Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Textbook Questions and Answers, Additional Important Questions, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
GSEB Class 12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes InText Questions and Answers
![]()
Question 1.
Write structures of the following compounds:
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iii) 4-tert. butyl-3-iodoheptane
(iv) 1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
(v) 1-Bromo-4-sec. butyl-2-methylbenzene.
Answer:
(i) CH3CH2CH(CH3)CHClCH3
(ii) 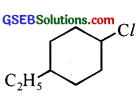
(iii) 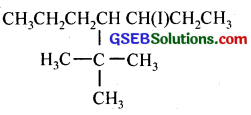
(iv) BrCH2CH = CHCH2Br
(v) 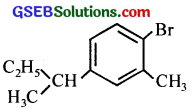
Question 2.
Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI?
Answer:
H2SO4 is an oxidizing agent. It oxidizes HI produce during the reaction to I2 and thus prevents the reaction between alcohol and HI to form an alkyl iodide.
KI + H2SO4 → KHSO4 + HI
2HI + H2SO4 → I2 + 2H2O + SO2
To remove this difficulty a non-oxidizing agent such as H3PO4 is used in place of H2SO4.
Question 3.
Write structures of different dihalogen derivatives of propane.
Answer:
- ClCH2CH2CH2Cl
- ClCH2CHClCH3
- Cl2CH2CH2CH3
- CH3CCl2CH3
![]()
Question 4.
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula C5H12, identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields
(i) a single monochloride.
(ii) three isomeric monochlorides
(iii) four isomeric monochlorides.
Answer:
(i) 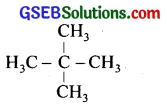
All the hydrogen atoms are equivalent and the replacement of any hydrogen will give the same product.
(ii) CaH3CbH2CcH2CbH2CaH3
The equivalent hydrogens are grouped as a, b and c. The replacement of equivalent hydrogens will give the same product.
(iii) 
Similarly, the equivalent hydrogens are grouped as a, b, c and d. Thus, four isomeric products are possible.
Question 5.
Draw the structures of major monohalo products in each of the following reactions:
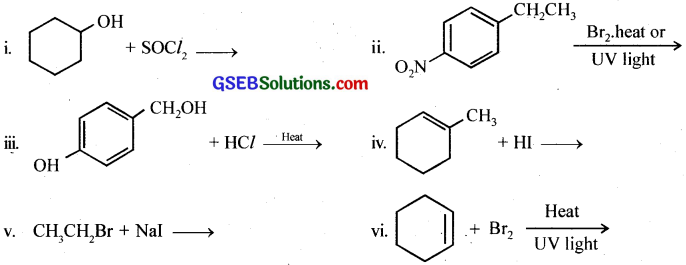
Answer:
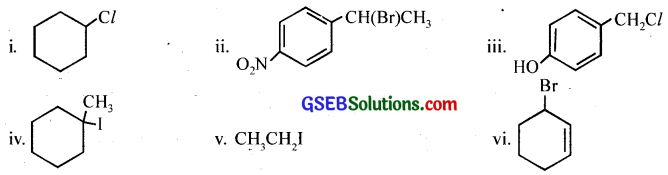
Question 6.
Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points.
(i) Bromomethane, Bromoform, Chloromethane, Dibromomethane.
(ii) 1-Chloropropane, Isopropyl chloride, 1-Chlorobutane.
Answer:
(a) For the same alkyl group boiling point increases with an increase in the molar mass of halogen atom; increase in the number of halogen atoms.
(b) For the same halogen with the increase in branching boiling point decreases.
On the basis of this following order is predicted :
(i) Chloromethane < Bromomethane < Dichloro-methane < Bromoform.
(ii) Isopropyl chloride < 1-Chloropropane < 1-Chlorobutane.
![]()
Question 7.
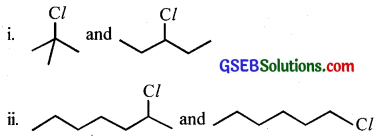
Which alkyl halide from the following pairs would you expect to react more rapidly by an SN2 mechanism? Explain your answer.
