹ 8,000 purchased on credit from Rajan.
(4) Goods of ₹ 2,000 given for donation.
(5) Given order to Shivani to dispatch goods of ₹ 3,000.
(6) Shivani has dispatched the goods as per our order.
(7) Paid ₹ 2,500 for life insurance premium.
Answer:
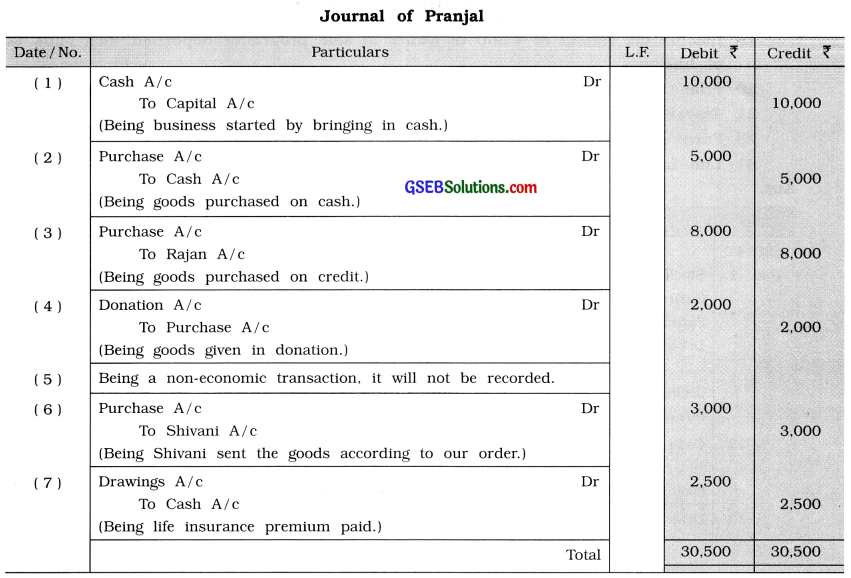
Explanation :
(1) Cash comes in business → Cash A / c → Debit what comes →Cash A / c will be debited.
Pranjal (Owner) is giver of cash → Capital A/c → Owner (Pranjal) is giver → Capital A/c will be credited.
(2) Goods comes in business → Purchase A / c → Debit what comes → Purchase A/c will be debited.
Cash goes out → Cash A/c ^Credit what goes out → Cash A/c will be credited.
(3) Goods comes in business → Purchase A / c → Debit what comes → Purchase A/c will be debited.
Rajan is giver of goods → Raj an A/c → Credit the giver → Raj an A/c will be credited.
(4) Charity / Donation is an expense of business → Charity / Donation A / c → Debit the expense and loss → Charity/Donation A/c will be debited.
Goods goes out by donation Purchase A / c → Credit what goes out → Purchase A/c will be credited at its cost price.
(5) Being a non-economic transaction, it will not be recorded.
(6) Life insurance premium is a personal expense → Drawings A / c → Debit the receiver → Drawings A/c will be debited.
Cash goes out from business → Cash A / c → Credit what goes out Cash A/c will be credited.
![]()
Question 6.
★ Transactions of Capital and Drawings :
Write journal entries for the following transaction in the books of Shubham:
2014
Jan. 1 Introduced goods of ₹ 10,000, cash ₹ 15,000, furniture ₹ 5,000, debtors of ₹ 10,000 and commenced business.
12 Personal motor-car sold for ₹ 80,000 and introduced ₹ 50,000 in business.
13 ₹ 1,000 withdrawn from bank for personal use.
15 Income tax refund of ₹ 500 of owner of sole proprietor deposited with bank account of business.
20 From business goods of ₹ 1,000 and cash ₹ 400 are withdrawn for personal use.
21 Travelling expense of daughter ₹ 1,500 paid from business.
28 Furniture of ₹ 2,000, purchased from Ganga Furniture Mart for house.
31 Life insurance premium of ₹ 500 paid by cheque.
Answer: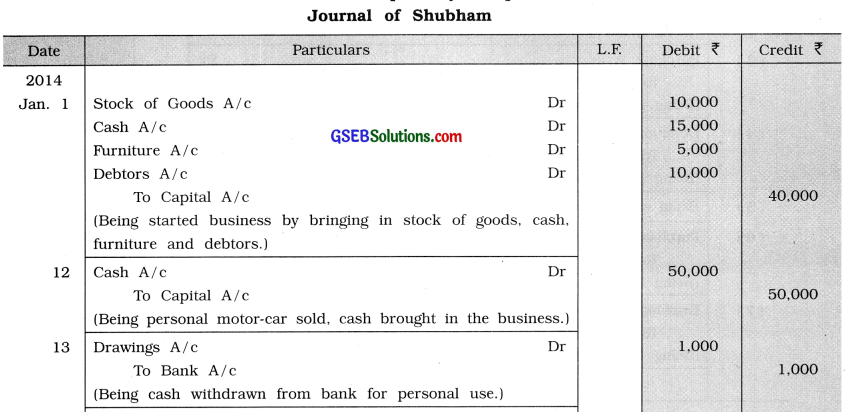
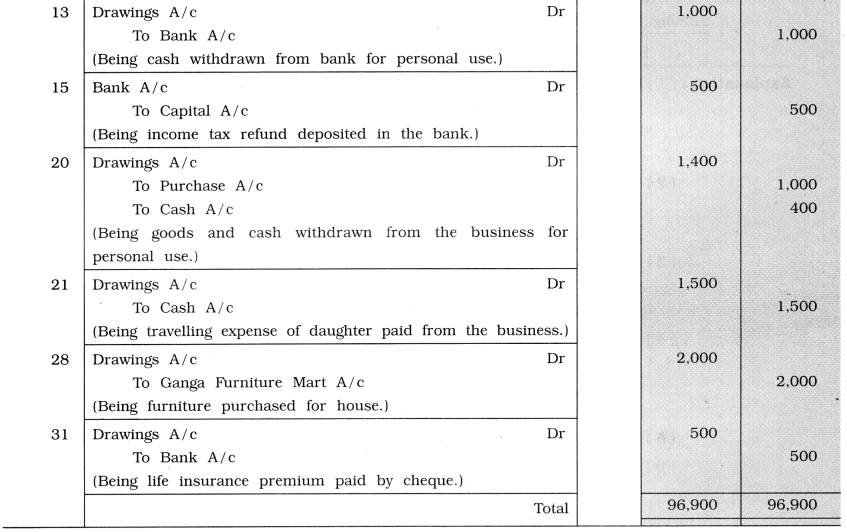
Explanation: Date
Jan. 1 Stock of goods, cash, furniture and debtors come into the business → Assets come into the business therefore they will be debited separately.
Owner is the giver of all assets, which is investment of owner in the business Called capital → Capital A/c will be credited.
Jan. 13 Cash withdrawn for personal use, which is personal expense → Drawings A/c will be debited.
Jan. 15 Income tax refund is an income of owner, which is brought in business Capital A/c will be credited.
Jan. 20 Cash and goods withdrawn for personal use Drawings A/c will be debited.
Goods goes out from the business → As per the rule → Purchase A/c credited with its cost price.
![]()
Question 7.
