Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.8 Textbook Questions and Answers.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 6 Maths Chapter 5 Understanding Elementary Shapes Ex 5.8
Question 1.
Examine whether the following are polygons. If any one among them is not, say why?
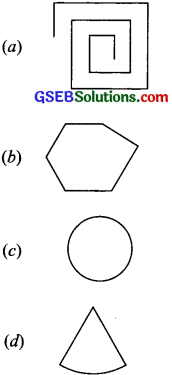
Solution:
(a) It is an open curve therefore it is not a polygon.
(b) Yes, it is a polygon of six sides.
(c) Circle is not made up of line segments. So it is not a polygon.
(d) The curve is not made up of line segments only. So it is not a polygon.
![]()
Question 2.
Name each polygon.
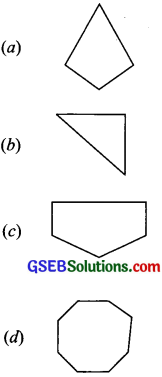
Make two more examples of each of these.
Solution:
(a) A quadrilateral
(b) A triangle
(c) A pentagon
(d) An octagon
Other examples:
Two quadrilaterals:
Two triangles:
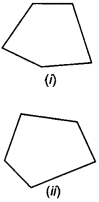
Two pentagons:
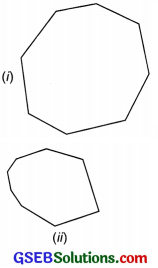
Two octagons:
![]()
Question 3.
Draw a rough sketch of a regular hexagon. Connecting any three of its vertices, draw a triangle. Identify’ the type of the triangle you have drawn.
Solution:
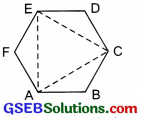
ABCDEF is a regular hexagon.
Joining its alternate vertices A, C and E we get ∆ACE,
which is a regular triangle.
Thus, the triangle so formed is an equilateral triangle.
Question 4.
Draw a rough sketch of a regular octagon. (Use squared paper if you wish). Draw a rectangle by joining exactly four of the vertices of the octagon.
Solution:
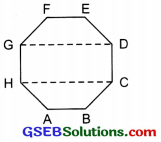
ABCDEFGH is a regular octagon.
Joining vertices G and D, we get \(\overline{\mathrm{GD}}\).
Again joining H and C, we get \(\overline{\mathrm{HC}}\).
Thus we get rectangle CDGH.
By joining its any two vertices, we get following diagonals:
Again by joining A, F and B, E, we can get another rectangle ABEF.
Question 5.
A diagonal is a line segment that joins any two vertices of the polygon and is not a side of the polygon. Draw a rough D sketch of a pentagon and draw its diagonals.
Solution:
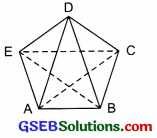
ABCDE is a pentagon. By joining its any two vertices, we get following diagonals:
\(\overline{\mathrm{AC}}\), \(\overline{\mathrm{AD}}\), \(\overline{\mathrm{BD}}\), \(\overline{\mathrm{BE}}\) and \(\overline{\mathrm{CE}}\)