Gujarat Board GSEB Textbook Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf.
Gujarat Board Textbook Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings
Gujarat Board Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings InText Questions and Answers
Page – 3
Question 1.
Which of the following are matter? Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Answer:
Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter. Matter can exist in three physical states – solid, liquid and gas.
- Solid state → Chair and almond
- Liquid state → Cold drink
- Gaseous state → Air and smell of perfume.
Note: The sense of smell is not matter. However, the smell or odour of a substance is classified as matter. The smell of any substance (say, perfume) is the gaseous form of that substance which our olfactory system can detect (even of very low concentrations). Hence, smell of perfume is matter.
![]()
Question 2.
Give reasons for the following observations. The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from the cold food you have to go close.
Answer:
The particles of matter possess kinetic energy and thus are constantly moving. At low temperatures, the kinetic energy is low and hence the particles move slowly. But as the temperature rises, the kinetic energy increases accordingly and hence the particles move faster.
Now since the particles of hot vapours coming out of hot sizzling food move faster, therefore, they easily reach you even when you are several metres away. On the other hand, the particles of vapours coming out of cold food travel only slowly and hence do not reach you. Therefore, to get the smell from cold food you have to go close to the food.
![]()
Question 3.
A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer:
The ability of a diver to cut through water in a swimming pool shows that matter is made up of particles.
Question 4.
What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
Answer:
The characteristics of particles of matter are:
- Particles of matter have spaces between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
Page – 6
Question 5.
The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density: air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Answer:
The given substances in the increasing order of their densities can be represented as:
Air < exhaust from chimney < cotton < water < honey < chalk < iron
Question 6.
(a) Tabulate the difference in characteristics of states of matter.
(b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density
Answer:
(a)
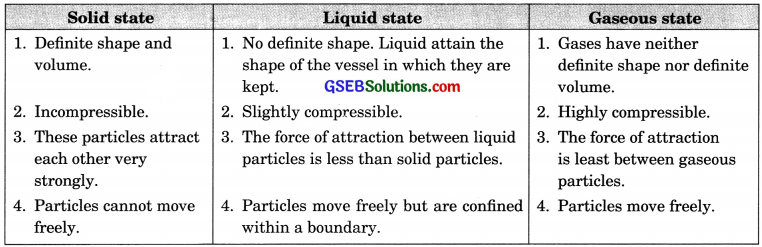
(b) Rigidity: It is the property due to which an object retains its shape and size. Solids are rigid while liquids and gases are not.
Compressibility: It is the property due to which a substance is reduced to a smaller volume when force is applied on it. Game’s are highly compressible while solids and liquids are not.
Fluidity: It is the property due to which a substance tends to flow. Gases and liquids can flow, hence they are known as fluids.
Filling a gas container: Particles of a gas move freely in all the directions and occupy all the space available to them. Hence, gas fills a container completely.
Shape: The structure of an object is called its shape. Solids have a definite shape while gases and liquids do not.
Kinetic energy: The energy of the particles of matter due to their movement is called their kinetic energy. Gases have maximum kinetic energy among the three states of matter. Kinetic energy in-creases with the rise in temperature and vice-versa.
Density: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called its density.
![]()
Unit of density are kg m 3 or g cm 3. Generally, a substance has maximum density in its solid state as compared to liquid or gaseous state.
![]()
Question 7.
Give reasons:
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Answer:
(a) The particles of a gas are constantly moving in all the directions with different speeds. Therefore, they do not have a fixed volume and hence completely fill the vessel in which they are kept.
(b) The particles of a gas are constantly moving in all directions with different speeds. As a result of this random motion, the particles of a gas collide with one another and also against the walls of the container. As a result of these collisions, the gas exerts some force on the walls of the container. This force per unit area is called pressure of the gas. Thus, gases exert pressure due to the collisions of the particles of the gas on the walls of the
containing vessel.
(c) A wooden table has a definite shape, distinct boundaries and a fixed volume, therefore, it should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air since the forces of attraction between the particles of a gas, i.e., air are very weak and hence can be easily overcome for the movement of the hand. In contrast, the particles of a solid are closely packed and hence the interparticle forces of attraction are very strong. As a result, they cannot be easily overcome for movement of the hand. In other words, we need a karate expert with almost incredible power to separate these particles.