★ Transactions of Loan and Interest :
Write following transactions in the journal of Pushkar:
2014
Feb. 1 Due to additional requirement of funds, 12 % loan of ₹ 20,000 borrowed from Ram.
3 ₹ 8,000 lent to Laxman at interest rate of 8 %.
8 Received cash ₹ 800 for loan lent to Bharat and ₹ 200 for interest.
10 ₹ 5,000 returned back to Seeta for borrowed loan and paid interest ₹ 400.
12 Received interest ₹ 200, for loan lent to Kaushal.
15 Interest for one month paid for loan obtained from Ram.
18 ₹ 75 became receivable for interest on loan of Laxman.
Answer:
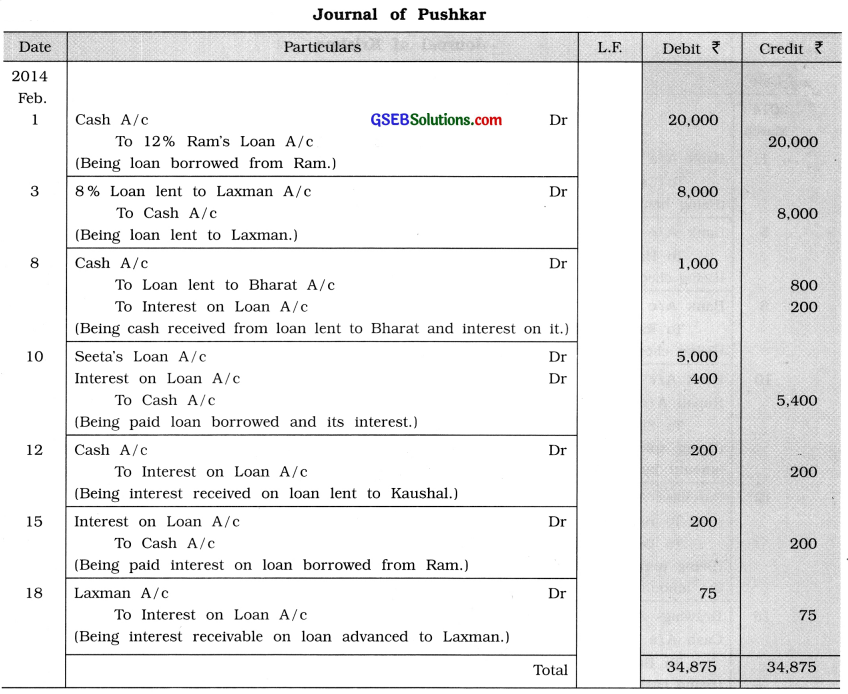
Explanation : Date
February 3 Given loan on interest is called investment → It is receivable → Loan lent to Laxman A/c will be debited.
8 Cash received from loan lent to Bharat → Cash A/c will be debited and Loan lent to Bharat A/c will be credited.
8 Interest on lent loan is an income Interest on Loan A/c will be credited.
![]()
Question 8.
★ Transaction of Bank :
Write Journal Entry for Krishna for the following transaction:
2014
March
1 ₹ 20,000 deposited with bank and opened account.
5 A cheque of ₹ 5,000 received from Hari, which immediately deposited with bank.
6 A cheque of ₹ 2,000 received from Ramaniklal for dues.
10 Goods sold to Rupali ₹ 14,000, out of which cheque received for half amount which deposited with bank.
12 Goods of ₹ 10,000 purchased from Deepkala and paid half amount by cheque.
15 ₹ 400 withdrawn from bank for personal expenses and ₹ 800 for office expense.
18 Life insurance premium ₹ 300 and fire insurance premium ₹ 450 paid by cheque.
20 Bank has approved overdraft of ₹ 25,000.
25 Bank has credited interest of ₹ 250 and debited bank charges of ₹ 100.
31 A cheque of ₹ 5,000 issued for foreign visit of son of owner from business.
Answer:
Journal of Krishna
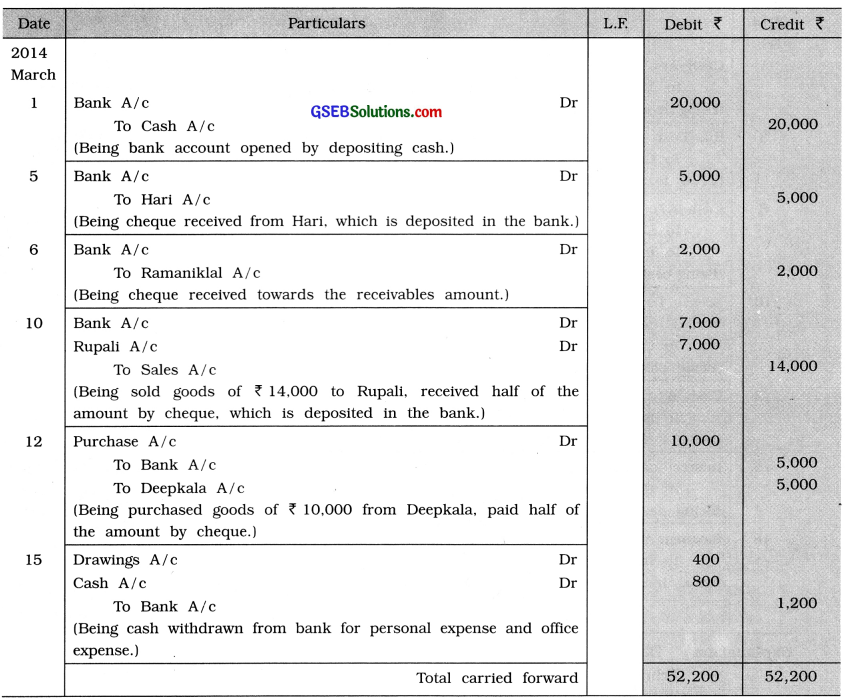
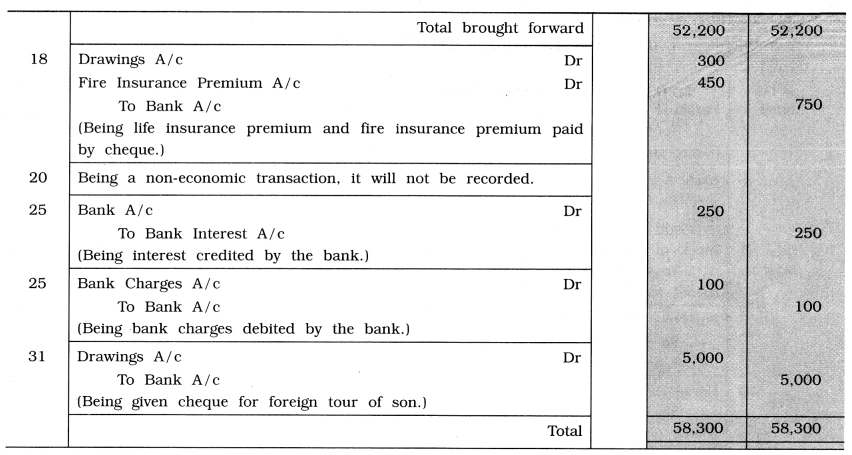
Explanation : Date
March 6 There is no mention about the type of cheque. On assuming that cheque is to be deposited into bank, Bank A/c is debited.