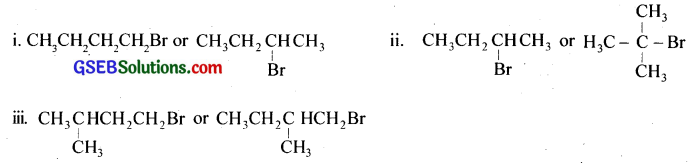
Answer:

Question 8.
In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction?
Answer:
(i) 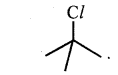
Tertiary halide reacts faster than secondary halide because of the greater stability of tert-carbocation.
(ii) 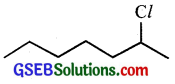
Because of the greater stability of secondary carbocation than primary.
Question 9.
Identify A, B, C, D, E, R, and R’ in the following.
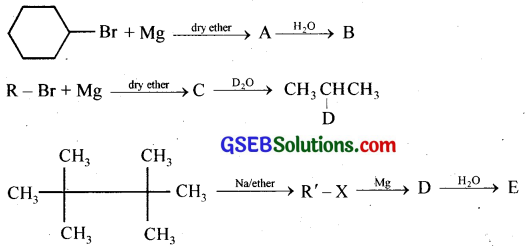
Answer:
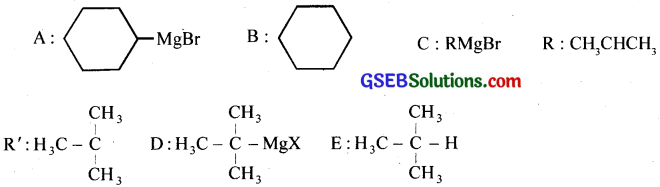
GSEB Class 12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl or aryl halides:
Answer:
(i) (CH3)2CHCH(Cl)CH3
(ii) CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH(C2H5)Cl
(iii) CH3CH2C(CH3)2CH2I
(iv) (CH3)3CCH2CH(Br)C6H5
(v) CH3CH(CH3)CH(Br)CH3
(vi) CH3C(C2H5)2CH2Br
(vii) CH3C(Cl)(C2H5)CH2CH3
(viii) CH3CH = C(Cl)CH2CH(CH3)2
(ix) CH3CH = CHC(Br)(CH3)2
(x) p-ClC6H4CH2CH(CH3)2
(xi) m-ClCH2C6H4CH2C(CH3)3
(xii) o-Br-C6H4CH(CH3)CH2CH3
Answer:
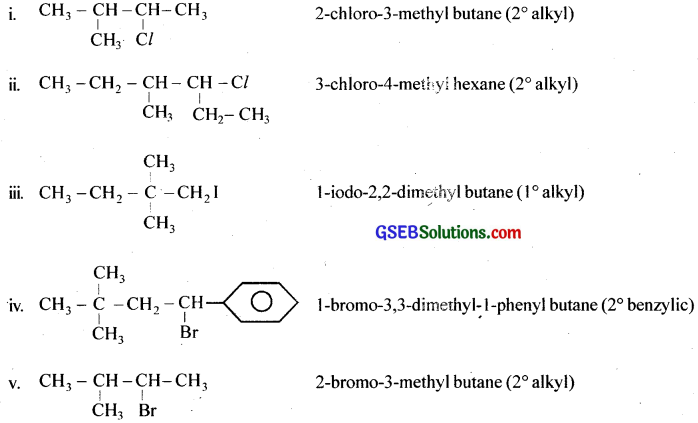
Question 2.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) CH3CH(Cl)CH(Br)CH3
(ii) CHF2CBrClF
(iii) ClCH2C ≡ CCH2Br
(iv) (CCl3)3CCl
(v) CH3C(p-ClC6H4)2CH(Br)CH3
(vi) (CH3)3CCH=ClC6H4I
Answer:
(i) 2-bromo-3-chlorobutane
(ii) 1-bromo-1-chloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane
(iii) 1-bromo-4-chlorobut-2-yne
(iv) 1,1,1,2,3,3,3 -heptachloro-(2-trichloromethyl) propane
(v) 1-[2-bromo-1-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-methyl propyl]-4-chlorobenzene
(vi) 1-chloro-1-(4-iodophenyl)-3,3-dimethylbut-1-ene
![]()
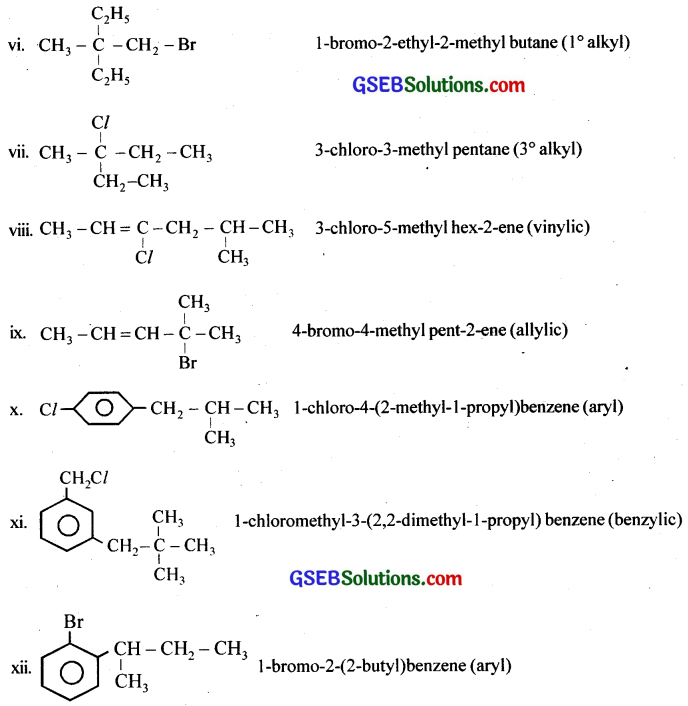
Question 3.
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds,
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) p-Bromochlorobenzene
