Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules Textbook Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules
GSEB Class 11 Biology Biomolecules Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are macromolecules? Give examples.
Answer:
Chemical compounds with molecular weights of more than one thousand daltons and found in the acid-insoluble fraction are called macromolecules. Eg: Polysaccharides, nucleic acids.
![]()
Question 2.
Illustrate a glycosidic, peptide and a phospho-diester bond.
Answer:
In a polypeptide or a protein, amino acids are linked by a peptide bond which is formed when the carboxyl (-COOH) group of one amino acid reacts with the amino (NH2) group of the next amino acid with the elimination of water (the process is called dehydration). In a polysaccharide, the individual monosaccharides are linked by a glycosidic bond. This bond is also formed by dehydration. This bond is formed between two carbon atoms of two adjacent monosaccharides.
In a nucleic acid, a phosphate moiety links the 3′-carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide to the 5′-carbon of the sugar of the succeeding nucleotide. The bond between the phosphate and hydroxyl group of sugar in an ester bond. As there is one such ester bond on either side, it is called phospho-diester bond (fig. 9.1)
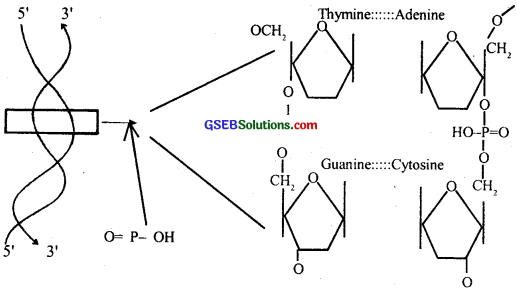
Question 3.
What is meant by the tertiary structure of proteins?
Answer:
The long protein chain which is folded upon itself like a hollow woolen ball is called the tertiary structure of the protein. It is necessary for many biological activities of proteins.
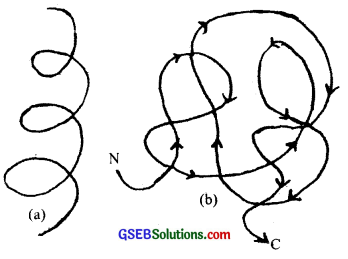
![]()
Question 4.
Find and write down structures of 10 interesting small molecular weight biomolecules. Find if there is any industry that manufactures the compounds by isolation. Find out who are the buyers?
Answer:
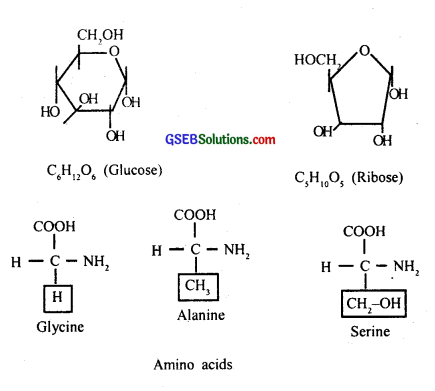
The most exciting aspect of chemistry deals with isolating thousand of compounds, small and big, from living organisms, determining their structure, and if possible synthesizing them. If one were to make a list of biomolecules, such a list would have thousands of organic compounds including amino acids, sugars, etc. Alkaloids, flavonoids, rubber, essential oils, antibiotics, colored pigments, scents, gums, Spices. These are called ‘secondary metabolites Many of them are useful to ‘human welfare’ (e.g., rubber, drugs, spices, scents, and pigments). Some of the secondary metabolites have ecological importance.
Question 5.
Proteins have a primary structure. If you are given a method to know which amino-acid is at either of the two termini (ends) of a protein, can you connect this information to the purity or homogeneity of a protein?
Answer:
Yes, if we are given a method to know the sequence of proteins, we can connect this information to the purity of a protein. The accurate sequence of a certain amino acid is very important for the functioning of the protein. Any change in the sequence can be linked to the purity or homogeneity of a protein.
![]()
Question 6.
Find out and make a list of proteins used as therapeutic agents. Find other applications of proteins (eg. Cosmetics etc.)
Answer:
- Human Albumin: Used in the sclerosis of the liver, Nephrotic Syndrome
- Antibodies: Gama globulins are used to treat many conditions like tetanus, snake bite, Gullane Barre Syndrome
- Enzyme: They are also protein used in many conditions like pancreatic malfunctioning-doctors prescribe pancreatin
- Polypeptide hormones are used to treat hormone deficiency diseases.
