Gujarat Board GSEB Solutions Class 8 Social Science Chapter 4 How the Traders Became Rulers Textbook Exercise Important Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 8 Social Science Chapter 4 How the Traders Became Rulers
GSEB Class 8 Social Science How the Traders Became Rulers Textbook Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
On an outline map of India, mark Satara, Nagpur and Jhansi which were annexed by Lord Dalhousie.
Answer:
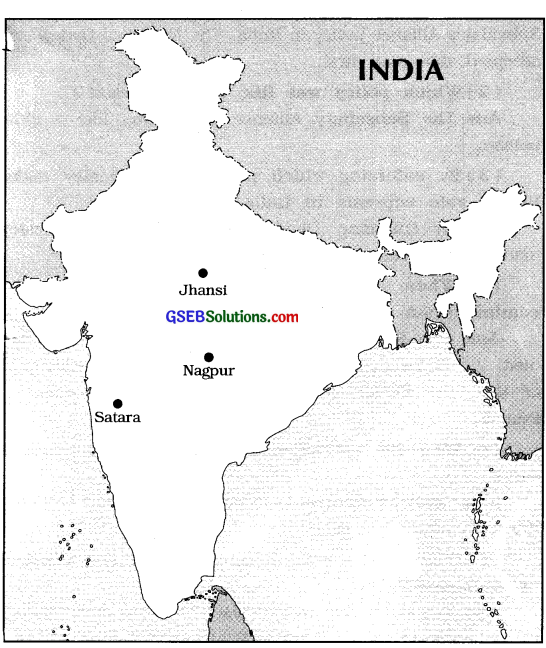
Question 2.
How did the British benefit by Subsidiary Alliance and Annexation Policy?
Answer:
There were many small and large states in India. There was no unity among them. Consequently, Indian states were ruined by the British policy of ‘Divide and Rule’. Many native kings became slaves of the British by accepting Lord Wellesley’s Subsidiary Alliance. In the time period of seven years, Wellesley expanded the company by Subsidiary Alliance and made British rule supreme in India.
The kings who accepted Subsidiary Alliance felt safe and became irresponsible. Consequently, there was absolute mismanagement of states. Dalhousie annexed many states by Annexation policy and established British rule over them. He defeated some states in battle and did not allow childless kings to adopt a son. Their states were also annexed and British rule was established. Thus, Dalhousie established British rule on the whole of India. This is how the British benefitted a lot due to Subsidiary Alliance and Annexation policies.
![]()
Question 3.
Why were the British not successful in establishing their rule in Punjab during the reign of Maharaja Ranjit Singh?
Answer:
Ranjit Singh ‘the Lion of Punjab’ was a very powerful King of Punjab. He had set up a strong army
with the help of European officers to protect his state.
He defeated the kings of nearby states of Punjab. Thus, Maharaja Ranjit Singh was a powerful and victorious ruler.
So the British were not successful in establishing their rule in Punjab during Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s reign.
Question 4.
What reforms were made by Dalhousie in India ?
Answer:
The reforms made by Dalhousie in India were as under :
(1) He started the railway, the telegraph and the postal system. The first railway line was started from Mumbai to Thane in the year 1853 C.E. He introduced the modern postal system in India. It was during his tenure that a telegraph system was started between England and India.
(2) He passed a law to ban child marriages and advocated widow remarriages.
(3) Universities were established in Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata in the year 1857 C.E. with Dalhousie’s efforts.
Question 5.
Discuss about the special features of Subsidiary Alliance and Annexation Policy.
Answer:
Subsidiary Alliance:
- Lord Wellesley introduced a new plan known as ‘Subsidiary Alliance’, to stop the French from becoming the strongest power in India and to make British rule the supreme power in the native states of India.
- The princely states that accepted this policy had to keep and maintain the British army as well as have a British representative in the Royal Court.
- This is how the British maintained their Army without spending money. At the same time they started enslaving and threatening the princely states.