(iii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iv) 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1-iodooctane
(v) Perfluorobenzene
(vi) 4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
(vii) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene
(viii) 1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
Answer:
Question 4.
Which one of the following has the highest dipole, moment?
(i) CH2Cl2
(ii) CHCl3
(iii) CCl4
Answer:
The three-dimensional structure of the compounds is given below.
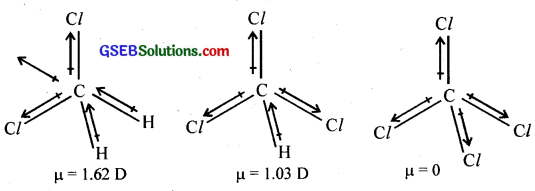
In CH2Cl2, the resultant of two C – Cl dipole moments is reinforced by the resultant of two C – H dipoles and the dipole moment is 1.62D. In CHCl3, the resultant of two C – Cl dipoles is opposed by the resultant of C – H and C-Cl bond dipoles and the dipole moment is 1.03 D. CCl4 being symmetrical, has zero dipole moment.
Thus, CH2Cl2 has the highest dipole moment.
Question 5.
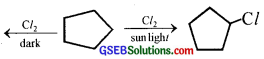
A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine in dark but gives a single monochloro compound C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon.
Answer:
- The molecular formula suggests that it can either be a cycloalkane or alkene.
- Since the hydrocarbon does not react with Cl2 in the dark, it cannot be alkene. Therefore, it must be a cycloalkane.
- The hydrocarbon reacts with Cl2 in the presence of bright sunlight to give a single mono-chloro compound C5H9Cl, therefore, all the ten H-atoms of cycloalkane must be equivalent.
Question 6.
Write the isomers of the compound having the formula C4H9Br.
Answer:

Question 7.
Write the equations for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from i. 1-butanol ii. 1-chlorobutane iii. but-1-ene.
Answer:
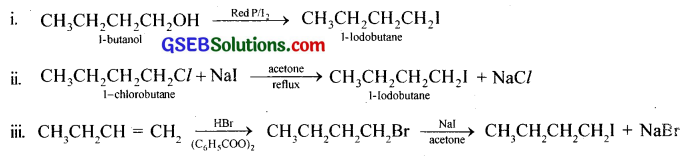
Question 8.