Question 8.
Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why?
Answer:
The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume). As the volume of a substance increases, its density decreases. Though ice is a solid, it has large number of empty spaces between its particles. These spaces are larger as compared to the spaces present between the particles of water. Thus, the volume of ice is greater than that of water. Hence, the density of ice is less than that of water. A substance with lower density than water can float on water. Therefore, ice floats on water.
![]()
Page – 9
Question 9.
Convert the following temperatures to the Celsius scale:
(a) 300 K
(b) 573 K.
Answer:
(a) 300 K = (300 – 273)°C
= 27°C
(b) 573 K = (573 – 273)°C
= 300°C
Question 10.
What is the physical state of water at:
(a) 250°C
(b) 100°C
Answer:
(a) Water at 250°C exists in gaseous state.
(b) At 100°C, the boiling point of water, water exists both as a liquid as well as a gas.
Question 11.
For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer:
During a change of state, the temperature remains constant. This is because all the heat supplied to increase the temperature is utilised in changing the state by overcoming the forces of attraction between the particles. Therefore, this heat does not contribute in increasing the temperature of the substance.
Question 12.
Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer:
The gases can be converted into liquids by bringing its particle closer, so atmospheric gases can be liquefied either by decreasing temperature or by increasing pressure.
![]()
Page – 10
Question 13.
Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer:
A desert cooler increases the humidity of the surrounding air. The water particles in the air take the heat from the surrounding objects and evaporates. In hot and dry days, the moisture level is very low in the atmosphere which increases the rate of evaporation. Because of faster evaporation, the cooler works well. That’s why a desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day.
Question 14.
How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matha) become cool during summer?
Answer:
There are some pores in an earthen pot through which the liquid inside the pot evaporates. The heat required for evaporation is taken from the water in the pot. This makes the water inside the pot cool. In this way, water kept in an earthen pot becomes cool during summer.
Question 15.
Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer:
Acetone, petrol and perfume evaporate at low temperatures. When some acetone, petrol or perfume is dropped on the palm, it takes heat from the palm and evaporates thereby making the palm cooler.
Question 16.
Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
Answer:
A liquid has a larger surface area in a saucer than in a cup. Thus, the liquid evaporates faster and cools faster in a saucer than in a cup. For this reason, we are able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup.
![]()
In-Text Activities Solved
(Textbook Page 1)
Activity 1.1
Answer:
Observation: common salt/ sugar is added to water, the particles of salt/sugar get into the empty spaces between particles of water. The salt will dissolve in water. There will be no change in the level of the solution by the addition of small amount.
Conclusion: This experiment indicates that there are some vacant spaces among the particles of water and the particles of salt occupies these spaces. The particles of matter have spaces between them, as a result.
(Textbook Page 1)
Activity 1.2
Answer:
Observation: A crystal of potassium permanganate contains millions of tiny particles which keep on dividing by addition of solvent / water, hence the dark purple colour of the potassium permanganate solution will somewhat decrease.
Conclusion: When this experiment is repeated 5-8 times, the purple colour of the potassium permanganate solution will not disappear completely. Some colour will always persist even when the solution is very dilute. Matter is made up of very small particles which cannot be observed under a powerful microscope.
(Textbook Page 2)
Activity 1.3
Answer:
Observation: In order to feel the smell of incense stick, we need to go near them. When the incense stick is lighted, the fragrance will immediately spread. Because as the temperature rises the kinetic energy of the incense particles increases. Hence, particles of incense more rapidly and thus intermix with the particles of the air rapidly. Yes we will get the smell sitting at a distance.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that particles of matter are always in motion. The movement of the particles is slow in case of unbumt incense stick. On the other hand, the movement of particles of matter is very fast when you supply heat energy by burning the incense stick.