Kings who had accepted the Subsidiary Alliance thought that the British were their friends and would protect them. So they became irresponsible and their administration started deteriorating.
Annexation Policy:
Dalhousie brought in the policy of Annexation which meant bringing an end to the rule sof native kings and bringing his state under the British fule directly.
- Absolute mismanagement of states due to irresponsible kings enabled Dalhousie to annex many states.
- If a king died without a son, his state was annexed. For e.g., Satara, Jaitpur, Jhansi, Sambalpur, Nagpur, Arkat, Tanjore, Karnataka, etc.
- Other states l were annexed by defeating them in battle. For e.g. he annexed Punjab by defeating the Sikhs. Another example is Myanmar. Thus, Lord Dalhousie made British rule I free from rivals with the help of ‘Victory, Confiscation p and Annexation’.
![]()
Activities
(1) Write five-six sentences in your notebook about the British who came to India.
(2) On an outline map of India, mark Avadh (Ayodhya), Satara, Punjab, Nagpur and Jhansi which were annexed by Dalhousie.
(3) Project: After learning the unit write your views about the British.
Answer:
The British were skilled and clever traders. Though they were cheaters, they were intelligent and shrewd politicians. They had advanced weapons like guns, rifles and cannons, by which they wanted to expand their rule in India. They were opportunists and autocrats. They introduced the ‘Divide and Rule’ policy to create unrest among Indian kings.
GSEB Class 8 Social Science How the Traders Became Rulers Intext Questions and Answers
Question 1.
If foreign companies come for trade in India today, can they establish their power?
Answer:
No. If foreign companies come for trade in India today, they cannot establish their power because today India is a democratic, sovereign, republic nation.
Question 2.
Why did the British establish their rule first in Bengal?
Answer:
Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, pulled down the new building of Fort William of Kolkata which was built by the British. So there was a battle between Siraj-ud-Daulah and British army under the leadership of Robert Clive in Plassey in 1757 C.E. The British were victorious in that battle. Consequently, the British got estates of 24 native states. The British had not come in conflict with any king in India before this. For the first time, they came in conflict with the Nawab of Bengal and were victorious. Thus, the British established their rule first in Bengal.
Question 3.
Why was it essential for the British to conquer the Sikh and Afghan territories ?
Answer:
The British needed to conquer the Sikh and Afghan territories in South India and Central India by Subsidiary Alliance and Annexation policy. After that, the British wished to establish their rule in North India. If they wanted to establish their rule in North India, they would have to establish their rule on the Sikh empire and Afghan states. Moreover, the Sikh empire and Afghan states were situated on the north-west border of India. If they could rule these states, they could stop any foreign attack from this border. So the British had to establish their rule over the Sikh empire and Afghan states.
Question 4.
How could the British establish their rule all over India despite having a small army ?
Answer:
When the British came to India, there were many small and large states in India. There was no internal unity among them. Sometimes a king would take the help of the British army to defeat another king. Though kings who accepted Subsidiary Alliance had the British army, they could not make use of it. Moreover, the British army had modern weapons like guns and cannons. The soldiers who were loyal to their leaders fought with discipline. Thus, despite the British had a small army, they could establish their rule all over India.
![]()
Question 5.
The British established their rule almost all over India in a very short time period with the policy of ‘Subsidiary Alliance’ and ‘Policy of Annexation’. How did this happen?
Answer:
When the British came to India, there were many small and large states in our country. There was no internal unity among them. Sometimes a king took the help of the British army to defeat another king. No king had the foresight to see the welfare of the whole nation. Many kings who accepted Subsidiary Alliance, became a slave of the British and also became irresponsible, idle and sensual. Their battle skill and bravery were ruined. Consequently, Lord Dalhousie conquered many states and brought them under the company rule with the help of his Annexation policy. In a short time, he established British rule all over India.
Question 6.
You get a book published in England with details of the Victory of the British in 1857. What will be your feedback or response after reading it?
