Gujarat Board GSEB Solutions Class 6 Social Science Chapter 2 Maps Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 6 Social Science Chapter 2 Maps
GSEB Class 6 Social Science Maps Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What is a map ? OR What is called a map ?
Answer:
A small scale representation of the whole or part of the earth on a flat surface is called a ‘map’.
Question 2.
List the main components of a map.
OR
What are the main components of a map ? Which are they?
Answer:
There are three main components of a map:
- direction
- Scale and
- Conventional signs.
![]()
Question 3.
Name three types of maps that you have seen.
Answer:
Three types of maps that I have seen are:
- Political Map
- Physical Map and
- Weather Map.
Question 4.
What is the difference between a Physical map and a Political map?
Answer:
In physical maps, various landforms such as mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers, deserts, coastal plains, etc. are shown with different colours. Their names are also mentioned. Whereas in political maps, the boundaries between countries, states of a country and the districts are shown. Names of the capitals and other cities of districts, nation and other countries are also shown in the political maps.
Question 5.
Which geographical features and natural resources are shown in the distribution maps ?
Answer:
Annual temperature, annual rainfall, atmospheric pressure, winds, agricultural crops, minerals, natural vegetation (forests), etc. are shown in the distribution maps.
Question 6.
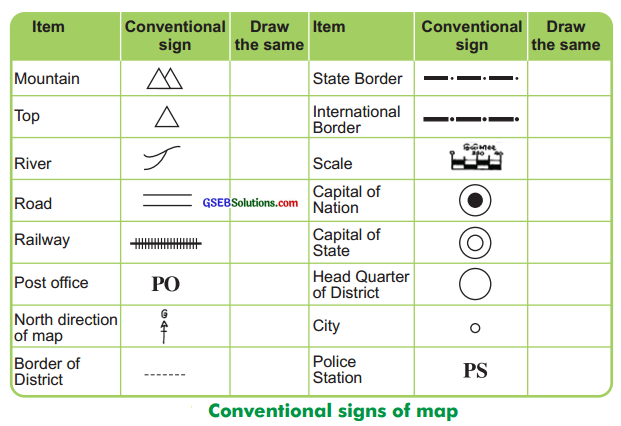
What do you mean by ‘Conventional Signs’ ? How are they used?
Answer:
The signs or symbols like various letters, shades, colours, pictures and lines are used to show natural and man-made landscapes in the map, which are well-known and understood by every one are called ‘conventional signs’. These signs are worldwide accepted language of a map. Maps can be easily drawn, understood and read with their help. Conventional signs give more information in less space.
2. Match the Column ‘A’ with the Column ‘B’:
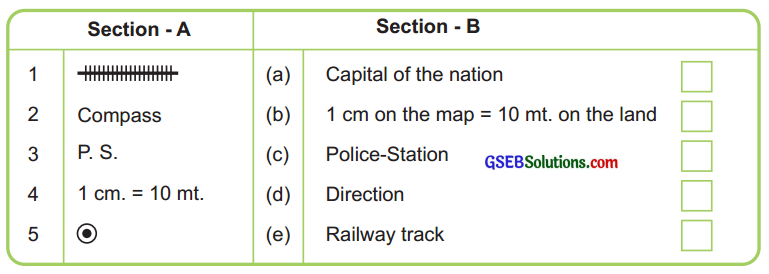
Answer:
1 – 5, 2 – 4, 3 – 3, 4 – 2, 5 – 1
![]()
3. Prepare the map of a room in your notebook with the help of matchsticks on the scale given below:
(1) Length : 20 feet
(2) Width : 10 feet
(3) Scale : 1 foot = 2 matchsticks
[Note : The map of the room as shown to the right is drawn on 5 feet = 1 matchstick scale.]
Answer:

GSEB Class 6 Social Science Maps Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write down the information which is common in all the maps.
OR
Write about the maps in general.
Answer:
Some common information about the map is as follows:
- North direction
- Scale
- Conventional signs and
- Layer Tint method.
Question 2.
How are maps prepared ?
Answer:
Maps are prepared by using direction, scale, conventional signs and different colours.
Question 3.
How can we draw a very large area on a small paper?
Answer:
We can draw a very large area on a small paper with the help of scale.
Activities
Question 1.
Show the conventional signs for the following in your notebook:
Mountain. River, Metalled road, Post office. State border (Boundary). State capital, District headquarter, The North direction in a map.
