Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.6 Textbook Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 7 Fractions Ex 7.6
Question 1.
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\) + \(\frac { 7 }{ 15 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 7 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 5 }{ 7 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(e) \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
(f) \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(g) \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(h) \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
(i) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
(j) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
(k) 1\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + 3\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
(l) 4\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + 3\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
(m) \(\frac { 16 }{ 5 }\) – \(\frac { 7 }{ 5 }\)
(n) \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
Solution:
(a) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{2 \times 7}{3 \times 7}\) = \(\frac { 14 }{ 21 }\) [∵ LCM of 3 and 7 = 21]
\(\frac { 1 }{ 7 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 3}{7 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 21 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 7 }\) = \(\frac { 14 }{ 21 }\) + \(\frac { 3 }{ 21 }\) = \(\frac { 14 + 3 }{ 21 }\) = \(\frac { 17 }{ 21 }\)
(b) \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\) + \(\frac { 7 }{ 15 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\) = \(\frac{3 \times 3}{10 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 30 }\) [∵ LCM of 10 and 15 = 30]
\(\frac { 7 }{ 15 }\) = \(\frac{7 \times 2}{15 \times 2}\) = \(\frac { 14 }{ 30 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\) + \(\frac { 7 }{ 15 }\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\) + \(\frac { 14 }{ 30 }\) = \(\frac { 9 + 14 }{ 30 }\) = \(\frac { 23 }{ 30 }\)
(c) \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 7 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\) = \(\frac{4 \times 7}{9 \times 7}\) = \(\frac { 28 }{ 63 }\) [∵ LCM of 9 and 7 = 63]
\(\frac { 7 }{ 15 }\) = \(\frac{2 \times 9}{7 \times 9}\) = \(\frac { 19 }{ 63 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 7 }\) = \(\frac { 28 }{ 63 }\) + \(\frac { 18 }{ 63 }\) = \(\frac { 28 + 8 }{ 63 }\) = \(\frac { 46 }{ 63 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 5 }{ 7 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 5 }{ 7 }\) = \(\frac{5 \times 3}{7 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 21 }\) [∵ LCM of 7 and 3 = 21]
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 7}{3 \times 7}\) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 21 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 5 }{ 7 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 21 }\) + \(\frac { 7 }{ 21 }\) = \(\frac { 15 + 7 }{ 21 }\) = \(\frac { 22 }{ 21 }\) ![]()
(e) \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac{2 \times 6}{5 \times 6}\) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 30 }\) [∵ LCM of 5 and 6 = 30]
\(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 5}{6 \times 5}\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 30 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 30 }\) + \(\frac { 5 }{ 30 }\) = \(\frac { 12 + 5 }{ 30 }\) = \(\frac { 17 }{ 30 }\)
(f) \(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac{4 \times 3}{5 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 15 }\) [∵ LCM of 5 and 3 = 15]
Now, \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{2 \times 5}{3 \times 5}\) = \(\frac { 10 }{ 15 }\)
\(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 15 }\) + \(\frac { 10 }{ 15 }\) = \(\frac { 22 }{ 15 }\) 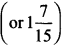
(g) \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac{3 \times 3}{4 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 12 }\) [∵ LCM of 4 and 3 is 12]
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 4}{3 \times 4}\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 12 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 12 }\) – \(\frac { 4 }{ 12 }\) = \(\frac { 9 – 4 }{ 12 }\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 12 }\)
(h) \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 2}{3 \times 2}\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 }\) [∵ LCM of 6 and 3 is 6]
Now, \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 5 – 2 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) ![]()
(i) \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{2 \times 7}{3 \times 7}\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 12 }\) [∵ LCM of 2, 3 and 4 = 12]
\(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac{3 \times 7}{4 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 12 }\)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 6}{2 \times 6}\) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 12 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 12 }\) + \(\frac { 9 }{ 12 }\) + \(\frac { 6 }{ 12 }\) = \(\frac{8+9+6}{12}\)
(j) \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 3}{2 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) [∵ LCM of 2, 3 and 6 = 6]
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 2}{3 \times 2}\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac{3+2+1}{6}\) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 6 }\) (or 1)
(k) 1\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + 3\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
Method I
We have: 1\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) and 3\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 11 }{ 3 }\)
Now, 1\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + 3\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 11 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 4 + 11 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 3 }\) = 5
