Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 12 Ratio and Proportion Ex 12.1 Textbook Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 12 Ratio and Proportion Ex 12.1
Question 1.
There are 20 girls and 15 boys in a class.
(a) What is the ratio of the number of girls to the number of boys?
(b) What is the ratio of the number of girls to the total number of students in the class?
Solution:
Number of girls in the class = 20
Number of boys in the class = 15
∴ Total number of students in the class = 20 + 15 = 35
Now,
(a) Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Number of girls }}{\text { Number of boys }}\) = \(\frac{20}{15}\) = \(\frac{20 \div 5}{15 \div 5}\) =\(\frac{4}{3}\) = 4 : 3
[∵ HCF of 15 and 20 is 5]
(b) Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Number of girls }}{\text { Total Number of students }}\) = \(\frac{20}{35}\) = \(\frac{20 \div 5}{35 \div 5}\) =\(\frac{4}{7}\) = 4 : 7
[∵ HCF of 20 and 35 is 5]
![]()
Question 2.
Out of 30 students in a class, 6 like football, 12 like cricket and remaining like tennis. Find the ratio of
(a) Number of students liking football to a number of students liking tennis.
(b) Number of students liking cricket to the total number of students.
Solution:
Total number of students = 30
∵ Number of students who
like football = 6
like cricket = 12
∴ Remaining number of students liking tennis = 30 – (12 + 6) = 30 – 18 = 12
Now,
(a) Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Number of students liking football }}{\text { Number of students who like tennis }}\) = \(\frac{6}{12}\) = \(\frac{6 \div 6}{12 \div 6}\) =\(\frac{1}{2}\) = 1 : 2
[∵ HCF of 6 and 12 is 6]
(b) Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Number of students liking cricket }}{\text { Total Number of students }}\) = \(\frac{12}{30}\) = \(\frac{12 \div 6}{30\div 6}\) =\(\frac{2}{5}\) = 2 : 5
[∵ HCF of 12 and 30 = 6]
![]()
Question 3.
See the figure and find the ratio of
(a) Number of triangles to the number of circles inside the rectangle.
(b) Number of squares to all the figures inside the rectangle.
(c) Number of circles to all the figures inside the rectangle.
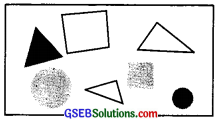
Solution:
Number of triangles = 3
Number of squares = 2
Number of circles = 2
∴ Total number of figures =3 + 2 + 2 = 7
Now,
(a) Ratio of triangles to circles = \(\frac{\text { Number of triangles }}{\text { Number of circles}}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\) = 3 : 2
(b) Ratio of squares to all figures = \(\frac{\text { Number of squares }}{\text { Number of all figures}}\) = \(\frac{2}{7}\) = 2 :7
(c) Ratio of circle to all figures = \(\frac{\text { Number of circles }}{\text { Number of all figures}}\) = \(\frac{2}{7}\)1 = 2 : 7
Question 4.
Distances traveled by Hamid and Akhtar in an hour are 9 km and 12 km. Find the ratio of the speed of Hamid to the speed of Akhtar.
Solution:
Speed of Hamid = 9 km/hr
Speed of the Akhtar = 12 km/hr
∴ Ratio = \(\frac{\text { Speed of Hamid }}{\text { Speed of the Akhtar }}\) = \(\frac{9}{12}\) = \(\frac{9 \div 3}{12 \div 3}\) =\(\frac{3}{4}\) = 3 : 4
[∴ HCF of 9 and 12 is 3]
Question 5.
Fill in the following blanks:
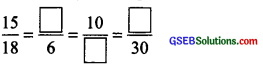
[Are these equivalent ratios?]