Answer:
The British took advantage of the weakness of Indian kings. Many kings became worthless due to the Subsidiary Alliance and the Annexation policies and accepted the British rule. Glimpses of heroism shown by Rani Laxmibai of Jhansi, Nana Saheb Peshwa, Mughal Emperor Bahadur Shah, Begam Hajarat Mahal of Ayodhya, Kunwarsingh the Jagirdar of Jagdishpur, Tatya Tope, etc. during the uprising of 1857 are not seen in this book.
The mutiny of 1857 was India’s first freedom fight. It is not mentioned anywhere in the book. The British accepted fraudulent politics in 1857 to gain victory. The whole book is written on the basis of falsehood with the feelings of partiality.
GSEB Class 8 Social Science How the Traders Became Rulers Additional Important Questions and Answers
Choose the correct alternative from those given below each question:
Question 1.
Which plan was like a slow poison ?
A. Annexation Policy
B. Subsidiary Alliance
C. Dual System Policy
D. The rule of Nawab Policy
Answer:
B. Subsidiary Alliance
Question 2.
Who started Subsidiary Alliance ?
A. Lord Wellesley
B. Lord Hastings
C. Lord Dalhousie
D. Lord William Bentinck
Answer:
A. Lord Wellesley
Question 3.
Who accepted Subsidiary Alliance first ?
A. Tipu Sultan
B. Hyder Ali
C. Ranjit Singh
D. Nizam
Answer:
D. Nizam
Question 4.
After the death of which Peshwa, was there war among Maratha States ?
A. Nana Saheb
B. Balaji Bajirao
C. Nana Fadanvis
D. Narayan Rao
Answer:
C. Nana Fadanvis
Question 5.
Within how many years did Wellesley expand the British company and make British rule supreme in India ?
A. Seven
B. Five
C. Six
D. Four
Answer:
A. Seven
![]()
Question 6.
Between which cities was the first railway line started in India ?
A. Between Mumbai and Satara
B. Between Mumbai and Thane
C. Between Mumbai and Surat
D. Between Mumbai and Pune
Answer:
B. Between Mumbai and Thane
Question 7.
When did the first railway line start in India ?
A. 1848 C.E.
B. 1853 C.E.
C. 1851 C.E.
D. 1858 C.E.
Answer:
B. 1853 C.E.
Question 8.
In which cities were universities established first in India ?
A. In Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata
B. In Mumbai, Delhi and Bengaluru
C. In Mumbai, Ahmedabad and Delhi
D. In Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata
Answer:
A. In Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata
Question 9.
In which year were the three universities established in India ?
A. In 1857 C.E.
B. In 1858 C.E.
C. In 1864 C.E.
D. In 1860 C.E.
Answer:
A. In 1857 C.E.
Question 10.
Which Policy of the British ruined the native kings of India ?
A. Imperialistic Policy
B. Trade and Rule Policy
C. Annexation Policy
D. Divide and Rule Policy
Answer:
D. Divide and Rule Policy
![]()
Fill in the blanks in the following statements with proper words or numbers:
1. Lord Wellesley introduced the ……………… Policy in India.
Answer:
Subsidiary Alliance
2. Subsidiary Alliance was like ………………. for native states.
Answer:
slow poison
3. ……………….. accepted the Subsidiary Alliance first.
Answer:
Nizam
4 Lord Wellesley made British rule supreme in India by …………….. .
Answer:
Subsidiary Alliance
5. ……………… was the powerful ruler of Punjab.