Method II
We have: 1\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = 1 + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) and 3\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = 3 + \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
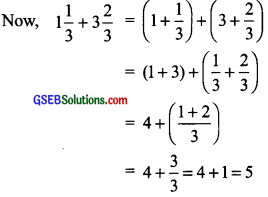
(l) 4\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + 3\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
We have: 4\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 14 }{ 3 }\) and 3\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 13 }{ 4 }\) [∵ LCM of 3 and 4 = 12]
∴ 4\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + 3\(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 14 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 13 }{ 4 }\)
\(\frac { 14 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{14 \times 4}{3 \times 4}\) = \(\frac { 56 }{ 12 }\)
and \(\frac { 13 }{ 4 }\) = = \(\frac{13 \times 3}{4 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 39 }{ 12 }\)
∴ \(\frac { 14 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 13 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 56 }{ 12 }\) + \(\frac { 39 }{ 12 }\)
= \(\frac{56+39}{12}\) = \(\frac { 95 }{ 12 }\) = 7 \(\frac { 11 }{ 12 }\)
(m) \(\frac { 16 }{ 5 }\) – \(\frac { 7 }{ 5 }\)
We have:
\(\frac { 16 }{ 5 }\) – \(\frac { 7 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac { 16 – 7 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 5 }\) = 1\(\frac { 4 }{ 5 }\)
(n) \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)
We have: \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{4 \times 2}{3 \times 2}\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 6 }\) [∵ LCM of 3 and 2 = 6]
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 3}{2 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\)
Now, \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 8 – 3 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\)
![]()
Question 2.
Sarita bought \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) metre of ribbon and Lalita \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) metre of ribbon. What is the total length of the ribbon they bought?
Solution:
∵ Ribbon bought by Santa = \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) metre
Ribbon bought by Lalita = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) metre
∴ Total ribbon bought by them = \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) m + \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) m
Now, \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac{2 \times 4}{5 \times 4}\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 20 }\) and \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac{3 \times 5}{4 \times 5}\) = \(\frac { 15 }{ 20 }\) [∵ LCM of 4 and 5 is 20]
∴ \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) m + \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) m = \(\frac { 8 }{ 20 }\) m + \(\frac { 15 }{ 20 }\) m = \(\frac{8 m+15 m}{20}\) = \(\frac { 23 }{ 20 }\) m
![]()
Question 3.
Naina was given 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) piece of cake and Najma was given 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) piece of cake. Find the total amount of cake given to both of them.
Solution:
Amount of cake given to Naina = 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) piece
Amount of cake given to Najma = 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) piece
∴ Total amount of cake given to them = 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) piece + 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) piece
We have:
1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) and 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\)
Also \(\frac { 3 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac{3 \times 3}{2 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 6 }\) and \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{4 \times 2}{3 \times 2}\) = \(\frac { 8 }{ 6 }\)
∴ 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) piece + 1 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = ![]() piece
piece
=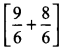 piece = \(\frac{9+8}{6}\) piece = \(\frac { 17 }{ 6 }\) piece
piece = \(\frac{9+8}{6}\) piece = \(\frac { 17 }{ 6 }\) piece
![]()
Question 4.
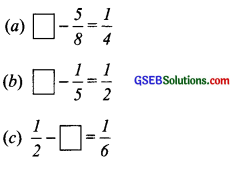
(a)
![]()
Here, the ‘missing fraction’ is more than \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) by \(\frac { 5 }{ 8 }\).
∴ Missing fraction = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) + \(\frac { 5 }{ 8 }\)
We have, \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 2}{4 \times 2}\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 8 }\)
∴ Missing fraction = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) + \(\frac { 5 }{ 8 }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 8 }\) + \(\frac { 5 }{ 8 }\) = \(\frac{2+5}{8}\) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 8 }\)
∴ 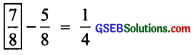
(b)
![]()
Here, the ‘missing fraction’ is more than \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) by \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\).
∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) = Missing fraction
or 
[∵ LCM of 2 and 5 = 10]
or \(\frac { 5 }{ 10 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 10 }\) = Missing fraction
or \(\frac{5+2}{10}\) or \(\frac { 7 }{ 10 }\) = Missing fraction
Thus, 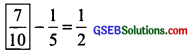
(c)
![]()
Here, the ‘missing fraction’ is less than \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) by \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
∴ Missing fraction = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
= \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)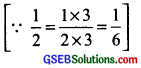
= \(\frac{3-1}{6}\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
∴ 
![]()
Question 5.