Solution:
By cross products, we have:
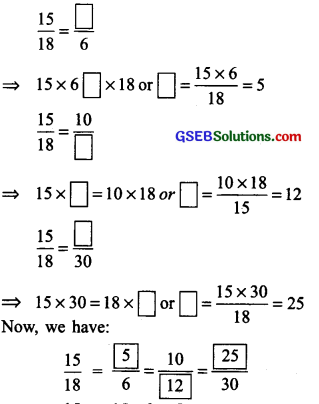
Again, \(\frac{15}{18}\) = \(\frac{15 \div 3}{18 \div 3}\) =\(\frac{5}{6}\)
[∵ HCF of 15 and 18 is 3]
And \(\frac{25}{30}\) = \(\frac{25 \div 5}{30 \div 5}\) =\(\frac{5}{6}\)
[∵ HCF of 25 and 30 is 5]
Also, \(\frac{10}{12}\) = \(\frac{10 \div 2}{12 \div 2}\) =\(\frac{5}{6}\)
[∵ HCF of 10 and 12 is 2]
∴ \(\frac{15}{18}\) = \(\frac{5}{6}\) = \(\frac{10}{12}\) = \(\frac{25}{30}\)\(\left(\text { each }=\frac{5}{6}\right)\)
Thus, ratios are equivalent.
![]()
Question 6.
Find the ratio of the following:
(a) 81 to 108
Solution:
\(\frac{81}{108}\) = \(\frac{81 \div 27}{108 \div 27}\) =\(\frac{3}{4}\) = 3 : 4
[∵ HCF of 81 and 108 = 27]
(b) 98 to 63
Solution:
\(\frac{98}{63}\) = \(\frac{98\div 7}{63 \div 7}\) =\(\frac{14}{9}\) = 14 : 9
[∵ HCF of 98 and 63 is 7]
(c) 33 km to 121 km
Solution:
\(\frac{33km}{121km}\) = \(\frac{33\div 11}{121 \div 11}\) =\(\frac{3}{11}\) = 3 : 11
[∵ HCF of 33 and 121 is 11]
(d) 30 minutes to 45 minutes
Solution:
\(\frac{30 minutes}{45 minutes}\) = \(\frac{30\div 15}{45 \div 15}\) =\(\frac{2}{3}\) = 2 : 3
[∵ HCF of 30 and 45 is 15]
Question 7.
Find the ratio of the following:
(a) 30 minutes to 1.5 hours
Solution:
\(\frac{30 \text { minutes }}{1.5 \text { hour }}=\frac{30 \text { minutes }}{90 \text { minutes }}\)
= \(\frac{30}{90}\) = \(\frac{30\div 30}{90\div 30}\) =\(\frac{1}{3}\) = 1 : 3
[∵ HCF of 30 and 90 is 30]
(b) 40 cm to 1.5 m
Solution:
\(\frac{40 \text { cm }}{1.5 \text { m }}=\frac{40 \text { cm }}{150 \text { cm }}\)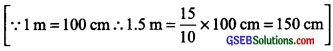
= \(\frac{40}{150}\) = \(\frac{40\div 10}{150\div 10}\)
[∵ HCF of 40 and 150 is 10]
= \(\frac{1}{15}\) = 4 : 15
(c) 55 paise to ₹ 1
Solution:
Ratio of 55 paise to ₹ 1
\(\frac { 55 paise }{ ₹ 1 }\) [∵ ₹ 1 = 100 paise]
\(\frac { 55 }{ 100}\) = \(\frac{55 \div 5}{100 \div 5}\)
[∵ HCF of 55 and 100 is 5]
\(\frac { 11 }{ 20}\) = 11 : 20
(d) 500 ml to 2 litres
Solution:
Ratio of 500 ml to 2 litres
\(\frac { 500 ml }{ 2 liters }\) [∵ 1 litre = 1000 ml]
\(\frac { 500 ml }{ 2ooo ml }\) = \(\frac { 500}{ 2ooo }\) = \(\frac{500\div 500}{2000\div 500}\) = 1 : 4
[∵ HCF of 500 and 2000 is 500]
![]()
Question 8.
In a year, Seema earns ₹1,50,000 and saves ₹ 50,000. Find the ratio of
(a) Money that Seema earns to the money she saves.
(b) Money that she saves to the money she spends.