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
Answer:
The nucleophile having two nucleophilic centers are called ambident nucleophiles. An example is the cyanide group because it can attack through C or N because of the following resonance structures:
![]()
![]()
Question 9.
Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with -OH?
- CH3Br or CH3I
- (CH3)3CCl or CH3Cl
Answer:
- CH3I because E is a better leaving group than Br3 ion.
- CH3Cl. Due to steric considerations, primary alkyl halides react faster than tertiary alkyl halides.
Question 10.
Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of the following halides with sodium ethoxide in ethanol and identify the major alkene:
(i) 1-Bromo-l-methylcyclohexane
(ii) 2-Chloro-2-methyl butane
(iii) 2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane.
Answer:
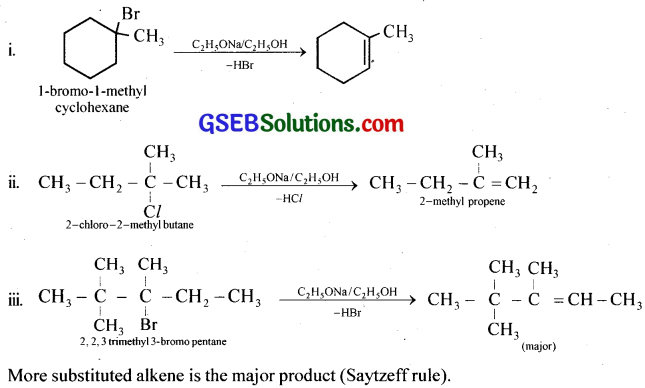
Question 11.
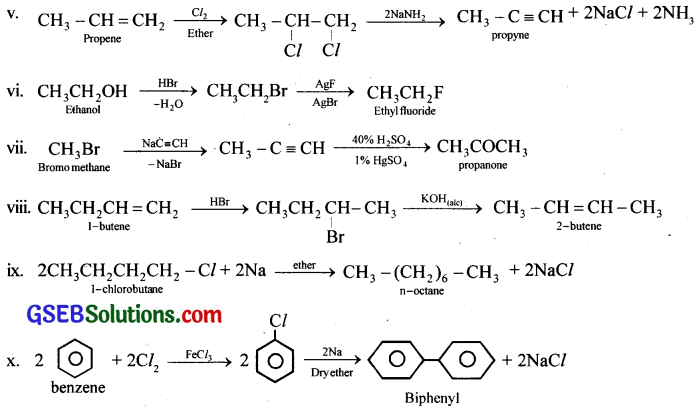
How will you bring about the following conversions?
(i) Ethanol to but-1-yne
(ii) Ethane to bromoethene
(iii) Propene to 1-nitropropane
(iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Propene to propyne
(vi) Ethanol to ethyl fluoride
(vii) Bromomethane to propanone
(viii) But-1-ene to but-2-ene
(ix) 1-Chlorobutane to n-octane
(x) Benzene to biphenyl
Answer:
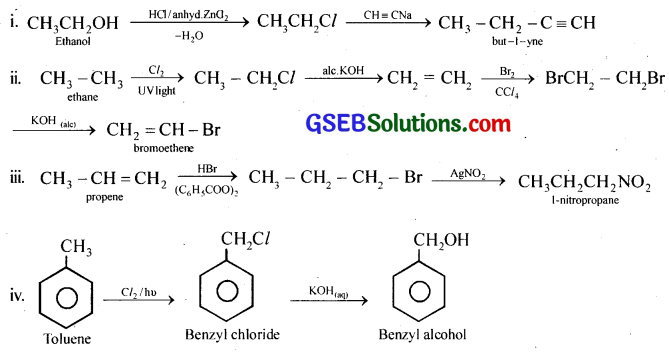
Question 12.
Explain why
(i) the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
(ii) alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water.
(iii) Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
Answer:
(i) The carbon atoms in chlorobenzene are sp2 hybridised while in cyclohexyl chloride they are sp3 hybridised. Thus, the C – Cl bond in chlorobenzene is less polar than in cyclohexyl chloride.
(ii) Alkyl halides cannot form hydrogen bonds with water and hence are insoluble in water.
(iii) Grignard reagents readily undergo hydrolysis to form alkane.