15 On withdrawing an amount from bank for personal expenses, Drawings A/c is debited while on withdrawing an amount for office expense, Cash A/c is debited because office expense yet is not paid.
20 Being a non-economic transaction, it will not be recorded.
25 Bank interest is an income for business, so Bank Interest A/c will be credited. While bank charges is an expense for business, so Bank Charges A/c will be debited.
![]()
Question 9.
★ Transaction of Goods :
Write journal entry for the following transactions in the books of Ramesh:
2014
April 1 Cash purchase ₹ 15,000 and cash sale ₹ 14,000.
5 A personal goods of ₹ 10,000, brought into the business.
7 Goods of ₹ 12,000 purchased from Harsh.
10 Out of goods purchased due to defective goods half goods returned to Harsh.
12 Goods of ₹ 10,000 purchased from Ramila and half amount paid by cheque.
15 Goods purchased from Ramila sold to Mita after adding 30 % profit, at 10 % trade discount.
18 Mita returned goods of ₹ 1,000.
20 Goods of ₹ 20,000 sold to Kalpana at 10 % trade discount and 5 % cash discount.
22 Goods of ₹ 2,000 destroyed by fire and insurance company admitted claim of ₹ 1,000.
25 Goods of ₹ 500 ruined in rain, ₹ 200 are realized by selling it.
27 Goods of ₹ 300 received as free sample.
29 Goods of ₹ 250 was received as free sample sold for ₹ 400.
30 A mobile of ₹ 1,500 purchased against exchange of goods of ₹ 1,000.
Answer:
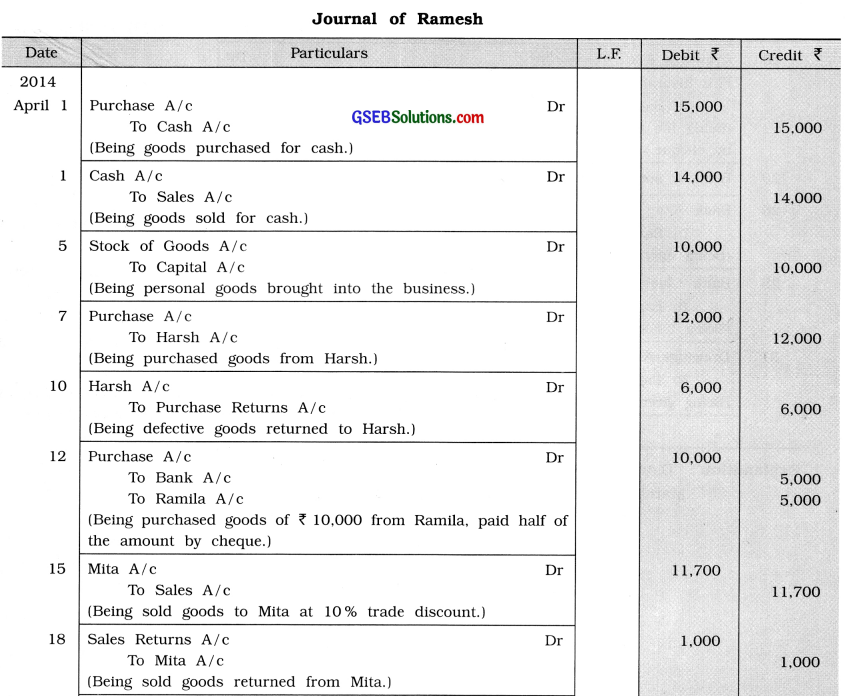
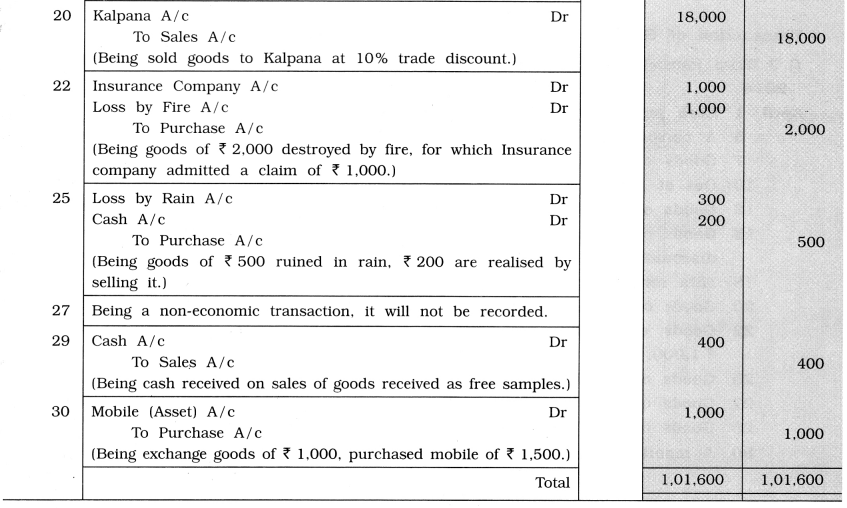
Explanation: Date
April 15 Sold goods purchased, from Ramila to Mita after adding 30% profit at 10 % trade discount.
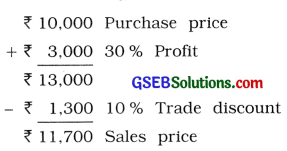
20 Cash discount cannot be calculated, there is nothing mention about cash going.
25 Goods of ₹ 500 ruined in rain, ₹ 200 realised on sale of it, there for difference amount of f 300 will be debited to Loss by rain A/c.
29 Transaction of goods received as free samples is not recorded in the books of accounts, therefore Sales A/c will credited at the time of seeling it.
![]()
Question 10.
★ Transactions of Asset :
Write journal entry for the following transactions in the books of Shri Laxman Chandera :
(1) A machine purchased by cheque f 20,000 and paid wages for machine installation ₹ 500 in cash.
(2) Furniture of ₹ 3,000 purchased from Kaveri Furniture Mart and carriage paid in cash ₹ 60.
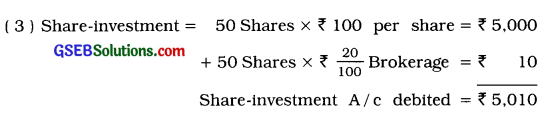
(3) 50 shares of Mahalaxmi Mill purchased at ₹ 100 per share and brokerage 20 paise per share, paid by cheque.
(4) For furniture of ₹ 5,000 goods given of ₹ 4,000.
(5) An old machine of ₹ 6,000 sold for X 5,000.
(6) Land purchased ₹ 50,000 and incurred ₹ 2,000 for documentation and legal charges Payment is made in cash.