- Insulin: Diabetes
- Growth Hormone: Dwarfism
Cosmetic use:
- Keratolytic protein substances are used to soften hard skin.
- Egg protein is used for skin tightening.
Question 7.
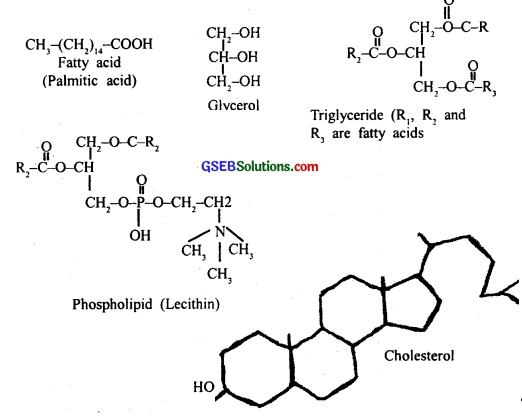
Explain the composition of triglyceride?
Answer:
Triglycerides are composed of a single molecule of glycerol to 3 fatty acids.
- Glycerol is 3 carbon alcohol with 30 n groups
- Fatty acids are long-chain hydrocarbon with a carboxylic group (COOH) at one end.
- Thus both form ester bonds.
- If single-bonded carbons, it is saturated, if c = c, it is unsaturated.
- The structure of fatty acids determines the physical nature of fat.
![]()
Question 8.
Can you describe what happens when milk is converted into curd or yogurt, from your understanding of proteins?
Answer:
In milk, there is lactase, which is converted into lactic acid when changed into curd or yogurt.
![]()
Lactases convert lactose (milk sugar) into lactic acid which is responsible for the coagulation of protein (casein)
Question 9.
Can you attempt building models or biomolecules using commercially available atomic models (Ball and stick models)
Answer:
We can make building models of biomolecules using commercially available atomic models.
Question 10.
Attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base and discover the number of dissociating (ionizable) functional groups in the amino acid.
Answer:
Amino acids are organic compounds containing an amino group and an acidic group as substituents on the same carbon. When we attempt titrating an amino acid against a weak base it dissociates and gives two functional group
- — CHOOH group (carboxylic group)
- Amino groups (NH2)
![]()
Question 11.
Draw the structure of the amino acid, alanine.
Answer:
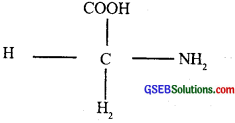
Question 12.
What are gums made of? Is Fevicol different?
Answer:
Gums are polymeric substances which come under secondary metabolites of plants. Fevicol is a synthetic gum.
Question 13.
Find out a qualitative test for proteins, fats and oils, amino acids and test any fruit juice, saliva, sweat, and urine for them.
Answer:
Test for Protein: (Biuret Test)
An alkaline suspension of a protein treated with an aqueous copper sulfate solution gives a violet color. As the color intensity represents the amount of protein this test is both qualitative and quantitative.
Fat: Dissolve the fat in alcohol and add a few drops of distilled water. An emulsion of liquid in water appears on the surface. Now add few drops of Sudan IV and oil red ‘O’ stain. The emulsion turns red.
Question 14.
Find out how much cellulose is made by all the plants in the biosphere and compare it with how much paper is manufactured by man and hence what is the consumption of plant material by man: annually. What a loss of vegetation!
Answer:
The largest portion of photosynthesis is converted into cellulose. But this quantity varies from one geographical area to another.
- In the Desert, it is less than 2 kg cal/m2/Day
- In grassland, deep lakes & mountain forest it is 2-12 kcal/m2/ Day
- In the moist forest, shallow lake, moist grassland, and moist agricultural and it is 2-40 kg cal/m2/Day
Similar data can be used to calculate cellulose secretion in the world per year.
Increase in industrialization, increasing the use of paper. Due to this reason vegetation is being lost to a great extent.
![]()
Question 15.
Describe the important properties of enzymes.
Answer:
- An enzyme like any protein has the primary structure (amino acid sequence). Secondary structure and tertiary structure.
- Every enzyme has an ’active site’ which is a crevice into which the substrate fits.
- Enzymes are specific in their action. The particular enzyme acts on a particular substrate. But different enzymes catalyze a unique chemical or metabolic reaction.
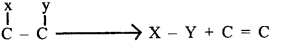
- It catalyzes the linking together of 2 compounds eg. c- o, c-s bonds, etc.