(Textbook Page 2)
Activity 1.4
Answer:
Observation: Due to weak attraction forces between the particles of ink the colour of the blue or red ink spreads throughout the water in the beaker immediately. The drop of honey also spreads but takes much more time than ink due to strong inter molecular forces. The total time taken by the drop of ink to spread evenly throughout the water is much move less than that of honey.
Conclusion: Thus, we can conclude that particles of liquid diffuse on its own because they are constantly in motion. However, the rate of diffusion of two different liquid particles may vary and depends upon the strength of forces. Stronger the forces of attraction lower is the average speed.
(Textbook Page 2)
Activity 1.5
Answer:
Observation: As the time passes, the water turns into purple colour solution in both the beakers because the particles of water and potassium permanganate get evenly mixed by the process of diffusion. But the water contained in the hot beaker turns into a purple colour solution at a faster rate as compared to water contained in the cold beaker. Yes, the rate of mixing changes with temperature. This is because, in hot water the particles of water and that of potassium permanganate have more kinetic energy and therefore move faster. Hence, they mix with each other more quickly.
Conclusion: This shows that particles of matter are constantly moving and their rate of diffusion into liquid varies with temperature.
![]()
(Textbook Page 3)
Activity 1.6
Answer:
Observation: The third group is easiest to break. This is because; in third group the students from chain by touching each other with only their fingertips. The group in which the particles hold each other with maximum force is first group, hence such human chain was most difficult break.
Conclusion: This shows that particles of matter which are held with each other with maximum force of attraction cannot separated easily.
(Textbook Page 3)
Activity 1.7
Answer:
Observation: It is very easy to break the piece of chalk into smaller particles due to weakest forces of attraction. On the other hand, the iron ball does not break even with a large force due to strong forces of attraction.
Conclusion: This shows that the force of attraction between the particles of chalk is quite weak; whereas the force of attraction between the particles of iron ball is very strong.
(Textbook Page 3)
Activity 1.8
Answer:
Observation: Yes, this shows that the interparticle attraction between particles of water (liquid state) is not very strong. The stream of water remains together because the particles of matter attract each other to form uniform layers.
Conclusion: This exhibit that particles of water have force acting between them which keeps them together. However, the strength of this force is not very strong.
(Textbook Page 4)
Activity 1.9
Answer:
Observation: Yes, all these articles have a definite shapes, distinct boundaries and a fixed volume. Pen will break, there will be no effect on book and thread and after long time needle will break. No, the articles are not capable of diffusing into each other. No, the articles do not get compressed.
Conclusion: Thus, we can conclude that solid articles have a definite shape, distinct boundaries and a fixed volume. They are rigid and non – compressible i.e., they may break under force but their shape cannot be changed.
![]()
(Textbook Page 4)
Activity 1.10
Answer:
Observation: All these liquids will flow when spilt on the floor. Volume of the liquid remains same i.e. 50 mL when it is transferred from one container to the other. The shape of a liquid is not fixed. It takes up the shape of the container in which it is put. Further, when the liquid is poured from one container to the other, it flows.
Conclusion: Thus, we can’conclude that liquids do not have a fixed shape but have a fixed volume, i.e., they take up the shape of the container in which they are poured but their volume does not change on changing the shape of the container. Liquids flow and hence they can be called as fluids.
(Textbook Page 5)
Activity 1.11
Answer:
Observation: The pistons of the syringes (containing chalk pieces and water) require a large amount of force, while the piston of the third syringe which contains air is comparatively easier to push.
Conclusion: Thus, we can conclude that a solid and a liquid does not get compressed on applying pressure, but a gas can be compressed easily by applying pressure. Therefore, gases are highly compressible liquids are almost incompressible while solids are completely incompressible.
(Textbook Page 6)
Activity 1.12
Answer:
Observation: On increasing the temperature of solids, the kinetic energy of the particles increases. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the particles start vibrating with greater speed. Hence, heat energy supplied is used up in overcoming the forces of attraction between the liquid water particles to change them from liquid water to steam.
Conclusion: The energy supplied by heat overcomes the forces of attraction between the particles. The particles leave their fixed positions and start moving more freely. A stage is reached when the solid melts and is converted in a liquid. This stage is called as the melting point of the solid.