Answer:
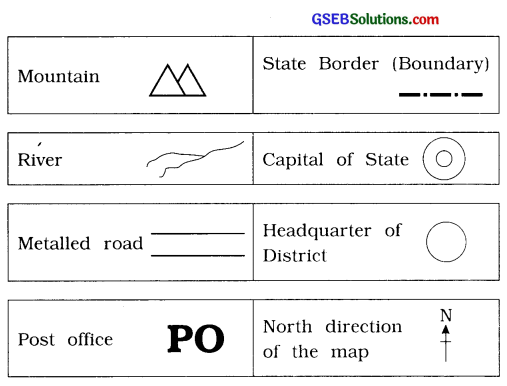
![]()
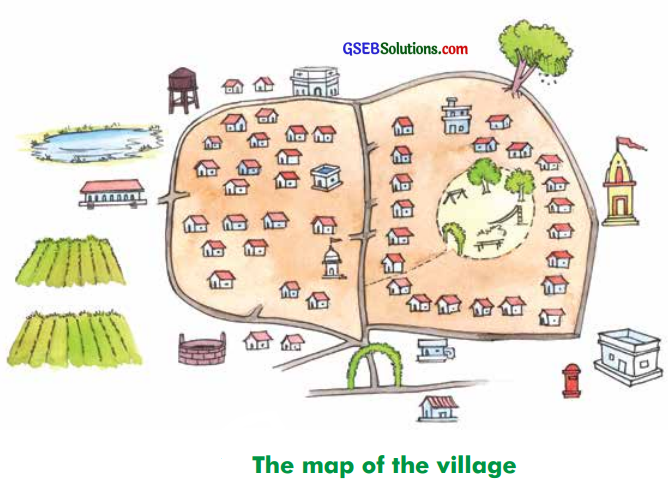
Question 2.
Draw the map of your village or town in your notebook.
(Scale 1 cm =100 metres)
GSEB Class 6 Social Science Maps Additional Important Questions and Answers
Answer the following activity-based questions:
Question 1.
In the table below, arrange the villages / cities nearer to your village/city serially, show their distances and ^lso draw a map of the route. (This table is an example only. Every student can prepare his individual table and answer the questions.)
Answer:
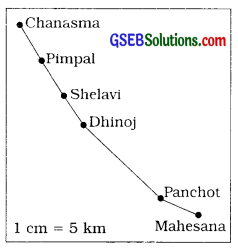
| Sr.No. | Name of the Place | Distance from Chanasma |
| 1. | Pimpal | 5 km |
| 2. | Shelavi | 10 km |
| 3. | Dhinoj | 14 km |
| 4. | Panchot | 28 km |
| 5. | Mahesana | 33 km |
Question 2.
Prepare a list of the maps seen in your school or a library. Note down the items shown in the map :
| Sr. No. | Name of the map | The information shown in the map |
| 1. | Political (India) | • States • Capitals • Major cities • Ports |
| 2. | Physical (India) | • Mountains • Plateaus • Plains • Peaks • Deserts • Coastal plains |
Question 3.
From the items which you saw in the maps in the school or a library, Having gathered enough information, classify the maps given below.
Answer:
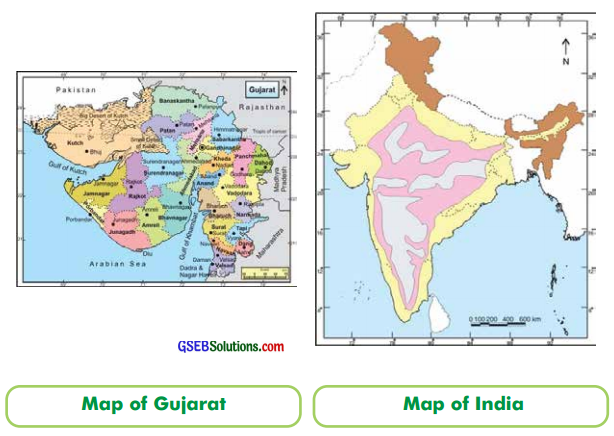
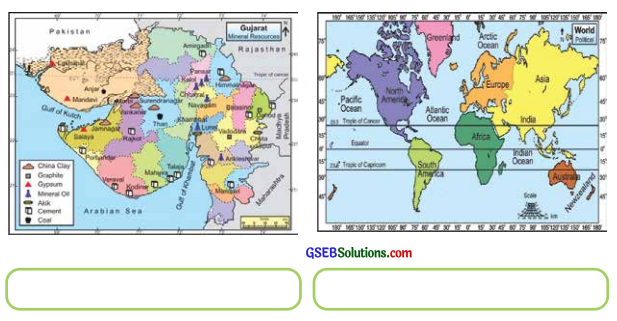

![]()
Question 4.