Complete the addition-subtraction box.
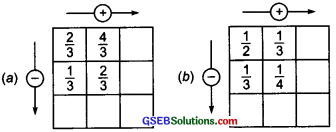
Solution:
(a) ∵ \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{2+4}{3}\) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 3 }\) = 2
And \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{1+2}{3}\) + \(\frac { 3 }{ 3 }\) = 1
Also, \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{2-1}{3}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)
and \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) – \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{4-2}{3}\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
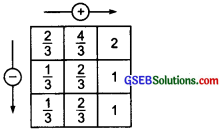
We also have:
2 – 1 = 1 and \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\) = 1
(b) ∵ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 3}{2 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) and \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 2}{3 \times 2}\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 }\)
∵ \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) + \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) [∵ LCM of 2 and 3 = 6]
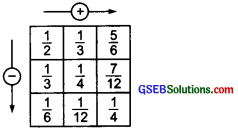
and \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 2 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\)
Again, \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 4}{3 \times 4}\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 12 }\) and \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 3}{4 \times 3}\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 12 }\) [∵ LCM of 3 and 4 = 12]
∴ \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 12 }\) + \(\frac { 3 }{ 12 }\) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 12 }\)
and \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 4 }{ 12 }\) – \(\frac { 3 }{ 12 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 12 }\)
Again, we have \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 12 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) and \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) – \(\frac { 7 }{ 12 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)
![]()
Question 6.
A piece of wire \(\frac { 7 }{ 8 }\) metre long broke into two pieces. One-piece was \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) metre long. How long is the other piece?
Solution:
Length of the original piece of wire = \(\frac { 7 }{ 8 }\) m As it is broken into two pieces, and one of the parts is \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) m,
∴ Length of the other part = ![]() m
m
Since, \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac{1 \times 2}{4 \times 2}\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ 8 }\)
∴ \(\frac { 7 }{ 8 }\) – \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac { 7 }{ 8 }\) – \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\)
∴ ![]() m = \(\frac { 7 }{ 8 }\)m
m = \(\frac { 7 }{ 8 }\)m
Thus, the length of the other part is \(\frac { 5 }{ 8 }\)m
![]()
Question 7.
Nandini s house is \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\) km from her school. She walked some distance and then took a bus for \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) km to reach the school. How far did she walk?
Solution:
Distance between Nandini’s house and school = \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 }\) km
Distance covered by bus = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) km
∴ Distance covered by walking = ![]() km
km

![]()
Question 8.
Asha and Samuel have bookshelves of the same size partly filled with books. Asha s shelf is \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) the full and Samuel’s shelf is \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) the full. Whose bookshelf is more full and by what fraction?
Solution:
‘ Portion of Asha’s shelf full of books = \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\)
Portion of Samuel’s shelf full of books = \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\)
Changing the fraction into equivalent fractions having the same denominator.
We have: \(\frac { 5 }{ 6 }\) = \(\frac{5 \times 5}{6 \times 5}\) = \(\frac { 25 }{ 30 }\) and \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac{2 \times 6}{5 \times 6}\) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 30 }\) [ ∵ HCF of 5 and 6 is 30]
Obviously, portion of Asha’s shelf is more full.
Now, \(\frac { 25 }{ 30 }\) – \(\frac { 12 }{ 30 }\) = \(\frac { 25 – 12 }{ 30 }\) = \(\frac { 13 }{ 30 }\)
∴ Fraction by which Asha’s shelf is more full = \(\frac { 13 }{ 30 }\)
![]()
Question 9.
Jaidev takes 2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) minutes to walk across the school ground. Rahul takes \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\) minutes to do the same. Who takes less time and by what fraction?
Solution:
To walk across the school ground:
Time taken by Jaidev = 2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) minutes
Time taken by Rahul = \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\) minutes
We have,
2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac { 11 }{ 5 }\) = \(\frac{11 \times 4}{5 \times 4}\) = \(\frac { 44 }{ 20 }\)
[∵ LCM of 4 and 5 = 20]
Also
Obviously, Rahul takes less time.
Now, \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\) = \(\frac{7 \times 5}{4 \times 5}\) = \(\frac { 35 }{ 20 }\)
∴ 2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 5 }\) minutes – \(\frac { 7 }{ 4 }\) minutes = \(\frac { 9 }{ 20 }\) minutes
Thus, Rahul takes \(\frac { 9 }{ 20 }\) minutes less time.