![]()
RMgX + H2 → R – H + Mg(OH)X
To prevent hydrolysis, it should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
Question 13.
Give the uses of freon 12, DDT, carbon tetrachloride and iodoform.
Answer:
- Freon 12 – Asa refrigerant, propellant in aerosols
- DDT – Used as insecticide
- CCl4 – As fire extinguisher
- Iodoform – As antiseptic
Question 14.
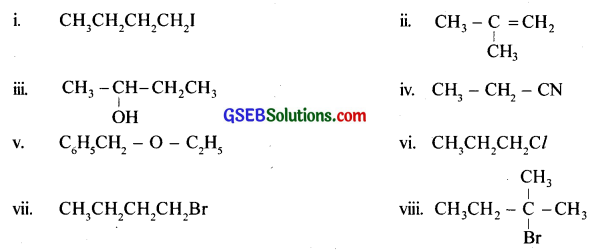
Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the following reactions:
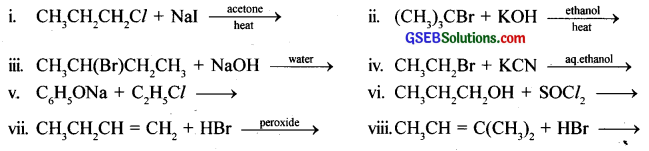
Answer:
Question 15.
Write the mechanism of the following reaction.
![]()
Answer:
CN– is an ambident nucleophile and can attack the carbon atom of C – Br bond in n – BuBr either . through C or N. Since C – C bond is stronger than C – N bond, attack occurs through C to form n-butyl cyanide.
Question 16.
Arrange the compounds of each set in order of reactivity towards SN2 displacement:
(i) 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane
(ii) 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 3-Bromo-2-methylbutane
(iii) 1-Bromobutane, 1-Bromo-2,2-dimethylpropane, 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromo-3- methylbutane.
Answer:
The order of reactivity is
(i) 1-bromopentane > 2-bromopentane > 2-bromo-2-methyl butane
(Due to steric effect, the order of reactivity in SN2 reaction is 1° > 2° > 3°)
(ii) 1-bromo-3-methyl butane > 3-bromo-2-methyl butane > 2-bromo-2-methyl butane
(This is due to steric effect)
(iii) 1 -bromobutane > 1 -bromo-3-methyl butane > 1 -bromo-2-methyl butane > 1-bromo-2,2-dimethyl propane