Answer:
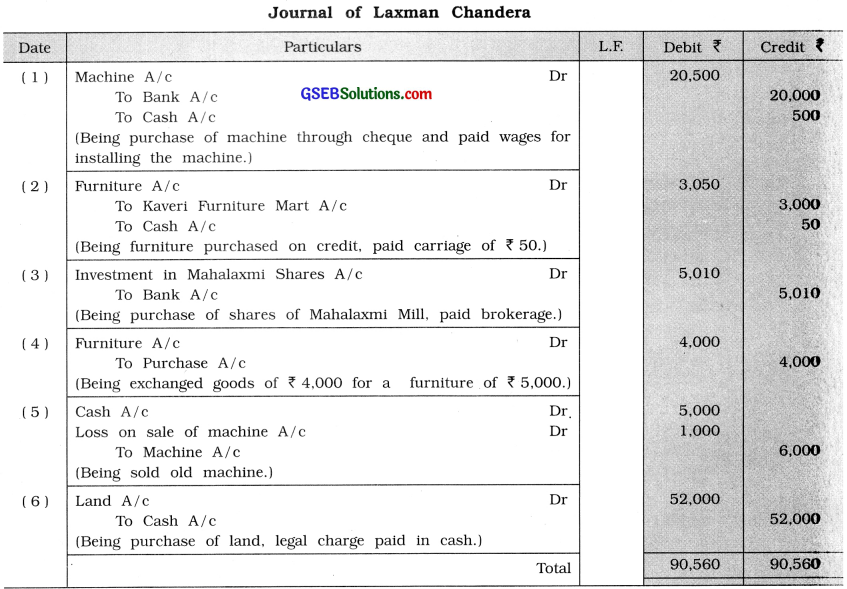
Explanation:
(1) Installation wages paid for machine will be added to cost of machine. Machine A/c will be debited by ₹ 20,500.
(6) Amount of land ₹ 50,000 + Documentation and legal charges of ₹ 2,000 = Land A/c debited by ₹ 52,000.
Question 11.
★ Transactions of Revenue – Expense :
For following transactions of May 2014, write journal entry in the books of Shashank: Date
1 Paid ₹ 500 for refreshment at inaugural function of shop.
2 Purchased necessary books of accounts ₹ 400 for business.
3 Paid ₹ 200 for wages and ₹ 100 for carriage.
5 Paid ₹ 500 for shop rent and ₹ 300 for house rent.
10 ₹ 400 received for commission.
12 A cheque of ₹ 800 received for brokerage.
15 Paid advertisement bill of Gujarat Samachar ₹ 300.
20 Received equity share dividend ₹ 500.
24 Essar company has paid debenture interest by cheque ₹ 1,000.
25 ₹ 3,000 paid for signboard of business.
Answer:
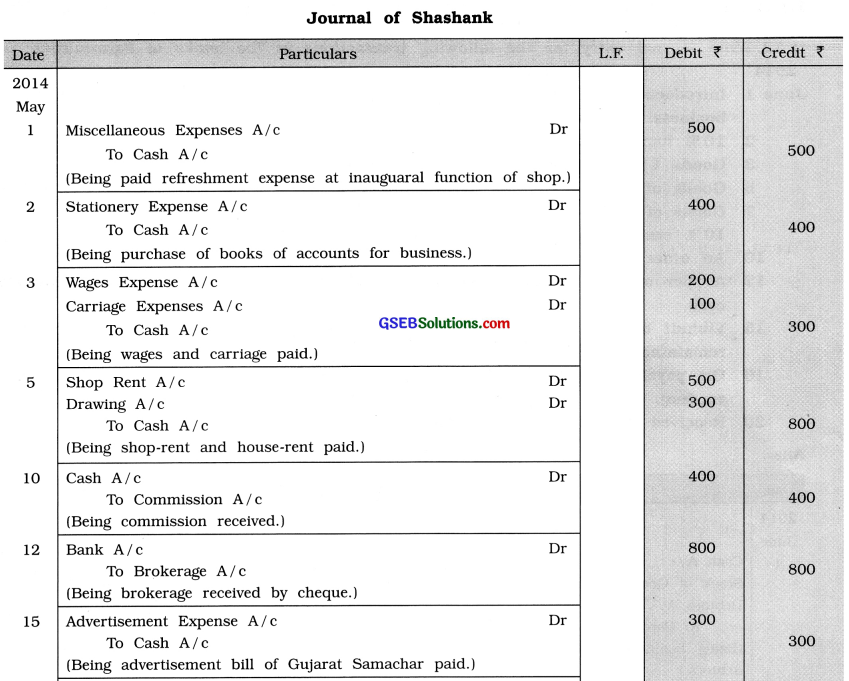
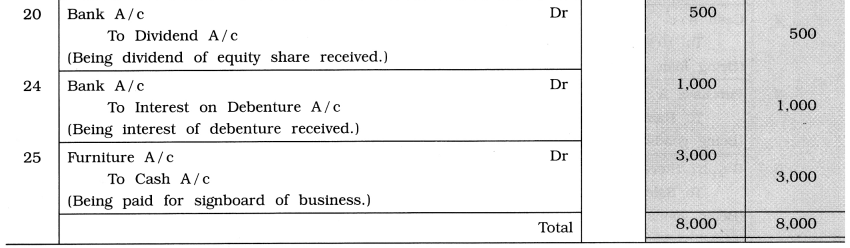
![]()
Question 12.
★ Transactions of Trade Discount, Cash Discount and Bad Debts:
Write journal entry for the following transactions in the books of Parmeshwar:
2014
June 1 Introduced cash ₹ 50,000, stock of goods ₹ 10,000, debtors of ₹ 15,000 and commenced business.
2 10 % loan of ₹ 20,000 is borrowed from Smt. Sharda.
3 Goods ₹ 8,000 purchased from Rameshwar Stores at 10% trade discount.
5 Goods of ₹ 5,000 sold to Gayatri Stores at 10 % trade discount.
7 Goods of ₹ 15,000 purchased from Radha-Kishan Stores at 10% trade discount and 10 % cash discount, issued cheque for half amount.