Answer:
Maharaja Ranjit Singh
6. Governor General …………………. brought the Sikh kingdom under British rule.
Answer:
Sir Henry Hardinge
![]()
7 Lord …………………. annexed states of those native kings who died without a son.
Answer:
Dalhousie
8 The first railway line was started from Mumbai to Thane in India during Lord ……………… ’s tenure.
Answer:
Dalhousie
9. The first railway line was started from …………….. to in ……………. India during Lord Dalhousie’s tenure.
Answer:
Dalhousie
10. Railway, telegraph and post system were started in India during Lord …………….. ’s tenure.
Answer:
Dalhousie
11. The first three universities were established in India in the year ……………… C.E.
Answer:
1857
12. Lord ……………… was the father of Annexation policy.
Answer:
Dalhousie
![]()
13. Lord ……………… made the British company the supreme power in India.
Answer:
Dalhousie
14. War started among Maratha states after the death of Peshwa ……………….. .
Answer:
Nana Fadanvis
State whether the following statements are true or false:
1 ‘Divide and Rule’ was the policy of the British.
Answer:
True
2. When Wellesley came to India as the Governor General there was cut-throat competition between England and Portugal.
Answer:
False
![]()
3. Many native states became victims of Lord Wellesley’s Annexation Policy.
Answer:
False
4. Subsidiary Alliance was accepted first by Marathas.
Answer:
False
5. War started among the Maratha states after the death of Peshwa Nana Fadanvis.
Answer:
True
6. Wellesley became friends with Maharaja Ranjit Singh.
Answer:
True
7. Proper administration was established in the states of native kings who accepted Wellesley’s Subsidiary Alliance Policy.
Answer:
False
8. Modern postal system was started during Wellesley’s tenure.
Answer:
False
![]()
Match the pairs correctly:
| Section ‘A’ | Section ‘B’ |
| (1) Subsidiary Alliance | (1) Dalhousie |
| (2) Annexation Policy | (2) 1857 C.E. |
| (3) Maharaja of Punjab | (3) 1875 C.E. |
| (4) Establishment of three universities in India | (4) Wellesley |
| (5) Ranjit Singh |
Answer:
(1 – 4), (2 – 1), (3 – 5), (4 – 2).
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
Who introduced the Subsidiary Alliance policy in India? Who accepted this plan first?
Answer:
Governor General Wellesley introduced the Subsidiary Alliance policy in India. The Nizam of Hyderabad accepted this plan first.
Question 2.
Which policy was like a slow poison ?
Answer:
The Subsidiary Alliance policy was like a slow poison.
Question 3.
By enforcing which policy did Wellesley make British rule supreme in India?
Answer:
By enforcing ‘Divide and Rule’ policy, Wellesley made British rule supreme in India.
![]()
Question 4.
When did the British interfere in the administration of Punjab ?
Answer:
After Ranjit Singh the powerful Maharaja of Punjab died, the Sikhs quarrelled for the legacy. Taking advantage of this, the British interfered in the administration of Punjab.
Question 5.
Who did not allow childless kings to adopt a son?
Answer:
Governor General Dalhousie did not allow childless kings to adopt a son.
Question 6.
Which states were declared heirless and annexed by Dalhousie ?
Answer:
The states that were declared heirless and annexed by Dalhousie : Satara, Jaitpur, Jhansi, Sambalpur, Nagpur, ‘ Arkat, Tanjore, Karnataka, etc.
Question 7.
When and where was the first railway line started in India?
Answer:
The first railway line was started from Mumbai to Thane in the year 1853 C.E.
Question 8.
In whose time did railway, telegraph and postal system start in India?
Answer:
Railway, telegraph and postal system started in India during the tenure of Governor General Dalhousie.
![]()
Question 9.
In which cities were Universities established during 1857 C.E. ?
Answer:
In 1857 C.E., universities were established in Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata.
Define the following words:
Question 1.
Subsidiary Alliance
Answer:
To ensure that the French did not become powerful _ in India, Governor General Wellesley introduced the policy of ‘Subsidiary Alliance’ to expand British rule in native states. The princely states that accepted this policy had to keep and maintain the British army as well as have a British representative in the Royal Court.
Question 2.
Annexation Policy
Answer:
Dalhousie brought in the Policy of Annexation which meant bringing an end to the rule of native kings and bringing his state under the British rule directly.