![]()
Question 17.
p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and solubility than those of o-and m-isomers. Discuss.
Answer:
p-isomer is more symmetrical and fits closely in the crystal lattice and has strong intermolecular attraction than o-and m-isomers
Question 18.
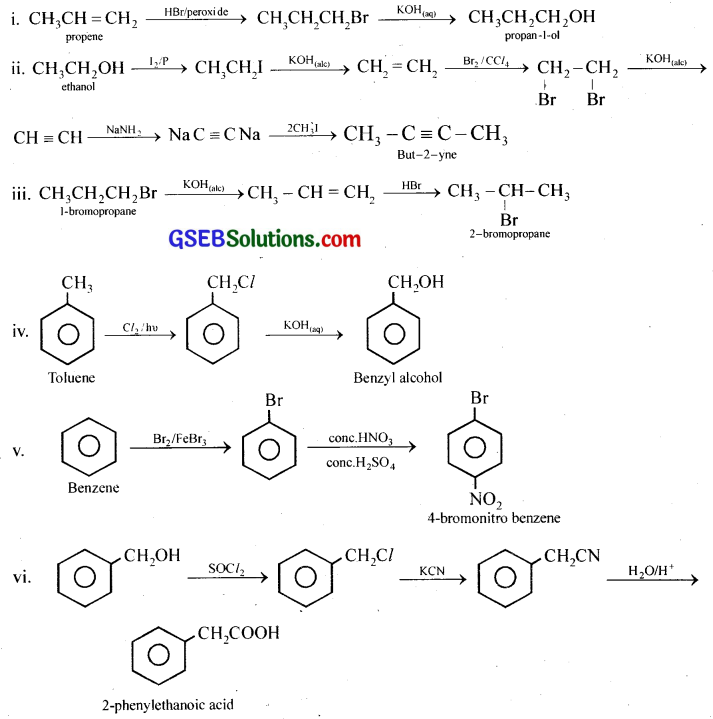
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol
(ii) Ethanol to but-2-yne
(iii) 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
(iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene
(vi) Benzyl alcohol to 2-phenylethanoic acid
(vii) Ethanol to propanenitrile
(viii) Aniline to chlorobenzene
(ix) 2-Chlorobutane to 3,4-dimethylbexane
(x) 2-Methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
(xi) Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid
(xii) But-l-eneton-butyliodide
(xiii) 2-Chloropropane to 1-propanol
(xiv) Chlorobenzene to p-pitrophenol
(xv) 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
(xvi) Chloroethane to butane
(xvii) Benzene to diphenyl
(xviii) tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide
(xix) Aniline to phenylisocyanide
Answer:
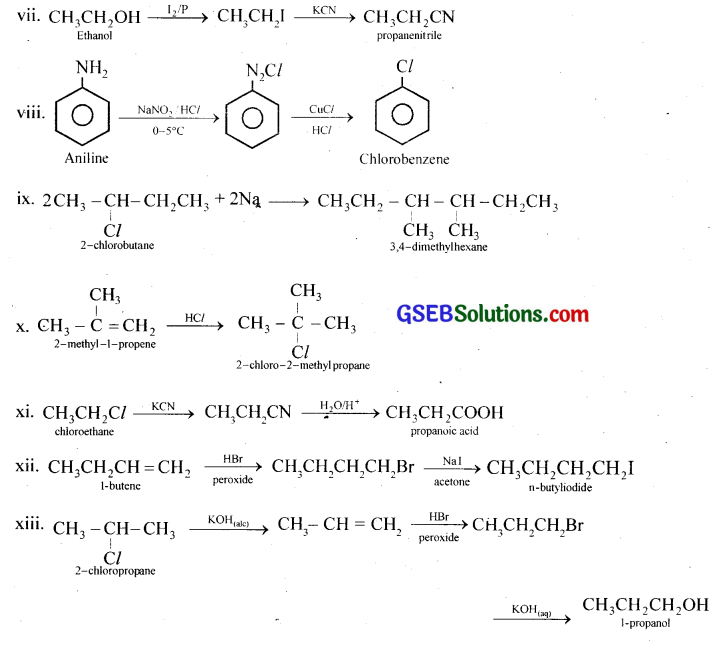
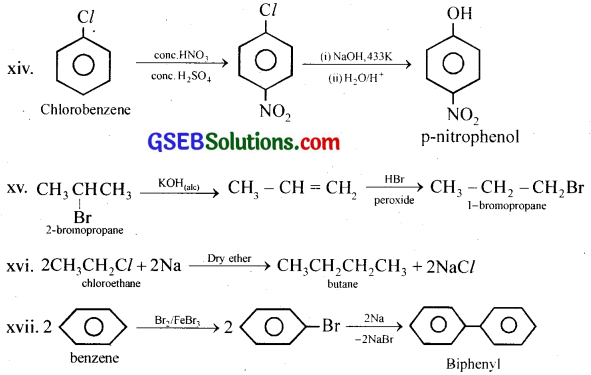
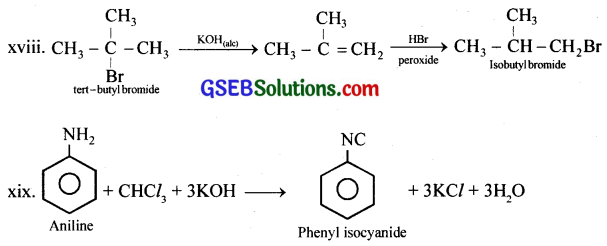
GSEB Class 12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Additional Important Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Give the structure and IUPAC names of any five haloalkanes having the molecular formula C5H11Cl.