10 An order of ₹ 5,000 received from Vibhuti to sent goods.
12 As per order of Vibhuti, goods sent at 10 % trade discount. Paid ₹ 50 carriage in cash.
15 Vibhuti became insolvent and bad debts recorded of ₹ 300, a cheque received for remaining amount.
16 On payable amount to Anup ₹ 1,050, paid ₹ 1,000 by cheque and settled the account.
20 Received ₹ 1,500 for written off bad debts of Imandar.
Answer:
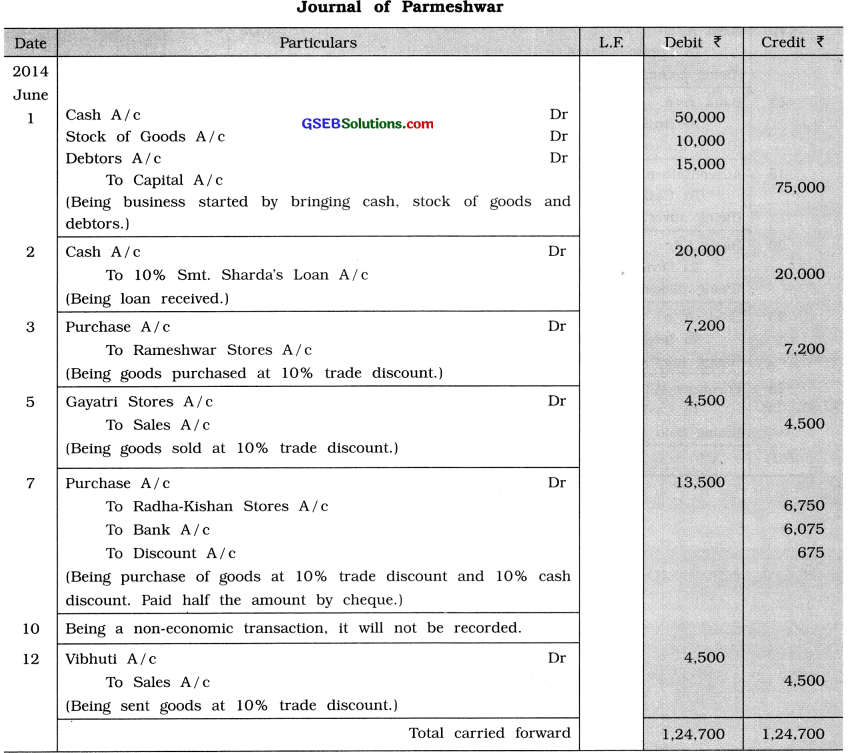
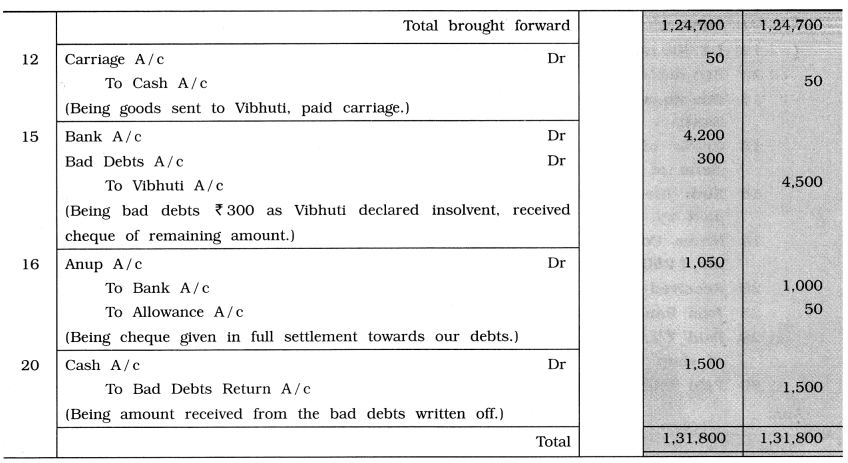
Explanation :

![]()
Question 13.
★ Transactions of inclusive of all :
Write journal entry of business commenced by Shri Maulik Shah with a name of Shah Traders :
2014
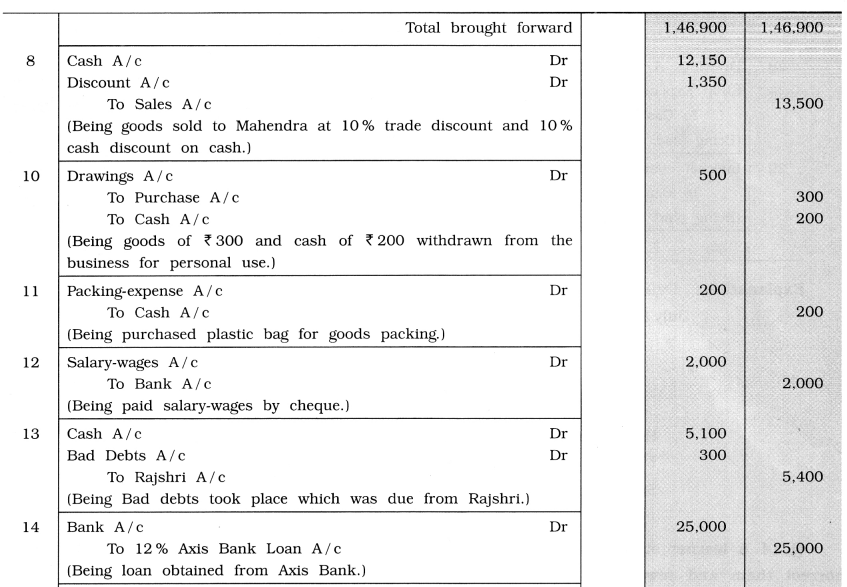
July 1 Brought ₹ 50,000 cash, debtors ₹ 20,000, stock of goods ₹ 10,000 and creditors of ₹ 5,000 and commenced business.
2 Deposited cash ₹ 20,000 with Vijaya Bank and opened account.
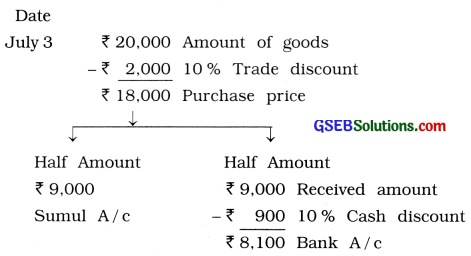
3 Goods of ₹ 20,000 purchased from Sumul at 10 % trade discount and 10 % cash discount. Paid half amount by cheque.
4 A furniture of ₹ 15,000 purchased on credit from ‘Punit Furniture Mart’. A carriage of ₹ 100 paid in cash.
5 A defective goods of ₹ 3,000 returned to Sumul.
6 Goods of ₹ 12,000 sold to Rajshri at 10 % trade discount and 10 % cash discount. Received half amount by cheque.
8 Goods of ₹ 15,000 sold to Mahendra on cash at 10% trade discount and 10% cash discount.
10 Withdrawn goods of ₹ 300 and cash ₹ 200 for personal use.
11 Purchased plastic bags of ₹ 200 for goods packing by cash.
12 ₹ 2,000 paid by cheque for salary and wages.
13 Bad debts took place ₹ 300, which was due from Rajshri and get the remaining amount.
14 Due to additional requirement of funds, 12 % loan of ₹ 25,000 obtained from Axis Bank.
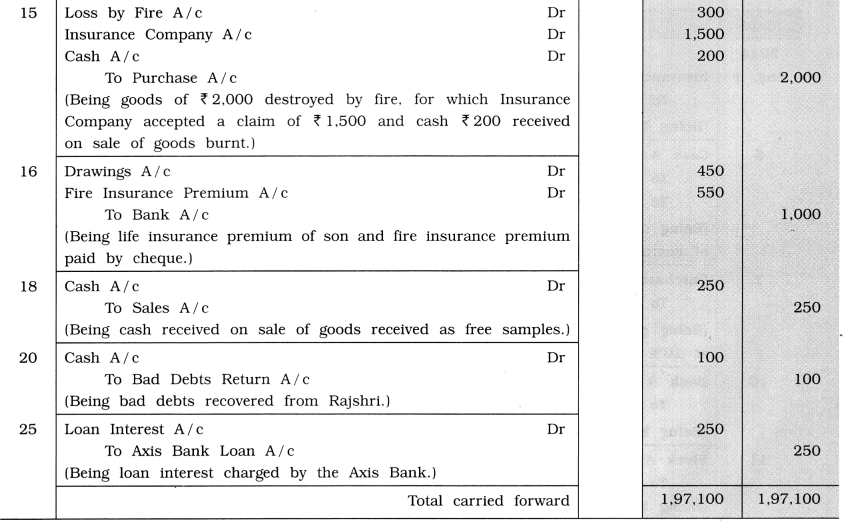
15 Goods of ₹ 2,000 destroyed by fire, for which insurance company has admitted claim of ₹ 1,500. Realized ₹ 200 from goods burnt by fire.