Take a compass from your school and find out what is seen in the north. Using the directions, find out in which directions are the school gate, post office, dispensary, library, river, pond bridge, etc. located. In the following table, write which things are located in which direction:
[Note: Write the directions in the table by keeping the map of your village in mind.]
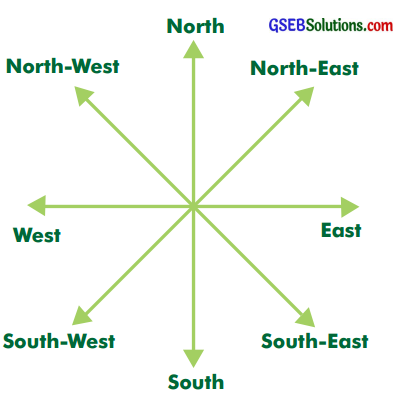
| From school | Direction |
| Gate | North |
| Post office | West |
| Dispensary | North |
| Library | South |
| River | South-West |
| Pond | North-West |
| Temple | South-West |
Question 5.
You might have seen ![]()
![]() such signs somewhere. There are other such signs surrounding us also. Show them here.
such signs somewhere. There are other such signs surrounding us also. Show them here.
Answer:
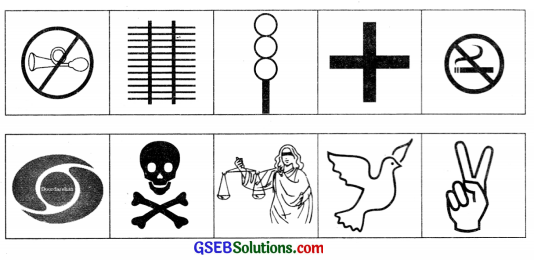
Question 6.
Find out the following conventional signs in your school maps with help of your Social Science teacher.
Answer:
Question 7.
“Come, let us draw a map”.
Students, measure the length and the width of your classroom with the help of a scale. Now, prepare a list of the things which cannot be shifted and decide their symbols also. Then decide a scale and the directions to draw them into a map on the paper.
2 scale = 1 pen cap, matchsticks, eraser, etc. can be taken as a scale, (e.g., if the length is about 10 scale, then 10 scale = 5 pen cap, matchsticks or erasers can be put on the paper and the map can be drawn.)
Answer:
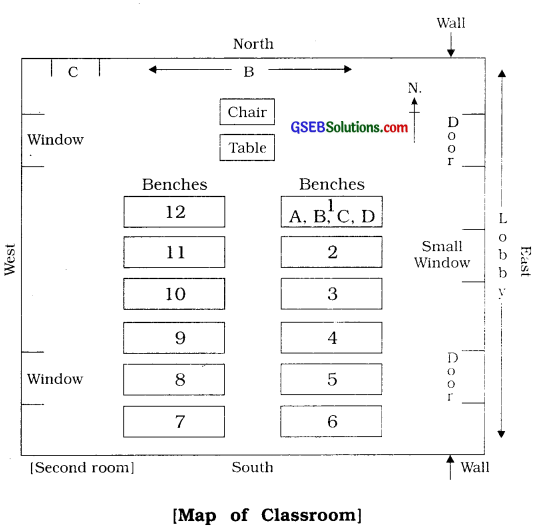
![]()
Choose the correct alternative from those given below each question:
Question 1.
What is the drawing of a flat area of the earth on a paper called ?
A. Conventional sign
B. Map
C. Scale
D. Route map
Answer:
B. Map
Question 2.
With whose help the correct picture of any area can be known ?
A. Map
B. Atlas
C. Route map
D. Direction
Answer:
A. Map
Question 3.
Where is the NATMO (National Atlas and Thematic Maping Organization) located ?
A. Amritsar
B. Dehra Dun
C. Mumbai
D. Kolkata
Answer:
D. Kolkata
Question 4.
Which colour is used to show height in a colour map ?
A. Green
B. Yellow
C. Brown
D. Blue
Answer:
C. Brown
Question 5.
Which colour is used to show forests and vegetation in a colour map ?
A. Green
B. Blue
C. Yellow
D. Brown
Answer:
A. Green
Question 6.
Which colour is used to show plains in a colour map ?