Solution:
Total earnings = ₹ 1,50,000
Savings =₹ 50,000
(a) Ratio of earnings to savings
\(\frac {₹ 150000 }{ ₹ 50000 }\) = \(\frac{150000\div 50000}{50000\div 50000}\)
[∵ HCF of 1,50,000 and 50,000 is 50,000]
\(\frac { 3 }{ 1 }\) = 3 : 1
(b) ∵ Money that Seema spends
= ₹ 150000 – ₹ 50000 = ₹ 1,00,000
.’. Ratio of savings to expenditure
\(\frac {₹ 50000 }{ ₹ 100000 }\) = \(\frac{50000\div 50000}{100000\div 50000}\)
[∵ HCF of 50000 and 100000 is 50000]
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = 1 : 2
![]()
Question 9.
There are 102 teachers in a school of 3300 students. Find the ratio of the number of teachers to the number of students.
Solution:
Number of teachers = 102
Number of the students = 3300
∴ Ratio of teachers to students
\(\frac { 102 }{ 3300 }\) = \(\frac{102 \div 6}{3300 \div 6}\)
[∵ HCF of 102 and 3300 is 6]
= \(\frac { 17 }{ 550 }\) = 17 : 550
Question 10.
In a college, out of4320 students, 2300 are girls. Find the ratio of
(a) Number of girls to the total number of students.
(b) Number of boys to the number of girls.
(c) Number of boys to the total number of students.
Solution:
Total number of students = 4320
Number of girls = 2300
Number of boys = 4320 – 2300 = 2020
(a) Ratio of number of girls to total number of students
\(\frac { 2300 }{ 4320 }\) = \(\frac{2300\div 20}{4320\div 20}\)
[∵ HCF of 2300 and 4320 is 20]
\(\frac { 115 }{ 216 }\) = 115 : 216
(b) Ratio of number of girls to total number of students
\(\frac { 2020 }{ 2300 }\) = \(\frac{2020\div 20}{2300\div 20}\)
[∵ HCF of 2020 and 2300 is 20]
\(\frac { 101 }{ 115 }\) = 101 : 115
(c) Ratio of number of girls to total number of students
\(\frac { 2020 }{ 4320 }\) = \(\frac{2020\div 20}{4320\div 20}\)
[∵ HCF of 2020 and 4320 is 20]
\(\frac { 101 }{ 216 }\) = 101 : 216
![]()
Question 11.
Out of 1800 students in a school, 750 opted basketball, 800 opted cricket, and the remaining opted table tennis. If a student can opt for only one game, find the ratio of
(a) Number of students who opted for basketball to the number of students who opted for table tennis.
(b) Number of students who opted for cricket to the number of students opting for basketball.
(c) Number of students who opted for basketball to the total number of students.
Solution:
Total number of students = 1800
Number of students who opted for basketball = 750
Number of students who opted for cricket = 800
Number of students who opted table tennis = 1800 – [750 + 800] = 1800 – 1550 = 250
Now,
(a) Ratio of number of students opting basketball to table tennis
\(\frac { 750 }{ 250 }\) = \(\frac{750\div 250}{250\div 250}\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ 1 }\) = 3 : 1
[ ∵ HCF of 750 and 250 is 250]
(b) Ratio of number of students opting cricket to basketball
\(\frac { 800 }{ 750 }\) = \(\frac{800\div 50}{750\div 50}\) = \(\frac { 16 }{ 15 }\) = 16 : 15
[∵ HCF of 800 and 750 is 50]
(c) Ratio of number of students opting basketball to total number of students.
\(\frac { 750 }{ 1800 }\) = \(\frac{750\div 150}{1800\div 150}\) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 12 }\) = 5 : 12
[∵ HCF of 750 and 1800 is 150]
![]()
Question 12.
Cost of a dozen pens is? 180 and cost of 8 ball pens are? 56. Find the ratio of the cost of a pen to the cost of a ball pen.
Solution:
Cost of 12 pens = ₹ 180
Cost of 1 pen = ₹ 180 + 12 = ₹ 15
Cost of 8 ball pens = ₹ 56
Cost of 1 ball pen = ₹ 56 + 8 = ₹ 7
Now, ratio of the cost of a pen to the cost of a ball pen = \(\frac { ₹ 15 }{ ₹ 7 }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = 15 : 7
Question 13.