16 Both life insurance premium of son ₹ 450, and fire insurance premium of ₹ 550 paid by cheque.
18 Nirma Company gave 30 number of soap free of cost as a sample, which are sold for ₹ 250.
20 Received ₹ 100 from Rajshri for bad debts written off.
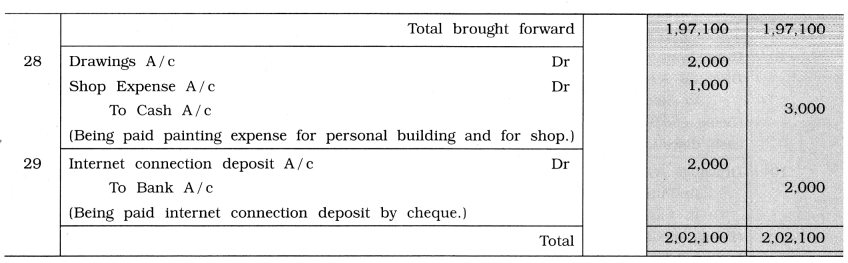
25 Axis Bank has charged loan interest of ₹250.
28 Paid ₹ 2,000 for painting work of personal building and ₹ 1,000 for painting work of shop.
29 Paid internet connection deposit ₹ 2,000 by cheque.
Answer:
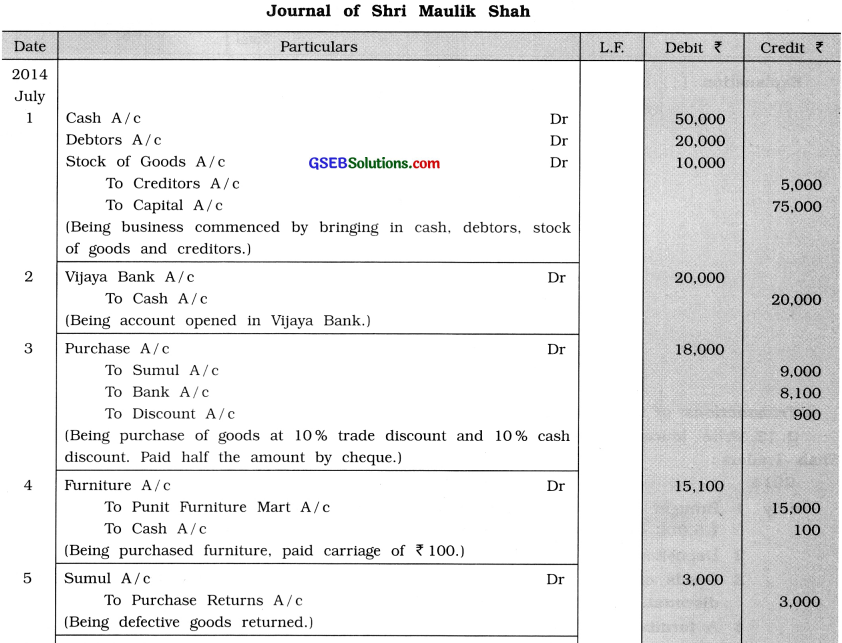

Explanation : Date
![]()
Question 14.
A learner student has written following journal entry. Journal entry which are incorrect, correct them and rewrite:
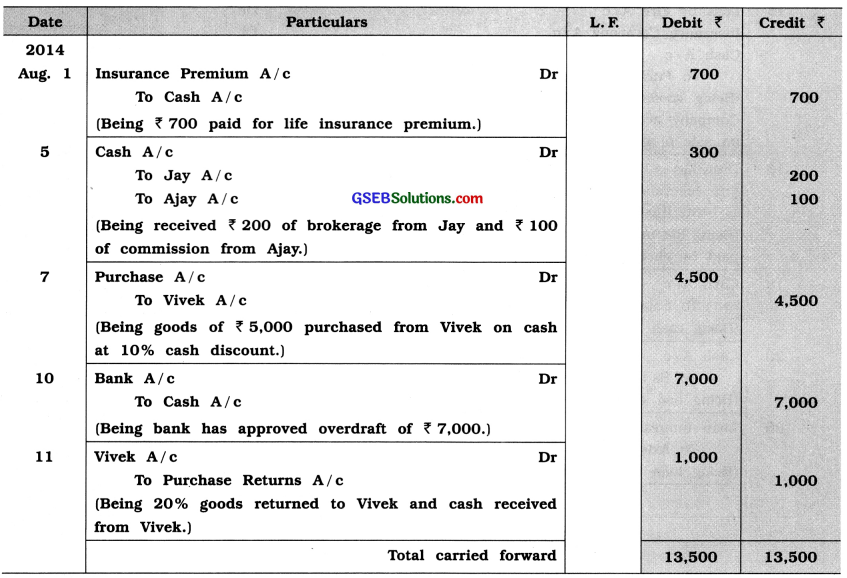
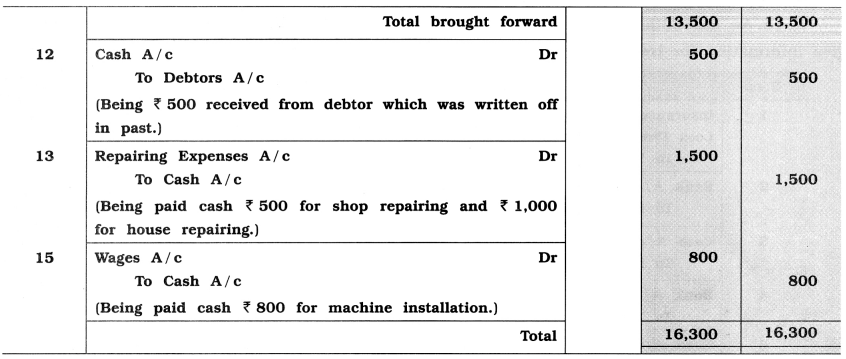
Answer:
Rectified journal are as under :
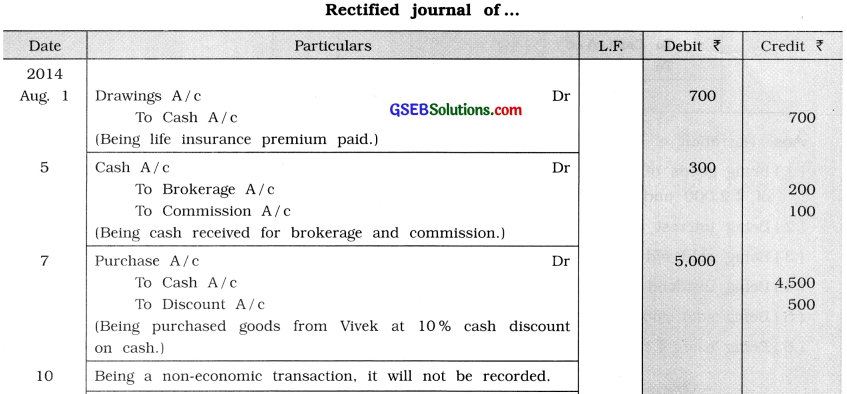
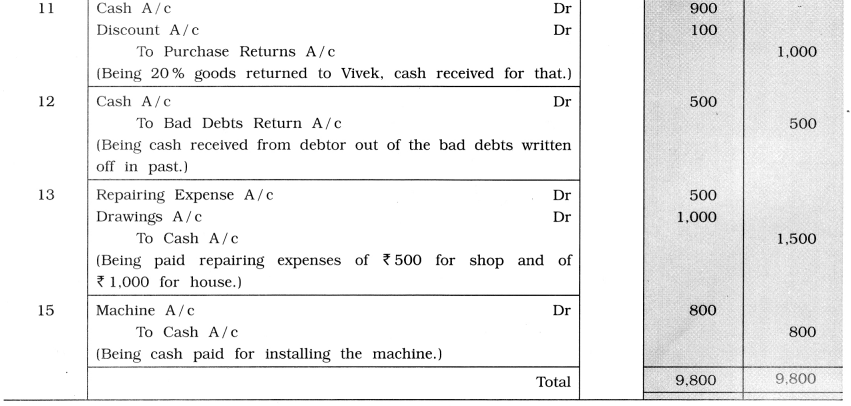
![]()
Question 15.