(Textbook Page 8)
Activity 1.13
Answer:
Observation: The solid ammonium chloride does not melt on heating. It is directly converted into vapours and gets deposited on the inner wall of the funnel as crystalline solid on coming in contact with the cold inner walls of the funnel.
Conclusion: A change of state directly from solid to gas without changing into liquid state or vice versa is called sublimation.
(Textbook Page 9)
Activity 1.14
Answer:
Observation: The surface area of water exposed to the atmosphere is minimum in case of a test tube, therefore, it takes a long time (2/3 days) for 5 mL of water to evaporate. Although the surface area of 5 ml. of water taken in two open china dishes is the same, yet water in the china dish placed near the window or under the fan evaporates more quickly than the water in the china dish placed inside a cupboard or on a shelf in your class room. All the three steps of activity will take longer time on a rainy day since the humidity is high.
Conclusion: Evaporation is a surface phenomena and so, when the surface area of the liquid is greater, the rate of evaporation will be more. The rate of evaporation of a liquid decreases with increase in the humidity of air and it increases with increase in the speed of the wind. Let us now differentiate evaporation and boiling.
Gujarat Board Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Convert the following temperatures to the Celsius scale:
(a) 300 K
(b) 573K
Answer:
(a) 300 K = (300 – 273)°C
= 27°C
(b) 573 K = (573 – 273)°C
=300°C
Question 2.
Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale:
(a) 25°C
(b) 373°C
Answer:
(a) 25°C = (25 + 273) K
= 298 K
(b) 373°C = (373 + 273) K
= 646 K
Question 3.
Give reasons for the following observations:
(а) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid,
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away.
Answer:
(a) Naphthalene shows the property of sublimation. Evaporation of naphthalene takes place easily and so it disappears in the course of time without leaving a solid.
(b) Perfume vapourises very fast and its vapours diffuse into air easily. That is why we can smell perfume sitting several metres away.
![]()
Question 4.
Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles: water, sugar, oxygen.
Answer:
Sugar is a solid, the forces of attraction between the particles of sugar are strong. Water is a liquid, the forces of attraction here are weaker than sugar. Oxygen is a gas, the forces of attraction are the weakest in gases. Thus, the increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles of water, sugar and oxygen is – Oxygen < Water < Sugar.
Question 5.
What is the physical state of water at:
(a) 25°C
(b) 0°C
(c) 100°C
Answer:
(а) At 25°C, the physical state of water is liquid.
(b) At 0°C, the physical state of water can be either a solid (ice) or a liquid.
(c) At 100°C, the physical state of water can be either a liquid or a gas (steam).
Question 6.
Give two reasons to justify –
(а) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer:
(a) At room temperature (25°C), water is a liquid because it has the following characteristic of liquid:
- At room temperature, water has no shape but has a fixed volume that is, it occupies the shape of the container in which it is kept.
- At room temperature, water flows.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature (25°C) because:
- It has a definite shape and volume like a solid at room temperature.
- It is rigid as solid at room temperature.
Question 7.
Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer:
Ice at 273 K has less energy than water (although both are at the same temperature). Water possesses the additional latent heat of fusion. Hence, at 273 K, ice is more effective in cooling than water.
![]()
Question 8.
What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer:
Steam produces more severe burns than boiling water. This is because steam has more energy than boiling water, present in it in the form of latent heat of vapourisation,
Question 9.
Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state.
Answer:
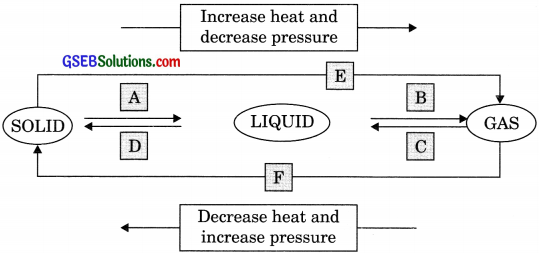
A → Melting/Fusion
B → Boiling/Vapourisation
C → Condensation
D → Soldification
E → Sublimation
F → Sublimation