Answer:
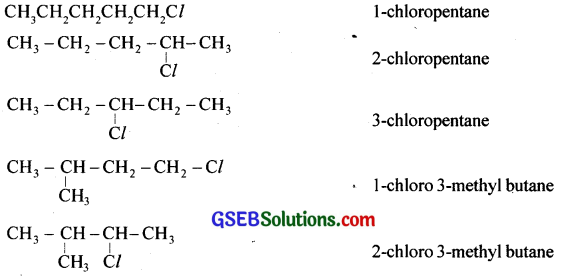
![]()
Question 2.
How will you prepare
(a) methane from methyl chloride
(b) ethane from methyl chloride
(c) toluene from methyl chloride
Answer:
(a) ![]()
(b) 2CH3Cl + 2Na → CH3CH3 + 2NaCl
(c) 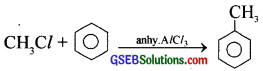
Question 3.
Grignard reagents are widely used in synthetic organic chemistry.
(i) What are Grignard reagents?
(ii) Give an example.
(iii) How are they prepared?
(iv) What happens when Grignard reagent is treated with water?
Answer:
(i) alkyl magnesium halides
(ii) methyl magnesium chloride, CH3MgCl
(iii) ![]()
(iv) CH3MgCl + H3O → CH4 + Mg(OH)Cl
Question 4.
Match the following

Answer:
i. d
ii. a
iii. e
iv. b
v. c
Question 5.
An organic compound ‘A’ reacts with chlorine gas in presence of FeCl3 to give B. B on reaction with a mixture of conc.HNO3 and conc.H2SO4 gives a mixture of ortho and para nitrochlorobenzene. Identify A and B. Write their IUPAC names.
Answer:
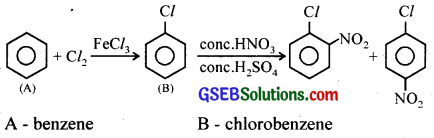
Question 6.
The teacher told the students to treat KOH solution with 1 -chloropropane. One student used alcoholic KOH solution while others used aqueous KOH solution.
(i) What would be the products obtained in each case?
(ii) Justify your answer with chemical equations.
Answer:
i. Student who used alcoholic KOH will get propene and who used aqueous KOH will get 1-propanol
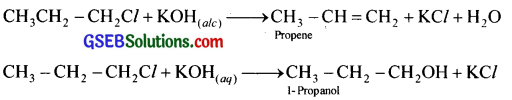
Question 7.
A hydrocarbon having molecular formula C5H12 when treated with chlorine in presence of sunlight can give only one type of monochloro derivative. Write the structure and IUPAC name of the reactant and product in this reaction.
Answer:
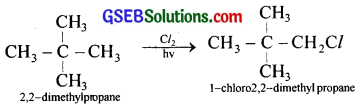
![]()
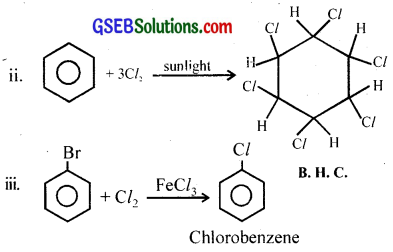
Question 8.
When benzene is treated with chlorine in the presence of sunlight a compound which is commonly used as an insecticide is formed.
(i) Identify the compound obtained.
(ii) Write the chemical equation.
(iii) If the reaction is carried out in the presence of FeCl3 and in the absence of sunlight, what would be the product obtained? Write the chemical equation.
Answer:
i. Benzene hexachloride (C6H6Cl6)
Question 9.
Complete the equation.
CH3 – CH- = CH2 + HBr → ………
i. Identify the product and why do we get this product?
ii. If the reaction is carried out in presence of benzyl peroxide what would be the product? Explain.
Answer:

Question 10.
How will you prepare 2-bromopropane from propene?
Answer:

Question 11.
How will you prepare 1-bromopropane from propene?
Answer:
![]()
![]()
Question 12.
Match the following
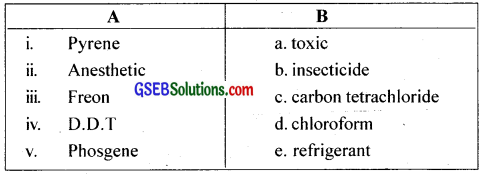
Answer:
i. c
iii. e
iv. b
ii. d
v. a