An accountant has written following journal entry without narration. You are required to give information for transactions from the following journal entry:
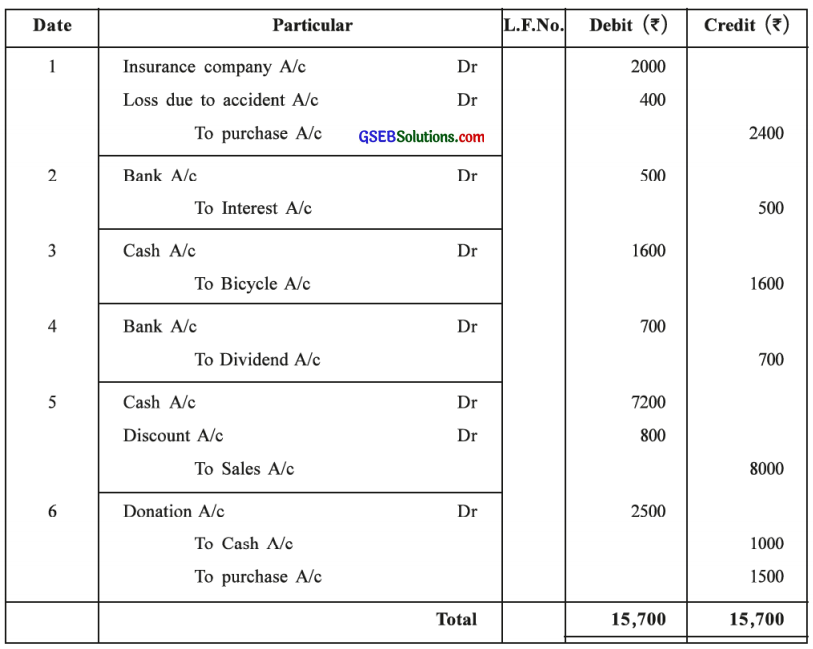
Answer:
Narration of the transaction from journal Is as under:
(1) BeIng goods of 2,400 destroyed in accident, for which Insurance Company accepted a claim of 2,000 and remaining amount Is debited to Loss by Accident A/c.
(2) BeIng interest of 500 credited by bank.
(3) Being sold old bicycle for 1,600 for cash.
(4) Being dividend of 700 credited by bank.
(5) Being sold goods of 8,000 for cash at 10 % cash discount.
(6) Being cash 1,000 and goods of 1,500 given as donation from the business.
Points to be Remembered When Write the Journal with GST Transactions
★ SGST with CGST is applicable for the Intrastate Supply.
★ UTGST with CGST is applicable for the Union Territory Supply.
★ IGST is applicable for the Interstate Supply.
| Transactions | GST for Intrastate Supply | GST for Interstate Supply |
| 1. For Purchase of Goods | Input Central GST A/c Dr Input State GST A/c Dr |
Input Intergrated GST A/c Dr |
| 2. For Purchase Returns | Input Central GST A/c Cr Input State GST A/c Cr |
Input Intergrated GST A/c Cr |
| 3. For Sale of Goods | Output Central GST A/c Cr Output State GST A/c Cr |
Output Intergrated GST A/c Cr |
| 4. For Sales Returns | Output Central GST A/c Dr Output State GST A/c Dr |
Output Intergrated GST A/c Dr |
| 5. For Service Expenses | Input Central GST A/c Dr Input State GST A/c Dr |
Input Intergrated GST A/c Dr |
| 6. For Service Incomes | Output Central GST A/c Cr Output State GST A/c Cr |
Output Intergrated GST A/c Cr |
| 7. For Purchase of Asset | Input Central GST A/c Dr Input State GST A/c Dr |
Input Intergrated GST A/c Dr |
![]()
Question 16.
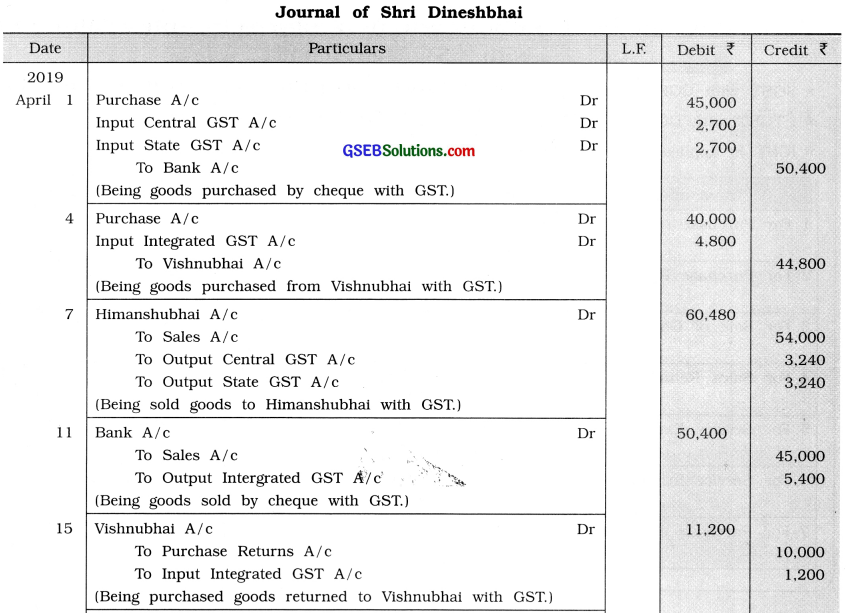
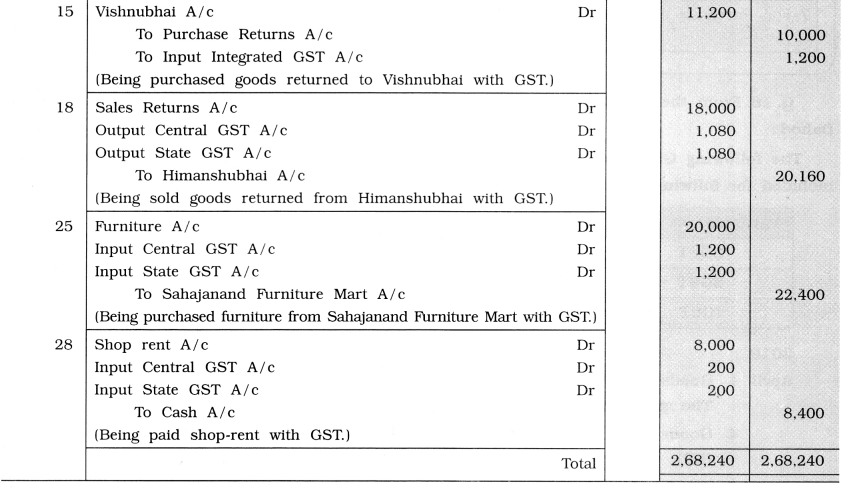
From the following transaction write journal entries in the books of Shri Dineshbhai of Dahod:
The following GST rates are applicable to business transactions of Shri Dineshbhai. GST is not included for follwing transactions. Add applicable amount of GST and write journal entries.
