Our Revision Notes for GSEB Class 9 Social Science Notes Chapter 1 Rise of British Rule in India summarises the key points of a chapter and useful resource to prepare effectively for the upcoming board exams.
Rise of British Rule in India Class 9 GSEB Notes Social Science Chapter 1
Rise of British Rule in India Class 9 GSEB Notes
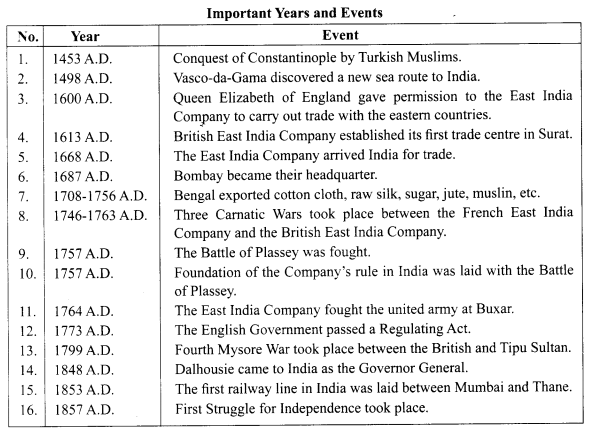
→ India has enjoyed incomparable position in the whole world due to its economic, cultural and religious inheritance.
→ There was a lot of demand for the Indian spices, muslin, silk cloth, indigo etc in the European countries.
→ Trade between India and Europe was carried out through land route and sea route and at the centre of these routes was Istanbul (Constantinople) in Turkey.
![]()
→ Constantinople was captured by Turkish Muslims, the sea route was closed for the Europeans. Since they could not leave without the spices the Europeans compelled to discover a new sea route.
→ Portuguese king Prince Henry, inspired, encouraged and helped people economically to discover new sea route.
→ Bartholomew Diaz discovered the ‘Cape of Good Hope’.
→ With the economic help of king of Spain Christopher Columbus started his journey to discovered a new sea route and stop at a island presently known as West Indies. He believed that he discovered India but clarification was made by Amerigo Vespucci, this new land began to be known as ‘America’.
→ The Portuguese sailor Vasco-da-Gama discovered a new sea route to India.
→ Thereafter Dutch,English and French came to India.
→ Queen Elizabeth of England gave the permission to the East India Company to carry out trade with the eastern countries.
![]()
→ First ship under the captain Hawkins arrived in Surat.
→ Mughal Emperor Jahangir permitted British East India Company to established its first trade centre in Surat.
→ Due to Marathas they set up their centres in Machlipattanam, Saint George and Fort William.
→ The French East India Company set up their trade centres in Mahe, Karaickal, Pondicherry, Chandranagar, Machlipattanam etc.
→ Portuguese were left with Diu, Daman. Goa. The Dutch had to leave forever.
→ Siraj-ud-Daula defeated in the battle of Plassey due to the conspiracy planned by Clive.
→ Mir Jafar was made the Nawab of Bengal, and company got a freehold over 24 Paraganas.
→ Thus the foundation of Company’s rule in India was aid with the Battle of Plassey.
→ Due to their greed to gain more powers the East ;India company managed to dethrone Mir Jafar and made Mir Qasim the Nawab of Bengal.
→ Mir Qasim proved more ambitious than Mir Jafar and thus he was replaced again by the Mir Jafar. Mir Qasim,
![]()
→ Nawab of Awadh and Shah Alam’s fight unitedly with East India company at Buxar on 22nd October, 1764 in which united army lost and company got the right to collect the revenue from Bengal, Bihar and Orissa.
→ Due to Regulating Act passed by the English government in 1773 A.D. Governor of Bengal made the governor general and all the trade and political activities of the Company were brought under his direct control.
→ Warren Hasting became the first Governor General of India.
→ After Hasting Cornwallis became the governor general. Due to his policies East India Company’s fame declined and Marathas became stronger.
→ Wellesley came with the responsibility of making company power supreme in India. So he introduced Subsidiary Alliance System.
→ Wellesley introduced Subsidiary Alliance system which was accepted by the Nizam, Mysore, Aw’adh, Gaikwad, Scindia, Bhosle and Holkar.
Rise of British Rule in India Class 9 GSEB Notes Important Terms
• Company will provide trained army
• States will give equivalent income in return.
• States will not w’age war or sign treaty without the permission of the company
• There will be one English representative in the state
• Other foreigners not to be employed in the state.
• The Subsidiary Alliance system was like a sweet poison.
• Wellesley annexed many provinces and expanded the rule of the East India company.
• Tipu sultan lost his life in fourth Mysore war.
![]()
• After wellesley Hastings came to India as Governor General.
• He waged war with Nepal and made Gurkhas to join the army.
• He defeated Pindharas and Marathas and made company power supreme in India.
• After his a liberal minded Governor General William Bentinck came to India.
• After him Dalhousie came to India with Annexation policy and by that Company expand its pow’er in India.
• Dalhousie was also a reformist he made many reforms like he started railwayline in India, wdreless system between India and England, established public works department, started English education, passed laws to ban child marriage and advocate widow remarriage.
• During the 100 years of company rule in India, India’s economic condition became worst. Prosperous Indian industries collapsed.
![]()
• Indian artist, traders and farmers condition became pathetic.
• During this time many wrong social customs, rites and rituals w ere banned by passing laws by Company.
• English education began to be imparted in India due to Lord Macaylay’s efforts.
• Charles Wood established universities in Mumbai, Madras, and Kolkata.
• Due to companies policies, England became prosperous at the cost of India and the reforms made by them in administration, for their own intrest indirectly proved to be beneficial for India.