A. Yellow
B. Red
C. Blue
D. Black
Answer:
A. Yellow
![]()
Fill in the blanks with proper words in the following statements:
1. While travelling by road, names of many places are read on the ………………….. along the road.
Answer:
mile stone
2. A ‘……………’ is a drawing of any part of the surface of the earth on a plain paper.
Answer:
map
3. The word ‘Map’ is derived from the Latin word ………………… .
Answer:
Mappa or Mappa- mundi
4. Generally, ![]() sign appears on the ………………. side of any map.
sign appears on the ………………. side of any map.
Answer:
upper
5. The ………………. distance between any two places can be known by the scale.
Answer:
actual
6. Brown colour is used in coloured maps to show
Answer:
height
![]()
7. Green colour is used in coloured maps to show ……………… .
Answer:
forests and vegetation
8. Yellow colour is used in coloured maps to show ………………. .
Answer:
plains
State whether the following statements are true or false:
1. An actual distance between two places can be known with the help of a map.
Answer:
False
2. Conventional signs are a part of maps.
Answer:
True
3. If we stand facing the rising sun, the north direction will be on our back side.
Answer:
False
4. Generally, ![]() sign appears on the upper side of a map.
sign appears on the upper side of a map.
Answer:
True
5. Conventional signs give much information in bigger space.
Answer:
False
![]()
6. Maps with scales are useful to foreigners while travelling.
Answer:
False
7. Various geographical information can be known due to different colours in the maps.
Answer:
True
8. PS is a conventional sign for post office.
Answer:
False
9. ![]() conventional sign for a river.
conventional sign for a river.
Answer:
True
10. ![]() is a conventional sign for a state capital.
is a conventional sign for a state capital.
Answer:
False
Match the appropriate pairs:
| Section ‘A’ | Section ‘B’ |
| 1. Sunrise | 1. Western direction |
| 2. Sunset | 2. Yellow colour |
| 3. Height in a map | 3. Southern direction |
| 4. Plain in the map | 4. Eastern direction |
Answer:
(1 – 4), (2 – 1), (3 – 5), (4 – 2).
![]()
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
What is meant by the organs of a map ?
Answer:
Some aspects which are necessary to understand or to prepare a map are called ‘the organs of a map’.
Question 2.
Give the full form of ‘NATMO’.
Answer:
The full name of ‘NATMO’ is National Atlas and Thematic Maping Organization.
Question 3.
Where is the NATMO (National Atlas and Thematic Maping Organization) institution located ?
Answer:
The NATMO (National Atlas and Thematic Maping Organization) is located at Kolkata.
Question 4.
What is the function of NATMO (National Atlas and Thematic Maping Organization) ?
Answer:
The NATMO (National Atlas and Thematic Maping Organization) produces distribution maps.
Question 5.
In which directions does the sun rise and set ?
Answer:
The sun rises in the east and sets in the west.
Question 6.
If you stand facing the rising sun, which side will be the west and which will be the east of you ?
Answer:
If I stand facing the rising sun, my back side will be west and the front side will be east.
![]()
Question 7.
Which sign generally appears on the upper side of a map ? N
Answer:
Generally,![]() is the sign which appears on the upper side of the map, and it shows the North direction.
is the sign which appears on the upper side of the map, and it shows the North direction.
Question 8.
After finding which direction in the map, all other directions are known automatically?
Answer:
After knowing the North direction in the map. all other directions are automatically known.
Question 9.
What is the importance of scale in a map ?
Answer:
With the help of the scale, the distance between any two places can be known easily.
Question 10.
Which colours are used to show which geographical information ?
Answer:
In a map, brown colour is used to show height, green colour to show forests and vegetation, yellow colour to show plains and blue colour to show water features.
Question 11.
Draw conventional signs used in maps for the following:
[Top (Peak), Metalled Road, Railway, State Border (Boundary), Post office, North direction]
Answer:

![]()
Give brief answers for the following questions:
Question 1.
How is the word ‘Map’ derived ?
Answer:
The word ‘Map’ is derived from the Latin word ‘Mappa’ or ‘Mappa-mundi’. It means a piece of cloth of the size of a handkerchief’.
Question 2.
How is a map useful ?
Answer:
Geographical information about various parts of the earth is easily available from the map. A map is used to know the geographical location of a place or an area. With the help of a map, a small and actual picture of an area can be known. A map serves as a guide to tourists and businessmen. A map is useful in many ways as it is a storehouse of geographical information.