Consider the statement: Ratio of breadth and length of a hall is 2:5. Complete the 1 following table that shows some possible breadths, and lengths of the hall.

Solution:

Thus, corresponding to the length of 50 m, the breadth is 20 m.
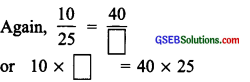
[using the cross product of equivalent fractions]
![]()
Thus, corresponding to the length of 40 m, the length is 100 m.
Now, the table is completed as given below:

Question 14.
Divide 20 pens between Sheela and Sangeeta in the ratio of 3 : 2.
Solution:
Total number of pens = 20
∵ Sheela’s share: Sangeeta’s share = 3 : 2
Sum of ratios = 3 + 2 = 5
∵ Share of Sheela in 5 pens is 3 and Sangeeta’s share in 5 pens = 2
∴ Sheela’s share in 20 pens = \(\frac { 3 }{ 5 }\) × 20 = 12
Sangeeta’s share in 20 pens = \(\frac { 2 }{ 5 }\) × 20 = 8
Question 15.
Does the mother want to divide? 36 between her daughters Shreya and Bhoomika in the ratio of their ages. If the age of Shreya is 15 years and the age of Bhoomika is 12 years, find how much Shreya and Bhoomika will get.
Solution:
Age of Shreya =15 years
Age of Bhoomika = 12 years
∴ Ratio of their ages = \(\frac { 15 years }{ 12 years }\) = \(\frac{15 \div 3}{12 \div 3}\) =\(\frac{5}{4}\)
[∵ HCF of 15 and 12 is 3]
Sum of the ratios = 5 + 4 = 9
Total amount to be divided = ₹ 36
∴ Shreya’s share = ₹ \(\frac { 5 }{ 9 }\) × 36 = ₹ 20
Bhoomika’s share = ₹ \(\frac { 4 }{ 9 }\) × 36 = ₹ 16
![]()
Question 16.
The present age of the father is 42 years and that of his son is 14 years. Find the ratio of
(a) Present age of father to the present age of the son.
(b) Age of the father to the age of the son, when the son was 12 years old.
(c) Age of father after 10 years to the age of son after 10 years.
(d) Age of father to the age of son when father was 30 years old.
Solution:
(a)∵ Present age of father = 42 years
Present age of son = 14 years
∴ Ratio of their ages = \(\frac { Age of father }{ Age of son }\)
\(\frac { 42 years }{ 14 years }\) = \(\frac{42 \div 14}{14 \div 14}\)
[∵ HCF of 14 and 42 is 14]
\(\frac { 3 }{ 1 }\) = 3 : 1
(b) Obviously when son’s age was 12 years
(i.e. 2 years ago), then father’s age was (42 years – 2 years) = 40 years.
∴ Ratio of father’s age to son’s age
\(\frac { 42 years }{ 12 years }\) = \(\frac{40 \div 14}{12 \div 14}\)
[∵ HCF of 40 and 12 is 4]
\(\frac { 10 }{ 3 }\) = 10 : 3
(c) After 10 years
Age of father= 42 years + 10 years = 52 years
Age of son= 14 years + 10 years = 24 years
∴ Ratio of father’s age to son’s age
\(\frac { 52 years }{ 24 years }\) = \(\frac{52 \div 14}{24 \div 14}\)
[∵ HCF of 52 and 24 is 4]
\(\frac { 13 }{ 6 }\) = 13 : 6
(d) ∵ 42 – 30 = 12
∴ 12 years ago, age of father was = 30 years
and 12 years ago, age of son was = 14 years – 12 years = 2 years
∴ Ratio of father’s age to the son’s age
\(\frac { 30 years }{ 2 years }\) = \(\frac{30 \div 2}{2 \div 2}\)
[∵ HCF of 30 and 2 is 2]
\(\frac { 15 }{ 1 }\) = 15 : 1