| Particular of GST | On goods | On services |
| CGST | 6% | 2.5 % |
| SGST | 6% | 2.5 % |
| IGST | 12% | 5.0% |
2019
April 1 Goods of ₹ 50,000 purchased at 10 % trade discount from Sureshbhai of Surendranagar. The payment is made by cheque.
4 Goods of ₹ 40,000 purchased at 10 % cash discount from Vishnubhai of Varansi (UP).
7 Goods of ₹ 60,000 sold at 10 % trade discount to Himanshubhai Himatnagar.
11 Goods of ₹ 50,000 sold at 10% trade discount to Shashikant of Simla (H.P.) and payment received through cheque.
15 \(\frac {1}{4}\) goods returned to Vishnubhai and proportionate GST is adjusted.
18 \(\frac {1}{3}\) goods returned by Himanshubhai and proportionate GST is adjusted.
25 A cupboard of ₹ 20,000 purchased from Sahajanand Furniture Mart of Ahmedabad.
28 Shop rent paid ₹ 8,000.
Answer:
![]()
Question 17.
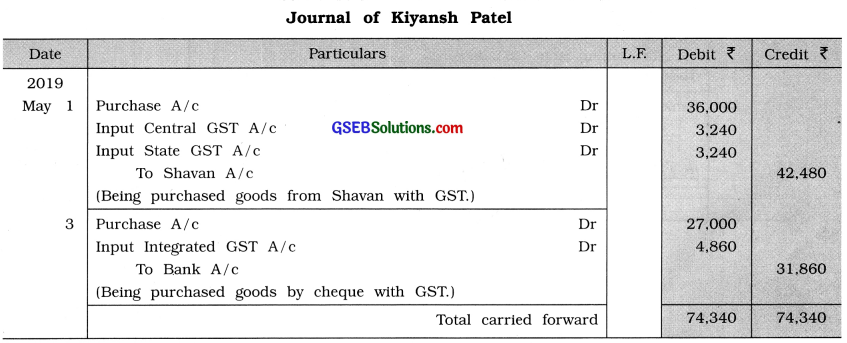
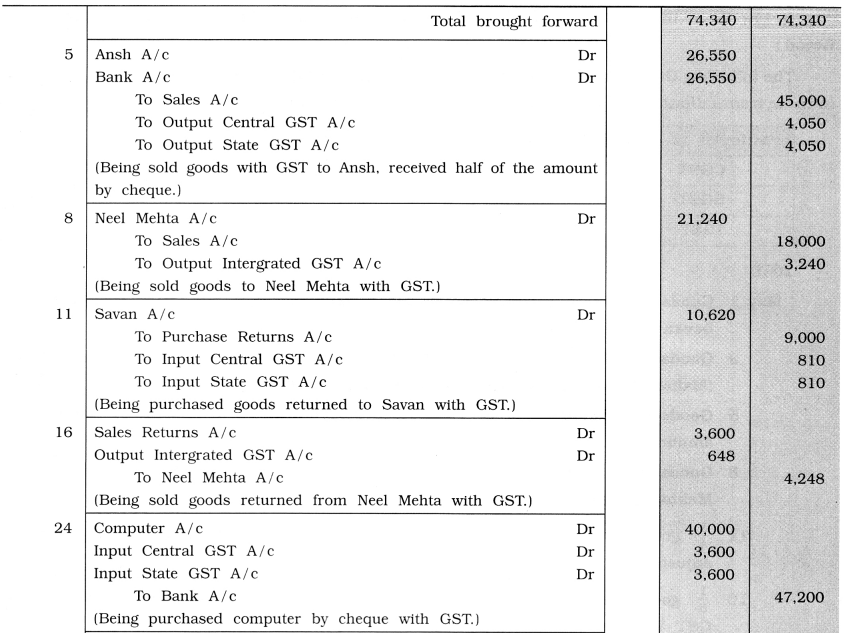
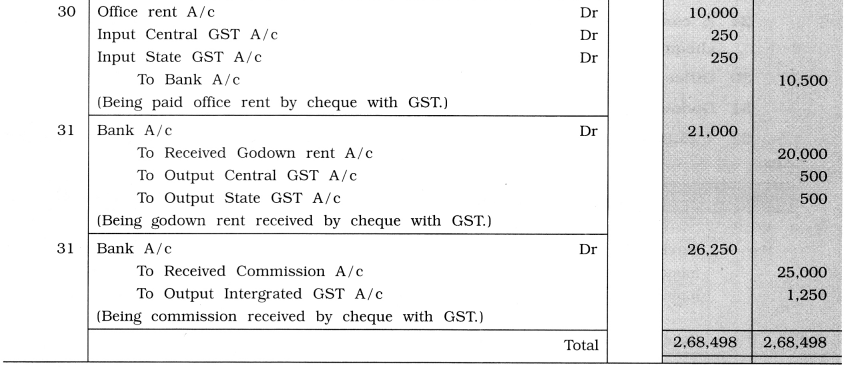
From the following transactions write journal entries in the books of Kiyansh Patel of Kesod:
The following GST rates are applicable to business transactions of Shri Kiyansh. GST is not included in these transactions. Add applicable amount of GST and write journal entries :
| Particular of GST | On goods | On services |
| CGST | 9% | 2.5 % |
| SGST | 9% | 2.5 % |
| IGST | 18% | 5.0 % |
2019
May 1 Goods of ₹ 40,000 purchased at 10 % trade discount and 10 % cash discount from Savan Patel of Surat.
3 Goods of ₹ 30,000 purchased at 10 % trade discount from Ayush Shah of Amravati (Maharashtra). The payment is made by cheque.
5 Goods of ₹ 50,000 sold at 10 % trade discount to Ansh Avasthi of Ahmedabad. Half amount received through cheque.
8 Goods of ₹ 20,000 sold at 10 % trade discount and at 5 % cash discount to Neel Mehta of Nagpur (Maharashtra).
11 \(\frac {1}{4}\) goods returned to Savan Patel of Surat. The proportionate amount of GST is
adjusted.
16 \(\frac {1}{5}\) goods received book from Neel Mehta of Nagpur the proportionate amount of GST is adjusted.
24 A computer of ₹ 40,000 for office from Shubh Infotech. The payment is made by cheque.
30 Office rent of ₹ 10,000 paid by cheque.
31 Godown rent of ₹ 20,000 received by cheque.
31 ₹ 25,000 received for commission by cheque from trader of Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh)
Answer: